Abstract
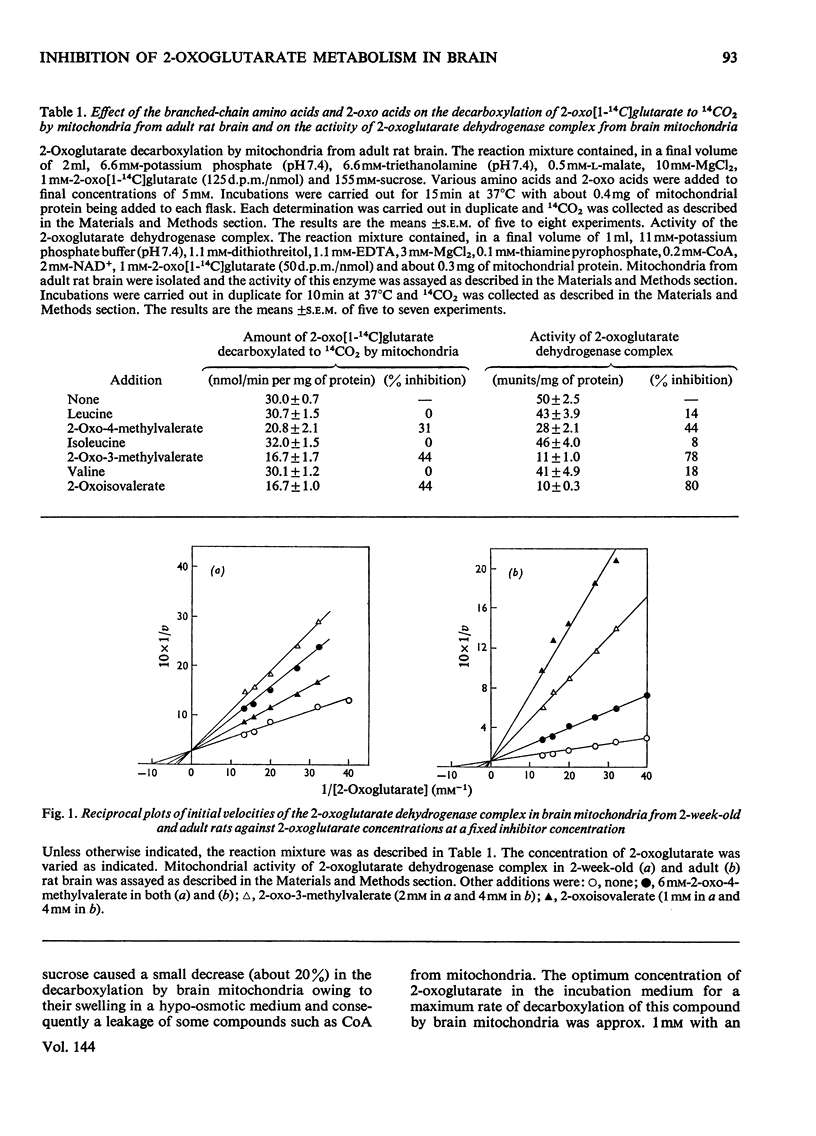
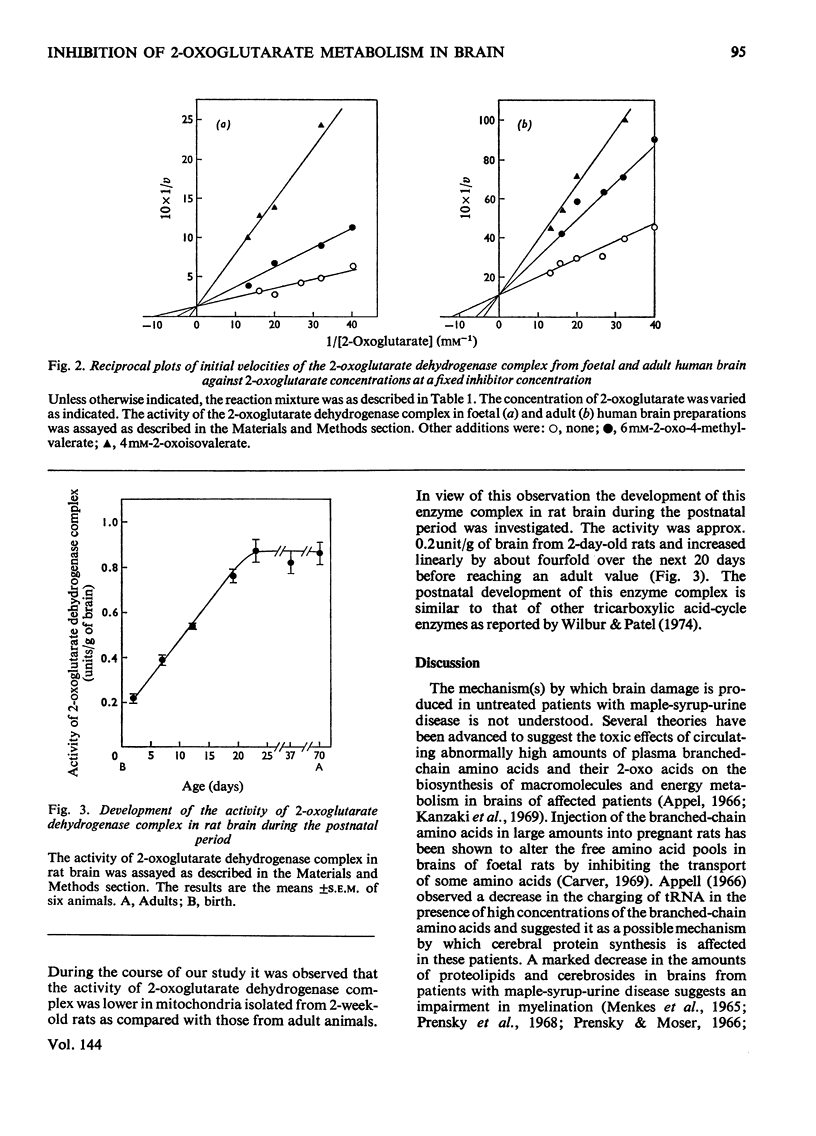
1. The effect of the branched-chain amino acids, namely leucine, isoleucine and valine and their corresponding 2-oxo acids on the metabolism of 2-oxoglutarate by developing rat and human brain preparations was investigated. 2. The decarboxylation of 2-oxo[1-14C]glutarate to 14CO2 by mitochondria from adult rat brain was inhibited by the branched-chain 2-oxo acids whereas the branched-chain amino acids had no inhibitory effect on this process. 3. The activity of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex was about 0.2unit/g of brain from 2-day-old rats and increased by about fourfold reaching an adult value by the end of the third postnatal week. 4. The Km value for 2-oxoglutarate of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in rat and human brain was 100 and 83μm respectively. 5. The branched-chain 2-oxo acids competitively inhibited this enzyme from suckling and adult rats brains as well as from foetal and adult human brains, whereas the branched-chain amino acids had no effect on this enzyme. 6. Approximate Ki values for the branched-chain 2-oxo acids found for this enzyme were in the range found for these 2-oxo acids in plasma from patients with maple-syrup-urine disease. 7. The possible significance of the inhibition by the branched-chain 2-oxo acids of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in brains of untreated patients with maple-syrup-urine disease is discussed in relation to the energy metabolism and the biosynthesis of lipids from ketone bodies.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel S. H. Inhibition of brain protein synthesis: an approach to the biochemical basis of neurological dysfunction in the amino-acidurias. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov;29(1):63–70. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1966.tb02252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blass J. P., Lewis C. A. Kinetic properties of the partially purified pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of ox brain. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):31–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1310031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden J. A., McArthur C. L., 3rd, Fried M. The inhibition of pyruvate decarboxylation in rat brain by -ketoisocaproic acid. Biochem Med. 1971 Apr;5(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(71)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver M. J. Free amino acids of fetal brain. Influence of the branched chain amino acids. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):113–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. B., Nicklas W. J. The metabolism of rat brain mitochondria. Preparation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4724–4731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANCIS J., LEVITZ M., MILLER S., WESTALL R. G. Maple syrup urine disease. Br Med J. 1959 Jan 10;1(5114):91–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5114.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENT C. E., WESTALL R. G. Studies in maple syrup urine disease. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Jun;36:259–268. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.187.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus P. M., Prensky A. L. Further observations on the biochemical lesion in maple syrup urine disease. Nature. 1967 Apr 15;214(5085):276–276. doi: 10.1038/214276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmond J. Ketone bodies as precursors of sterols and fatty acids in the developing rat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPER S., SEGAL H. L. Kinetic studies of rat liver glutamicalanine transaminase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL R. K., LEE M. Influence of alpha-ketoacids on the respiration of brain in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jul;113:660–663. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Connelly J. L. Studies on the mutual influences of substrates on bovine -keto acid metabolism. Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 20;11(13):2416–2421. doi: 10.1021/bi00763a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Hayakawa T., Hamada M., Fukuyoshi Y., Koike M. Mammalian alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. IV. Substrate specificities and kinetic properties of the pig heart pyruvate and 2-oxyoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1183–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysiak W., Muzalewska A., Angielski S. Branched-chain aminotransferase in brain tissue. Acta Biochim Pol. 1970;17(2):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKENZIE D. Y., WOOLF L. I. Maple syrup urine disease; an inborn error of the metabolism of valine, leucine, and isoleucine associated with gross mental deficiency. Br Med J. 1959 Jan 10;1(5114):90–91. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5114.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H., HURST P. L., CRAIG J. M. A new syndrome: progressive familial infantile cerebral dysfunction associated with an unusual urinary substance. Pediatrics. 1954 Nov;14(5):462–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H. Maple syrup disease; isolation and identification of organic acids in the urine. Pediatrics. 