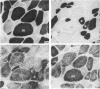
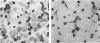
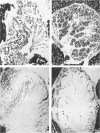
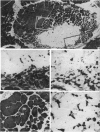
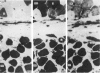
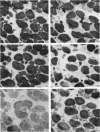
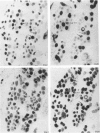
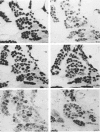
Full text
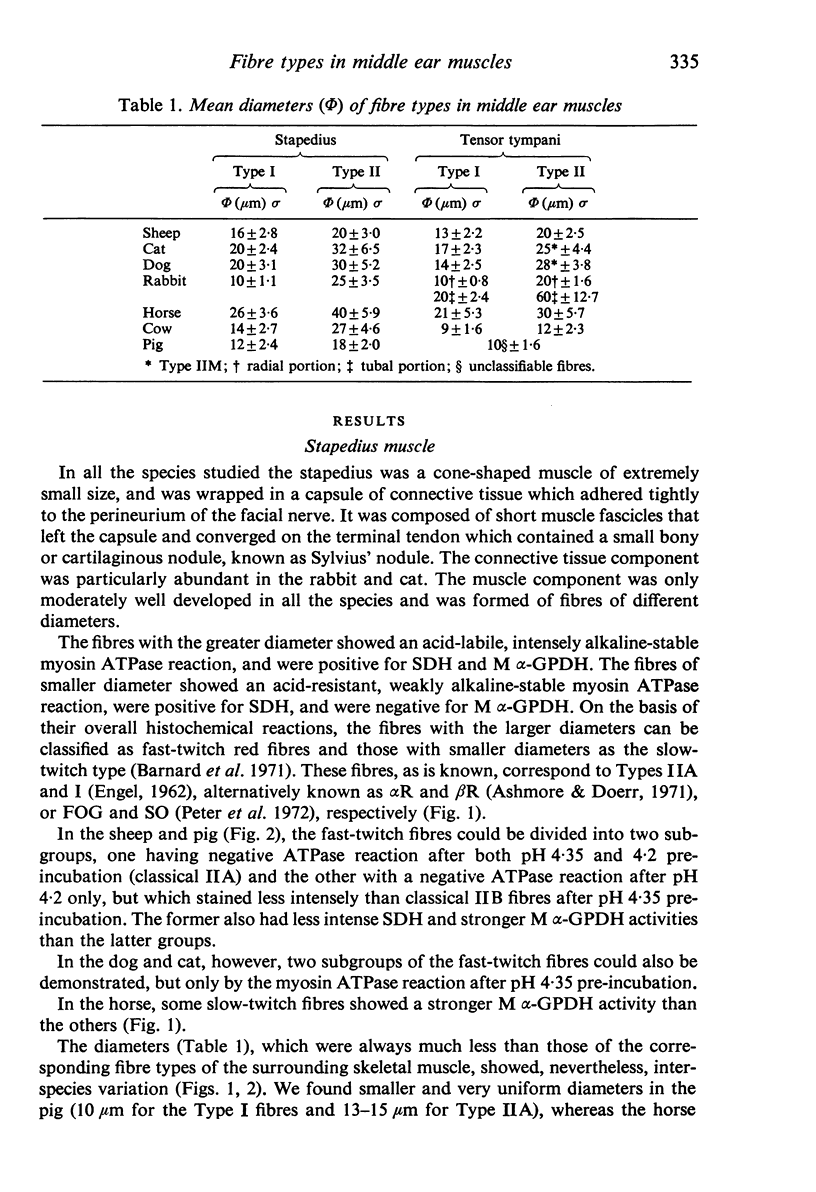
PDF

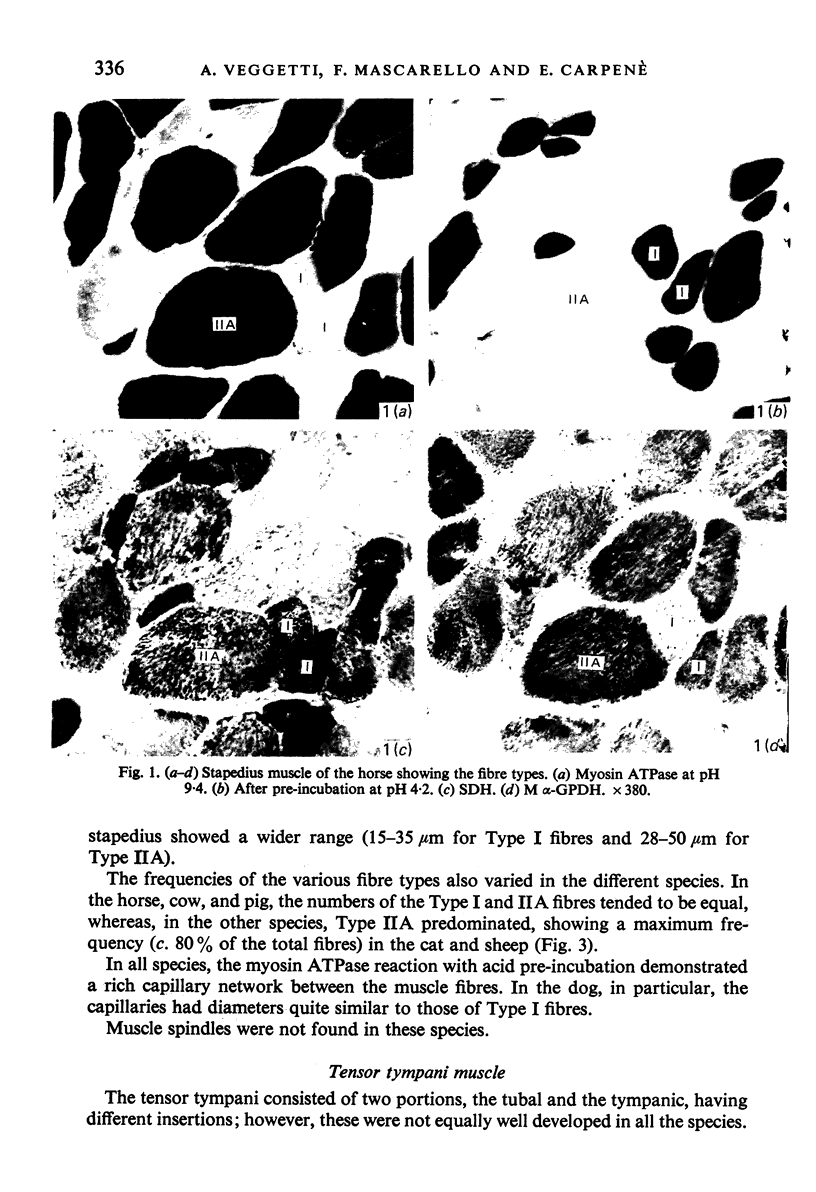





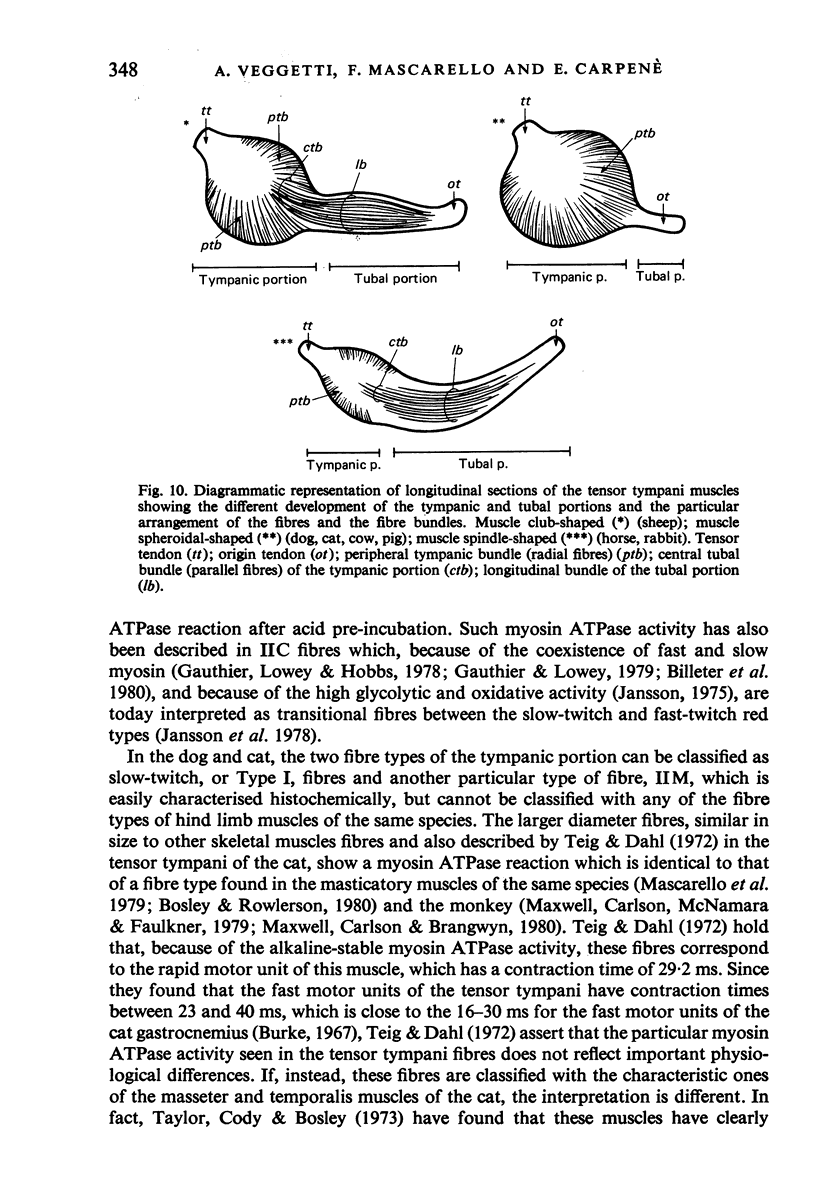




Images in this article
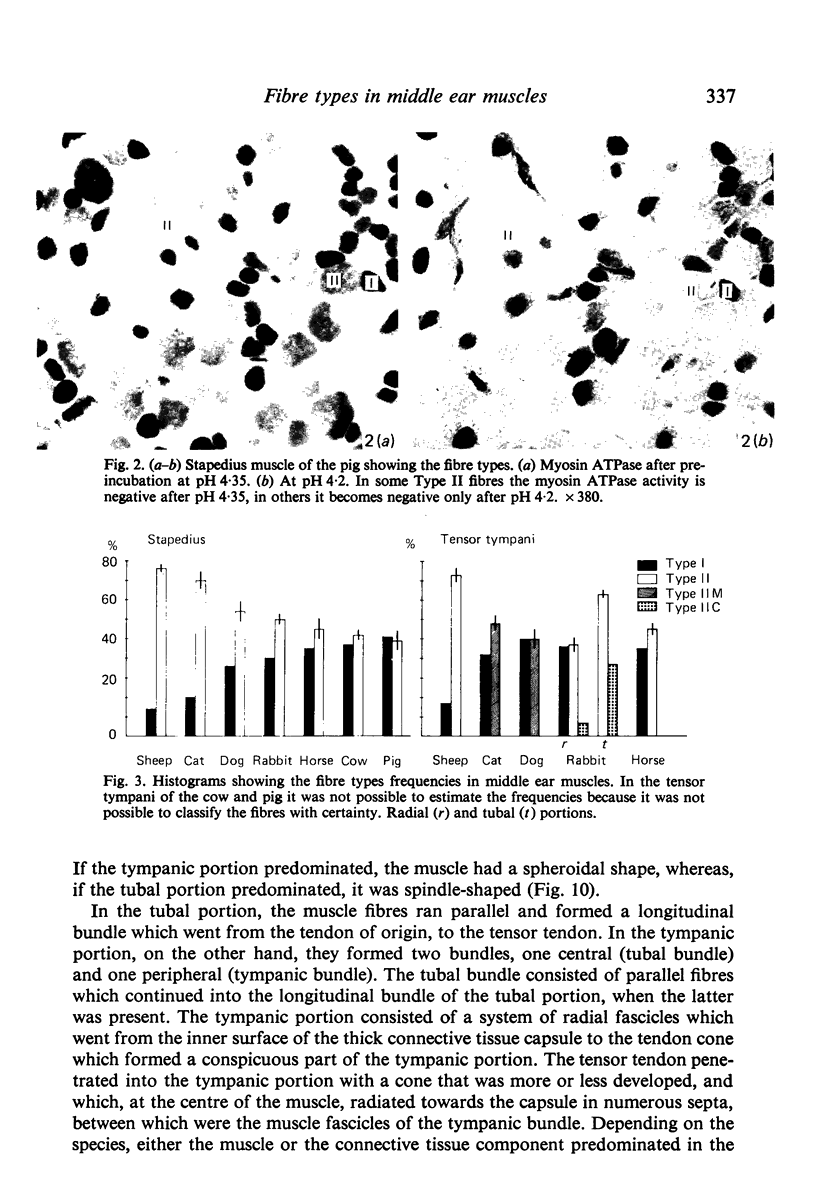
Selected References
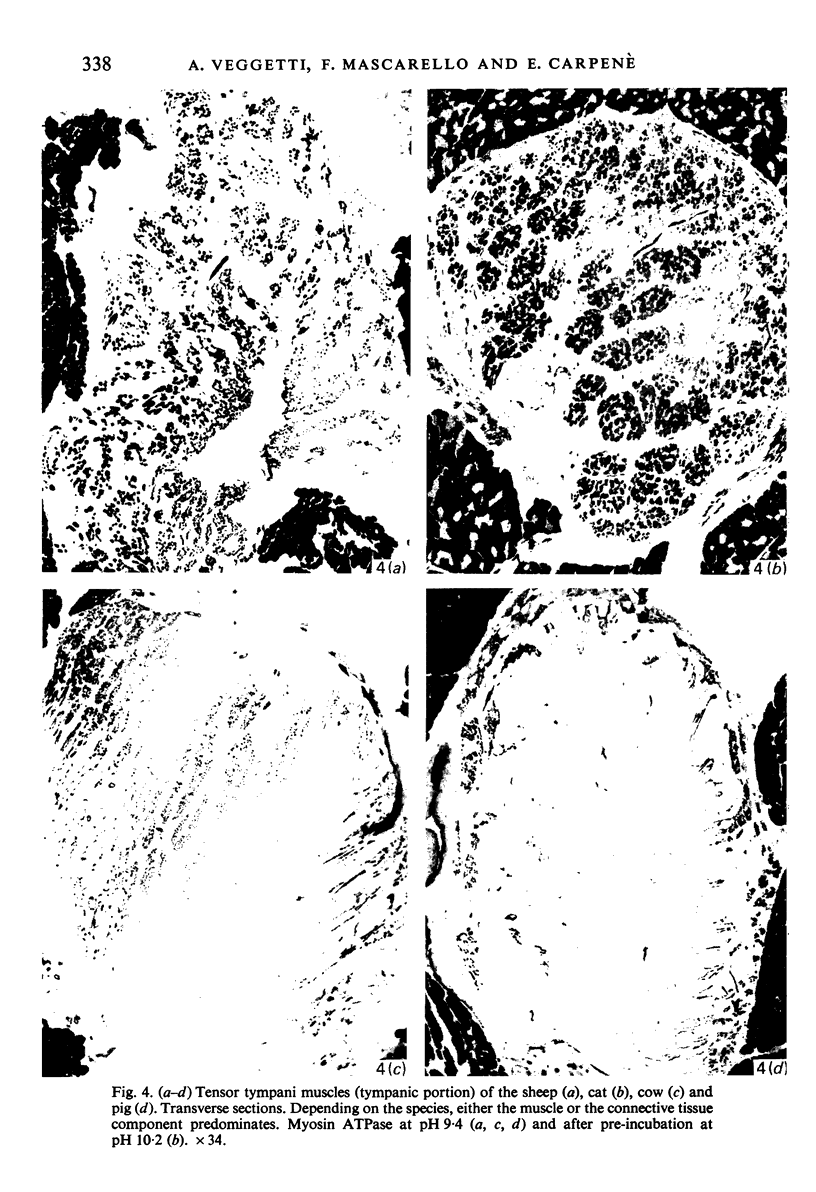
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Henriksson J. Training induced changes in the subgroups of human type II skeletal muscle fibres. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jan;99(1):123–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore C. R., Doerr L. Comparative aspects of muscle fiber types in different species. Exp Neurol. 1971 Jun;31(3):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(71)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanas V., Engel W. K. Distinct subtypes of type I fibers of human skeletal muscle. Neurology. 1975 Sep;25(9):879–887. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.9.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asmussen G., Wohlrab F. Enaymhistochemische Differenzierung von Muskelfasertypen im M. tensor tympani von Kaninchen und Katzen. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1971;83(4):507–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEVINS C. E. INNERVATION OF THE TENSOR TYMPANI MUSCLE OF THE CAT. Am J Anat. 1963 Sep;113:287–301. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEVINS C. E. STUDIES ON THE INNERVATION OF THE STAPEDIUS MUSCLE OF THE CAT. Anat Rec. 1964 May;149:157–171. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Furukawa T., Peter J. B. Histochemical, biochemical, and contractile properties of red, white, and intermediate fibers. