Abstract
Background and Aims:
For the aggressive treatment of postoperative pain, nonpharmacological methods (NPMs) are gaining importance complementary to routine multimodal pain management. The primary aim of the study was to assess the incidence of use of NPMs in our hospital. Secondary objectives were to correlate the pain scores, patient satisfaction, and percentage of time the patient was in severe pain within 72 h postsurgery with the use of NPMs when in pain/not in pain. The effect of NPMs on the physical and emotional outcome of patients as per the American Pain Society Patient Outcome Questionnaire (APS-POQ) was also assessed.
Material and Methods:
After obtaining approval from the institutional ethics committee (IEC), the trial was registered with the Clinical Trials Registry of India (CTRI). Informed consent was obtained from adult patients on the third postoperative day of elective surgeries. Their responses to the APS-POQ and to a few additional questions about their beliefs on the use of NPM were recorded.
Results:
Only one-fourth of the total study population were using NPMs for pain management in the hospital. After propensity matching for surgery and postoperative analgesia, two groups were made: one using NPM for pain relief (n = 49) and the other not using NPM (n = 98). There was no significant difference among the satisfaction score (P = 0.31), least pain score (P = 0.68), and worst pain score (P = 0.43) within 72 h postoperatively in either of the groups. Emotional and physical outcomes as per the APS-POQ were similar in both the groups.
Conclusion:
NPMs are rarely practiced and used during postoperative pain in our hospital. No difference in pain scores, patient satisfaction, and emotional and physical outcomes of the APS-POQ was seen in the group that indulged in NPMs.
Keywords: Nonpharmacological methods of pain relief, pain acute, postoperative pain
Introduction
Postoperative pain is an expected, yet an undesirable effect of surgery. It is essential to aggressively treat postoperative pain to enable adequate rehabilitation and limit the consequences of untreated pain.[1] Unrelieved pain can affect patient satisfaction in the immediate postoperative period and predispose the chronicity of the symptom itself.[1]
Drugs used for management of pain relief are not without side effects. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) are often used to treat mild to moderate acute pain. They are found to be associated with gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer, and renal insufficiency.[2] Opioids administered for treating moderate to severe pain can cause respiratory depression and other side effects like nausea, vomiting, and constipation, which delays postoperative recovery. Risk of addiction even after a short-term use is also a concern.[3] There is a growing interest in the use of nonpharmacological therapy methods (NPMs) in postoperative pain. NPMs can be classified into two types: the first includes the physical interventions which block the nociceptive input and the pain perception (positioning, massage, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation, acupuncture, progressive muscle relaxation) and the second includes the psychological interventions (cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness-based stress reduction, acceptance and commitment therapy, spirituality and religion, and music therapy).[4] Even though NPMs cannot be used alone, they can be combined with pharmacological methods to focus on better pain management.[5] The revised draft of the American Pain Society Patient Outcome Questionnaire (APS-POQ) has emphasized on the use of NPMs for postoperative pain relief.[6]
In our hospital, multimodal pain management forms the basis of postoperative pain management. NPMs are probably underutilized, with caregivers not actively advising these methods.[7] However, patients’ involvement in distraction practices like watching television and listening to music remains largely unknown. We believe that there would be some natural involvement in these activities in the immediate postoperative period (72 h postsurgery), without the patient being aware of the benefits of the same in pain management.
This prospective observational study is aimed to understand the current use of NPMs for pain relief and the use of any distraction modalities being currently practiced by patients in the hospital in the postoperative period. Secondary objectives were to correlate the pain scores, patient satisfaction, and percentage of time the patient was in severe pain within 72 h postsurgery with the use of NPMs when in pain/not in pain. The effect of NPMs on the physical and emotional outcome of patients as per the APS-POQ was also assessed.
