Abstract
The purpose of this study is to examine how co-pyrolysis of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and rice husk is impacted by LDPE. It also looks into the physicochemical characteristics, thermal behavior, and kinetic parameters of these materials. To understand the thermal behavior through TGA, rice husk and LDPE blends in the ratios of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25) were prepared and tested. These tests were carried out in the presence of a nitrogen environment at a flow rate of 20 ml/min with a different heating rate of 10 to 40 °C/min from 30 to 600 °C.In this paper, activation energy (Ea) was measured using the integral method (coats and Redfern) and two distinct iso-conversional approaches are Flynn wall Ozawa (FWO) and Kissinger Akahira Sunose (KAS). According to this study, the Ea values during co-pyrolysis varied with the conversion points, demonstrating the complex nature of the materials that resulted from the process. Moreover, it can be said that the assessment of low-density polyethylene in conjunction with rice husk led to noteworthy changes in thermos kinetic behaviors. In the meantime, the calculated average activation energy is, in turn, 110–117, 101–102, and 102–107 kJ/mol. In this study, we analyze the thermodynamic parameters, including enthalpy, Gibbs free energy, and entropy, and also pyrolysis performance index was thoroughly explored to understand the co-pyrolysis process of rice husk and plastic waste. To develop efficient reactors for continuous operation regardless of feedstock composition, it was necessary to establish the significance of blending biomass with plastics in terms of augmented carbon conversion, volatiles, and reaction rate.
Keywords: Co pyrolysis, Rice husk, Low-density polyethylene, TGA, Iso-conversional method, Thermodynamic parameter
Subject terms: Energy science and technology, Engineering
Introduction
Fossil fuels are used as an energy source nowadays, and because of urbanization and the reliance of many business sectors, fossil fuels currently dominate the global energy market1,2. Scientists from all around the world are developing additional renewable resources that will be used as energy fuels to address these problems2,3,]. A safe and environmentally beneficial source of clean energy is biomass, which is also biodegradable4,5.
The primary goal of this work is to use biomass sources as energy sources. In this regard, rice husk has been chosen for this study because of the high annual production rate in Punjab and Haryana, which comes from rice mills in metric tons. A small portion is used for animal feed, and the majority is burned or landfilled. We also use plastic waste as a way to lower the environmental carbon percentage. They may be more important in our daily lives than other conventional materials like plastics and biomass (agricultural waste), and their affordability, versatility, and cheap cost of production make their increasing use acceptable6. Since plastic is non-biodegradable and burning it in the open is bad for the environment and people, illegal plastic dumping is a concern for the ecosystem. However, in a controlled heating environment, researchers used a thermogravimetric analysis in an inert environment to explore the co-pyrolysis characteristics of blending rice husk with LDPE to learn more about the interactions between the two. Numerous writers have investigated plastic pyrolysis and demonstrated how the technology might be used to try to address plastic waste7. The several pyrolysis process types, reactor designs, and operating parameters that impact product quality were all covered in detail by8. The IAE annual report9 covers the larger process of decomposition product creation from agricultural biomass. Thermogravimetric measurements indicate that biomass starts to disintegrate at lower temperatures10. On the other hand, products made of plastic break down at 400–500 ℃ depending on the type of plastic11. Thermal gravimetric analysis has been used extensively in recent decades to examine the thermal results and kinetics associated with the degradation of carbon-based materials, as well as to regulate how weight loss in the sample varies with temperature and time.
A thorough grasp of thermogravimetric analysis and de-volatilization kinetics will make planning, building, and managing industrial pyrolysis systems easier12,13. One of the easiest methods for assessing the kinetics and thermal breakdowns of the pyrolysis process for solid raw natural resources like plastic and biomass is a thermo-gravimetric examination14,15. Numerous investigators have examined the kinetics of pyrolysis procedures by utilizing the Arrhenius equation to calculate specific mass degradation slopes16,17. Therefore, a detailed examination of the co-pyrolysis method and the kinetic behavior of plastic waste and biomass under the same experimental conditions is crucial for analysis and comparison. A highly efficient method for using thermogravimetric (TG) analysis to investigate the pyrolytic properties and dynamics of plastics-biomass. The chemistry, pyrolytic properties, and kinetics of the fundamental pyrolysis process must be understood to design and operate thermochemical conversion units efficiently18. The co-pyrolysis of solid material and plastic waste has the potential to improve the final product’s quality19. The ratio of H/C in plastic wastes is high, while the ratio of O/C is comparatively low. This can facilitate co-pyrolysis of solid biomass, which by nature has a high O/C ratio and a low H/C ratio, enhancing product quality and uniformity and lowering coke deposition from the pyrolysis of plastic waste because co-pyrolysis does not require waste separation (Chattopadhyay et al. 201620). Combining LDPE and biomass pyrolyzing increases oil’s heating value significantly. By lowering the number of oxygenated molecules, the combined pyrolysis of biomass (sugarcane bagasse) and plastic waste produced high HHV (approximately 40 MJ/Kg). Low-density polyethylene can function as an H-donor medium in the co-pyrolysis process to facilitate liquid formation21. To forecast a material’s pyrolysis behavior, construct a suitable reactor, and mathematically model the reactor for process optimization, it is often necessary to understand the pyrolysis kinetics of the principal thermal breakdown process. Process parameters, mass and heat transfer limitations, sample physical and chemical properties, systematic errors, and other variables can all have an impact on the kinetic parameters22. Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic studies can be used to determine the characteristics of co-pyrolysis. The kinetic parameters can be computed using a variety of kinetic models. Burra and Gupta, 2018 found synergy in the co-pyrolysis of PP and PET with biomass by using the distributed activation energy model (DAEM). The co-pyrolysis kinetics of polymers and their mixtures with biomass were examined. This study demonstrates that the Ea values in the first and second breakdown phases increase and decrease, respectively, based on the number of plastics in the mixture. Researchers have also used various conversion methods, like the FWO technique and the KAS strategy23,24, to forecast the kinetic variables associated with the pyrolysis process. To ascertain the distribution of activation energy across the reaction/process, iso-conversational approaches make use of thermal degradation data at various temperatures (Ahmad et al. 201725). Huang used a thermogravimetric analyzer to assess the heat degradation of soybean straw in non-isothermal conditions. Three distinct techniques were utilized to study the kinetic parameters: OFW, KAS, and CR. Using the KAS and FWO methods, the average Ea was determined to be 154.15 kJ mol−126. In a TGA, Varma and Mondal4 investigated the physicochemical characteristics and pyrolysis kinetics of sugarcane bagasse (SB) using the KAS and FWO systems. The values of 91.64 and 104.43 kJ mol−1 were reported to be the average Ea of SB. The kinetic parameters at active heating rates of Prosopis Juli flora fuel wood were studied by Chandrasekaran through thermogravimetric analysis. Several techniques were used to compute the energy needed to activate the pyrolysis, including the Friedman, OFW, Kissinger, and KAS models. The findings revealed that the activation energies were 164.6, 203.2, 204, and 219.3 kJ mol−1, in that order27. The intricacy of thermal deterioration at different conversion phases can be explained by a variable activation energy. Despite several studies on biomass kinetics, no effort has been made to determine the kinetics of the co-pyrolysis reaction between LDPE and RH feedstocks to produce useful chemicals and green fuels. While several research have looked into the kinetics of various types of biomasses, no attempt has ever been made to identify the kinetics of the co-pyrolysis reactions of LDPE and RH biomass to produce lucrative chemicals and sustainable fuel. Previous studies have shown that combining plastics like LDPE with biomass can enhance bio-oil yield and improve its quality due to synergistic effects during co-pyrolysis. Our study further explores these interactions with a focus on improving fuel properties, thereby addressing practical applications in energy recovery. I will clarify these synergistic advantages to highlight the relevance of our feedstock choices for bio-oil production.
In this study, the Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO) and Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS) methods were specifically chosen for kinetic analysis due to their robustness and reliability in determining activation energy without the need for a predefined reaction model. These iso-conversional methods are well-regarded for their ability to provide accurate kinetic parameters over a range of conversion rates, making them particularly suitable for complex processes like pyrolysis28. Although numerous studies have looked at co-pyrolysis of biomass such as bamboo or rice husk with LDPE, my work focuses especially on the kinetic features of this process. Unlike earlier research that mostly investigates co-pyrolysis results, my study offers thorough kinetic modeling to grasp the reaction rates, activation energy, and effect of certain variables like temperature and heating rate7.
