Abstract
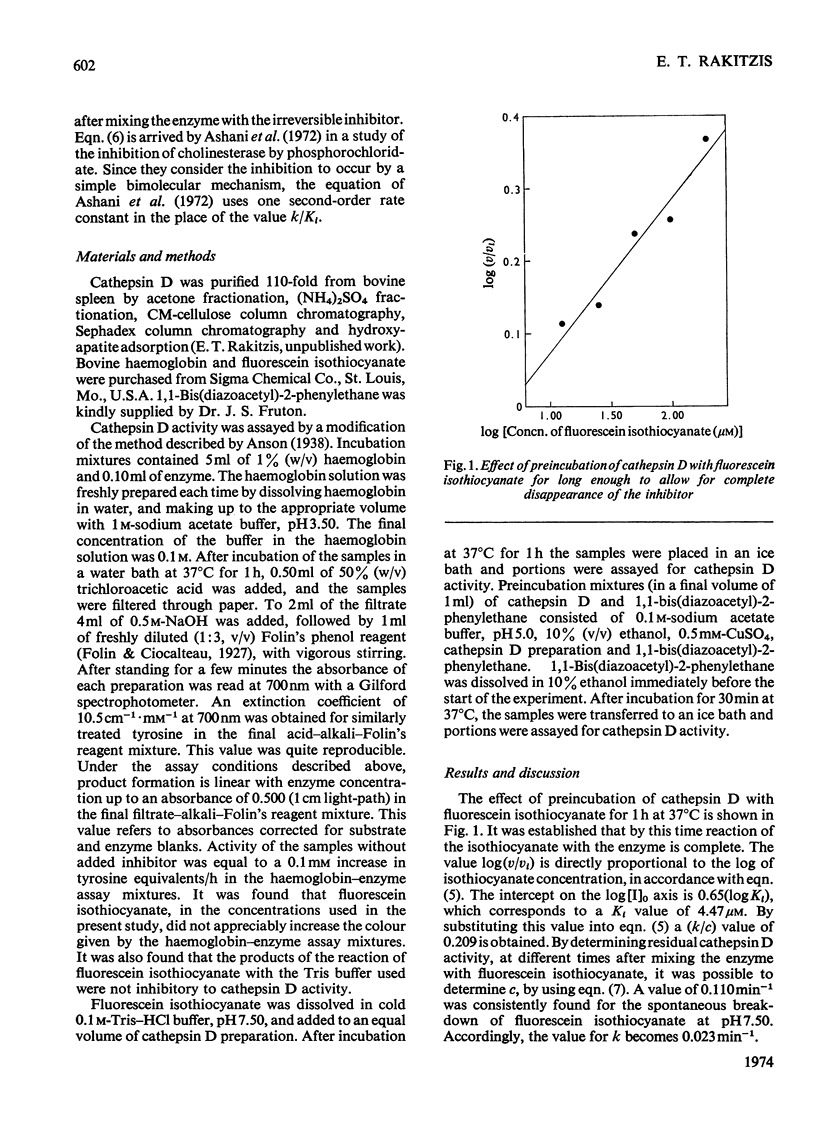
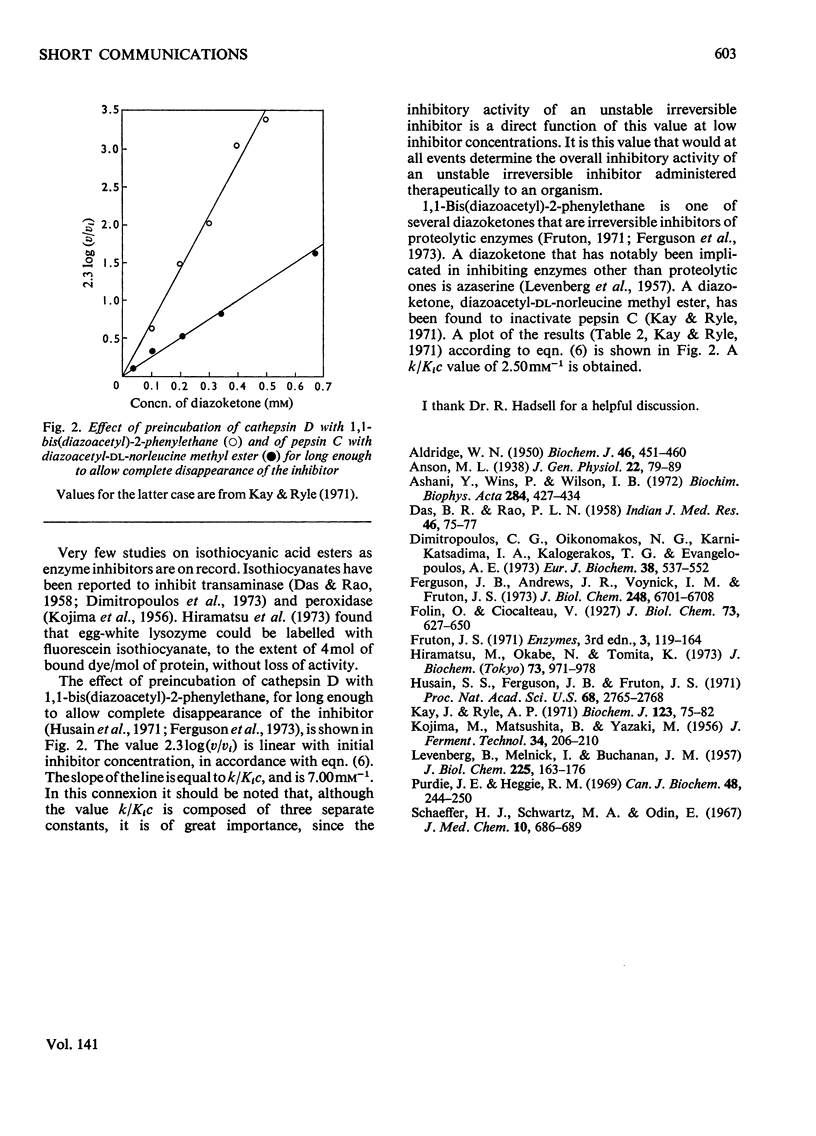
A mathematical treatment for the general case of enzyme inactivation by an inhibitor that breaks down in solution in a first-order reaction is presented. Cathepsin D was inactivated by fluorescein isothiocyanate with a Ki of 4.47μm. Kinetic constants were also determined for the inactivation of cathepsin D by 1,1-bis(diazoacetyl)-2-phenylethane, and the inactivation of pepsin C by diazoacetyl-dl-norleucine methyl ester.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Some properties of specific cholinesterase with particular reference to the mechanism of inhibition by diethyl p-nitrophenyl thiophosphate (E 605) and analogues. Biochem J. 1950 Apr;46(4):451–460. doi: 10.1042/bj0460451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashani Y., Wins P., Wilson I. B. The inhibition of cholinesterase by diethyl phosphorochloridate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 12;284(2):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAS B. R., NARASIMHA RAO P. L. Antibiotic principle from Moringa pterygosperma. IX. Inhibition of transaminase by isothiocyanates. Indian J Med Res. 1958 Jan;46(1):75–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitropoulos C. G., Oikonomakos N. G., Karni-Katsadima I. A., Kalogerakos T. G., Evangelopoulos A. E. Experimental evidence for a hydrophobic active center of glutamic-aspartic transaminase. Specific interaction of holoenzyme and apoenzyme with two fluorescein derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):537–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J. B., Andrews J. R., Voynick I. M., Fruton J. S. The specificity of cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6701–6708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu M., Okabe N., Tomita K. Preparation and properties of lysozyme modified by fluorescein-isothiocyanate. J Biochem. 1973 May;73(5):971–978. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain S. S., Ferguson J. B., Fruton J. S. Bifunctional inhibitors of pepsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2765–2768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J., Ryle A. P. An active site peptide from pepsin C. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):75–82. doi: 10.1042/bj1230075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENBERG B., MELNICK I., BUCHANAN J. M. Biosynthesis of the purines. XV. The effect of aza-L-serine and 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine on inosinic acid biosynthesis de novo. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):163–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie J. E., Heggie R. M. The kinetics of the reaction of N,N-dimethyl-2-phenylaziridinium ion with bovine erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Can J Biochem. 1970 Mar;48(3):244–250. doi: 10.1139/o70-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Schwartz M. A., Odin E. Enzyme inhibitors. XVII. Kinetic studies on the irreversible inhibition of adenosine deaminase. J Med Chem. 1967 Jul;10(4):686–689. doi: 10.1021/jm00316a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