Material and Methods
This was a prospective, observational study conducted in our hospital from August 2020 to November 2020. After obtaining approval from the institutional ethics committee (IEC), the trial was registered with the Clinical Trials Registry of India (CTRI/2020/08/027455). Consecutive patients who underwent major elective surgeries and fulfilled the inclusion criteria were enrolled in the trial after written and informed consent was obtained from them. The study included all patients in the age group 18–75 years who were planned for major coelomic surgeries and surface surgeries with an expected hospital stay of more than 72 h. Patients with prolonged stay in the intensive care unit (ICU)/post-anesthesia recovery room (PACU) for more than 24 h postsurgery, patients not willing to participate in the study, patients or relatives who cannot understand English or Hindi/Marathi, patients with tracheostomy in the postoperative period, and patients discharged from the hospital within 24–48 h postsurgery were excluded.
The patients who underwent major surgeries and met the inclusion criteria were approached on the third postoperative day (not including the day of surgery), and after informed consent was obtained from them, they were enrolled in the trial. Investigators conducted a short interview with the patients. Individual details like age, gender, education, and type of room (category- general ward/shared room/single occupancy) were noted. Details with respect to surgery and instructions with respect to ambulation and the need for active chest physiotherapy were recorded. Whether the patient was under active surveillance by the acute pain service (APS) and was visited by a physiotherapist was also noted. For the study, active chest physiotherapy meant any patient who was advised deep coughing and chest patting exercises. Under active surveillance by the APS meant patients who were visited at least twice a day by the APS team. Reponses to the questions included in the revised APS-POQ were captured.[6] This is a validated questionnaire used extensively as a quality improvement tool.[6] In addition, patients’ view and practice with respect to NPMs when in pain/not in pain and the frequency of use at home/hospital were recorded [refer to Annexure 1]. During the course of the interview, we first asked the patients if they engaged in any nonpharmacological methods during pain/as a routine. Then, their opinion if this intervention/diversion helped in pain management was sought. Lastly, they were explained about the evidence suggesting that patients who engaged in these activities had better pain relief, following which their willingness in participation in these activities was sought.
The above interview was conducted by the investigators team through questions asked to patients in the presence of their relatives in the language best understood by them.
Statistical analysis
For simplicity in analysis, surgeries were clubbed as surface surgeries, bone and soft tissue tumors, laparotomies (open), laparotomies (minimally invasive), thoracotomies (open), and thoracotomies (minimally invasive). Patients’ education was recorded as primary schooling, undergraduate, graduate, postgraduate, and illiterate. Postoperative pain management was clubbed as epidural analgesia, regional catheters, opioid-based patient-controlled analgesia, and round-the-clock medications (inclusive of single-shot regional techniques). All scores were expressed as median with interquartile range (IQR).
The incidence of use of NPMs was expressed as a percentage. The effect of use of NPMs on pain scores and various physical and emotional outcomes of the patients (APS-POQ) were compared using nonparametric tests. The correlation between patient location and type of surgery with the use of NPMs for pain relief was ascertained using Chi-square or Fischer’s exact test. For impact of the use of NPMs on pain scores and satisfaction, propensity matching was done with respect to type of surgery and postoperative analgesia. Since these data did not follow a normal distribution, scores in the two groups were compared by Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Shapiro–Wilk nonparametric study of normality.
All statistical analyses were done by Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software version 20.0 for Windows (SPSS, IBM). P value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
A total of 400 patients from daily surgeries were screened from 9/1/2020 to 11/16/20. Data was collected from 200 patients who met the inclusion criteria [Figure 1]. Demographic details of patients included in the study have been elaborated in Table 1.
Figure 1.
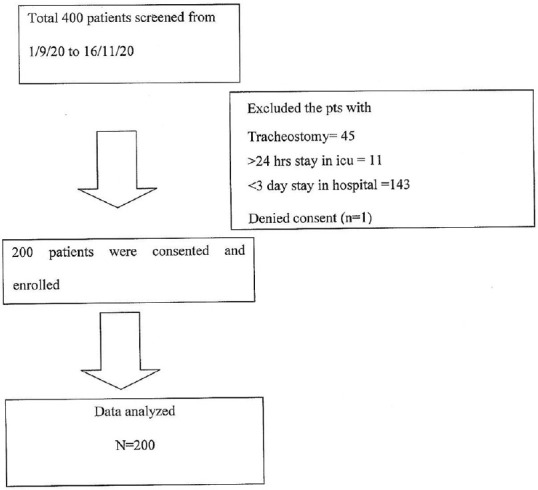
Consort diagram showing recruitment of patients in the trial
Table 1.