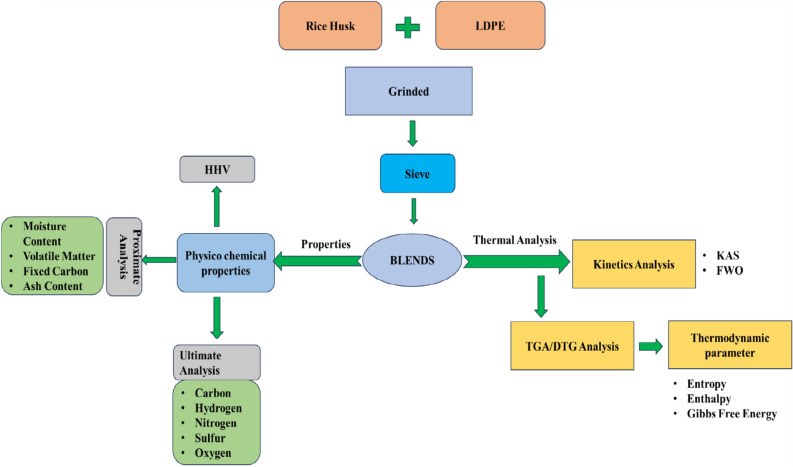
This study offers detailed insights into the physicochemical features and pyrolysis traits of raw rice husk samples mixed in various ratios with low-density polyethylene blends. Additionally, four different heating rates (10–40 °C/min) were used for the Thermal Analysis. Three distinct iso-conversional approaches (KAS, OFW, coats and Redfern) were used to calculate the activation energy for pyrolysis. Three other thermodynamic parameters were also calculated: change in entropy (ΔS), change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) and change in enthalpy (ΔH). Additionally, we determined the CPI index for each blended ratio of LDPE and RH. These results make a substantial contribution to a thorough comprehension of the blended sample pyrolysis process. The importance of co-pyrolysis in influencing the development of sustainable energy solutions is highlighted by this research on the process and its uses. The entire process is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Process flowchart of rice husk and LDPE co-pyrolysis.
The feasibility and benefits of combining LDPE with RH are examined in this study as presented in Fig. 1. After the kinetics parameters were determined by fitting the TGA data at various heating rates, the kinetic parameter (E) was found using two separate techniques: the KAS and FWO methods. To examine whether these samples are suitable as energy feedstock, their activation energy is compared to samples of blended feedstock.
Moreover, an extensive investigation was conducted to determine the thermodynamic parameters of blended samples, including variations in enthalpy (ΔH), entropy (ΔS), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG), and how these changes affected the samples’ pyrolysis behavior.
Experimental procedures
Materials
The RH used in this study is gathered from Barghat, Madhya Pradesh. When the biomass samples were collected, they had a lot of moisture content and were non-uniform in size and shape. It was therefore first cleaned with tap water, then left outside to sun-dried naturally for a few days before preparation of the sample. The LDPE (packaging plastic) cut into small, uniform pieces to ensure a particle size similar to the rice husk. This helps create a more homogeneous mixture and prevents larger LDPE chunks from agglomerating. Now, the samples are uniform in size and completely sundried for further process and the fine particles were sieved to a size of 1–2 mm before the trials.
The particle size of the samples was designed to be below 2 mm to prevent heat and mass transfer effects inside the biomass particles. Moreover, when both biomass and plastics contain identical particle sizes, they may be combined more uniformly, resulting in an improved contact surface (Wu et al. 201529).
The blended sample was dried at 101 °C until it attained a consistent weight before being wrapped in bags and other sample LDPE (packaging plastic) collected from the different streets of Phagwara. When the material was collected, it was washed with water and sundried then cut into small pieces through scissors, and then blended the ratio of RH with LDPE. now, the samples of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25) are ready for further processing.
Methods
Physicochemical classification
The blended samples LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25) were proximately analyzed in the muffle furnace to determine the proximate analysis with ASTM standard methods and elemental analysis also determined by using CHNS analyzer with ASTM standard. The oxygen concentration is determined by taking the difference between the total amount of ash, carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, and nitrogen and removing 100% from it. The total amount of energy generated by full combustion is referred to as the higher heating value, which is a highly essential component in establishing sample quality. The calorific values of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25) were examined by using a bomb calorimeter. Theoretically, the higher heating value will be determined by two different formulas.
Dulong Formula
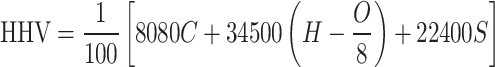 |
1 |
Channiwala Formula
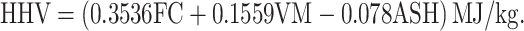 |
2 |
Thermo gravimetric characterization
Pyrolysis studies were conducted using a thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA 4000, PerkinElmer). Al2O3 crucibles were utilized in each run, and the tests were performed under non-isothermally30. Pyrolyzing a sample at 10–40 °C/min with a maintained flow rate of sweep gas as N2(20 mL/min) resulted in a temperature of 600 °C. To achieve homogeneity, the RH and LDPE samples were mixed in different weight ratios of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25). The kinetic study was performed using two different established methods. Based on TGA thermo-gravimetric data, these methods are used to evaluate various kinetical factors such as Ea and A.
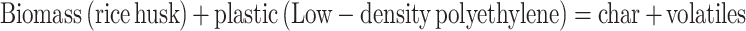 |
Kinetic theory
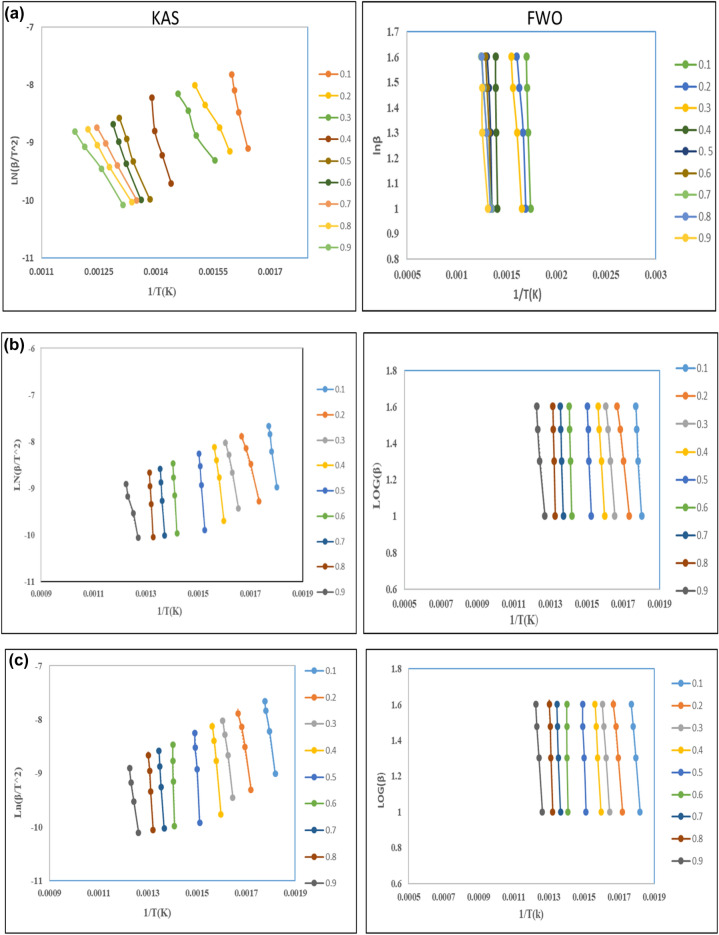
In contrast to other approaches that solely consider the maximum temperature, Kissinger Akahira Sunose and Ozawa Flynn are the iso-conversion methods. When evaluating the activation energy of blended rice husk and low-density polyethylene ratio regarding the degree of conversion at assorted heating rates, wall approaches provide more optimistic values31. In Fig. 3 FWO and KAS methods, are favored for pyrolysis investigations. This decision is based on its straightforwardness and precision in estimating activation energy. These approaches use samples at varied heating rates. They connect conversion temperature with heating rate to generate kinetics parameters26.
Fig. 3.
