Abstract
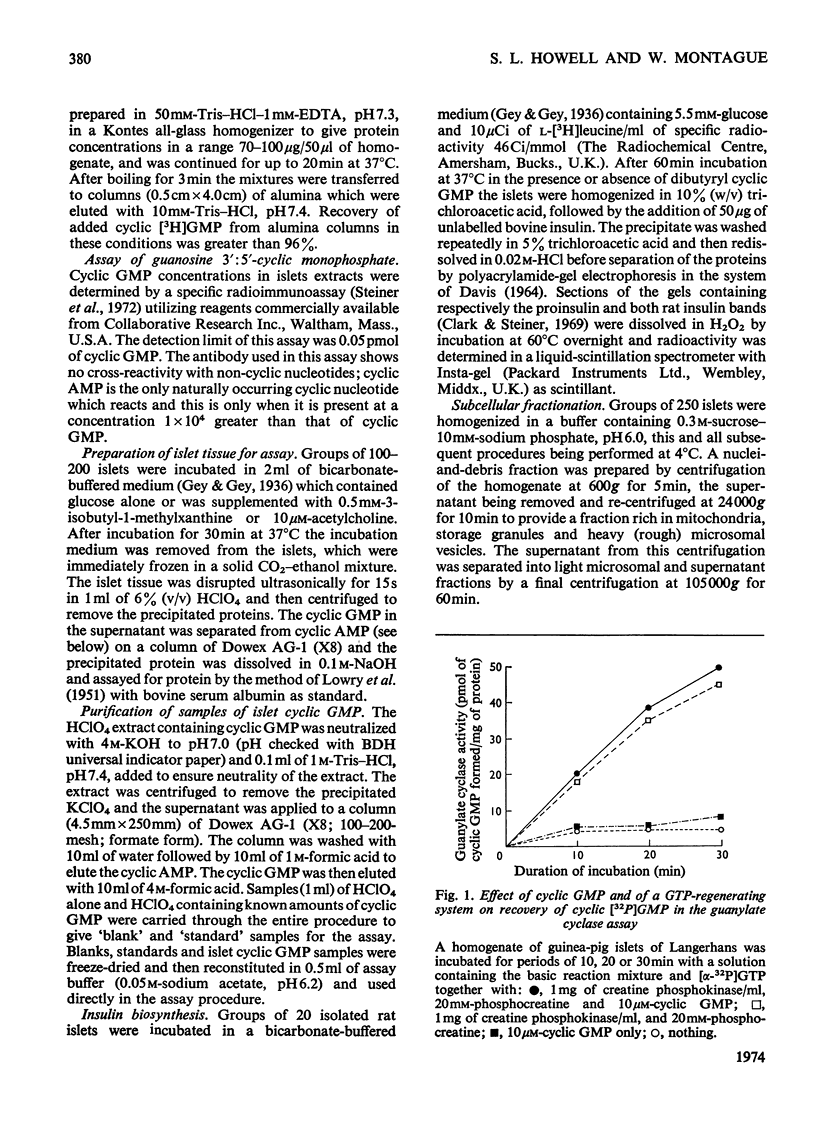
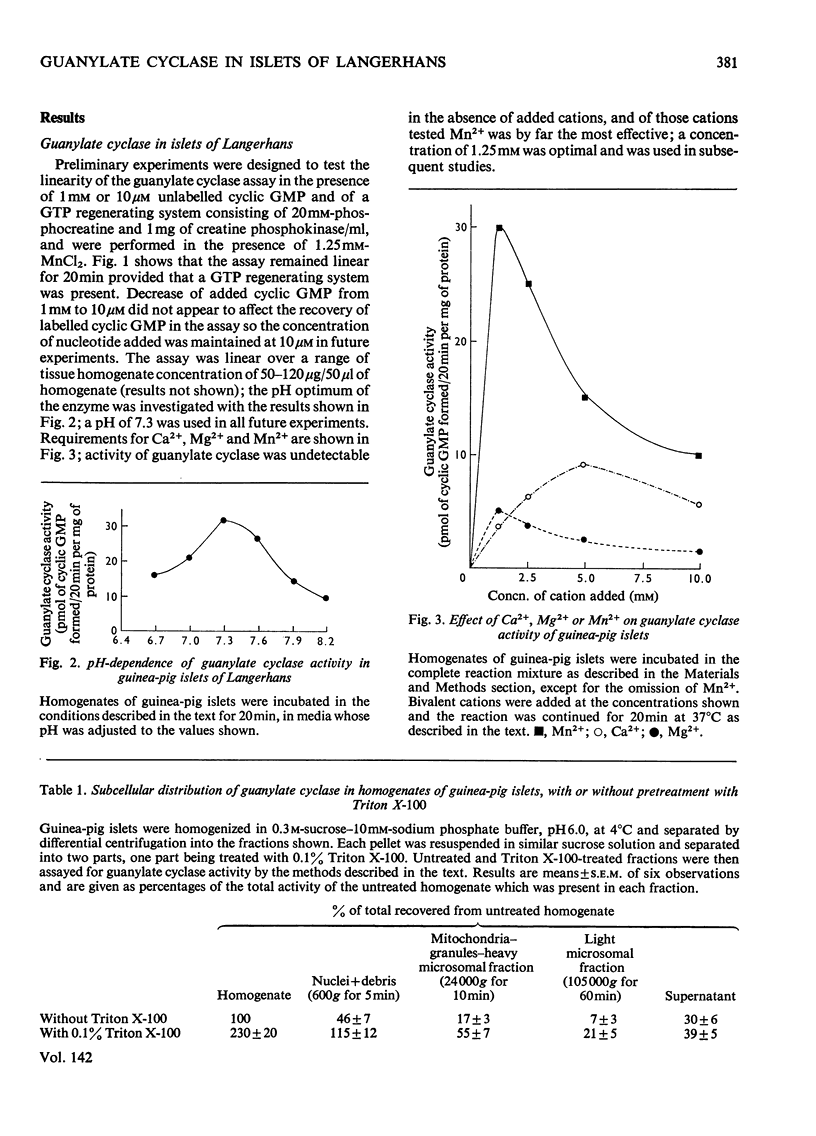
1. Guanylate cyclase activity was determined in homogenates of guinea-pig islets of Langerhans by measurement of the conversion of [α-32P]GTP into cyclic [32P]GMP, the reaction products being separated on columns of neutral alumina. 2. The pH optimum of the enzyme was 7.3; it showed a requirement for bivalent cations, the effectiveness of the cations tested being Mn2+»Ca2+>Mg2+. 3. About 70% of enzyme activity was sedimented by centrifugation at 105000g for 60min; activity was increased 2.3-fold by treatment of homogenates with 0.1% Triton X-100. 4. Guanylate cyclase activity of homogenates was increased by acetylcholine, secretin or pancreozymin, but was inhibited by adrenaline, noradrenaline or ATP. Insulin, glucagon, prostaglandins E1 or E2, glucose, F−, diazoxide or glibenclamide were ineffective. 5. Determination of cyclic GMP amounts in islets by radioimmunoassay showed a basal concentration of 2.0pmol/mg of protein, which was increased by incubation of the islets in the presence of acetylcholine or the phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, but was unaffected by glucose. 6. Dibutyryl cyclic GMP had significant stimulatory effects on rates of insulin biosynthesis in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. 7. These results suggest a possible role for cyclic GMP in the regulation of insulin biosynthesis and secretion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensinger R. E., Fletcher R. T., Chader G. J. Guanylate cyclase: inhibition by light in retinal photoreceptors. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):86–87. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Steiner D. F. Insulin biosynthesis in the rat: demonstration of two proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):278–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Lazarus N. R. Insulin release from mouse islets. Effect of glucose and hormones on adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1290373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. J., Polson J. B., O'Toole A. G., Goldberg N. D. Elevation of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in rat heart after perfusion with acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):398–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Virmaux N., Urban P. F., Mandel P. Guanyl cyclase in a mammalian photoreceptor. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 1;30(2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I. C., Howell S. L., Montague W., Taylor K. W. Regulation of insulin release from isolated islets of Langerhans of the rat in pregnancy. The role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):481–487. doi: 10.1042/bj1340481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W. Guanyl cyclase, an enzyme catalyzing the formation of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate from guanosine trihosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6363–6370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Green