Demographic details (n=200)
| Variable | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 113 | 56.5 |
| Female | 87 | 43.5 |
| Education | ||
| Primary schooling | 69 | 34.5 |
| Undergraduate | 39 | 19.5 |
| Graduate | 61 | 30.5 |
| Postgraduate | 8 | 4.0 |
| Illiterate | 23 | 11.5 |
| Type of surgeries | ||
| Surface surgeries | 44 | 22.0 |
| Bone and soft tissue | 25 | 12.5 |
| Laparotomy (open) | 96 | 48 |
| Laparotomy (minimally invasive) | 13 | 6.5 |
| Thoracotomy (open) | 15 | 7.5 |
| Thoracotomy (minimally invasive) | 7 | 3.5 |
| Post-op ward (room type) | ||
| General ward | 166 | 83 |
| Room sharing basis | 25 | 12.5 |
| Individual occupancy | 9 | 4.5 |
| Post-op analgesia | ||
| Epidural analgesia | 69 | 34.5 |
| Regional catheters | 5 | 2.5 |
| Patient-controlled analgesia | 11 | 5.5 |
| Round-the-clock analgesics | 115 | 57.5 |
| Patient advised ambulation | 192 | 96 |
| Visited by physiotherapist | 140 | 70 |
| Active chest physiotherapy advised | 59 | 29.5 |
Data analyzed from the responses of 200 patients showed that only 49 out of 200 patients (24.5%) used various methods of NPMs for postoperative pain relief. Around 15 patients were engaging in two NPMs and seven patients revealed use of more than two NPMs. More than half (27 patients) replied to be getting the benefit of only one of the NPMs.
Maximum number of people (11.5%) were using prayer as the NPM during pain. Cold pack, heat, and imagery were not used by anyone. About 5%–6% were using deep breathing and distractions such as watching television, reading newspaper, and walking and very few used music, meditation, and massage as the NPM for pain control [Figure 2]. Twenty-eight percent of patients reported their frequency of use of NPMs as often (two to three times a day). When asked about the use of NPMs in the hospital when not in pain, 46% of patients said they were adopting some kind of NPM in their hospital routine. Walking (23.5%) was an activity most patients indulged in. This was followed by deep breathing (14%) and prayer (18.5%) as the activities practiced by patients.
Figure 2.
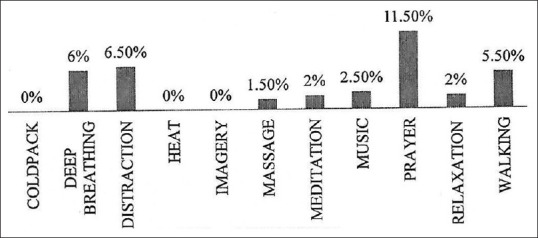
Bar graph for the type of NPM practiced by patients when in pain. NPM = nonpharmacological method
When asked about their routine at home, the responses suggest that 29% of the patients were are engaged in some kind of physical or physiological behavior for healthier living on a daily basis in their routine life, which included music, meditation, yoga, and long walks. However, less than 17% of patients preferred to use nonpharmacological therapies to relieve pain at home. The use of NPMs was seen more in females (P = 0.02), but was not influenced by patients’ age (P = 0.10). There was no significant correlation found between education (P = 0.102), postoperative ward (P = 0.504), and the type of surgery (P = 0.571) and the practice of NPM.
After propensity matching for surgery and postoperative analgesia, two groups were made: one group using NPMs for pain relief (n = 49) and the other not using NPMs (n = 98). From this matched database, the following results were drawn. There was no significant difference between the least, worst pain satisfaction scores in the first 72 h between these two groups, [refer Table 2]. The patients in the group not using NPMs during pain spent less time (20%; IQR: 10–40) in severe pain when compared to those who used NPMs during pain (30%; IQR: 20–40), though this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.10). There was no difference in the physical and emotional outcome as per the American pain questionnaire in patients who were and were not using NPMs during pain.