(a) Kinetic curves in the different conversion of LDPE: RH (50:50). (b) Kinetic curves in the different conversions of LDPE: RH (25:75). (c) Kinetic curves in the different conversion of LDPE: RH (75:25).
The following mathematical formula can define the (α) throughout the pyrolysis process.
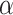 This can be conveyed as
This can be conveyed as
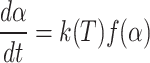 |
3 |
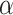 is a degree of conversion, it can be written as
is a degree of conversion, it can be written as
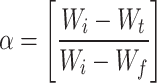 |
4 |
where Wi = weight of the sample at the initial stage.
Wt = Sample weight at time t.
Wf = Sample weight at the final stage.
The rate constant k(T) is expressed using the Arrhenius equation as follows:
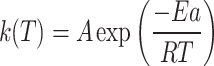 |
5 |
where A is the pre-exponential factor (s−1), Ea is the activation energy (kJ/mol), R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol.K) and T is the temperature (K).
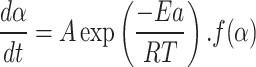 |
6 |
The parameter β(°C/min), referred to as the heating rate, is described as:
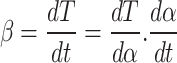 |
7 |
Combining the equation
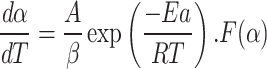 |
8 |
integrating this Equation within the limit of α = 0 to α and T = 0 to T gives
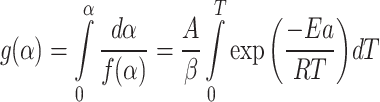 |
9 |
Numerical solutions for this equation have been obtained using model-free and reaction-fitting models, employing suitable approximations.
Coats–Redfern method
The Coats–Redfern method is used to evaluate the activation energy (Ea), pre-exponential factor (A) and apparent reaction order.
From using Eq. 9
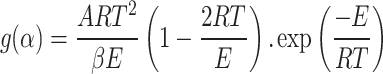 |
10 |
or,
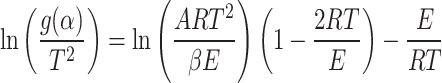 |
11 |
Since E is high, the term 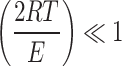 can be neglected to get,
can be neglected to get,
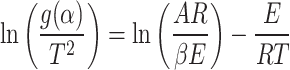 |
12 |
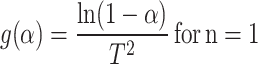 |
13 |
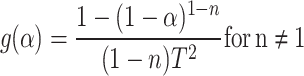 |
14 |
The slope and intercept of the plot between 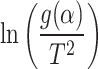 verses 1/T give the value of E and A, respectively.
verses 1/T give the value of E and A, respectively.
KAS model
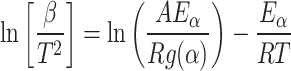 |
15 |
The figure’s slope represents the magnitude of the kinetic parameter for every conversion.
lnβ/T2 vs. 1/T (Akahira 197132).
Where T = temperature in K.
R = gas constant = 8.314 J mol−1 K−1, β = heating rate in ℃/min.
FWO model
For the FWO method28, to calculate the threshold energy values of the biomass and plastic sample, multiple TG-DTG curves are used concurrently. The TG-DTG curve rises in temperature as the rate of heating rises. The slope of the plot of log (β) vs. 1/T at a certain conversion level is used to define the activation energy at the same conversion levels.
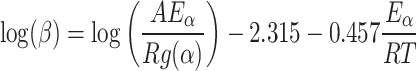 |
16 |
The magnitude of kinetic parameters for every conversion is characterized by the slope of figure Logβ/T2 vs. 1/T where the notations stand the same as the previous method.
Thermodynamic parameter
The activation energy (Ea) for the raw and torrefied sample from the preceding equation was utilized to compute the pre-exponential factor (A) using Eq. 17 and change in enthalpy (ΔH) using Eq. (18), respectively. Equation (19) calculates the Gibbs free energy based on activation energy and pre-exponential component. Equation (20) calculates the change in entropy (ΔS) using enthalpy changes (ΔH) and Gibbs free energy (ΔG) by using the KAS method and FWO method to calculate the thermodynamic factors.
The FWO method and KAS method were employed to estimate the thermodynamic triplets like ΔH, ΔG, and ΔS using the relations below33.
The pre-exponential factor (A) is considered from the obtained Ea values using Eq. 6.
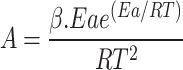 |
17 |
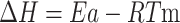 |
18 |
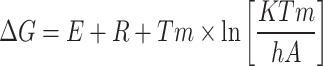 |
19 |
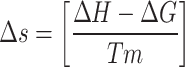 |
20 |
Here K is the Boltzmann constant (1.381 × 10–23 J/K) and h represents Planck’s constant (6.626 × 10–34 J-s).
Comprehensive Pyrolysis Index (CPI) analysis
To assess the pyrolysis performance of both raw and torrefied samples at various heating rates, the Comprehensive Pyrolysis Index (CPI) was utilized. This index provides a quantitative measure of pyrolysis efficiency by considering multiple parameters. The following parameters were investigated to evaluate the pyrolysis performance index:
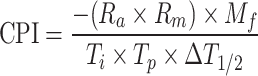 |
21 |
The pyrolysis performance of biomass and plastic waste may be evaluated using the following parameters34.
Ti–initial degradation time, Tp- DTG maximum peak time,
ΔT1/2—half-peak width range, Mf—final mass loss, Ra—Average decomposition rate, Rm- maximum decomposition rate, CPI- comprehensive pyrolysis index.
Results and discussion
Physicochemical classification
Table 1 provides a summary of the elemental and proximate composition of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25). The moisture content of the current samples is very high at 2.7%, 3.4%, and 1.2%. For the pyrolysis process, biomasses with a low moisture content (less than 10%) are often favored. The findings demonstrate that all three samples have high volatile contents (80, 71, and 88 weight percent), it is well suited for thermal decomposition through combustion due to their high reactivity, ease of devolatilization, and capacity to yield a sizable amount of bio-oil35. The ash content (11.3, 13.6, and 5.7%) and fixed carbon (5.5%, 11.2%, and 5.1%) in these samples are extremely low. The difference between the fixed carbon and oxygen levels is calculated. The elemental analysis reveals that incorporating LDPE with rice husk increases the carbon content while decreasing the oxygen content in the samples. Higher carbon and lower oxygen levels are advantageous for the pyrolysis process, leading to a higher energy yield, improved bio-oil quality, better char formation, reduced tar production, enhanced reaction efficiency, and a more straightforward upgrading process36.
Table 1.
Physical chemical Properties of samples LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), LDPE: RH (75:25).
| Composition (weight %) | LDPE: RH (50:50) | LDPE: RH (25:75) | LDPE: RH (75:25) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC (%) | 2.7 | 3.4 | 1.2 |
| VM (%) | 82.5 | 72.8 | 89.2 |
| FC (%) | 5.5 | 11.2 | 5.1 |
| AC (%) | 9.3 | 12.6 | 4.5 |
| Carbon (%) | 47.2 | 43.71 | 56.78 |
| Hydrogen (%) | 10.68 | 8.77 | 12.16 |
| Oxygen (%) | 41.27 | 46.83 | 29.63 |
| Nitrogen (%) | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.2 |
| Sulfur (%) | 0.56 | 0.32 | 1.23 |
| H/C | 2.72 | 2.41 | 2.57 |
Higher heating value
Biomass has a higher oxygen concentration, less hydrogen and carbon, and less hydrogen overall. The HHV of the samples is 18.34 MJ/kg, 16.91 MJ/kg, and 18.63 MJ/kg. The results of the elemental analysis of all three blended samples present 47.2%, 44.71%, and 56.78% of carbon content and 5.68%, 8.77%, and 12.16 of hydrogen content and 46.83%, 45.84% and 29.62% of oxygen content. Table 2, shows the experimental and theoretical calorific values of blended samples LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25). The calorific values of these samples can be used to examine the P.E. content for pyrolysis characteristics. The higher heating values of experimental data is 17.34 MJ/kg, 15.91 MJ/kg, and 20.61 MJ/kg respectively. When comparing the experimental value with the theoretical value the difference is very low (0.70%).
Table 2.
