Abstract
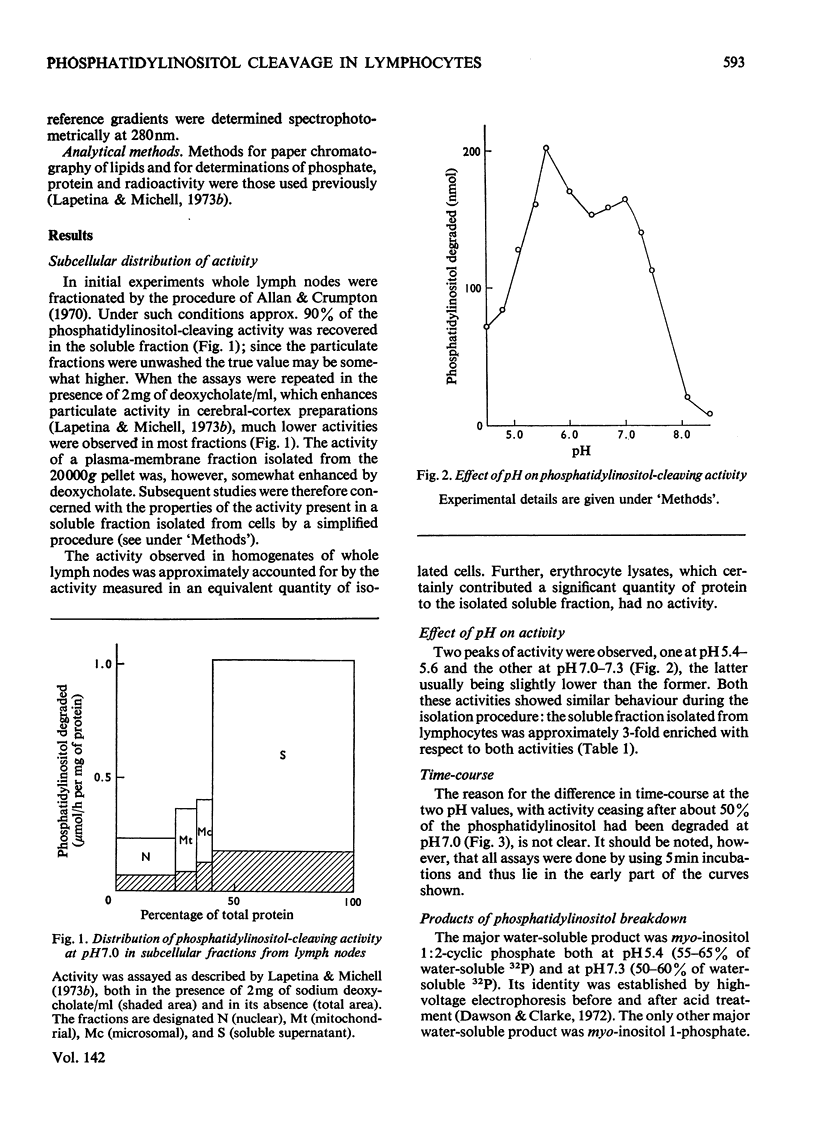
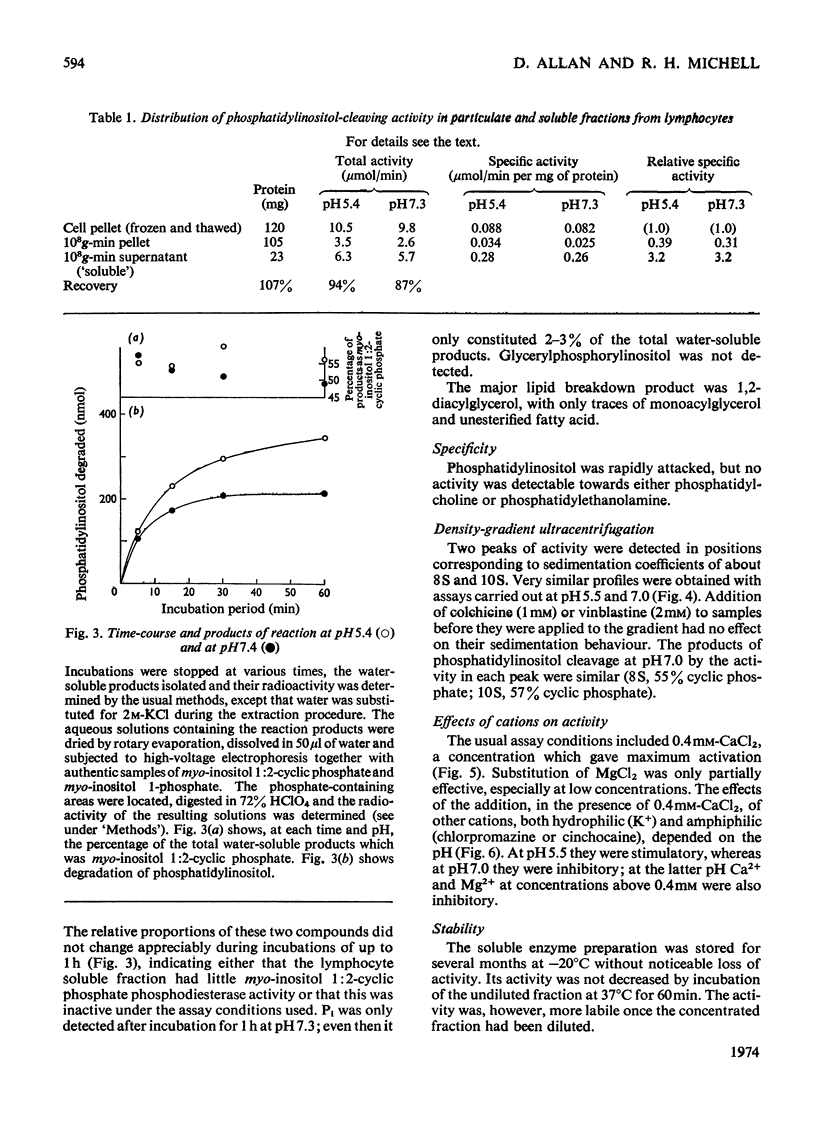
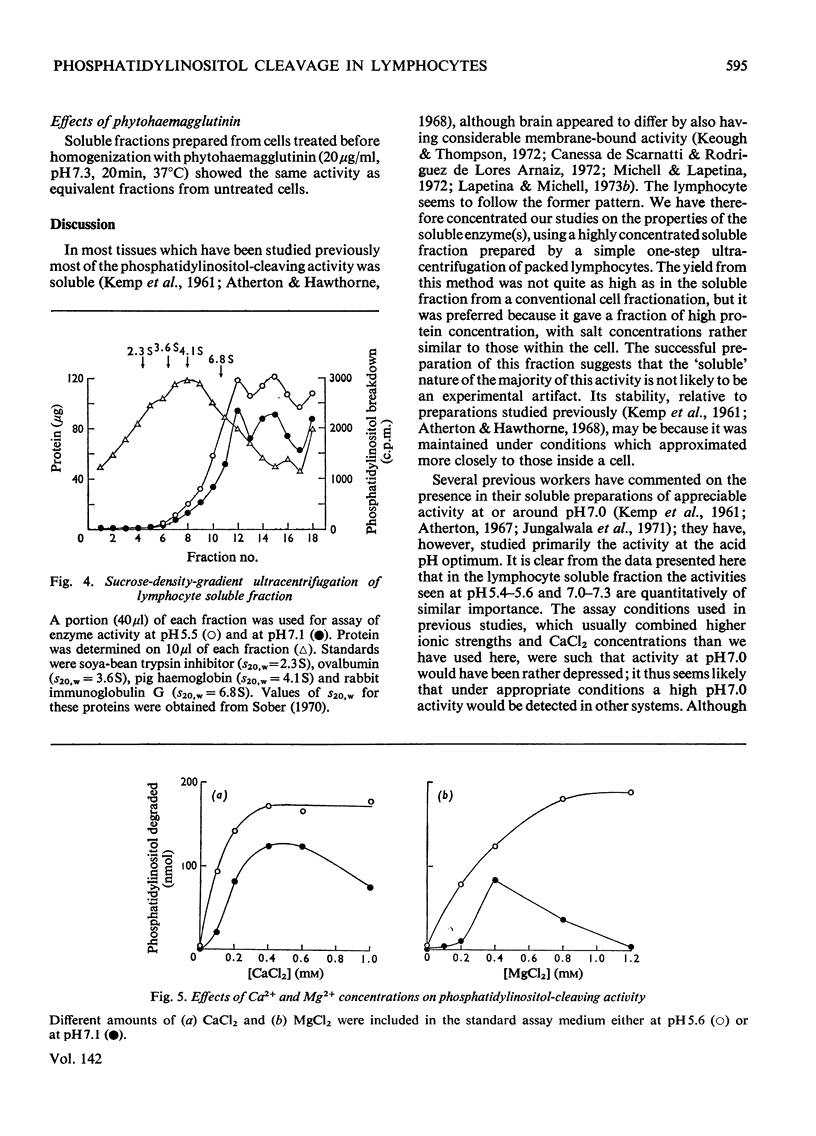
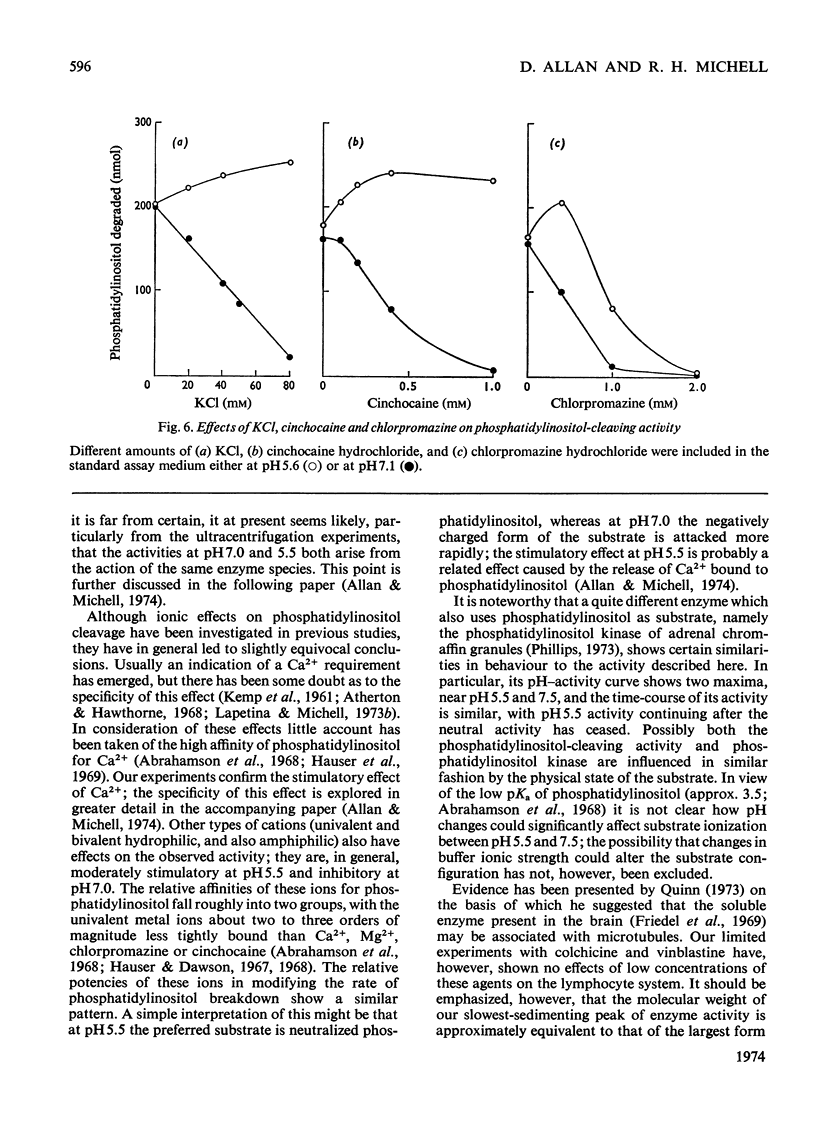
Phosphatidylinositol breakdown by subcellular preparations of small lymphocytes from pig mesenteric lymph nodes was investigated. Activity was higher than in preparations from the tissues studied previously; it was recovered largely in the soluble fraction, which showed pH optima at both 5.4–5.6 and 7.0–7.3. As in other tissues, phosphatidylinositol cleavage produced 1,2-diacylglycerol and a mixture of myo-inositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate and myo-inositol 1-phosphate. It was stimulated by addition of CaCl2 and, less effectively, by MgCl2. On sucrose-density-gradient ultracentrifugation at pH7.0 two peaks of activity were observed (approx. sedimentation coefficients 8S and 10S); the activity profiles on the gradients were similar when assayed at pH7.0 and 5.5. Activity at pH7.0 (and 0.4mm-CaCl2) was decreased by agents, such as salts and lipophilic cations, which tend to neutralize the negative charge of phosphatidylinositol; at pH5.5 these agents slightly stimulated activity. It is suggested that the same enzyme(s) may be responsible for activity at both pH optima and that previous workers may have underestimated the pH7.0 activity because of the inhibitory influence of cations under the usual assay conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson M. B., Colacicco G., Curci R., Rapport M. M. Ionic properties of acidic lipids. Phosphatidylinositol. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1692–1698. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Auger J., Crumpton M. J. Interaction of phytohemagglutinin with plasma membranes of pig lymphocytes and thymus cells. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90689-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Crumpton M. J. Preparation and characterization of the plasma membrane of pig lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):133–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1200133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol cleavage in lymphocytes. Requirement for calcium ions at a low concentration and effects of other cations. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):599–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1420599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton R. S., Hawthorne J. N. The phosphoinositide inositolphosphohydrolase of guinea-pig intestinal mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):68–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa de Scarnati O., Rodriguez de Lores Arna Acetylcholine stimulation on phosphatidylinositolinositol phosphohydrolase of rat brain cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 19;270(2):218–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Clarke N. D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1270113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Freinkel N., Jungalwala F. B., Clarke N. The enzymic formation of myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate from phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):605–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1220605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. Molecular biology of synaptic receptors. Science. 1971 Mar 12;171(3975):963–971. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3975.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell J., Garland J. T., Friedel R. O. Acetylcholine action: biochemical aspects. Science. 1969 Aug 29;165(3896):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3896.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Mueller G. C. An early alteration in the phospholipid metabolism of lymphocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1396–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Dawson R. M. Role of inositol cyclic phosphate in stimulated tissues. Nature. 1973 Jun 29;243(5409):535–537. doi: 10.1038/243535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedel R. O., Brown J. D., Durell J. The enzymic hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol by guinea pig brain: Sub-cellular distribution and hydrolysis products. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D., Davies M., Hokin L. E. The effects of secretagogues on the incorporation of (2- 3 H)myoinositol into lipid in cytological fractions in the pancreas of the guinea pig in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):736–745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Chapman D., Dawson R. M. Physical studies of phospholipids. XI. Ca2+ binding to monolayers of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 15;183(2):320–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The displacement of calcium ions from phospholipid monolayers by pharmacologically active and other organic bases. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):909–916. doi: 10.1042/bj1090909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Dynamic aspects of phospholipids during protein secretion. Int Rev Cytol. 1968;23:187–208. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin M. R. Studies on chemical mechanisms of the action of neurotransmitters and hormones. II. Increased incorporation of 32P into phosphatides as a second, adaptive response to pancreozymin or acetylcholine in pigeon pancreas slices. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol provoked by muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1420583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Freinkel N., Dawson R. M. The metabolism of phosphatidylinositol in the thyroid gland of the pig. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):19–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1230019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP P., HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. Phosphoinositides. 3. Enzymic hydrolysis of inositol-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0790193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keough K. M., Thompson W. Soluble and particulate forms of phosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 7;270(3):324–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkof P. R., Tata J. R. The subcellular distribution of 32P-labelled phospholipids, 32P-labelled ribonucleic acid and 125I-labelled odoprotein in pig thyroid slices. Effect in vitro of thyrotrophic hormone and dibutyryl-3',5'-(cyclic)-adeosine onophosphate. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):729–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1120729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. A membrane-bound activity catalysing phosphatidylinositol breakdown to 1,2-diacylglycerol, D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate an D-myoinositol 1-phosphate. Properties and subcellular distribution in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1310433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in cells receiving extracellular stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas D. O., Shohet S. B., Merler E. Changes in phospholipid metabolism which occur as a consequence of mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa Y., Osawa T., Inoue K., Nojima S. Effects of various mitogens on the phospholipid metabolism of human peripheral lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Lapetina E. G. Production of cyclic inositol phosphate in stimulated tissues. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 27;240(104):258–260. doi: 10.1038/newbio240258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase. A component of the chromaffin-granule membrane. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):579–587. doi: 10.1042/bj1360579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J. The association between phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase activity and a specific subunit of microtubular protein in rat brain. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):273–281. doi: 10.1042/bj1330273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Good J. J., Barclay M., Reggio R. B. Quantitative analysis of simple lipid classes by thin-layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 10;152(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