Table 2.
Comparison of outcomes between Group Y (patients who used NPM when in pain at the hospital, n=49) and Group N (patients who did not use NPM when in pain at the hospital, n=98) patients, matched for the type of surgery and pain management
| Variables | Median (IQR) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Group N Not using NPM (n=98) | Group Y Using NPM (n=49) | ||
| Least pain in first 72 h | 2 (2) | 2 (5) | 0.68 |
| Worst pain first 72 h | 6 (2) | 6 (2) | 0.43 |
| Percentage of time the patient had severe pain in the first 72 h | 20 (30) | 30 (20) | 0.10 |
| Satisfaction score of patients in the first 72 h | 9 (1) | 9 (1) | 0.31 |
| Pain interfering in turning, sitting, repositioning | 3 (4) | 3 (4) | 0.13 |
| Pain interfering in walking, sitting on chair, standing at the sink | 3 (4) | 3 (4) | 0.09 |
| Pain interfering in falling asleep | 0 (3) | 0 (3) | 0.87 |
| Pain interfering in staying asleep | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.56 |
| Pain causing anxiety | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.47 |
| Pain causing depression | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.87 |
| Pain causing fright | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.59 |
| Pain causing helplessness | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.69 |
IQR=Interquartile range, NPM=Nonpharmacological method
To understand the role of NPM as a distractor (i.e., practiced when patient is not in pain and in the hospital), we looked at patients using NPMs in the hospital when not in pain and compared their pain scores with those who did not use NPMs at all. The data were matched for the type of surgery and postoperative analgesia. Two groups of 87 patients in each were included. There was no difference in the scores of least pain score, worst pain score, and patient satisfaction. However, the patients not using NPMs when not in pain tended to spend more percentage of time in severe pain with median =30%, IQR =10–60, compared to a median of 20% and IQR =20–40 in the positive group (P = 0.10).
We looked at the belief and attitudes regarding use of NPMs. Only 35% of patients believed in NPMs for the management of pain. Also, 48% of patients agreed to participate in NPMs on being told that NPMs have a positive role in pain management. Around 36% of patients were sure to advice others about the use of NPMs. Moreover, 45% of patients agreed that it is desirable to have a discussion of nonpharmacological pain management before surgery, of which 8% were keen to have a discussion about NPMs.
We looked at the impact of education on patients’ belief in NPMs for pain relief and their willingness to participate. We found a significant correlation with positive belief in NPMs among the graduate and postgraduate patients (P = 0.03). The same group agreed to participate in NPMs if found beneficial in controlling pain (P = 0.002) [Table 3].
Table 3.
Impact of education on belief and willingness to participate in NPMs (n=200)
| Education | Illiterate | Primary schooling | Undergraduate | Graduate | Postgraduate | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Believe in NPM | P<0.001 | |||||
| Agree | 6 | 17 | 13 | 29 | 4 | |
| Neutral | 10 | 12 | 8 | 11 | 0 | |
| Disagree | 7 | 40 | 18 | 21 | 4 | |
| Willingness to participate in NPM | P=0.001 | |||||
| Probable | 6 | 20 | 13 | 32 | 4 | |
| Neutral | 10 | 9 | 10 | 5 | 0 | |
| Improbable | 7 | 40 | 16 | 24 | 4 |
NPM=Nonpharmacological method
Discussion
Though our hospital has an established APS for around two decades, NPMs are not routinely advised or practiced. This is the first survey to understand if our patients indulge in any form of NPM when in pain or otherwise in the hospital in the immediate postoperative period.
We found only one-fourth of the total study population were using NPMs for pain management, though encouragingly, half of the patients engaged in complementary therapies in the hospital when not in pain. There was no significant difference in least pain score, worst pain scores, and patient satisfaction between the two groups. Emotional and physical outcome as per the APS-POQ was similar in both the groups.