The Higher heating value of all three samples LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), LDPE: RH (75:25).
| Heating value (MJ/kg) | LDPE: RH (50:50) | LDPE: RH (25:75) | LDPE: RH (75:25) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HHV (Experiment) | 17.34 | 15.91 | 20.61 |
| HHV (Theoretical) | 17.03 | 15.46 | 20.31 |
| HHV (Theoretical) | 16.61 | 14.85 | 19.73 |
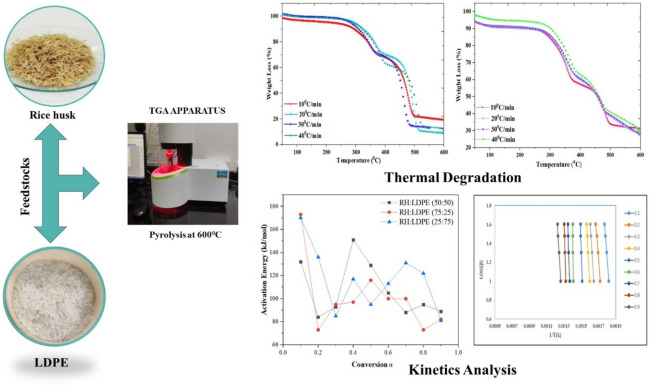
Thermal analysis of the sample
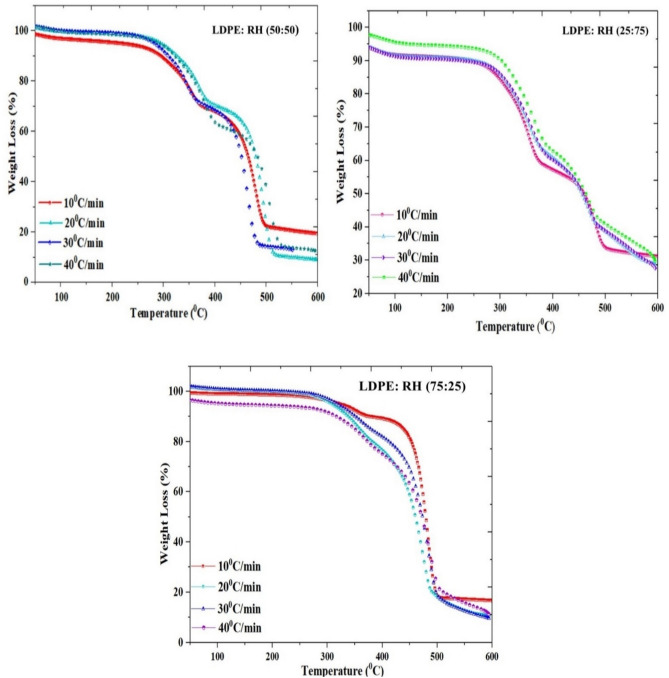
Tables 3, 4 and 5 provide information on the weight loss process in three stages of the blended samples RH: LDPE (50:50), RH: LDPE (75:25), and RH: LDPE (25:75) and amount of weight loss that started initially and increased due to the water content of the biomass components in the mix. Nonetheless, only 1.42–4.40% of the sample’s initial weight was lost during this initial phase as presented in Fig. 2. A temperature range of 200–500 °C is the maximum weight loss that the mixture can experience during the 2nd stage of the volatile region degradation process, which occurs when the temperature is higher by 50–70%. In the last stage only 4–5% weight loss because of adding LDPE on it so ash content will be low.
Table 3.
Thermal process in different temperature ranges of LDPE: RH (50:50).
| First phase | Second phase | Third phase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating rate (℃/min) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) |
| 10 | 30.2 | 111.3 | 3.2 | 271 | 497 | 70 | 499 | 598 | 3.11 |
| 20 | 30.8 | 192 | 3.0 | 254 | 503 | 56.2 | 514 | 600 | 2.3 |
| 30 | 30.15 | 210 | 2.8 | 261 | 520 | 55.4 | 527 | 600 | 1.8 |
| 40 | 31.8 | 232 | 2.1 | 266 | 522 | 54.2 | 525 | 600 | 1.53 |
The start is the initial temperature of a decomposition process that has been indicated. The end is used to describe the final temperature of a decomposition phase.
Table 4.
Thermal process in different temperature ranges of LDPE: RH (25:75).
| First phase | Second phase | Third phase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating rate (℃/min) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) |
| 10 | 30.2 | 96 | 3.7 | 256 | 500 | 70 | 502 | 599 | 4 |
| 20 | 31.8 | 104 | 3.2 | 249 | 510 | 77 | 510 | 600 | 3.1 |
| 30 | 30.15 | 107 | 2.8 | 266 | 530 | 75 | 530 | 606 | 2.4 |
| 40 | 30.19 | 111 | 2.1 | 273 | 560 | 76 | 560 | 600 | 2.3 |
The start is the initial temperature of a decomposition process that has been indicated. The end is used to describe the final temperature of a decomposition phase.
Table 5.
Thermal process in different temperature ranges of LDPE: RH (75:25).
| First phase | Second phase | Third phase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating rate (℃/min) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) | Initial temp |
Final temp |
Loss in weight (%) |
| 10 | 30.2 | 91.2 | 2.1 | 243 | 483 | 56 | 483 | 599 | 4 |
| 20 | 31.8 | 92.1 | 1.8 | 248 | 485 | 60 | 485 | 598 | 3.3 |
| 30 | 30.15 | 99 | 1.5 | 266 | 497 | 62 | 497 | 599 | 3.1 |
| 40 | 30.19 | 105 | 1.2 | 273 | 472 | 68 | 472 | 600 | 2.3 |
The start is the initial temperature of a decomposition process that has been indicated. The end is used to describe the final temperature of a decomposition phase.
Fig. 2.
Thermal analysis of all three graphs (a) LDPE: RH (50:50) (b) LDPE: RH (25:75), (c) LDPE: RH (75:25).
Kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of a rice husk and LDPE using Coats–Redfern method
The Coats-Redfern method utilizes a graph plotting the natural logarithm of a certain function against the reciprocal of absolute temperature (1/T) to originate the activation energy (E) from the slope of the graph. Additionally, it allows for the determination of kinetic parameters based on the calculated activation energy values. The expressions used to determine these parameters are based on three general categories of reaction mechanisms, which include mechanisms reliant on the rate-determining reactions.
Kinetic analysis
When co-pyrolyzing plastic and solid biomass, TGA is a commonly employed method to study reaction kinetics and synergistic effects. Understanding how plastic and solid biomass are converted into fuel, as well as optimizing process parameters and designing effective gasification and pyrolysis reactors, all depend on thermal and kinetic analyses of the materials. Additionally, for quantitative kinetic analysis, Ea, A, and n can play a significant role. These findings can subsequently be used in mathematical modeling to create improved reactors23. By estimating Ea and A using three distinct techniques, such as KAS, FWO, and coats and Redfern methods, the kinetic parameter for the pyrolysis process is determined and for kinetic analysis of all three samples, the pyrolysis range is between 200 and 600 °C. The value of Ea in LDPE: RH (50:50) is determined to be 107 kJ/mol from the slope of the KAS plot and 102 kJ/mol from the FWO plot. For the second sample, the LDPE: RH (25:75) has a value of activation energy is 100 kJ/mol from KAS and 101 kJ/mol from the OFW plot, and the third sample: RH (75:25) value of Ea is 110 kJ/mol for the KAS plot and 117 kJ/mol for the FWO plot shown in Fig. 3a–c. The activation energy is reduced while increasing the heating rate. As opposed to existing studies, which only consider binary mixes, future studies should consider the co-degradation of waste plastic, LDPE mixes with solid biomass RH as feedstocks. It is tedious to separate a single recyclable plastic or just one fragment of solid biomass from waste materials, combine the selected feedstock to meet the optimal conditions to produce the necessary co-pyrolysis results, and then leave the resultant mixture alone. Therefore, it is necessary to look at multicomponent feedstock that is comparable to actual garbage mixtures. As a result, Rice husk with Plastic waste has enhanced pyrolysis properties in terms of Ea, heating value, volatile content, and carbon content. Ashes, nitrogen, sulfur, and moisture, on the other hand, exhibit a decrease. The activation energy, calorific value, and reduced char residues of LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25) are all greatly increased by the addition of low-density polyethylene. The performance of rice husk was improved by the thermal properties, which led to a substantial energy release and reduced ash residue, according to the pyrolysis results of rice husk and Plastic waste. The findings of rice husk and low-density polyethylene pyrolysis demonstrate the viability of using these sources of alternative energy as a fuel.
