Abstract
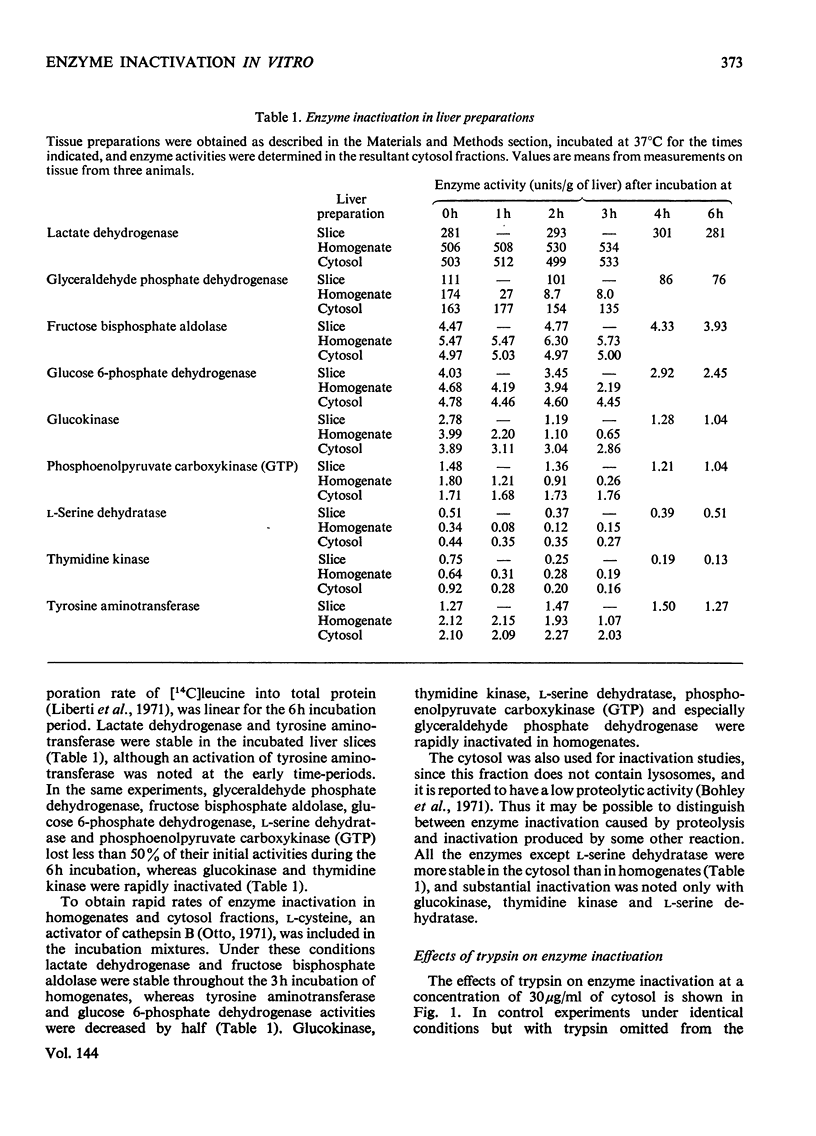
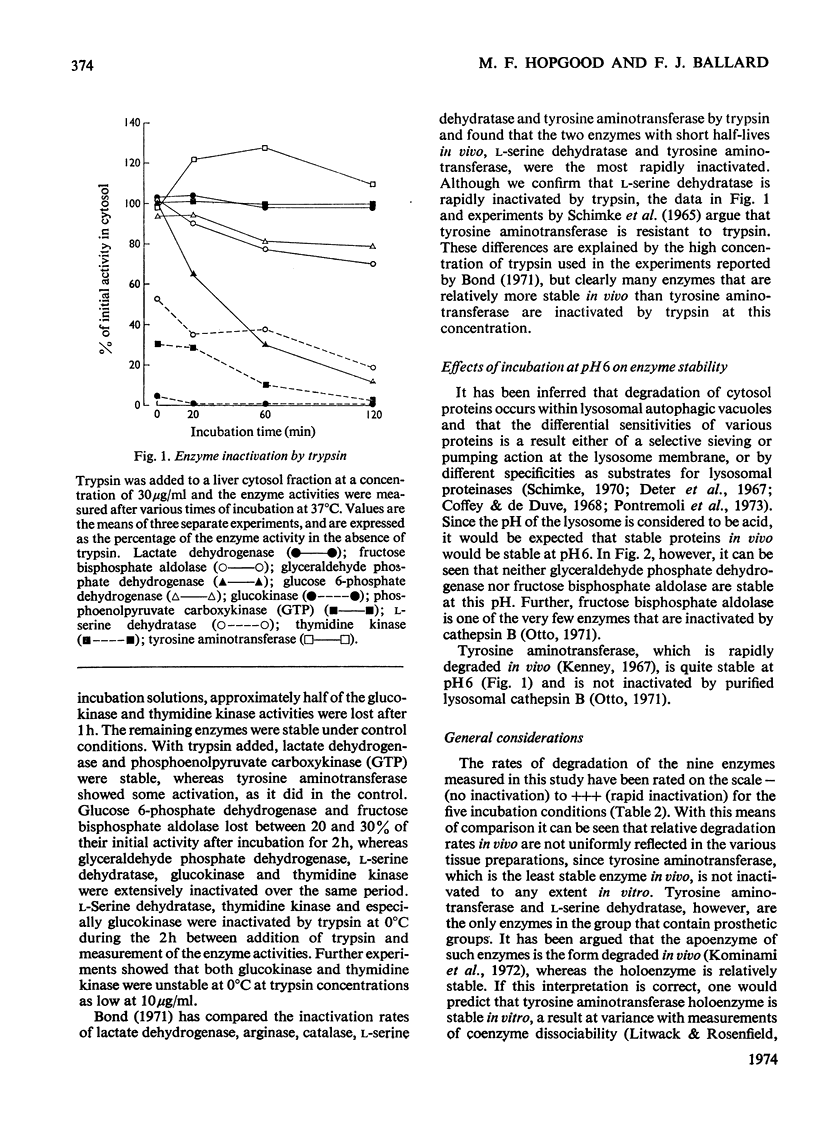
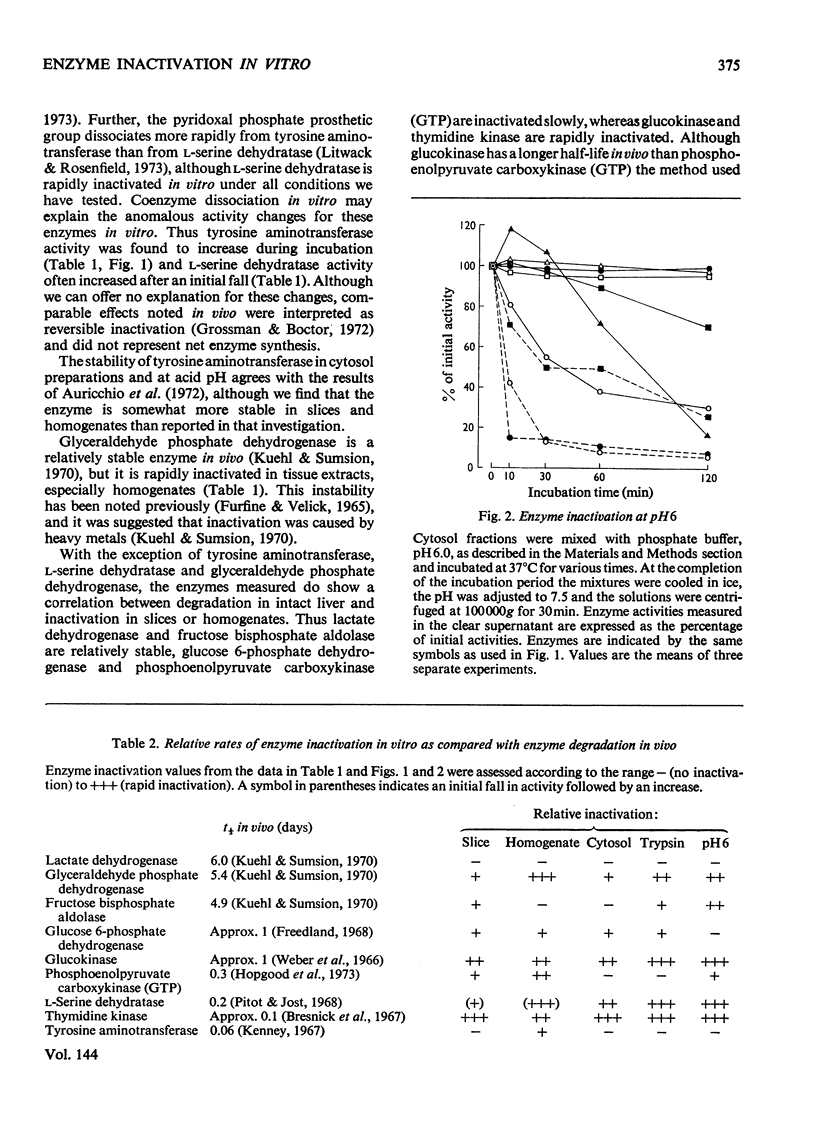
1. Relative rates of enzyme inactivation were measured in liver slices, homogenates and cytosol fractions as well as in the presence of trypsin and at acid pH. The enzymes chosen are all present in the cytosol fraction of rat liver, and have widely different degradation rate constants in vivo. 2. The inactivation rates of lactate dehydrogenase, fructose bisphosphate aldolase, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, glucokinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP), l-serine dehydratase and thymidine kinase in liver preparations at neutral pH are in a similar order to the rate constants of degradation of these enzymes in the intact animal. 3. The two exceptions of this general correlation were tyrosine aminotransferase, which was stable in vitro but not in vivo, and glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, which shows the reverse pattern. 4. These findings generally support the concept that the same factors are responsible for enzyme inactivation in vitro as occur in the intact tissue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auricchio F., Mollica L., Liguori A. Inactivation of tyrosine aminotransferase in neutral homogenates and rat liver slices. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1131–1138. doi: 10.1042/bj1291131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOSTEIN R., RUTTER W. J. COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF LIVER AND MUSCLE ALDOLASE. II. IMMUNOCHEMICAL AND CHROMATOGRAPHIC DIFFERENTIATION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3280–3285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Filsell O. H., Jarrett I. G. Effects of carbohydrate availability on lipogenesis in sheep. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1260193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. Purification of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from the cytosol fraction of rat liver and the immunochemical demonstration of differences between this enzyme and the mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5625–5630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hopgood M. F. Phosphopyruvate carboxylase induction by L-tryptophan. Effects on synthesis and degradation of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):259–264. doi: 10.1042/bj1360259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hopgood M. F., Reshef L., Hanson R. W. Degradation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (guanosine triphosphate) in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj1400531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Oliver I. T. Ketohexokinase, isoenzymes of glucokinase and glycogen synthesis from hexoses in neonatal rat liver. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):261–268. doi: 10.1042/bj0900261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Ansorge S., Hanson H. Intrazellulärer Proteinabbau. 3. Intrazelluläre Verteilung des Zytosolproteinabbaues bei neutralem p. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;27(2):229–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S. A comparison of the proteolytic susceptibility of several rat liver enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90757-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E., Williams S. S., Mossé H. Rates of turnover of deoxythymidine kinase and of its template RNA in regenerating and control liver. Cancer Res. 1967 Mar;27(3):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey J. W., De Duve C. Digestive activity of lysosomes. I. The digestion of proteins by extracts of rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3255–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURFINE C. S., VELICK S. F. THE ACYL-ENZYME INTERMEDIATE AND THE KINETIC MECHANISM OF THE GLYCERALDEHYDE 3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:844–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A., Boctor A. Evidence for reversible inactivation of induced tyrosine aminotransferase in rat liver in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1161–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Tomkins G. M. Studies on the degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cells in culture. Influence of the composition of the medium and adenosine triphosphate dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Ballard F. J. Synthesis and degradation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in rat liver and adipose tissue. Changes during a starvation-re-feeding cycle. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;134(2):445–453. doi: 10.1042/bj1340445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKAWA E., NINAGAWA T., SUDA M. HORMONAL AND DIETARY CONTROL OF SERINE DEHYDRATASE IN RAT LIVER. J Biochem. 1965 Apr;57:506–513. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney F. T. Turnover of rat liver tyrosine transaminase: stabilization after inhibition of protein synthesis. Science. 1967 Apr 28;156(3774):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer H. G., Haynes G. R. Thymidine kinase in rat liver during development. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(4):541–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1080541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami E., Kobayashi K., Kominami S., Katunuma N. Properties of a specific protease for pyridoxal enzymes and its biological role. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6848–6855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl L., Sumsion E. N. Turnover of several glycolytic enzymes in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6616–6623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Knox W. E. Inactivation of tryptophan oxygenase in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7550–7555. doi: 10.2172/4660691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberti J. P., DuVall C. H., Wood D. M. In vitro induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in liver slices by hydrocortisone. Can J Biochem. 1971 Dec;49(12):1357–1361. doi: 10.1139/o71-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Rosenfield S. Coenzyme dissociation, a possible determinant of short half-life of inducible enzymes in mammalian liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90971-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Balestrero F., Franzi A. T., De Flora A., Horecker B. L. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: the role of lysosomal enzymes in the modification of catalytic and structural properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):303–305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H., Snyder S. H. Amine synthesis in regenerating rat liver: extremely rapid turnover of ornithine decarboxylase. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 May;5(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Doyle D. Control of enzyme levels in animal tissues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:929–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sweeney E. W., Berlin C. M. Studies of the stability in vivo and in vitro of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4609–4620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. IV. Sequential degradation of insulin by rat kidney, heart and skeletal muscle homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 21;295(2):630–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Singhal R. L., Stamm N. B., Lea M. A., Fisher E. A. Synchronous behavior pattern of key glycolytic enzymes: glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:59–81. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