Patients tend to have a varied stay in ICU/PACU. In these places, patient may not be in a position or may feel inhibited to use NPMs as per their desire. Hence, patients with prolonged stay in the ICU/PACU for more than 24 h postsurgery were excluded, and patients expected to stay at least 72 h in the hospital were included. The interview was taken in the third postoperative period to understand the impact of use of NPM in this period.
Komann et al.[8] conducted a survey in 12 hospitals from different countries to assess the frequency of usage of these methods in the hospital and their pain relief. This study showed that women used NPMs significantly more often than men (P < 0.001) and elders used NPMs significantly less than younger patients (P < 0.001). Similarly, in our study, we found females were using more NPMs than males and no difference was found with respect to age.
Our study has taken an overview of the usage of NPMs as a postoperative pain control measure. Most of the patients studied used prayer, deep breathing, and walking as ways of distraction during pain. Very few used music and meditation during pain, even though they were practicing some or the other method of distraction therapy routinely in their home and in the hospital when they were not in pain.
There are several literature reports about the individual methods of NPM and their benefits in postoperative period.[9,10,11,12,13,14] The randomized controlled trial by Nilsson and Rawal[15] studied the effect of intraoperative and postoperative music on the perioperative pain. They found that after 1 h in the PACU, postoperative music group had significantly lower anxiety score and significantly lower pain score compared to the control group, and also, reduction in the amount of morphine consumed. Another trial found that combination of spiritual deep breathing and exercise therapy reduced pain and anxiety among postoperative orthopedic fracture patients.[16] Studies have shown reduction in pain intensity and unpleasantness along with reduction in anxiety following use of massage therapy as an adjuvant.[17]
It is important to note that in these randomized controlled trials, NPMs were not practiced during the episodes of pain. Patients engaged in NPM as a part of routine postoperative care, and this probably helped in reducing overall pain experience and was found to be beneficial. In a randomized controlled trial, the intervention was more controlled and time devoted to NPM was ensured. In our study, we did find that patients who engaged in NPM when not in pain spent less time in severe pain than those who did not engage in any NPM. However, this difference was not statistically significant. To understand this, we need to admit that, per se the hospital does not have/provide any special room/access to music or mediation (except in private rooms, which have access to television). As a result, the patient and the relatives on their own initiative have to indulge in any diversion activity. This may be the reason why we found a varied level of participation in the kind of NPM and time spent on the same.
However, we found that patients using NPM method during pain spent more time in pain (though not statistically significant) than the control group. Our results correlated with the result by the PAIN OUT database.[18] They found that the patient who did not use NPM had lower pain scores than those who used NPMs. This could be related to the possibility that NPM may have been used by patients when in severe pain only. Also, it is essential to remember that NPM should not replace analgesic interventions with proven effectiveness.[15]
In our study, we found that there was a lack of encouragement of patients by doctors and nurses, with only 10% of patients positively agreeing to encouragement by caregivers. One of the reasons could be poor knowledge about the benefit of use of NPMs among nurses themselves. Literature suggests that nurses can play a lead role in educating patients about the benefits of NPM, and patients are more motivated to try these modalities following this interaction.[19] Nurses’ education about NPMs will definitely go a long way in reaping the benefits of NPMs in pain relief. Unfortunately, we have not yet surveyed nurses’ knowledge about the use of NPMs in our hospital.
In this study, most of the less-educated (illiterate and who had done primary schooling) responded as they disagreed or had a neutral approach to the question of belief in NPMs. Well-educated patients believed in NPMs, and their participation is likely to increase if counseled about the beneficial role of NPMs in pain management. Evidence suggests education helps in more participation.[20] Also, health literacy intervention helps in adherence, especially more so in people of low-income group and ethnic minority compared to the more privileged population.[21] We hope that with education, the willingness to participate in NPMs would be more positive even in the less-educated group in future.