The Coats-Redfern method often yields lower activation energy values because it assumes a simplified single-step reaction mechanism, averaging out complexities and potentially underestimating the actual energy barriers. In contrast, the Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS) and Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO) methods provide higher activation energy values as they do not assume specific reaction mechanisms. Instead, they focus on the temperature dependence of the reaction rate and consider the entire range of conversion, leading to a more accurate representation of the pyrolysis kinetics37. Although the KAS and FWO approaches are extensively used for kinetic analysis in pyrolysis research, it is important to address the fundamental assumptions of these techniques and the justification for parameter choice to guarantee methodological rigor. Across the selected temperature range, the KAS and FWO techniques assume a linear connection in the Arrhenius equation, thereby suggesting that activation energy is constant across this range. These presumptions may not always apply, however, in co-pyrolysis where complicated interactions between biomass and polymers take place.
Table 6 shows the activation energies and pre-exponential factors using the coats and Redfern method. In the context of pyrolysis, the pre-exponential component is critical for understanding the kinetics of thermal breakdown. It aids in evaluating how frequently reactant molecules collide and react to generate products under specific conditions. This component, together with the activation energy, enables the prediction of reaction rates at various temperatures, which is critical for optimizing pyrolysis process parameters such as temperature, heating rate, and residence time38.
Table 6.
Kinetic analysis of raw samples through coats and Redfern method.
| Mechanism |  |
Heating rates | RH: LDPE (75:25) | RH: LDPE (50:50) | RH: LDPE (25:75) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction order-based models | E (KJ/mol) | A (min−1) | E(KJ/mol) | A (min−1) | E(KJ/mol) | A (min−1) | ||
| 1st order | 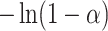 |
10 | 21.6 | 1.02 × 102 | 37.4 | 1.82 × 102 | 42.3 | 5.12 × 102 |
| 20 | 19.2 | 4.12 × 101 | 35.6 | 3.32 × 101 | 39.2 | 4.22 × 101 | ||
| 30 | 15.2 | 2.4 × 101 | 32.7 | 4.4 × 101 | 35.3 | 3.4 × 101 | ||
| 40 | 15.6 | 2.01 × 101 | 24.5 | 3.11 × 101 | 30.7 | 2.01 × 101 | ||
| 2nd Order | 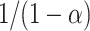 |
10 | 9.6 | 3.94 × 100 | 11.2 | 3.24 × 100 | 14.2 | 4.34 × 100 |
| 20 | 8.3 | 3.50 × 101 | 10.2 | 2.50 × 101 | 18.3 | 2.22 × 101 | ||
| 30 | 7.2 | 1.20 × 102 | 8.4 | 1.60 × 102 | 20.1 | 3.21 × 102 | ||
| 40 | 6.3 | 3.64 × 102 | 7.7 | 2.64 × 102 | 22.3 | 3.60 × 102 | ||
| 3rd order | 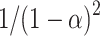 |
10 | 23.2 | 4.20 × 102 | 31.4 | 4.16 × 102 | 40.2 | 5.10 × 102 |
| 20 | 21.2 | 1.02 × 102 | 29.4 | 2.32 × 102 | 36.3 | 3.12 × 102 | ||
| 30 | 15.1 | 5.64 × 101 | 27.2 | 4.64 × 101 | 31.6 | 4.34 × 101 | ||
| 40 | 13.2 | 2.8 × 102 | 22.5 | 2.18 × 102 | 27.3 | 2.28 × 102 | ||
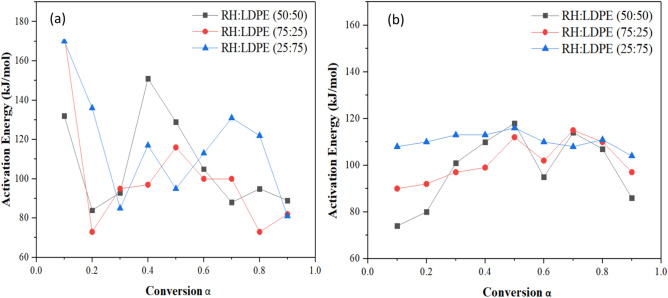
Tables 7, 8 and 9 show the activation energies, regression coefficient, and associated fitted calculations for conversion values between 0.1, 0.2,….0.9 computed by using these 2 different methods. The pyrolysis kinetic parameters of the RH and LDPE mixture were determined using TGA data based on KAS and OFW methods for the final activation energy. Depending on the heating rate and kind of biomass, pyrolysis involves a nonlinear process called thermal degradation that happens in stages. As a function of conversion, the general rate equation for the pyrolysis of blended samples LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75), and LDPE: RH (75:25). Additionally, it is demonstrated in Fig. 4 that the KAS method has higher activation energy than the OFW method, and the kinetic parameter from both models rises with the conversion rate from 0.4 to 0.9. The variety in reaction mechanisms for the pyrolysis process is what causes the difference in Ea with a conversion factor. The lowest amount of energy needed to start a reaction, according to the definition of Ea, is lower and indicates a quicker reaction39.
Table 7.
Thermo kinetic Insights: Ea(kJ/mol) and Regression Factors for LDPE: RH (50:50) Using KAS and FWO methods.
| KAS | FWO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Equation | R2 | Ea | Equation | R2 | Ea |
| 0.1 | Y = − 19962x + 43.09 | 0.99 | 132 | Y = − 4074x + 25.50 | 0.99 | 74 |
| 0.2 | Y = − 10145x + 9.84 | 0.99 | 84 | Y = − 3318.2x + 11.76 | 0.99 | 60 |
| 0.3 | Y = − 11192x + 11.53 | 0.99 | 93 | Y = − 5574x + 10.22 | 0.99 | 101 |
| 0.4 | Y = − 18227x + 30.45 | 0.99 | 151 | Y =− 7148x + 39.26 | 0.99 | 130 |
| 0.5 | Y = − 15528x + 15.57 | 0.99 | 129 | Y = − 8919x + 15.68 | 0.99 | 162 |
| 0.6 | Y = − 12630x + 15.29 | 0.99 | 105 | Y = − 4550x + 12.11 | 0.99 | 82 |
| 0.7 | Y = − 10602x + 5.70 | 0.99 | 88 | Y = − 6312.9x + 9.49 | 0.99 | 114 |
| 0.8 | Y = − 11435x + 9.28 | 0.99 | 95 | Y = − 5928.4x + 10.27 | 0.99 | 107 |
| 0.9 | Y = − 10739x + 11.89 | 0.99 | 89 | Y = − 4743.1x + 9.85 | 0.99 | 86 |
| Average | 107 | 102 | ||||
Table 8.
Thermo kinetic Insights: Ea(kJ/mol) and Regression Factors for LDPE: RH (25:75) Using KAS and FWO methods.
| KAS | FWO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Equation | R2 | Ea | Equation | R2 | Ea |
| 0.1 | y = − 9361x + 23.4 | 0.99 | 130 | y = − 13000x + 41.9 | 0.97 | 108 |
| 0.2 | y = − 7490x + 20.7 | 0.99 | 136 | y = − 13125x + 37.2 | 0.98 | 109 |
| 0.3 | y = − 4694x + 25.1 | 0.99 | 95 | y = − 13602x + 48.1 | 0.99 | 113 |
| 0.4 | y = − 6445x + 28.8 | 0.99 | 117 | y = − 13310x + 67.1 | 0.99 | 110 |
| 0.5 | y = − 5238x + 43.6 | 0.97 | 95 | y = − 14041x + 109.5 | 0.97 | 116 |
| 0.6 | y = − 6230x + 55.2 | 0.99 | 113 | y = − 13238x + 31.4 | 0.96 | 110 |
| 0.7 | y = − 7253x + 38.6 | 0.98 | 131 | y = − 13084x + 80.2 | 0.99 | 108 |
| 0.8 | y = − 6712x + 21.4 | 0.99 | 122 | y = − 13356x + 86.6 | 0.98 | 111 |
| 0.9 | y = − 4491x + 42.8 | 0.98 | 81 | y = − 12613x + 30.4 | 0.99 | 104 |
| Average | 117 | 110 | ||||
Table 9.
