Abstract
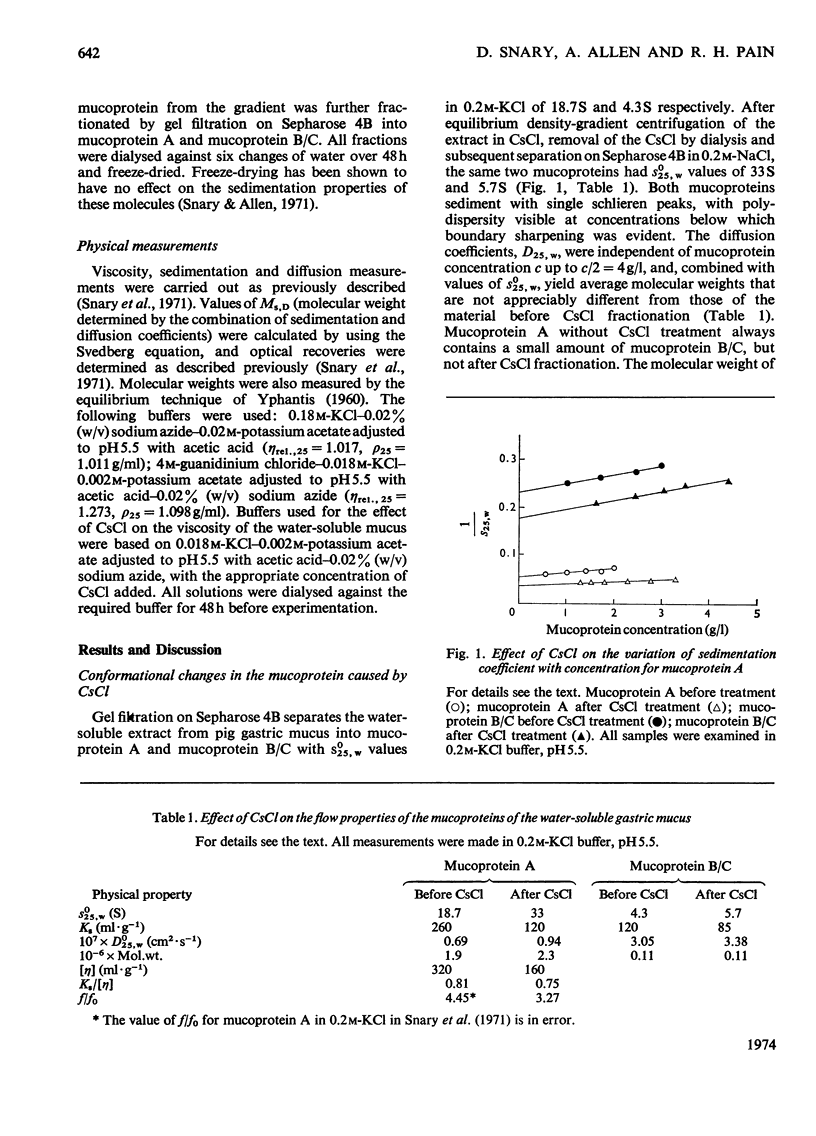
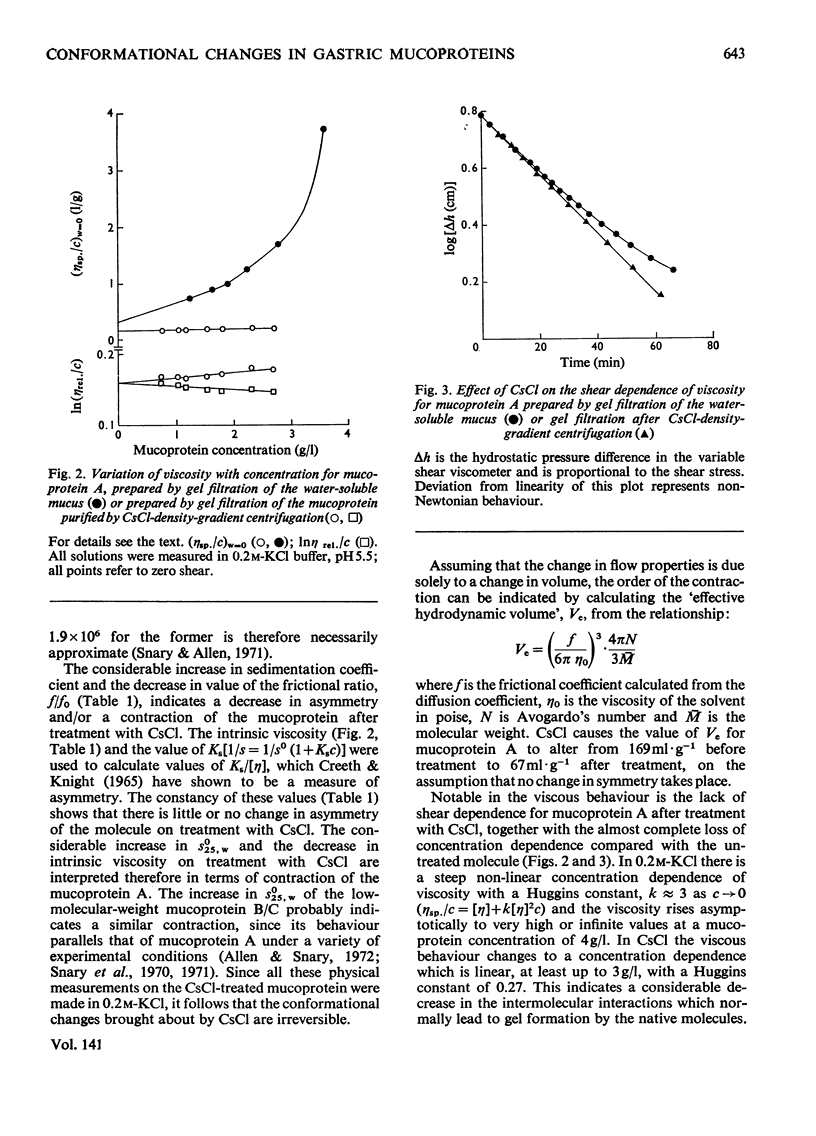
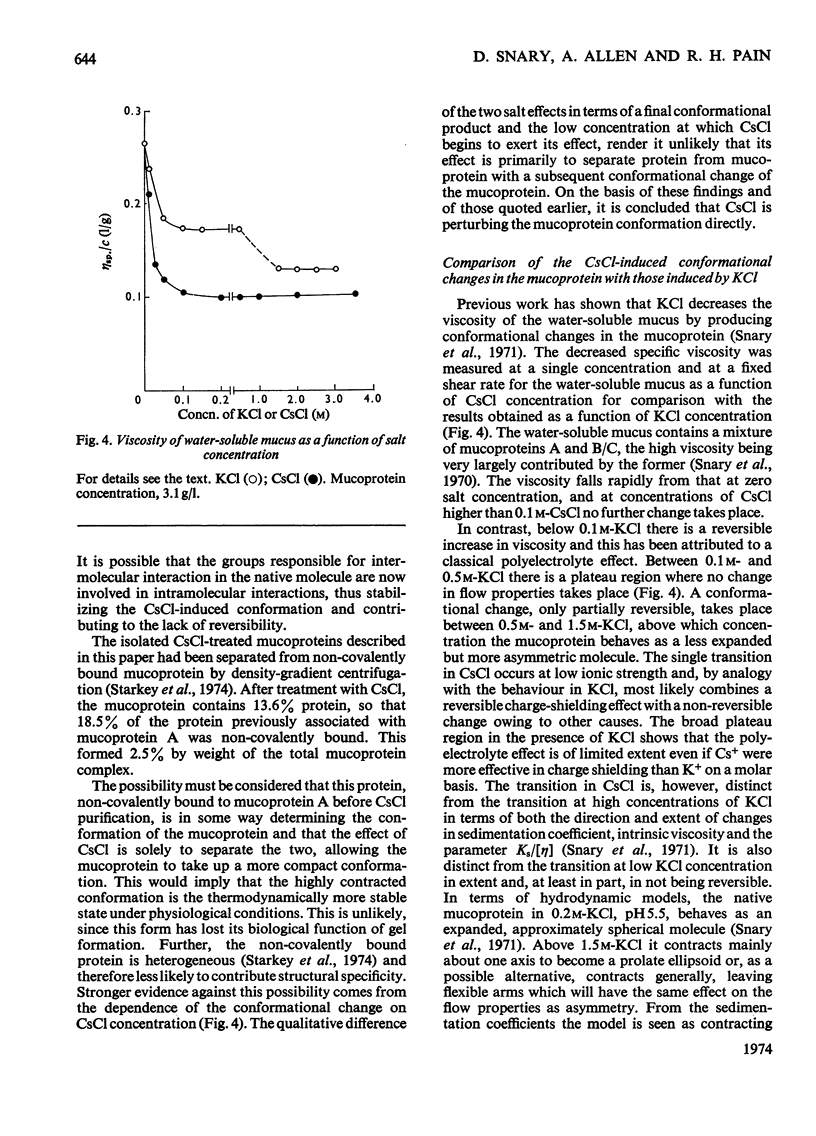
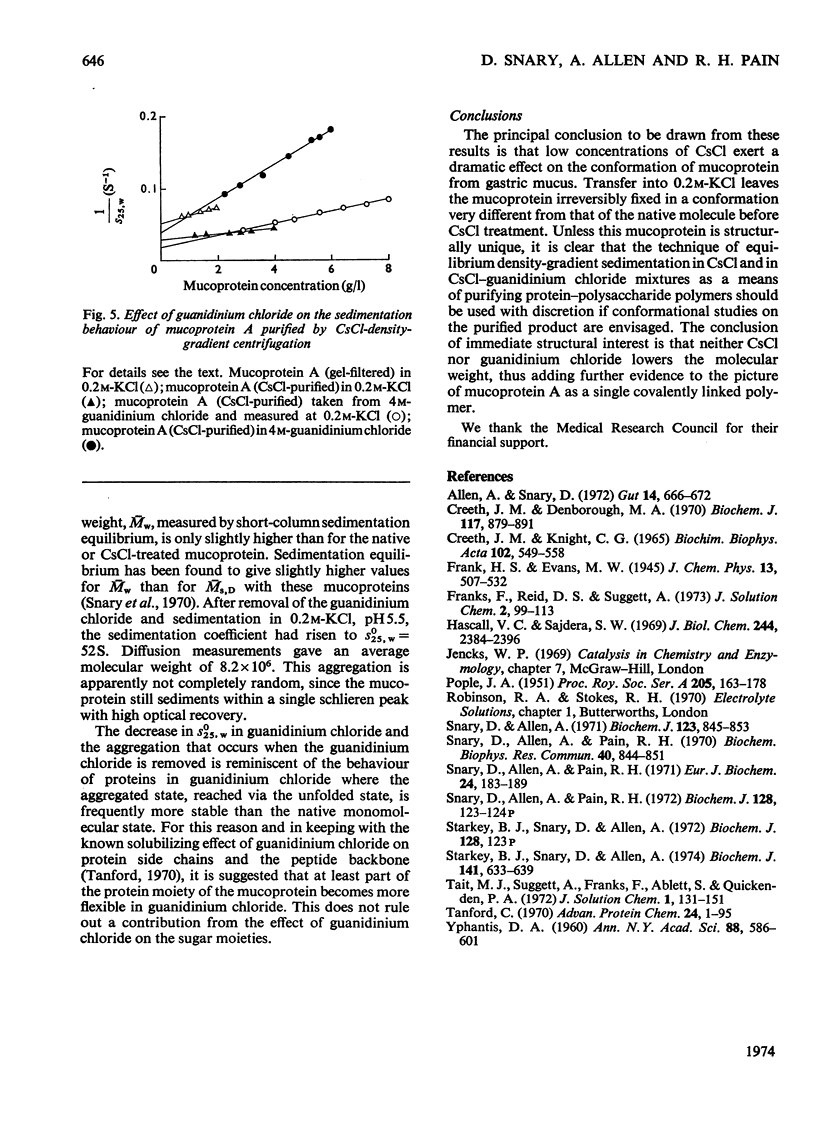
1. Caesium chloride and guanidinium chloride were shown to cause conformational changes in the high-molecular-weight mucoprotein A of water-soluble gastric mucus with no change in molecular weight. 2. Increasing concentrations of CsCl decrease the viscosity of the mucoprotein bringing about a transition which is essentially complete in 0.1m-CsCl. The shear-dependence of viscosity of the mucoprotein is abolished by low concentrations of CsCl. The normally highly expanded molecule becomes contracted in CsCl to a molecule having the same symmetry but a smaller volume and decreased solvation, in keeping with an increased sedimentation coefficient (18.7S→33S). 3. This contracted form does not revert to the native conformation on removal of the CsCl. 4. A mechanism is discussed in terms of the effect of the Cs+ and Cl−ions on water structure and the water–mucoprotein interaction. 5. Guanidinium chloride causes the CsCl-treated material to expand, in keeping with a decrease in s025,w (33S→26S). This is analogous to the known unfolding effect of guanidinium chloride on proteins and suggests that guanidinium chloride solubilizes groups involved in stabilizing the contracted structure. Removal of the guanidinium chloride results in a limited aggregation of four mucoprotein molecules. 6. These results show that caution must be exercised before interpreting the physical properties of mucoproteins which have been treated with CsCl and/or guanidinium chloride.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A., Snary D. The structure and function of gastric mucus. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):666–672. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Denborough M. A. The use of equilibrium-density-gradient methods for the preparation and characterization of blood-group-specific glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):879–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1170879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Knight C. G. On the estimation of the shape of macromolecules from sedimentation and viscosity measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 22;102(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Allen A., Pain R. H. Structural studies on gastric mucoproteins: lowering of molecular weight after reduction with 2-mercaptoethanol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):844–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90980-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Allen A., Pain R. H. The structure of pig gastric mucus. Conformational transitions induced by salt. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):183–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Allen A. Studies on gastric mucoproteins. The isolation and characterization of the mucoprotein of the water-soluble mucus from pig cardiac gastric mucosa. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):845–853. doi: 10.1042/bj1230845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey B. J., Snary D., Allen A. Characterization of gastric mucoproteins isolated by equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation in caesium chloride. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):633–639. doi: 10.1042/bj1410633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. C. Theoretical models for the mechanism of denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:1–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANSTIS D. A. Rapid determination of molecular weights of peptides and preteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Aug 31;88:586–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