Our study has data collected from patients with varied surgery and postoperative pain management. The influence of use of NPMs on pain score and patient satisfaction was studied in a matched database. Based on the results of this survey, we have initiated a randomized controlled trial to study the benefit of use of NPMs, wherein the patients are actively motivated to involve in some kind of diversion/distraction modalities in the immediate postoperative period (CTRI/2021/10/037146)
The study is not without limitations. We agree that the original APS-POQ questionnaire was designed to be used after 24 h. We have used the same questionnaire after 72 h. We did not collect any feedback after 24 h, and hence, we cannot compare/comment on the difference in psychometric evaluation on the day of surgery versus that on postoperative day 3. No educational session was conducted before the interview; this was done with the aim to capture their existing practices. During the course of the interview, patients’ awareness and perceptions and their willingness to participate in NPMs were assessed. It is possible that the willingness to participate in NPMs expressed in this survey may be falsely high. We hope that our ongoing randomized trial may shed more light in this less-studied topic.
Other limitations of the study are that the survey was on during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. With more private rooms getting converted to COVID wards, we had changes in the bed availability during the study period. As a result, we had more admissions in the shared and general ward areas, with few patients getting admitted in the individual room occupancy. Also, the possibility of the pandemic affecting/limiting human to human interaction between fellow patients, their relatives, and caregivers cannot be ruled out. We, however, included a few questions on the belief and practice of NPM at home to understand patients’ acceptability and willingness to adopt NPMs in similar situations in the future.
Lastly, in this initial survey and among the few of its kind, the number of respondents using NPM itself was very less. Hence, we are unable to correlate the use of NPMs with surgical approaches like open versus minimally invasive or explain the patterns as to why females preferred to use NPMs more than males.
Conclusion
Nonpharmacological methods are less frequently practiced and still rarely used during pain in our hospital. Lack of motivation from caregivers and patients not being aware of the benefits of nonpharmacological methods appear to be the lead reasons. Education seems to have a positive impact on compliance, with more educated patients showing significant willingness to adopt NPMs in future.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Annexure 1
Case record forma
Prevalence of use of nonpharmacological methods of pain relief among patients following onco surgery – A prospective observational study
Trial no:
Age: sex: date of surgery:
Education: primary schooling/undergraduate/graduate/postgraduate
Type of surgery: surface surgeries/bone and soft tissue/laparotomies(open)/laparotomies (minimally invasive)/thoracotomies(open)/thoracotomies (minimally invasive)
Mode of analgesia post-op: epidural/Patient controlled analgesia (PCA)/regional techniques (catheters)/round-the-clock medications (inclusive of single-shot techniques)
Postoperative ward: general/sharing/individual
Ambulation advised: Y/N
Have you been visited by the acute pain service: Y/N
Have you been visited by physiotherapy: Y/N
Has active chest physiotherapy been advised: Y/N
American Pain Society-Patient Outcome Questionnaire (APS-POQ)
1. On this scale, please indicate the least pain you had in the first 72 h.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
no worst pain
2. On this scale, please indicate the worst pain you had in the first 72 h.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
no worst pain
3. How often were you in severe pain in the first 72 h? Please circle your estimate of percentage of time you experienced severe pain.
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 10%
never in severe pain always in severe pain
4. Circle the one number below that best describes how much pain interfered or prevented you from
A. doing activities in bed, such as turning, sitting up, repositioning
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
does not completely
interfere interferes
B. doing activities out of bed, such as walking, sitting in chair, standing at the sink
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
does not completely
interfere interferes
C. falling asleep
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
does not completely
interfere interferes
D. staying asleep
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
does not completely
interfere interferes
5. Pain can affect our mood and emotions. On this scale, please circle the one number that best shows how much pain caused you to feel
A. anxious
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at all extremely
B. depressed
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at all extremely
C. frightened
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at all extremely
D. helpless
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at all extremely
6. Have you had any of the following side effects? Please circle “0” if no; if yes, please circle one number that best shows the severity of each.
A. Nausea
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none severe
B. Drowsiness
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none severe
C. Itching
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none severe
D. Dizziness
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
none severe
7. In the first 72 h, how much pain relief did you receive? Please circle the one percentage that best shows how much pain relief you received from all of your pain treatments combined (medical and nonmedical treatments)
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 10%
no complete
relief relief
8. Were you allowed to participate in decisions about your pain treatment as much as you wanted to?
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at all very much
9. Circle the number that best shows how satisfied you are with the results of your pain treatment while in the hospital.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
extremely extremely
dissatisfied satisfied
10. Did you receive any information about your pain treatment options? ------No ----------Yes
If yes, please circle the number that best shows how helpful the information was.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
not at extremely
all helpful helpful
11. Did you use any nonmedical methods to relieve your pain? ----------No -----------Yes.
If yes, check all that apply.