Thermo kinetic insights: activation energies (kJ/mol) and Regression Factors for LDPE: RH (75:25) Using KAS and FWO methods.
| KAS | FWO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Equation | R2 | Ea | Equation | R2 | Ea |
| 0.1 | y = − 9512x + 34.49 | 0.98 | 173 | y = − 10893x + 66.4 | 0.99 | 90 |
| 0.2 | y = − 4049.2x + 16.6 | 0.99 | 73 | y = − 10892x + 26.99 | 0.98 | 90.5 |
| 0.3 | y = − 5273x + 21.3 | 0.99 | 95 | y = − 11750x + 38.18 | 0.99 | 97 |
| 0.4 | y = − 5373x + 27.18 | 0.99 | 97 | y = − 11971x + 59.07 | 0.98 | 99 |
| 0.5 | y = − 6411x + 42.8 | 0.98 | 116 | y = − 14881x + 105.89 | 0.99 | 121 |
| 0.6 | y = − 5509x + 56.08 | 0.99 | 100 | y = − 12325x + 126.7 | 0.99 | 102 |
| 0.7 | y = − 5500x + 49.9 | 0.98 | 100 | y = − 13851x + 106.4 | 0.99 | 114 |
| 0.8 | y = − 4016x + 58.5 | 0.99 | 73 | y = − 12893x + 121.3 | 0.99 | 107 |
| 0.9 | y = − 4532x + 17.29 | 0.98 | 82 | y = − 11683x + 20.07 | 0.98 | 97 |
| Average | 101 | 100 | ||||
Fig. 4.
(a) Comparison analysis of KAS Method (b) Comparison analysis of FWO Method.
Synergistic effects of co-pyrolysis
The synergistic effect is the most important element in increasing output yield and quality of pyrolysis because of feedstock interactions and process factors during co-pyrolysis, the synergistic mechanism might be complex. The type and connectivity of the pyrolysis feedstock, and operating parameters such as temperature, heating rate, and number of catalysts can influence the output product and quality40. When it came to the breakdown of RH and LDPE, the process began with the thermal breakdown of rice husk, which happened at a lower temperature than that of LDPE. At a 400 °C pyrolysis temperature, solids from the degradation of biomass were used as radical donors. Plastic polymer chain scission was brought on by the produced radicals, which provided the biomass particles with hydrogen donors. The polymer chain’s first scission was unaffected by the percentage of biomass blending41. Hou et al. (202242) investigate the bamboo and trash face masks were co-pyrolyzed to look for similar synergistic effects. Bamboo’s lignocellulosic nature is similar to rice husk, but its contact with face masks (mostly made of polypropylene) results in various chemical reactions. Hou et al. found that face mask polypropylene supplied hydrogen-donating radicals, resulting in increased oil yields comparable to LDPE in rice husk co-pyrolysis, however, the temperature ranges and radical intensities varied owing to the polymers’ different breakdown temperatures. Current studies that show synergistic effects during the co-pyrolysis of polymers and biomass are listed in Table 10.
Table 10.
Insights into activation energy: comparative analysis of different feedstocks with present sample.
| Samples | Ea (kJ/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|
| LDPE: RH (50:50) | 102–107 | Present study |
| LDPE: RH (25:75) | 101–102 | Present study |
| LDPE: RH (75:25) | 110–117 | Present study |
| Rice husk | 51–100 | (Chen et al. 201643) |
| Plastic bag | 211 | 44 |
| CS-PET | 171.4 | (Kumara et al. 2020) |
| HS-PET | 139.04 | (Kumara et al. 2020) |
| SFR-PET | 261.38 | (Kumara et al. 2020) |
| ER-PET | 316.7 | (Kumara et al. 2020) |
| PAW | 189–190 | 45 |
| 50PAW:50PP | 137–141 | 45 |
| 75PAW:25PP | 136–140 | 45 |
| 25PAW:75PP | 152–158 | 45 |
| PP | 149–153 | 45 |
PAW-Paulownia wood, PP –polypropylene, PET- polyethylene terephthalate, Cotton stalk, hazelnut shell, sunflower residue, and Euphorbia rigida.
Thermodynamic parameters
The thermodynamic parameters derived from Eqs. (18–20), are displayed in Table 11. The energy variance between the products and the reactants is shown by the ∆H throughout the reaction phase. Additionally, it shows if the process is endothermic or exothermic. The study discovered a small energy variation (~ 5 kJ/mol) among the enthalpy change and Ea, suggesting that the chemical reaction started quickly. The synthesis of activated complexes is made easier by the minute difference between Ea and ∆H, which also shows that the products can be produced with very little additional energy (Kumar et al.33. The maximum amount of work is determined using the ∆G of the thermodynamic system at a particular T and P45. The magnitude of ∆S indicates that the substance has passed the energy barrier and is getting close to thermodynamic equilibrium. Production of products requires a long time owing to the less reactivity in this current state. On the other hand, a substance with a high entropy score interacts quickly and produces a product soon. Table 8 shows the average values ΔH, ΔS and ΔG for the KAS model for the following samples: LDPE: RH (50:50), which has 113 kJ/mol, − 0.063 J/molK, and 130 kJ/mol, LDPE: RH (25:75), which has 107 kJ/mol, − 0.072 J/mol.K, and 129 kJ/mol,and sample LDPE: RH (75:25), which has 115 kJ/mol, − 0.058 J/molK, and 136 kJ/mol. Similarly, for the OFW model, the values of ΔS, ΔH, and ΔG were 150.63 kJ/mol, 6.34 J/molK, and 151.64 kJ/mol, respectively. The near-approximation of the results for different thermodynamic parameters assessed with three iso-conversional model-free procedures specifies the reliability of the thermodynamic analysis and the conclusions drawn from it. These explanations and deductions linking disparity in thermodynamic triplets to distinct stages of the breakdown process are helpful for a comprehensive analysis of the pyrolysis reaction.
Table 11.
A comparative analysis of thermodynamic parameters in LDPE: RH (50:50), LDPE: RH (25:75) and LDPE: RH (75:25).
| Thermodynamic parameter | LDPE: RH (50:50) | LDPE: RH (25:75) | LDPE: RH (75:25) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KAS method | |||
| ∆H(kJ/mol) | 112 | 107 | 115 |
| ∆G(kJ/mol) | 130 | 129 | 136 |
| ∆S(J/molK) | − 0.063 | − 0.072 | − 0.058 |
| FWO method | |||
| ∆H(kJ/mol) | 107 | 106 | 122 |
| ∆G(kJ/mol) | 128 | 126 | 143 |
| ∆S(J/molK) | − 0.059 | − 0.076 | − 0.051 |
The thermodynamic parameters such as Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, and entropy significantly influence the pyrolysis process, determining the yield and quality of bio-oil produced. In the context of co-pyrolysis of LDPE and rice husk, the enthalpy of the reaction provides insight into the endothermic nature of the process, particularly at higher temperatures that favor enhanced bio-oil yield. Studies have shown that raising the temperature in co-pyrolysis can improve the thermal cracking of plastic, leading to a higher conversion rate of LDPE into liquid products46. Additionally, changes in Gibbs free energy at various stages of pyrolysis reflect the feasibility of the reaction under high-temperature conditions, confirming that reactions at elevated temperatures can shift the equilibrium towards desired pyrolysis products such as bio-oil47. Entropy changes are also crucial, as a rise in system entropy may correspond to an increase in gas production, a trend that is observed in studies exploring biomass-plastic pyrolysis, especially at temperatures exceeding 500 °C48. Such an in-depth thermodynamic analysis emphasizes the importance of maintaining optimized reaction conditions for achieving industrially viable yields. Figure 5 shows that graphical picture for Pyrolysis, Thermal Degradation and Kinetics Analysis.
Fig. 5.
Shows that graphical picture for pyrolysis, thermal degradation and kinetics analysis.
