Abstract
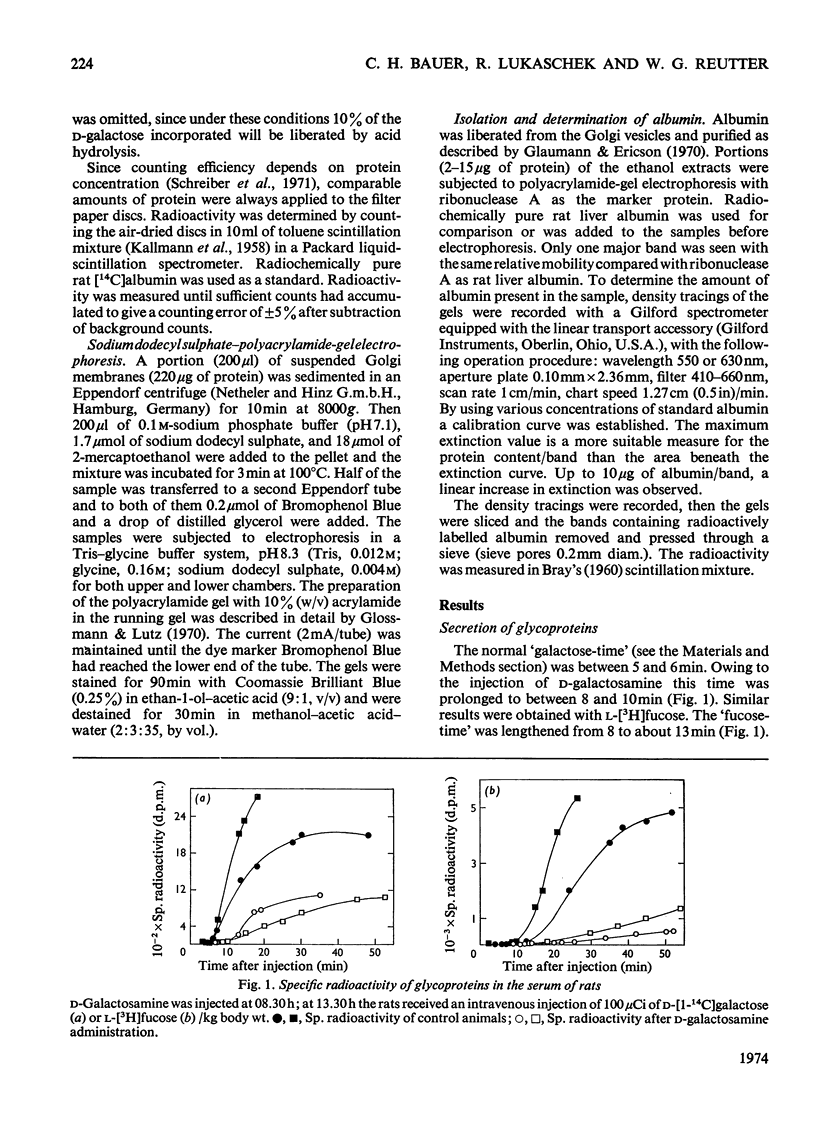
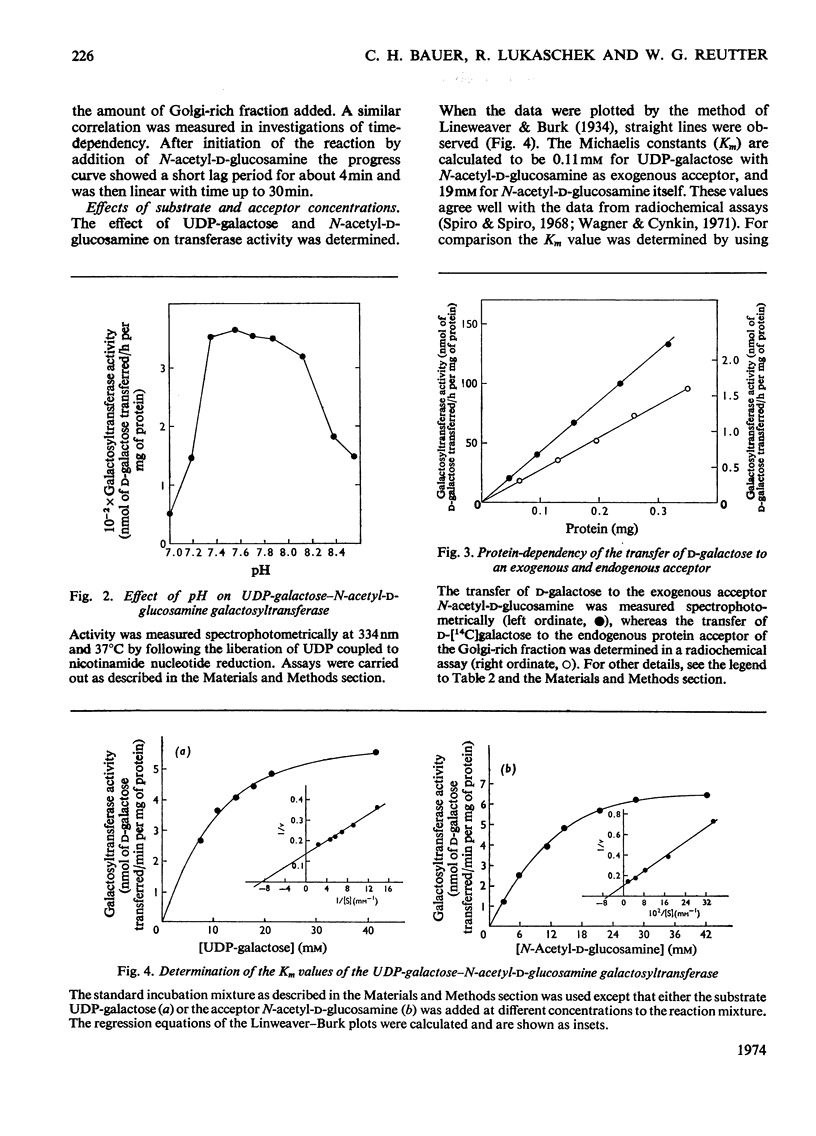
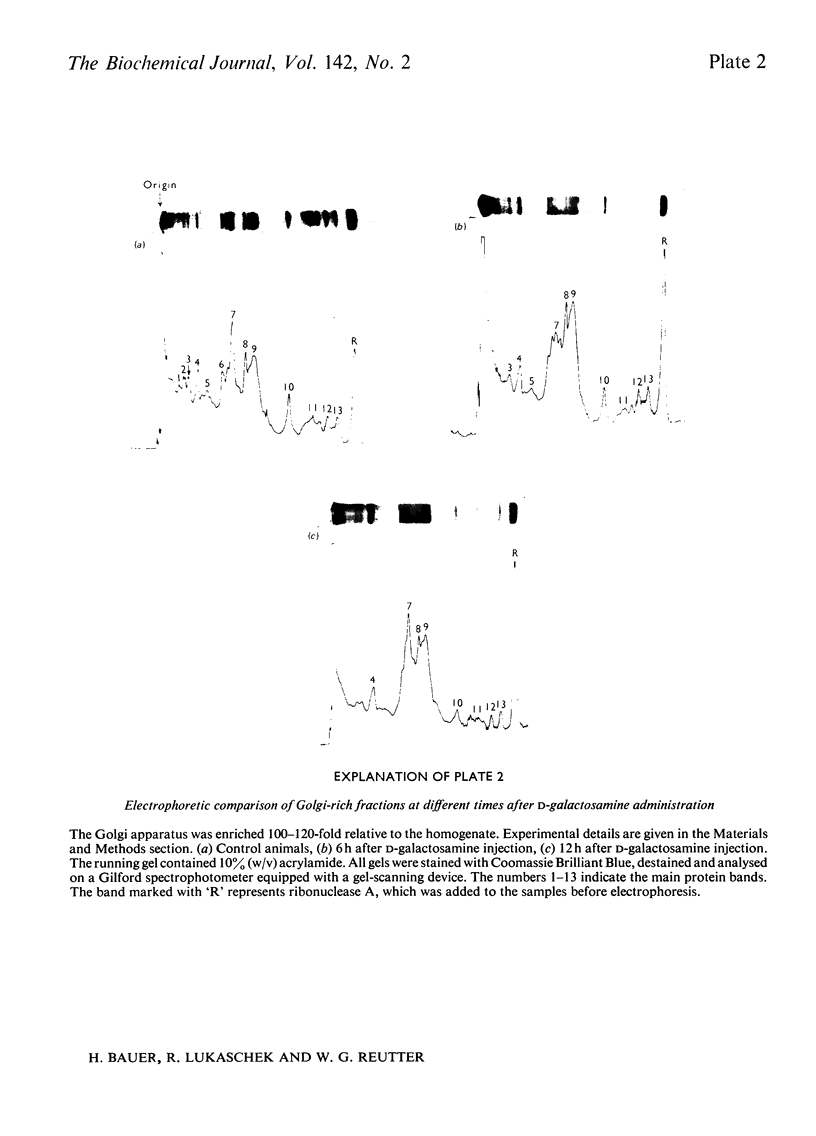
1. The administration of d-galactosamine leads to inhibition of protein and glycoprotein secretion by rat liver. To test the secretory function, the secretion times for galactose-and fucose-containing glycoproteins were determined; they were lengthened from 6 to 9min and from 8 to 13min respectively. 2. The Golgi apparatus was enriched 100–120-fold relative to the homogenate. A new linked-assay system for the marker enzyme, UDP-galactose–N-acetyl-d-glucosamine galactosyltransferase, is presented. The activity of the enzyme was measured spectrophotometrically by following the formation of UDP coupled to nicotinamide nucleotide reduction. The Michaelis constants were calculated to be 0.11mm for UDP-galactose with N-acetyl-d-glucosamine as exogenous acceptor and 19mm for N-acetyl-d-glucosamine itself. 3. The physiological substrate of the galactosyltransferase, UDP-galactose, can be replaced by UDP-galactosamine, which accumulates after d-galactosamine administration. Under conditions in vitro the rate of d-galactosamine transfer to an endogenous acceptor protein of the Golgi fraction reaches 9% of that with d-galactose; this finding is noteworthy, because normally a non-acetylated amino sugar does not occur in glycoproteins. 4. The albumin content of the Golgi-rich fraction was diminished to 55% of the reference value 6h after the injection of 375mg of d-galactosamine hydrochloride/kg body wt. The transfer of d-[1-14C]galactose to an endogenous acceptor protein fell to 60% compared with Golgi-rich fractions from untreated animals. Analysis of the Golgi-rich fraction by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis showed a decrease or loss of several protein bands. 5. Protein synthesis can be restored by up to 80% if the UTP pool, decreased after d-galactosamine administration, is filled up by several injections of uridine. 6. From the results presented it can be concluded that the disturbed secretion of proteins and glycoproteins was due to a cumulative effect of galactosamine by: (a) inhibition of protein synthesis leading to a diminution of the endogenous acceptor pool of the galactosyltransferase; (b) inhibition of the galactosyltransferase activity by galactosamine metabolites and (c) replacement of UDP-galactose by UDP-galactosamine.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C., Bachmann W., Reutter W. Studies on galactosamine hepatitis: determination of galactosamine metabolites in the developing rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1053–1058. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C., Reutter W. Inhibition of uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase by galactosamine-I-phosphate and UDP-galactosamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., PALADE G. E. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS, STORAGE, AND DISCHARGE IN THE PANCREATIC EXOCRINE CELL. AN AUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Mar;20:473–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccam J. F., Jackson J. J., Eylar E. H. The biosynthesis of mannose-containing glycoproteins: a possible lipid intermediate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K., Keppler D., Pausch J. The regulation of pyrimidine nucleotide level and its role in experimental hepatitis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1973;11:205–230. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(73)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H. On the biological role of glycoproteins. J Theor Biol. 1966 Jan;10(1):89–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Fleischer S., Ozawa H. Isolation and characterization of Golgi membranes from bovine liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):59–79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Fleischer S. Preparation and characterization of golgi membranes from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 1;219(2):301–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaumann H., Ericsson J. L. Evidence for the participation of the Golgi apparatus in the intracellular transport of nascent albumin in the liver cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):555–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Lutz F. Molecular weights of pig liver cell membrane proteins. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1583–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad A., Smith M. D., Herscovics A., Nadler N. J., Leblond C. P. Radioautographic study of in vivo and in vitro incorporation of fucose-3H into thyroglobulin by rat thyroid follicular cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):856–877. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian A., Bosmann H. B., Eylar E. H. Glycoprotein biosynthesis: the localization of polypeptidyl: N-acetylgalactosaminyl, collagen: glucosyl, and glycoprotein:galactosyl transferases in HeLa cell membrane fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Nov;128(2):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Murray R. K., Pinteric L., Morris H. P., Schachter H. The use of nucleotide-sugar: glycoprotein glycosyltransferases to assess Golgi apparatus function in Morris hepatomas. Can J Biochem. 1971 Jan;49(1):61–70. doi: 10.1139/o71-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D. O., Rudigier J. F., Bischoff E., Decker K. F. The trapping of uridine phosphates by D-galactosamine. D-glucosamine, and 2-deoxy-D-galactose. A study on the mechanism of galactosamine hepatitis. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):246–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Decker K. Studies on the mechanism of galactosamine-1-phosphate and its inhibition of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Lesch R., Reutter W., Decker K. Experimental hepatitis induced by D-galactosamine. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Oct;9(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Rudigier J., Decker K. Enzymic determination of uracil nucleotides in tissues. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford G. R., Schachter H. Biosynthesis of glycoprotein by liver. The incorporation in vivo of 14C-glucosamine into protein-bound hexosamine and sialic acid of rat liver subcellular fractions. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5408–5418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesch R., Reutter W., Keppler D., Decker K. Liver restitution after acute galactosamine hepatitis: autoradiographic and biochemical studies in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Feb;12(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., ROBINSON G. B., WINZLER R. J. BIOSYNTHESIS OF GLYCOPROTEINS. IV. THE SUBCELLULAR SITES OF INCORPORATION OF GLUCOSAMINE-1-14-C INTO GLYCOPROTEIN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1882–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Lequire V. S. Characterization of lipoprotein particles isolated from the Golgi apparatus of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medline A., Schaffner F., Popper H. Ultrastructural features in galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Apr;12(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morre J., Merlin L. M., Keenan T. W. Localization of glycosyl transferase activities in a Golgi apparatus-rich fraction isolated from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 20;37(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90964-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M., Leblond C. P. Radioautographic comparison of the uptake of galactose-H and glucose-H3 in the golgi region of various cells secreting glycoproteins or mucopolysaccharides. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):137–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Hernandez W., Leblond C. P. Detection of complex carbohydrates in the Golgi apparatus of rat cells. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):395–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutter W., Bachmann W. Galaktosamin-Hepatitis: Schädigung der Plasmamembran der leberzelle nach Gabe von D-Galaktosamin. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1971;77:1177–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutter W., Keppler D., Lesch R., Decker K. Zum Glykoproteidstoffwechsel bei der Galaktosamin-induzierten Hepatitis. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1969;75:363–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reutter W., Lesch R., Keppler D., Decker K. Galactosamin-Hepatitis. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Oct;55(10):497–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00599726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. D., Reutter W. Inhibition of induction of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase by D-galactosamine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1562–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber G., Rotermund H. M., Maeno H., Weigand K., Lesch R. The proption of the incorporation of leucine into albumin to that into totaprotein in rat liver and hepatoma Morris 5123 TC. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber G., Urban J., Zähringer J., Reutter W., Frosch U. The secretion of serum protein and the synthesis of albumin and total protein in regenerating rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4531–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka H., Farber J. L., Konishi Y., Anukarahanonta T. D-galactosamine and acute liver cell injury. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1516–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro M. J., Spiro R. G. Glycoprotein biosynthesis: studies on thyroglobulin. Thyroid galactosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6529–6537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetas M., Chao H., Molnar J. Incorporation of carbohydrates into endogenous acceptors of liver microsomal fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 May;138(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Cynkin M. A. Enzymatic transfer of 14C-glucosamine from UDP-N-acetyl-14C-glucosamine to endogenous acceptors in a Golgi apparatus-rich fraction from liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 10;35(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90495-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Cynkin M. A. Glycoprotein biosynthesis. Incorporation of glycosyl groups into endogenous acceptors in a Golgi apparatus-rich fraction of liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):143–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Cynkin M. A. The incorporation of 14C-glucosamine from UDP-N-acetyl-14C-glucosamine into liver microsomal protein in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jan;129(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]