Abstract
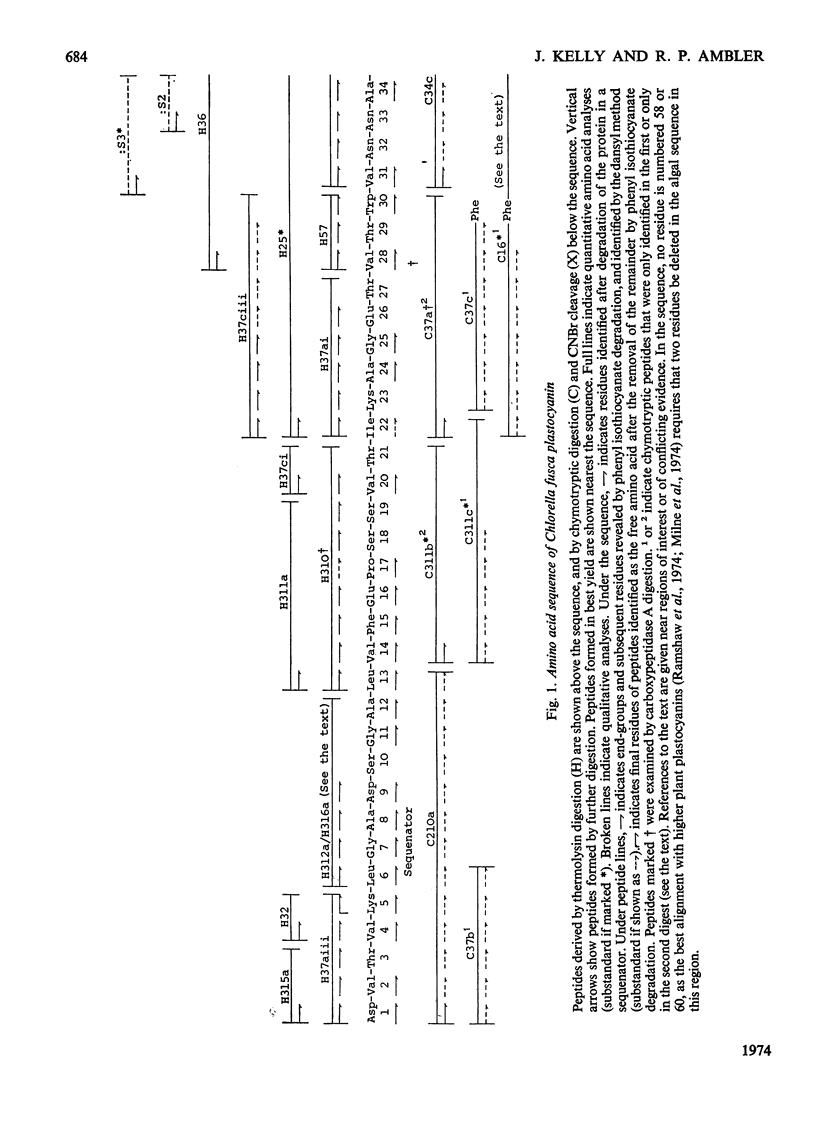
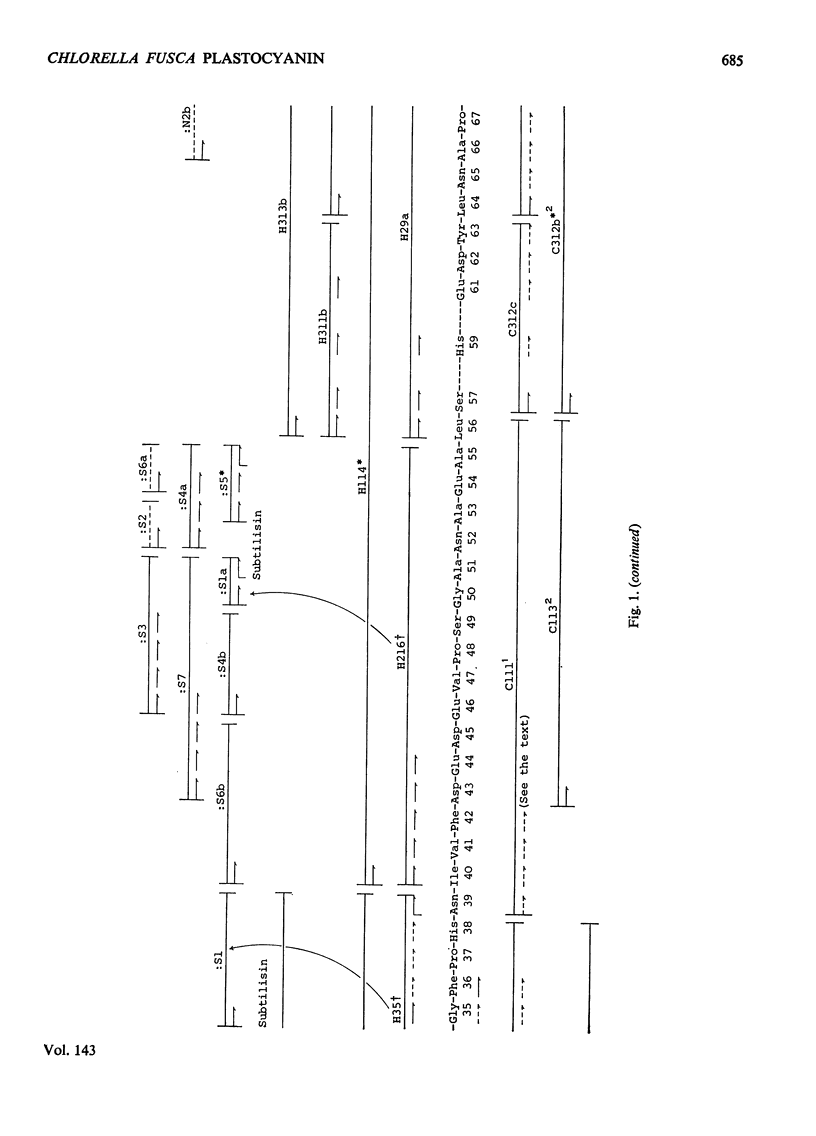
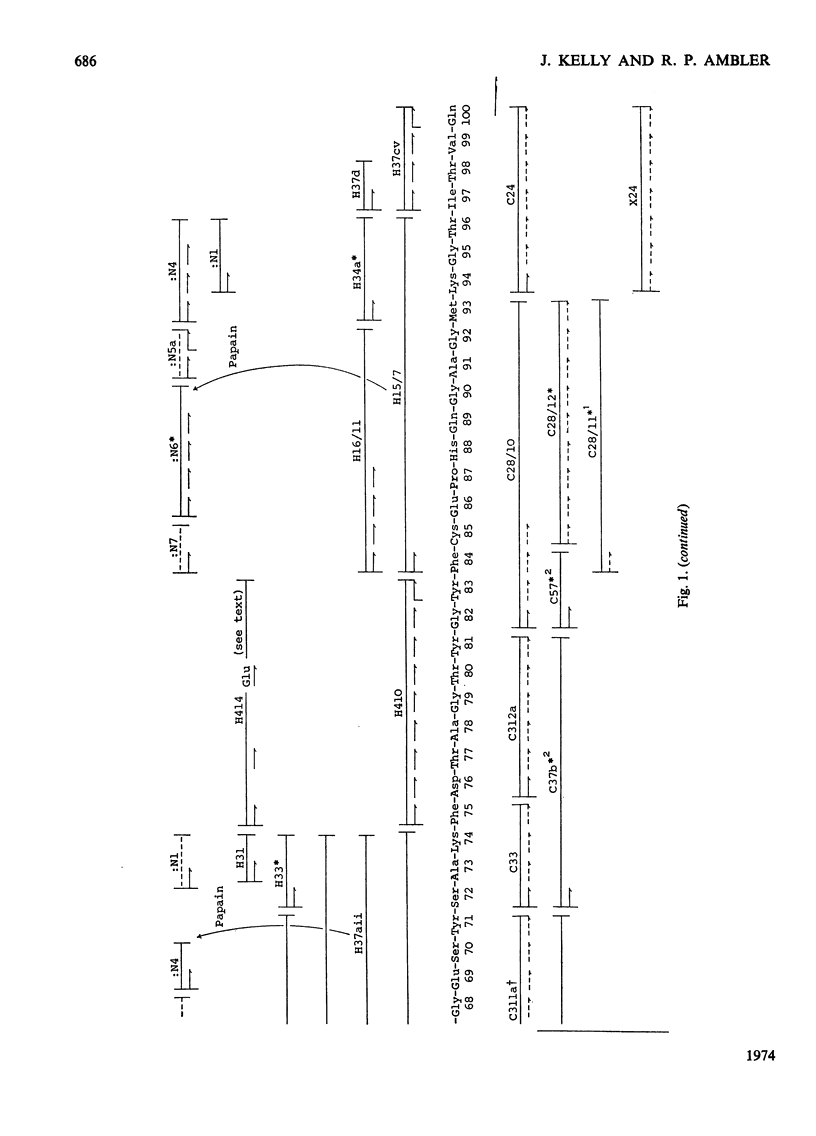
The amino acid sequence of the plastocyanin from the green alga Chlorella fusca was determined. The protein consists of a single polypeptide chain of 98 residues, and was determined by characterization of chymotryptic and thermolysin peptides. The amino acid sequence shows considerable similarity to that of higher plant plastocyanins. The protein contains a single cysteine, and the sequence in the vicinity of this residue is similar to that around the cysteine residue of bacterial azurins. The plastocyanin contains some uncharacterized carbohydrate. Detailed evidence for the sequence of the protein has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50 036 (17pp., 1 microfiche) at the British Library (Lending Division) (formerly the National Lending Library for Science and Technology), Boston Spa, Yorks. LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies may be obtained on the terms given in Biochem. J. (1973) 131, 5.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Brown L. H. The amino acid sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens azurin. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):784–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1040784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of cytochrome c' from Alcaligenes sp. N.C.I.B. 11015. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):751–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1350751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Wynn M. The amino acid sequences of cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):485–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1310485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I., Chain R. K., McSwain B. D., Tsujimoto H. Y., Knaff D. B. Evidence from chloroplast fragments for three photosynthetic light reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1404–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Photosynthetic Electron Transport Chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. IV. Purification and Properties of Plastocyanin. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1637–1642. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATOH S. A new copper protein from Chlorella ellisoidea. Nature. 1960 May 14;186:533–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATOH S., SHIRATORI I., TAKAMIYA A. Purification and some properties of spinach plastocyanin. J Biochem. 1962 Jan;51:32–40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATOH S., SUGA I., SHIRATORI I., TAKAMIYA A. Distribution of plastocyanin in plants, with special reference to its localization in chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Jul;94:136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J. J., Krogmann D. W. Isolation and properties of plastocyanin from Anabaena variabilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 9;131(3):508–515. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Malmström B. G. The state and function of copper in biological systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:177–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström B. G., Reinhammar B., Vänngård T. The state of copper in stellacyanin and laccase from the lacquer tree Rhus vernicifera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 7;205(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne P. R., Wells J. R., Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of plastocyanin from French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):691–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1430691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne P. R., Wells J. R. Structural and molecular weight studies on the small copper protein, plastocyanin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1566–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw J. A., Brown R. H., Scawen M. D., Boulter D. Higher plant plastocyanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 20;303(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw J. A., Scawen M. D., Bailey C. J., Boulter D. The amino acid sequence of plastocyanin from Solanum tuberosum L. (potato). Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):583–592. doi: 10.1042/bj1390583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON E. O. Modification of tyrosine during performic acid oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):440–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