CPI Index
The Comprehensive Pyrolysis Index (CPI) improved considerably as the heating rate increased. Table 12 shows that increasing the heating rate promotes pyrolysis. The total Volatile Release Index (CPI) for RH: LDPE at various ratios for RH: LDPE (50:50), RH: LDPE (75:25), and RH: LDPE (25:75) at 600 °C in N2 atmospheres ranged from 1.2 to 4.9, 2.1–4.1, and 1.9–6.5 times that of the reactions in the entire process, respectively. The CPI value is RH and the LDPE sample increases with increasing heating rate so we find out that it is more convenient for the pyrolysis process. The Ra (Average Decomposition Rate), Rm (Maximum Decomposition Rate), and CPI values all increased significantly, demonstrating that the high heating rate increases pyrolysis performance. The CPI index is calculated using Eq. 21. The CPI index provides information about the thermal efficiency of the process by integrating temperature impacts, yield composition, and chemical reaction rate characteristics. In the LDPE-rice husk system, optimizing the CPI index at different temperatures aids in determining the optimal conditions for maximum bio-oil outputs. These comparisons, both within the LDPE-rice husk system and against different biomass-plastic systems, provide a quantitative framework for evaluating and optimizing co-pyrolysis processes.
Table 12.
CPI Index of a raw and torrefied sample at different heating rates.
| Feedstock | Heating rate | Ti | Tp | − Ra | − Rm | ΔT1/2 | CPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Raw RH: LDPE (50:50) |
10 | 293 | 381 | 1.40 | 18.10 | 80.3 | 1.2 |
| 20 | 300 | 400 | 2.82 | 30.3 | 77.7 | 2.5 | |
| 30 | 314 | 412 | 3.53 | 42.3 | 75.7 | 3.6 | |
| 40 | 321 | 420 | 4.69 | 58.08 | 58.9 | 4.9 | |
|
Raw RH: LDPE (75:25) |
10 | 256 | 369 | 1.23 | 10.5 | 82.5 | 2.1 |
| 20 | 263 | 375 | 2.21 | 21.09 | 78.2 | 2.9 | |
| 30 | 270 | 382 | 3.26 | 43.7 | 76.2 | 3.5 | |
| 40 | 278 | 390 | 4.38 | 64.7 | 72.11 | 4.1 | |
|
Raw RH: LDPE (25:75) |
10 | 345 | 418 | 1.54 | 28.32 | 36.2 | 1.9 |
| 20 | 350 | 424 | 2.12 | 29.7 | 41.8 | 2.8 | |
| 30 | 360 | 433 | 3.06 | 51.07 | 38.02 | 4.3 | |
| 40 | 381 | 440 | 4.10 | 67.9 | 42.9 | 6.5 |
Ra -average decomposition rate (40–600 °C), Rm- weight loss at 600 °C, CPI-comprehensive pyrolysis index at 600 °C, CPI unit: 10−6/℃3 min2.
Further details on the CPI of samples at different ratios of rice husk and LDPE are provided in Table 12.
Challenges and application of industrial implementation for the co-pyrolysis
Before proceeding, it is imperative to assess the economic feasibility of the procedure, encompassing the expenses associated with the procurement of raw materials, energy utilization, and the potential market worth of the bio-oil and any accompanying by-products. Co-pyrolysis presents a favorable approach for transforming waste materials into useful goods, but it faces competition from alternative waste management and energy production techniques. Furthermore, it is important to evaluate the technology’s potential to scale. Laboratory-scale tests frequently do not readily translate to industrial sizes, therefore pilot studies are important to identify possible obstacles in scaling up the process, such as reactor design, heat transfer efficiency, and feedstock management. Thirdly, environmental and regulatory problems must be addressed. The co-pyrolysis process should comply with environmental standards, limiting emissions and handling any hazardous by-products. Additionally, integrating this technology into current waste management and energy systems might boost its practicality by leveraging existing infrastructure. Finally, the dependability and consistency of the co-pyrolysis process should be investigated. The fluctuation in the composition of rice husk and LDPE might affect the quality and production of the bio-oil, thus techniques to maintain consistent feedstock quality and process control are crucial. By examining these issues, the authors can fully review the practical concerns for industrial implementation of co-pyrolysis of LDPE and rice husk49. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic waste is consistent with worldwide aims for reducing plastic pollution and managing agricultural wastes, both of which pose environmental difficulties. The environmental advantages of diverting LDPE from landfills and reusing rice husk, which would otherwise contribute to open burning and air pollution. Furthermore, discussion should be made on the possible decrease in greenhouse gas emissions from bio-oil production as an alternative to fossil fuels, which is supported by studies that evaluate emissions in scaled-up co-pyrolysis plants.50
Conclusions
The comparative co-degradation kinetics of RH with LDPE ratios of 50:50, 25:75, and 75:25 were investigated in this work. Thermal properties suggest that a combination of low-density polyethylene and rice husk can be utilized as feedstocks for the thermochemical conversion methods. This study resulted that 50:50 ratio provided good results as compared to 25:75 and 75:25. The calculation of activation energy was made using the KAS and FWO methods, yielding results of 107 and 102 kJ/mol with the LDPE: RH (50:50), 101 and 100 kJ/mol with the LDPE: RH (25:75), and 117 and 110 kJ/mol with the LDPE: RH (75:25). The experimental heating value of LDPE: RH (75:25), was 20.61 MJ/kg whereas the theoretical value recorded was 20.31 MJ/kg. Additionally, the CPI index for each blended ratio of LDPE and RH has been determined. The results of the present study make a substantial contribution to a thorough comprehension of the blended sample pyrolysis process and its application in the energy sector. As the present study limits its domain the co-pyrolysis of two feedstocks, the further directions for the present research work can be taken on the path of using catalyst during the co-pyrolysis process. The influence of catalyst on reaction kinetics can be studied by employing various kinetic models. Also the application part of the end products like, bio-oil, char and gas can be effectively studied to extend the boundary of the present work.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Department of Physics, School of Chemical Science and Physical Science at Lovely Professional University (LPU) Phagwara, Punjab, and the SAIF KOCHI for providing the test facilities during the elemental analysis.
Abbreviations
- LDPE
Low-density polyethylene
- RH
Rice husk
- VM
Volatile matter
- MC
Moisture content
- AC
Ash content
- FC
Fixed carbon
- KAS
Kissinger Akahira Sunose
- FWO
Flynn wall Ozawa
- CR
Coats and Redfern
- CPI
Comprehensive pyrolysis index
Author contributions
Divya Bisen- Conceptualization, writing-original draft preparation, Editing. Ashish Pratap Singh Chauhan—supervision and finalize the draft Anil Sharma- formal analysis and editing Sakthivel Rajamohan- Review and Validation Dhinesh Balasubramanian—Review and Validation Elumalai PV- Software and visualization Aschalew Cherie- Resources and analysis Aschalew Cherie —Supervision, review and editing. Sakthivel Rajamohan- Review and Validation. Elumalai PV—Review and Validation. Dhinesh Balasubramanian—Review and Validation. Aschalew Cherie—- Review and Validation. All authors have read and approved the published version of the text.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Data availability
The datasets during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent for publication
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Divya Bisen, Email: divebisen23@gmail.com.
Dhinesh Balasubramanian, Email: dhineshbala91@mepcoeng.ac.in.
Aschalew Cherie, Email: aschalew.cherie@amu.edu.et.
References
- 1.Alhumade, H. et al. Investigation of pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behavior of Invasive Reed Canary, bioenergy potential. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol.140, 385–392 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ranjit, P. S. et al. Direct utilisation of straight vegetable oil (SVO) from Schleichera oleosa (SO) in a diesel engine—a feasibility assessment. Int. J. Ambient Energy43(1), 7694–7704. 10.1080/01430750.2022.2068063 (2022). [Google Scholar]
- 3.Muigai, H. H., Choudhury, B. J., Kalita, P. & Moholkar, V. S. Co–pyrolysis of biomass blends: Characterization, kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Biomass Bioenergy143, 105839 (2020). [Google Scholar]
- 4.Varma, A. K. & Mondal, P. Physicochemical characterization and pyrolysis kinetics of wood sawdust. Energy Sources Part A Recov. Util. Environ. Effects38(17), 2536–2544 (2016). [Google Scholar]
- 5.Garba, M. U. et al. Thermogravimetric characteristic and kinetics of catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass with low- and high-density polyethylenes. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery8, 143–150 (2016). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Al-Salem, S. M., Antelava, A., Constantinou, A., Manos, G. & Dutta, A. A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW). J. Environ. Manag.197, 177–198 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou, L. M., Wang, Y. P., Huang, Q. W. & Cai, J. Q. Thermogravimetric characteristics and kinetic of plastic and biomass blend co-pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol.87, 963–969 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zaman, C. Z., Pal, K., Yehye, W. A., Sagadevan, S., Shah, S. T., Adebisi, G. A. & Johan, R. B. (2017). Pyrolysis: A sustainable way to generate energy from waste. Pyrolysis.