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):410–414. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter R., Weber H., Lutz H., Howald H., Eppenberger H. M., Jenny E. Myosin types in human skeletal muscle fibers. Histochemistry. 1980;65(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00493174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins C. E. Innervation patterns of the human stapedius muscle. Arch Otolaryngol. 1967 Aug;86(2):136–142. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1967.00760050138003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins C. E. Motor units in the stapedius muscle. Arch Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar;87(3):249–254. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1968.00760060251007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormioli S. P., Sartore S., Vitadello M., Schiaffino S. "Slow" myosins in vertebrate skeletal muscle. An immunofluorescence study. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):672–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormioli S. P., Torresan P., Sartore S., Moschini G. B., Schiaffino S. Immunohistochemical identification of slow-tonic fibers in human extrinsic eye muscles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979 Mar;18(3):303–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Schmalbruch H. Motor unit of mammalian muscle. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):90–142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgener J., Mayr R. Guinea pig stapedius muscle. A histochemical, light and electron microscopic study. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1980;161(1):65–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00304669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Zajac F. E., 3rd Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit types of cat triceps surae muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candiollo L., Guglielmone R. Further observations concerning the proprioceptive innervation of the tensor tympani muscle. Anat Anz. 1969;125(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candiollo L. Ricerche anatomo-comparative sul muscolo tensore del timpano, con riferimento alla innergazione propriocettiva. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 Jul 5;67(1):34–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David H., Gerhardt H. J., Uerlings I. Die submikroskopische Struktur des Musculus Stapedius des Meerschweinchens. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;70(3):334–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERULKAR S. D., SHELANSKI M. L., WHITSEL B. L., OGLE P. STUDIES OF MUSCLE FIBERS ON THE TENSOR TYMPANI OF THE CAT. Anat Rec. 1964 Jun;149:279–297. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernand V. S., Hess A. The occurrence, structure and innervation of slow and twitch muscle fibres in the tensor tympani and stapedius of the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):547–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GETTY R., FOUST H. L., PRESLEY E. T., MILLER M. E. Macroscopic anatomy of the ear of the dog. Am J Vet Res. 1956 Jul;17(64):364–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R. A., O'Donovan M. J., Stephens J. A., Taylor A. Motor unit organization of human medial gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:33–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S. Distribution of myosin isoenzymes among skeletal muscle fiber types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):10–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S., Hobbs A. W. Fast and slow myosin in developing muscle fibres. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):25–29. doi: 10.1038/274025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. Fact and artifact in the histochemical procedure for myofibrillar ATPase. Exp Neurol. 1973 Nov;41(2):440–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J. Qualitative differences between actomyosin ATPase of slow and fast mammalian muscle. Exp Neurol. 1969 Sep;25(1):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., OLSON C. B. RELATIONS BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN THE DESIGN OF SKELETAL MUSCLES. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:581–598. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama M., Daly J. F. Ultrastructure of middle ear muscle in the rabbit. I Stapedius muscle. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Jan-Feb;77(1):13–18. doi: 10.3109/00016487409124592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama M., Davidowitz J., Daly J. F. Ultrastructure of middle ear muscle in the rabbit. II. Tensor tympani. Acta Otolaryngol. 1974 Mar;77(3):171–175. doi: 10.3109/00016487409124614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T. [The structure of the tympanic muscles of humans and guinea pigs]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1967 Apr;70(4):802–815. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.70.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson E., Sjödin B., Tesch P. Changes in muscle fibre type distribution in man after physical training. A sign of fibre type transformation? Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Oct;104(2):235–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kevanishvili Z. S., Gvacharia Z. V. On the role of the tensor tympani muscle in sound conduction through the middle ear. Acta Otolaryngol. 1972 Oct;74(4):231–239. doi: 10.3109/00016487209128444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff A. R., Atwood H. L. Membrane properties and contraction of single muscle fibers in the mouse. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello F., Veggetti A. A comparative histochemical study of intrinsic laryngeal muscles of ungulates and carnivores. Basic Appl Histochem. 