Abstract
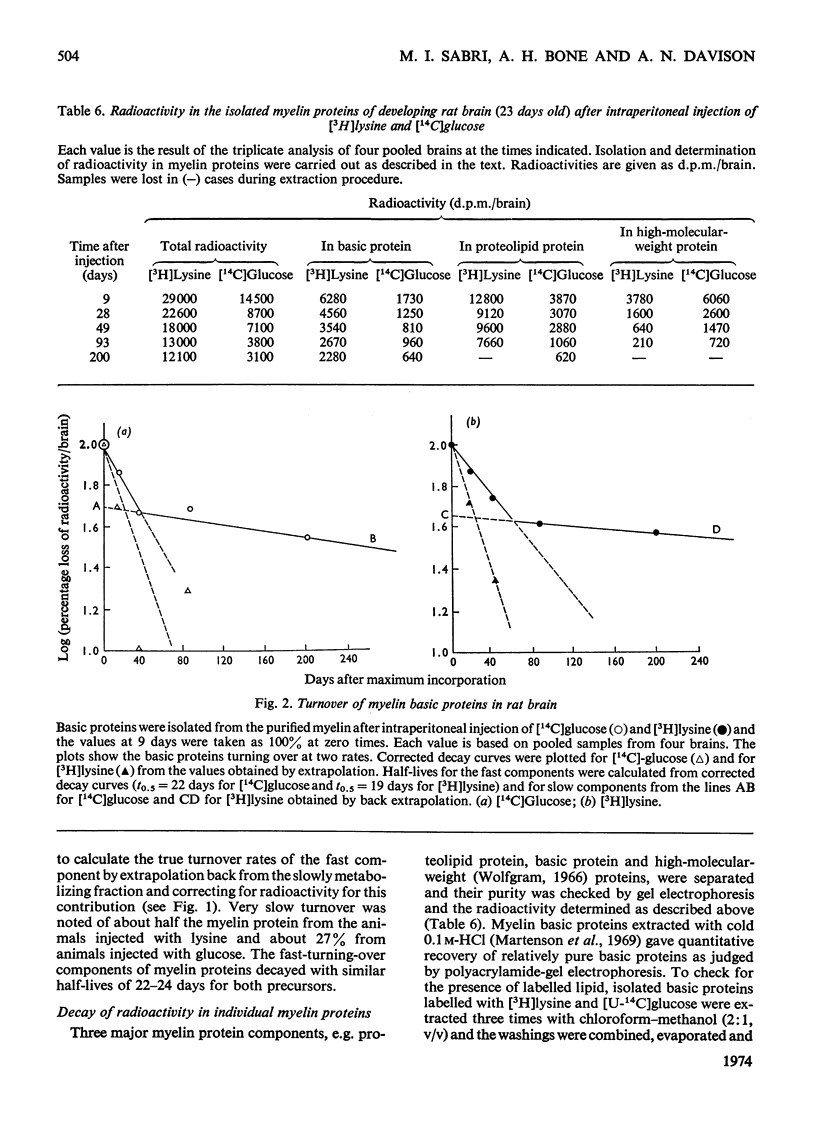
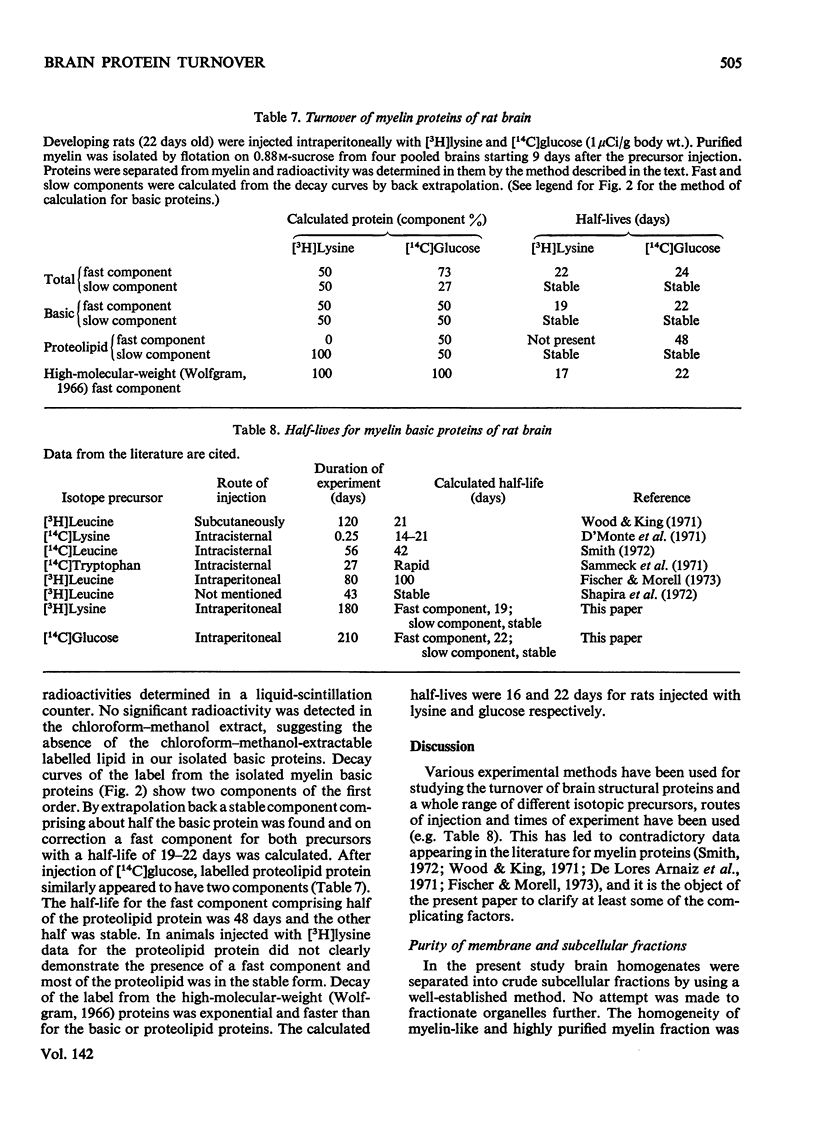
1. Protein metabolism of myelin and other subcellular components from developing rat brain was studied for periods from 5h to 210 days after intraperitoneal injection of [3H]lysine and [14C]glucose. 2. Half-lives for total brain proteins (t0.5) were 27 days after [3H]lysine and 4 days after [14C]glucose injection. 3. Factors accounting for the difference in the turnover rates obtained with different precursors, and the problem of reutilization of the label were investigated. 4. The catabolism of purified myelin proteins was studied and the half-lives of individual myelin proteins were calculated. 5. Myelin basic proteins turned over at two different rates. Half-life of the fast component of myelin basic proteins was 19–22 days and the slow component exhibited a high degree of metabolic stability. 6. Proteolipid protein underwent slow turnover. High-molecular-weight Wolfgram (1966) proteins underwent (relatively) fast metabolism (t0.5 of 17–22 days).