- 9.International Energy Agency. (2006). Annual report, 2006: IEA bioenergy: task 34, pyrolysis of biomass. International Energy Agency, Paris, France.
- 10.Oyedun, A. O., Gebreegziabher, T. & Hui, C. W. Mechanism and modeling of bamboo pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol.106, 595–604 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 11.Miskolczi, N. & Nagy, R. Hydrocarbons obtained by waste plastic pyrolysis: A comparative analysis of decomposition described by different kinetic models. Fuel Process. Technol.104, 96–104 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grønli, M. G., Várhegyi, G. & Di Blasi, C. Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.41, 4201–4208 (2002). [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhou, L., Luo, T. & Huang, Q. Co-pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of coal and plastic blends. Energy Convers. Manag.50, 705–710 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hatakeyama, T. & Quinn, F. X. Thermal analysis—fundamentals and applications to polymer science (Wiley, 1999). [Google Scholar]
- 15.Koufopanos, C. A., Maschio, G. & Lucchesi, A. Kinetic model of the pyrolysis process of biomass and components. Can. J. Chem. Eng.67, 75 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mansaray, K. G. & Ghaly, A. Determination of reaction kinetics of rice husks in air using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Sources21, 899 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nassar, M. N. Thermal analysis kinetics of rice husk and bagasse. Energy Sources21, 131 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhao, H. et al. Thermogravimetry study of the pyrolytic characteristics and kinetics of macro-algae Macrocystis pyrifera residue. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.111, 1685–1690 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oh, S.-Y. & Seo, Y.-D. Polymer/biomass-derived bio-char for use as a sorbent and electron transfer mediator in environmental applications. Bioresour. Technol.218, 77–83 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chattopadhyay, J., Pathak, T. S., Srivastava, R., & Singh, A. C. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of paper biomass and plastic mixtures (HDPE (high density polyethylene), PP (polypropylene) and PET (polyethylene terephthalate)) and product analysis. Energy, 103, 513–521 (2016).
- 21.Dewangan, A., Pradhan, D. & Singh, R. K. Co-pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse and low-density polyethylene: Influence of plastic on pyrolysis product yield. Fuel85, 508–516 (2016). [Google Scholar]
- 22.Prajapati, S. B. et al. Co-pyrolysis behavior, kinetic and mechanism of waste-printed circuit board with biomass. Processes11(1), 229 (2023). [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chee, A. et al. Kinetic analysis of rice husk pyrolysis using Kissinger-Akahira-Sunose (KAS) method. Procedia Eng.148, 1247–1251 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li, D., Chen, L., Zhang, X., Ye, N. & Xing, F. Pyrolytic characteristics and kinetic studies of three kinds of red algae. Biomass Bioenergy35, 1765–1772 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ahmad, M. S., Mehmood, M. A., Al Ayed, O. S., Ye, G., Luo, H., Ibrahim, M., ... & Qadir, G. Kinetic analyses and pyrolytic behavior of Para grass (Urochloa mutica) for its bioenergy potential. Bioresource technology, 224, 708–713 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Vyazovkin, S. & Wight, C. A. Isothermal and non-isothermal kinetics of thermally stimulated reactions of solids. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem.17, 407–433 (1998). [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chandrasekaran, A., Ramachandran, S. & Subbiah, S. Modeling, experimental validation and optimization of Prosopis juliflora fuelwood pyrolysis in fixed-bed tubular reactor. Bioresour. Technol.264, 66–77 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ozawa, T. A new method of analyzing thermo-gravimetric data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn.38, 1881–1886 (1965). [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu, X., Wu, Y., Wu, K., Chen, Y., Hu, H., & Yang, M. Study on pyrolytic kinetics and behavior: The co-pyrolysis of microalgae and polypropylene. Bioresource technology, 192, 522–528 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 30.Senthilkumar, P. B. et al. The effect of thermal degradation and thermogravimetric analysis on pyrolysis oil production from waste milk packet for CI engine application. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.147(17), 9677–9691. 10.1007/s10973-022-11226-6 (2022). [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sriram, A. & Swaminathan, G. Pyrolysis of Musa balbisiana flower petal using thermo-gravimetric studies. Bioresour. Technol.265, 236–246 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Akahira, T., & Sunose, T. Method of determining activation deterioration constant of electrical insulating materials (Research Report No. 16, pp. 22–23). Chiba Institute of Technology.10.1016/j.softx.2019.100359 (1971).
- 33.Kumar, M., Upadhyay, S. N. & Mishra, P. K. A comparative study of thermochemical characteristics of lignocellulosic biomasses. Bioresour. Technol. Reports8, 100186. 10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100186 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang, J., Liu, J., Evrendilek, F., Zhang, X. & Buyukada, M. TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS analyses of pyrolysis behaviors and products of cattle manure in CO2 and N2 atmospheres: Kinetic, thermodynamic, and machine-learning models. Energy Convers. Manag.195, 346–359 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 35.Saikia, N. & Bardalai, M. Thermal analysis and kinetic parameters determination of biomass using differential thermal gravimetric analysis in N2 atmosphere. Mater. Today Proc.5, 2146–2156 (2018). [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mishra, R. K. & Mohanty, K. Kinetic analysis and pyrolysis behavior of waste biomass towards its bioenergy potential. Bioresour. Technol.311, 123480 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shagali, A. A. et al. Thermal behavior, synergistic effect and thermodynamic parameter evaluations of biomass/plastics co-pyrolysis in a concentrating photothermal TGA. Fuel331, 125724 (2023). [Google Scholar]
- 38.Raza, M., Abu-Jdayil, B. & Inayat, A. Pyrolytic kinetics and thermodynamic analyses of date seeds at different heating rates using the Coats-Redfern method. Fuel342, 127799 (2023). [Google Scholar]
- 39.Anshar, M., Tahir, D. & Ani, F. N. Pyrolysis characteristic of rice husk with plastic bag as fuel for power generation by using a thermo-gravimetric analysis. Earth Environ. Sci.105, 012034 (2018). [Google Scholar]
- 40.Çepelioğullar, Ö. & Pütün, A. E. Thermal and kinetic behaviors of biomass and plastic wastes in co-pyrolysis. Energy Convers. Manag.75, 263–270 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mortezaeikia, V., Tavakoli, O. & Khodaparasti, M. S. A review on kinetic study approach for pyrolysis of plastic wastes using thermogravimetric analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis160, 105340 (2021). [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hou, Y., Feng, Z., He, Y., Gao, Q., Ni, L., Su, M., ... & Hu, W. Co-pyrolysis characteristics and synergistic interaction of bamboo residues and disposable face mask. Renewable Energy, 194, 415–425 (2022).
- 43.Chen, Y., Wang, F., Duan, L., Yang, H., & Gao, J. Tetracycline adsorption onto rice husk ash, an agricultural waste: Its kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 222, 487–494 (2016).
- 44.Olszak-Humienik, M. & Możejko, J. Thermodynamic functions of activated complexes created in thermal decomposition processes of sulphates. Thermochim. Acta344, 73–77 (2000). [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ruvolo-Filho, A. & Curti, P. S. Chemical kinetic model and thermodynamic compensation effect of alkaline hydrolysis of waste (PET) in non-aqueous ethylene glycol solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.45, 7985–7996 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim, Y. S., Kim, Y. S. & Kim, S. H. Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the thermal decomposition of plastic waste−waste lube oil compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol.44, 5313–5317. 10.1021/es101163e (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Raza, S. et al. Synergistic effect on co-pyrolysis of rice husk and sewage sludge by thermal behavior, kinetics, thermodynamic parameters and artificial neural network. Waste Manag.85, 131–140. 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.12.031 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xu, Y. & Chen, B. Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol.146, 485–493. 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.086 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Li, J. et al. Investigation on the co-pyrolysis of agricultural waste and high-density polyethylene using TG-FTIR and artificial neural network modeling. Process Saf. Environ. Protect.160, 341–353 (2022). [Google Scholar]
- 50.Burra, K. G. & Gupta, A. K. Kinetics of synergistic effects in co-pyrolysis of biomass with plastic wastes. Appl. Energy220, 408–418 (2018). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.