1959 Feb;23(2):348–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H., PHILIPPART M., FIOL R. E. CEREBRAL LIPIDS IN MAPLE SYRUP DISEASE. J Pediatr. 1965 Mar;66:584–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H., Solcher H. Maple syrup disease. Effects of dietary therapy on cerebral lipids. Arch Neurol. 1967 May;16(5):486–491. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470230038004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATRICK A. D. Maple syrup urine disease. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Jun;36:269–272. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.187.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Auerbach V. H., Grover W. D., Wilbur D. O. Effect of the branched-chain alpha-keto acids on pyruvate metabolism by homogenates of human brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jun;20(6):1793–1796. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S. The effect of phenylpyruvate on pyruvate metabolism in rat brain. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):677–684. doi: 10.1042/bj1280677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky A. L., Carr S., Moser H. W. Development of myelin in inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Arch Neurol. 1968 Dec;19(6):552–558. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480060022002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky A. L., Moser H. W. Brain lipids, proteolipids, and free amino acids in maple syrup urine disease. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):863–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. H., Chappell J. B. The inhibition of malate, tricarboxylate and oxoglutarate entry into mitochondria by 2-n-butylmalonate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 21;28(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDERMAN S. E., NORTON P. M., ROITMAN E., HOLT L. E., Jr MAPLE SYRUP URINE DISEASE, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO DIETOTHERAPY. Pediatrics. 1964 Oct;34:454–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg D. H. Maple syrup urine disease metabolites studies in cerebellum cultures. J Neurochem. 1969 Jul;16(7):1141–1146. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODY N. C., HARRIS J. A. FAMILY SCREENING STUDIES IN MAPLE SYRUP URINE DISEASE (BRANCHED-CHAIN KETOACIDURIA). J Pediatr. 1965 Jun;66:1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur D. O., Patel M. S. Development of mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):709–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuwiler A., Geller E. Serotonin depletion by dietary leucine. Nature. 1965 Oct 2;208(5005):83–84. doi: 10.1038/208083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