Full text
PDF



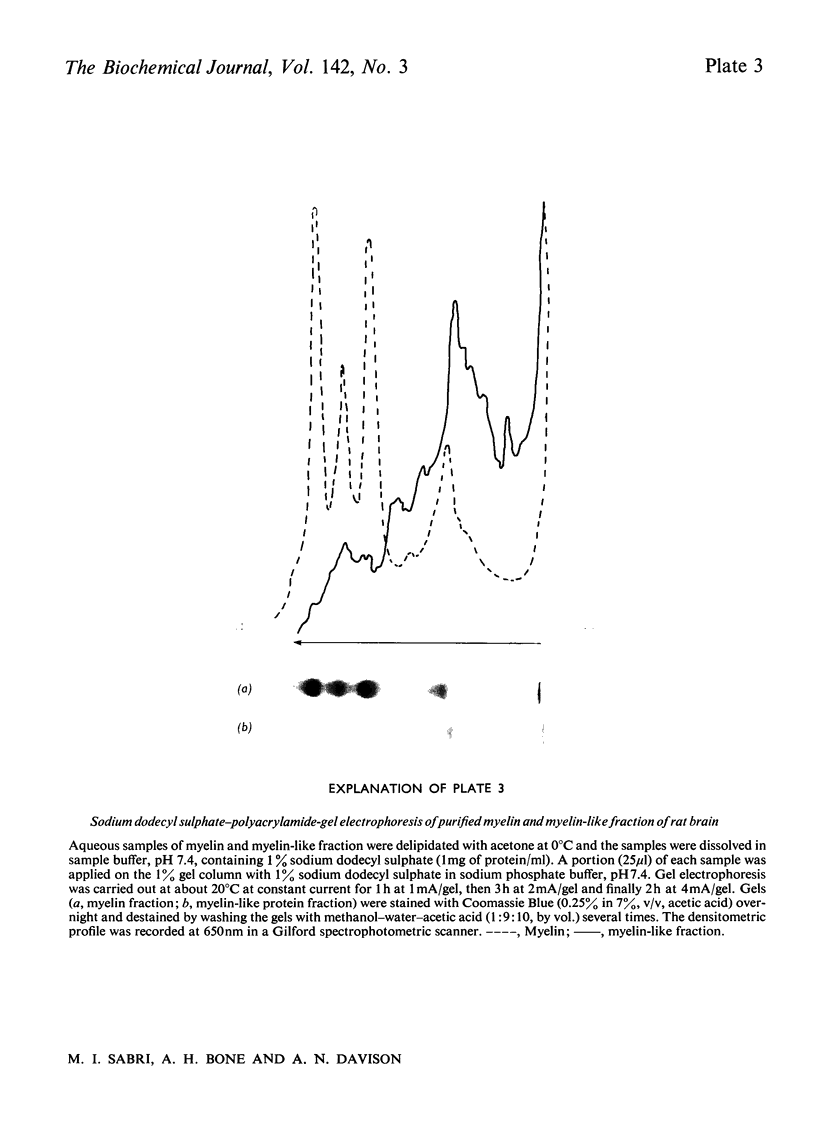


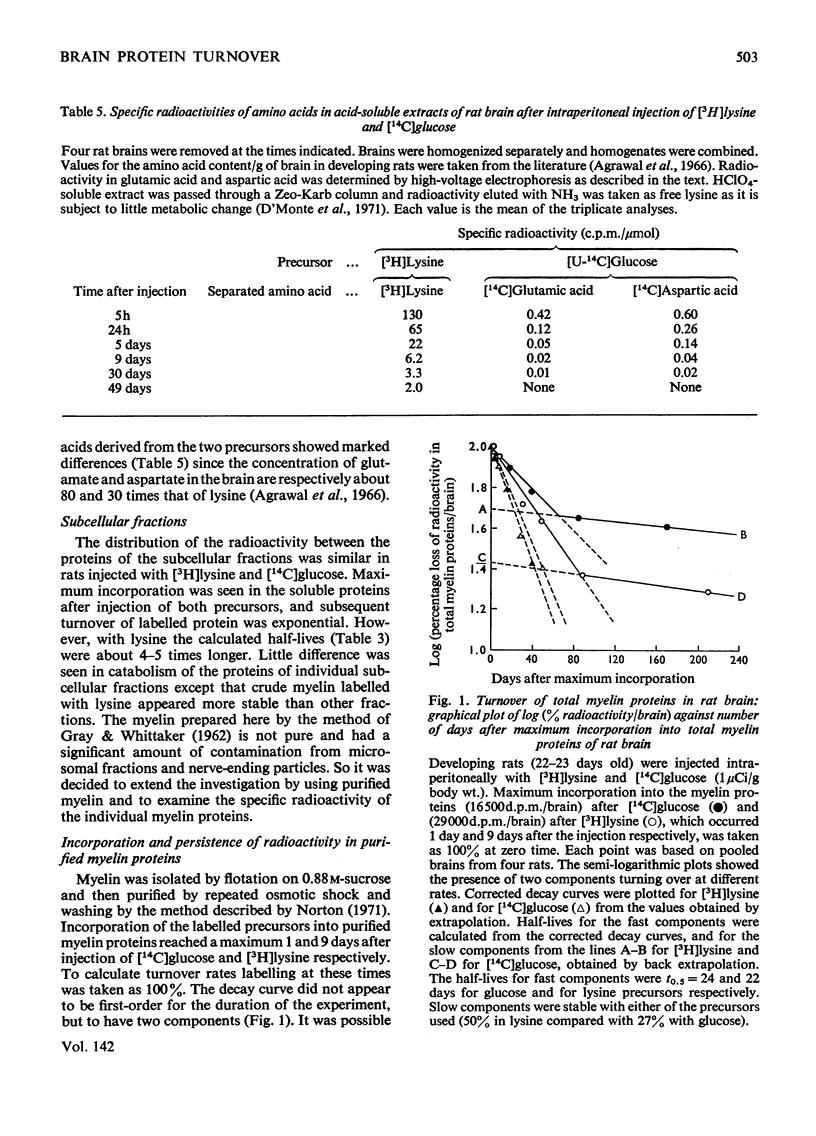


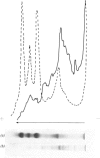
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., Banik N. L., Bone A. H., Davison A. N., Mitchell R. F., Spohn M. The identity of a myelin-like fraction isolated from developing brain. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):635–642. doi: 10.1042/bj1200635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal H. C., Burton R. M., Fishman M. A., Mitchell R. F., Prensky A. L. Partial characterization of a new myelin protein component. J Neurochem. 1972 Sep;19(9):2083–2089. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb05118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal H. C., Davis J. M., Himwich W. A. Postnatal changes in free amino acid pool of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Jul;13(7):607–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb11957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au W. Y., Dring L. G., Grahame-Smith D. G., Isaac P., Williams R. T. The metabolism of 14 C-labelled -methyldopa in normal and hypertensive human subjects. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj1290001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin L., Lowry O. H., Brown J. G., Carter J. G. The turnover of protein in discrete areas of rat brain. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):351–359. doi: 10.1042/bj1260351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banik N. L., Davison A. N. Isolation of purified basic protein from human brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb05994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Monte B., Mela P., Marks N. Metabolic instability of myelin protein and proteolipid fractions. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):355–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N. Metabolically inert proteins of the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle and tendon. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:272–282. doi: 10.1042/bj0780272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURST S., LAJTHA A., WAELSCH H. Amino acid and protein metabolism of the brain. III. Incoporation of lysine into the proteins of various brain areas and their cellular fractions. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):216–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Marshall I. A technique for measuring brain protein synthesis. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Extraction of rat myelin basic protein free of other basic proteins of whole central nervous system tissue. An analysis of its electrophoretic heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4268–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. S., Hydén H. A study of specific brain proteins on the semi-micro scale. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):823–833. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piha R. S., Cuénod M., Waelsch H. Metabolism of histones of brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2397–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrĩguez de Lores Arn, Alberici de Canal M., De Robertis E. Turnover of proteins in subcellular fractions of rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1971 Aug 7;31(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90642-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Nagai Y., Tsumita T. A novel method for the extraction of encephalitogenic protein from bovine brain. Jpn J Exp Med. 1972 Oct;42(5):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammeck R., Martenson R. E., Brady R. O. Studies of the metabolism of myelin basic proteins in various regions of the central nervous system of immature and adult rats. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmukler M., Yiengst M. J. A biuret method for determination of protein in Hyamine hydroxide and NCS solutions used for liquid scintillation counting in toluene. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):406–411. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E. The turnover of myelin proteins. Neurobiology. 1972;2(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uda Y., Nakazawa Y. Proteolipid of bovine brain white matter: phospholipid components. J Biochem. 1973 Apr;73(4):755–761. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waehneldt T. V., Mandel P. Isolation of rat brain myelin, monitored by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of dodecyl sulfate-extracted proteins. Brain Res. 1972 May 26;40(2):419–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram F. A new proteolipid fraction of the nervous system. I. Isolation and amino acid analyses. J Neurochem. 1966 Jun;13(6):461–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., King N. Turnover of basic protein of rat brain. Nature. 1971 Jan 1;229(5279):56–58. doi: 10.1038/229056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]