1979;23(2):103–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell L. C., Carlson D. S., Brangwyn C. E. Lack of 'acid reversal' of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase in masticatory muscle fibres of rhesus monkeys. Histochem J. 1980 Mar;12(2):209–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01024551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell L. C., Carlson D. S., McNamara J. A., Jr, Faulkner J. A. Histochemical characteristics of the masseter and temporalis muscles of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Anat Rec. 1979 Mar;193(3):389–402. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P., Hofer H. W., Pette D. Metabolic heterogeneity of muscle fibers classified by myosin ATPase. Histochemistry. 1979 Sep;63(2):191–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00644541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):170–195. doi: 10.1177/3.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B., Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Gillespie C. A., Stempel K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2627–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiden D. Slow muscle fibers in the tensor tympani muscle of the guinea pig. Am J Anat. 1971 Oct;132(2):267–273. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001320211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Cody F. W., Bosley M. A. Histochemical and mechanical properties of the jaw muscles of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1973 Jan;38(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teig E., Dahl H. A. Actomyosin ATPase activity of middle ear muscles in the cat. Histochemie. 1972;29(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00305695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teig E. Force and contraction velocity of the middle ear muscles in the cat and the rabbit. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teig E. Tension and contraction time of motor units of the middle ear muscles in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]