Abstract
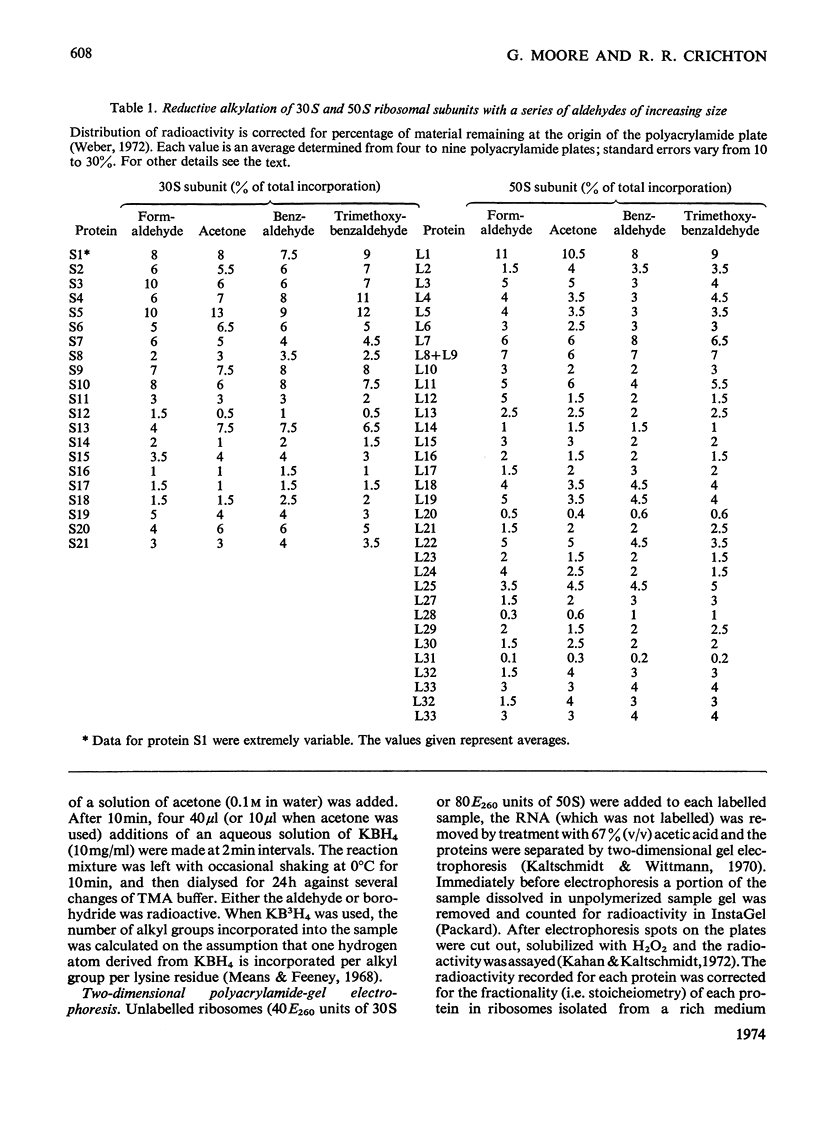
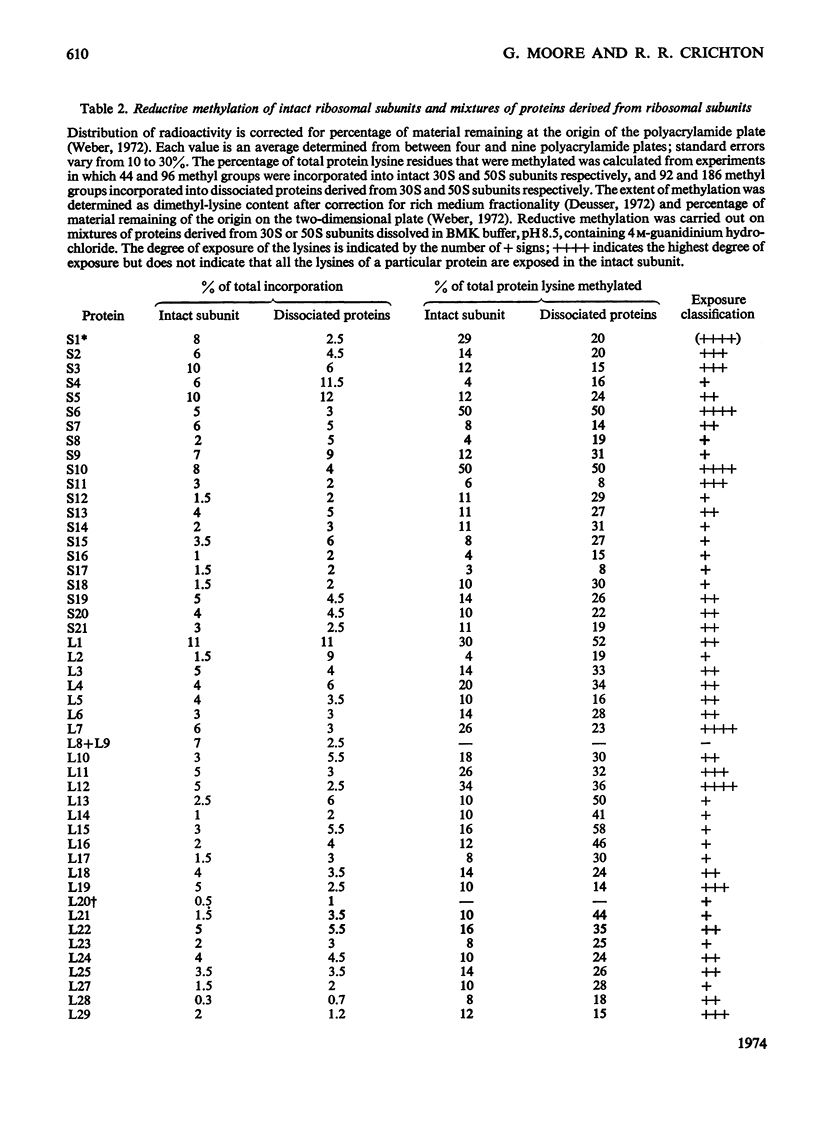
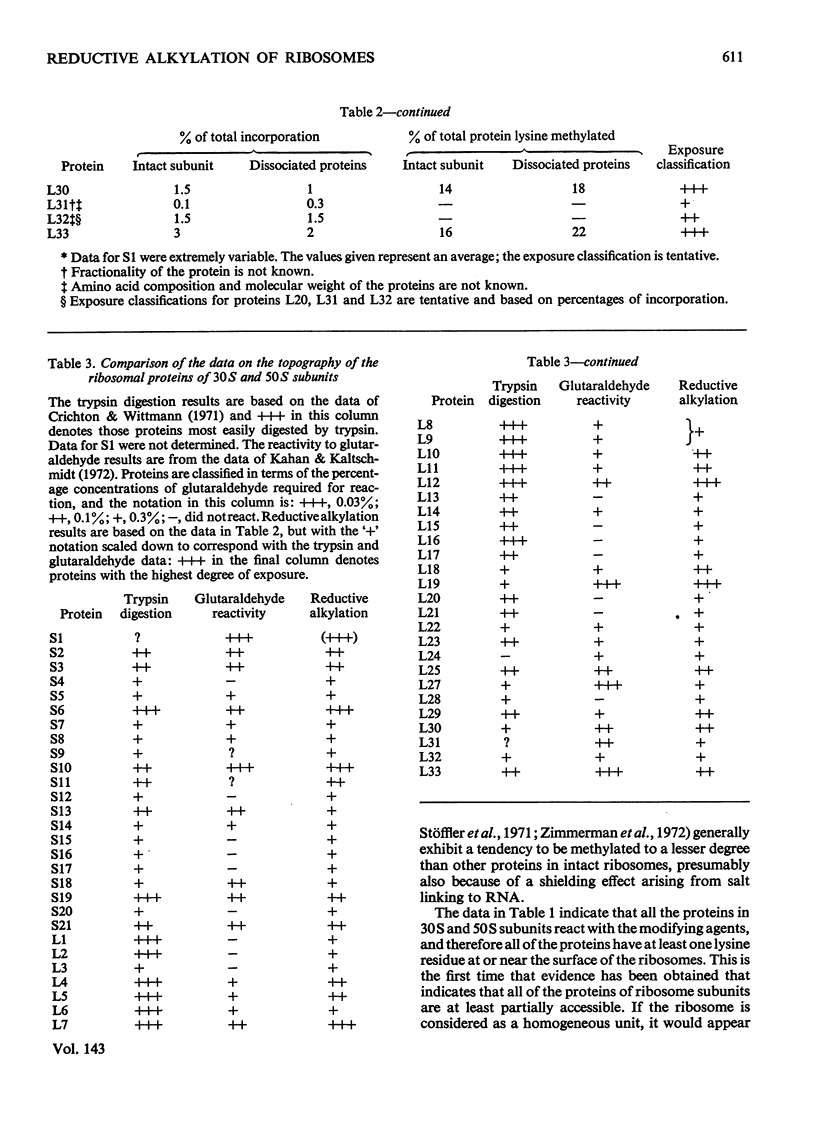
Escherichia coli ribosomes were treated with a number of different aldehydes of various sizes in the presence of NaBH4. After incorporation of either 3H or 14C, the ribosomal proteins were separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and the extent of alkylation of the lysine residues in each protein was measured. The same pattern of alkylation was observed with the four reagents used, namely formaldehyde, acetone, benzaldehyde and 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde. Every protein in 30S and 50S subunits was modified, although there was considerable variation in the degree of alkylation of individual proteins. A topographical classification of ribosomal proteins is presented, based on the degree of exposure of lysine residues. The data indicate that every protein of the ribosome has at least one lysine residue exposed at or near the surface of the ribonucleo-protein complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Topography of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit and streptomycin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1321–1328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Gupta V. Three-dimensional organization of the 30S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. I. Preliminary classification of the proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1329–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXIV. Trypsin digestion as a possible probe of the conformation of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00332780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusser E. Heterogeneity of ribosomal populations in Escherichia coli cells grown in different media. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan L., Kaltschmidt E. Glutaraldehyde reactivity of the proteins of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2691–2698. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means G. E., Feeney R. E. Reductive alkylation of amino groups in proteins. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2192–2201. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G., Crichton R. R. Reductive methylation: a method for preparing functionally active radioactive ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 15;37(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. A., Garrett R. A., Zeichhardt H., Stöffler G. Proteins occurring at, or near, the subunit interface of E. coli ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 31;127(4):359–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00267106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaup H. W., Green M., Kurland C. G. Molecular interactions of ribosomal components. I. Identification of RNA binding sites for individual 30S ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00267007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaup H. W., Green M., Kurland C. G. Molecular interactions of ribosomal components. II. Site-specific complex formation between 30S proteins and ribosomal RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00266926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P., Breiman A. The effect of trypsin on 30 -S and 50 -S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 30;254(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90880-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Daya L., Rak K. H., Garrett R. A. Ribosomal proteins. XXVI. The number of specific protein binding sites on 16 s and 23 s RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Hasenbank R., Lütgehaus M., Maschler R., Morrison C. A., Zeichhardt H., Garrett R. A. The accessibility of proteins of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit to antibody binding. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):89–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00333659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H. J. Stoichiometric measurements of 30S and 50S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):233–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00333861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Muto A., Fellner P., Ehresmann C., Branlant C. Location of ribosomal protein binding sites on 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1282–1286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