I. C., Montague W. A possible role of adenylate cyclase in the long-tern dietary regulation of insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):343–349. doi: 10.1042/bj1360343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Montague W. Adenylate cyclase activity in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Effects of agents which alter rates of insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Effects of glucose concentration on incorporation of [3H]leucine into insulin using isolated mammalian islets of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Whitfield M. Cytochemical localization of adenyl cyclase activity in rat islets of Langerhans. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Nov;20(11):873–879. doi: 10.1177/20.11.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa E., Ishikawa S., Davis J. W., Sutherland E. W. Determination of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and of guanyl cyclase in rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6371–6376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. N., Hodgins D. S., Kuo J. F. Adenylate cyclase in islets of Langerhans. Isolation of islets and regulation of adenylate cyclase activity by various hormones and agents. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2705–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia V., Varrone S. Mechanism of TSH action. Studies with dibutyryl cyclic AMP and dibutyryl cyclic GMP. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 2;13(6):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz H., Maier V., Hinz M., Nierle C., Pfeiffer E. F. Stimulation of H-3-leucine incorporation into the proinsulin and insulin fraction of isolated pancreatic mouse islets in the presence of glucagon, theophylline and cyclic AMP. Diabetes. 1973 Jun;22(6):433–441. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.6.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Williams R. H., Little S. A. Studies on the assay and activities of guanyl and adenyl cyclase of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):206–213. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varrone S., Di Lauro R., Macchia V. Stimulation of polypeptide synthesis by cyclic 3'-5'-guanosine monophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyles N., Gutman R. A., Selawry H., Fink G., Penhos J. C., Recant L. Interaction of various stimulators and inhibitors on insulin secretion in vitro. Horm Res. 1973;4(2):65–73. doi: 10.1159/000178291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. A., Zenser T. V. Separation of cyclic 3',5'-nucleoside monophosphates from other nucleotides on aluminum oxide columns. Application to the assay of adenyl cyclase and guanyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):372–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Field J. B. Elevation of cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in dog thyroid slices caused by acetylcholine and sodium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7062–7066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


