Abstract
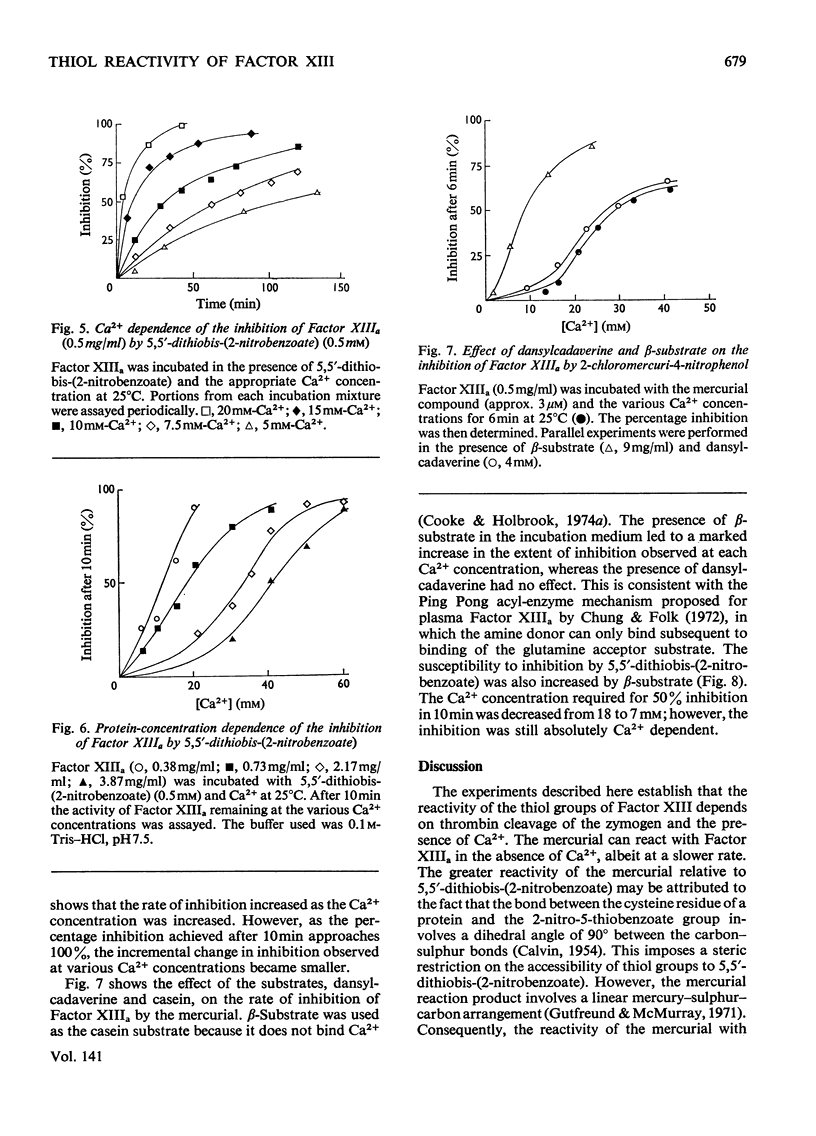
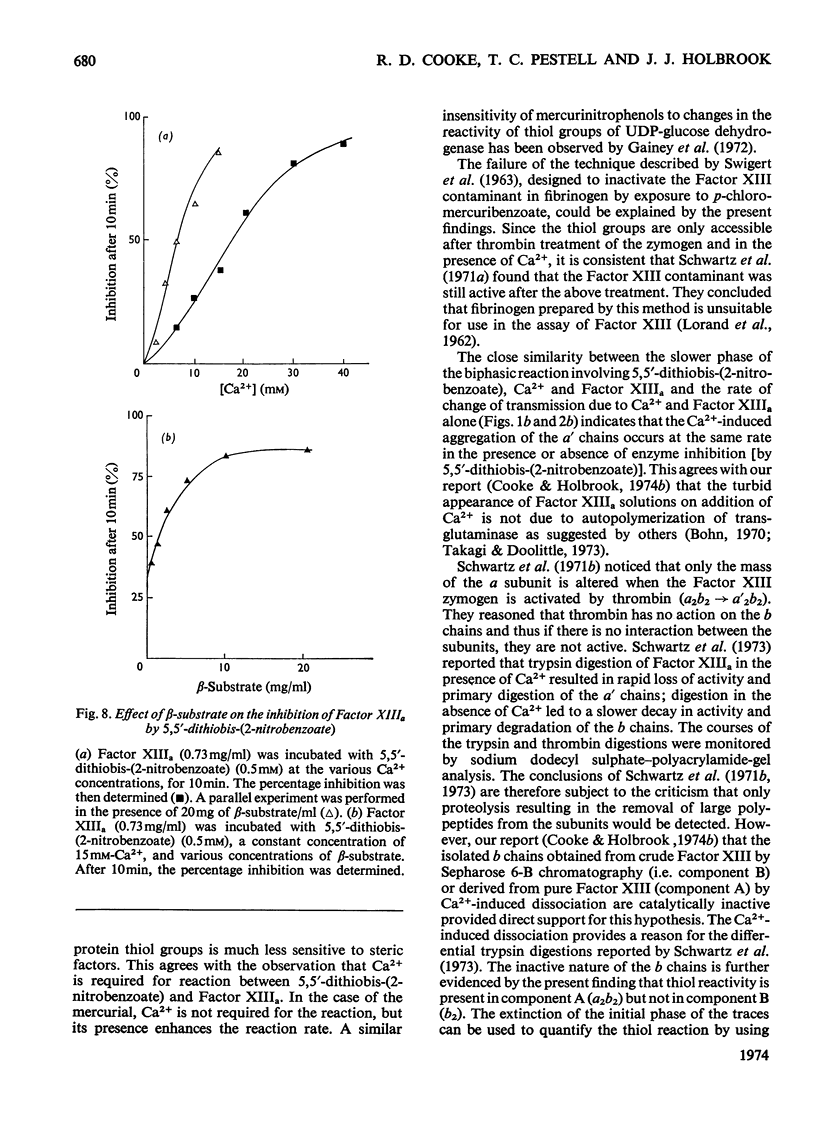
1. The reaction of iodoacetate, 2-chloromercuri-4-nitrophenol and 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoate) with thrombin-cleaved Factor XIII (i.e. Factor XIIIa) was accompanied by enzyme inhibition. 2. The reaction with iodoacetate and 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoate) was absolutely dependent on Ca2+, and the rate of reaction increased with the Ca2+ concentration up to very high, non-physiological concentrations. 3. 2-Chloromercuri-4-nitrophenol reacted with Factor XIIIa in the absence of Ca2+, but at a much slower rate. 4. Stopped-flow methods were used to quantify the reaction with 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitro-benzoate) because of the Ca2+-dependent dissociation of Factor XIIIa (a′2b2) and subsequent aggregation of the a′ chains into turbid precipitates. 5. The 3-carboxy-4-nitrothio-phenolate released was consistent with the reaction of 2 thiol groups/molecule of Factor XIIIa. The isolated b chains of Factor XIII did not react with either of the chromophoric reagents. This indicated that the a′ chains of Factor XIIIa were responsible for the thiol reactivity of the enzyme. 6. The Ca2+ dependence of the enzyme inhibition by these thiol reagents was very dependent on protein concentration. This is discussed in relation to the Ca2+-induced dissociation of Factor XIIIa. 7. The acceptor substrate, casein, decreased the Ca2+ concentration required for enzyme inhibition by both the mercurial and the aromatic disulphide compounds. Dansylcadaverine did not affect Ca2+ dependence of inhibition.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BETTELHEIM F. R., BAILEY K. The products of the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Nov;9(5):578–579. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H. Isolierung und Charakterisierung des fibrinstabilisierenden Faktors aus menschlichen Thrombozyten. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Jun 30;23(3):455–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Folk J. E. Kinetic studies with transglutaminases. The human blood enzymes (activated coagulation factor 13 and the guinea pig hair follicle enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2798–2807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connellan J. M., Chung S. I., Whetzel N. K., Bradley L. M., Folk J. E. Structural properties of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. D. Calcium-induced dissociation of human plasma factor XIII and the appearance of catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):683–691. doi: 10.1042/bj1410683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. D., Holbrook J. J. Calcium and the assays of human plasma clotting factor XIII. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):71–78. doi: 10.1042/bj1410071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. D., Holbrook J. J. The calcium-induced dissociation of human plasma clotting factor XIII. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):79–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1410079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Stenberg P., Chou C. H., Gray A., Brown K. L., Lorand L. Titration and subunit localization of active center cysteine in fibrinoligase (thrombin-activated fibrin stabilizing fector). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90952-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUCKERT F., JUNG E., SHMERLING D. H. A hitherto undescribed congenital haemorrhagic diathesis probably due to fibrin stabilizing factor deficiency. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Cole P. W. Identification of a functional cysteine essential for the activity of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3238–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. VI. Order of substrate addition. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3707–3713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORMSEN J., SIVERTSEN U. THE EFFECT OF SULFHYDRYLINHIBITORS AND GLYCINE DERIVATIVES ON FIBRIN POLYMERIZATION AND THE PHYSICAL STRENGTH OF FIBRIN IN PLASMA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:454–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainey P. A., Pestell T. C., Phelps C. F. A study of the subunit structure and the thiol reactivity of bovine liver uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):821–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1290821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H., McMurray C. H. Stoicheiometric, reactivity and environmental probes for sulphydryl groups in enzymes. Biochem Soc Symp. 1970;31:39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Cooke R. D., Kingston I. B. The amino acid sequence around the reactive cysteine residue in human plasma Factor XII. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):901–903. doi: 10.1042/bj1350901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDER E., BLOMSTRAND R. Technic for collection of thoracic duct lymph of man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Mar;97(3):653–657. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWY A. G., DUNATHAN K., GALLANT J. A., GARDNER B. Fibrinase III. Some enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2644–2647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L., KONISHI K. ACTIVATION OF THE FIBRIN STABILIZING FACTOR OF PLASMA BY THROMBIN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:58–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L., KONISHI K., JACOBSEN A. Transpeptidation mechanism in blood clotting. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1148–1149. doi: 10.1038/1941148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chou C. H., Simpson I. Thiolester substrates for transamidating enzymes: studies on fibrinoligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2645–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matacić S., Loewy A. G. Transglutaminase activity of the fibrin crosslinking enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):858–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray C. H., Trentham D. R. A new class of chromophoric organomercurials and their reactions with D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):913–921. doi: 10.1042/bj1150913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P. [Cross-link in fibrin polymerized by factor 13: epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine]. Science. 1968 May 24;160(3830):892–893. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3830.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWIGERT S., KOPPEL J. L., OLWIN J. H. Selective inactivation of fibrin stabilizing factor contaminant in fibrinogen. Nature. 1963 May 25;198:797–798. doi: 10.1038/198797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Human Factor XIII from plasma and platelets. Molecular weights, subunit structures, proteolytic activation, and cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1395–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The subunit structures of human plasma and platelet factor XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor). J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5851–5854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Self-induced crosslinking of factor XIII. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90526-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler H. M. Fibrin crosslinking demonstrated by thrombelastography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Nov 15;22(2):398–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]