Cold pack Meditation
Deep breathing Listening to music
Distraction such as watching TV, reading Prayer
Heat Relaxation
Imagery/visualization Walking
Massage Other (please describe) ---------------------------
If yes, how frequently? (mark separately for each individual method)
Rarely (one or two times in 72 h) sometimes (once a day) often (two or three times a day) always (once in every 2–3 h)
12. How often did a nurse or doctor encourage you to use nonmedical methods?
-------never ------------------sometimes ----------------others
13. 13. How often did you engage with any of the below-mentioned activities in the postoperative period (72 h) when not in pain? Check all that apply.
Cold pack Meditation
Deep breathing Listening to music
Distraction such as watching TV, reading Prayer
Heat Relaxation
Imagery/visualization Walking
Massage
Other (please describe) ---------------------------
Never, rarely (one or two times in 72 h), sometimes (once a day), often (two or three times a day), always (once in every 2–3 h)
14. Do you generally engage in the above-mentioned activities in your routine life?
Never, seldom (one or two times/year), sometimes (one or two times/month), often (one or two times/week), always (every day)
15. Do you practice nonpharmacological methods to relieve your pain at home?
Never, seldom (one or two times/year), sometimes (one or two times/month), often (one or two times/week), always (every day)
16. Do you believe nonpharmacological methods may help in pain relief?
Strongly disagree/disagree/neither agree nor disagree/agree/strongly agree
17. If you were told nonpharmacological methods could have a positive role in pain management, would you have participated more in these activities?
Not probable/somewhat improbable/neutral/somewhat probable/very probable
18. In continuation, would you now advise other patients to use nonpharmacological methods for pain relief?
Not probable/somewhat improbable/neutral/somewhat probable/very probable
19. Do you think a nurse or doctor should advise or discuss your pain management plan prior to surgery?
Very undesirable/undesirable/neutral/desirable/very desirable
20. Do you think a nurse or doctor should also advise or discuss the use of nonpharmacological methods of pain relief prior to surgery?
Very undesirable/undesirable/neutral/desirable/very desirable
a Includes questions from the revised APS-POQ. Additional questions specific to this survey appear in Italics
Funding Statement
Nil
References
- 1.Gan TJ. Poorly controlled postoperative pain: Prevalence, consequences, and prevention. J Pain Res. 2017;10:2287–98. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S144066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blondell RD, Azadfard M. Pharmacologic therapy for acute pain. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:766–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Garimella V, Cellini C. Postoperative pain control. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2013;26:191–6. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1351138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.El Geziry A, Toble Y, Al Kadhi F, Pervaiz M, Al Nobani M. Pain Management in Special Circumstances. IntechOpen; 2018. Non-Pharmacological Pain Management [Internet] Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.79689. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hargett JL, Criswell AC. Non-pharmacological interventions for acute pain management in patients with opioid abuse or opioid tolerance: A scoping review protocol. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019;17:1283–9. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gordon DB, Polomano RC, Pellino TA, Turk DC, McCracken LM, Sherwood G, et al. Revised American Pain Society Patient Outcome Questionnaire (APS-POQ-R) for quality improvement of pain management in hospitalized adults: Preliminary psychometric evaluation. J Pain. 2010;11:1172–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gatlin CG, Schulmeister L. When medication is not enough: Nonpharmacologic management of pain. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2007;11:699–704. doi: 10.1188/07.CJON.699-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Komann M, Weinmann C, Schwenkglenks M, Meissner W. Non-pharmacological methods and post-operative pain relief: An observational study. Anesth Pain Med. 2019;9:e84674. doi: 10.5812/aapm.84674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chuang CC, Lee CC, Wang LK, Lin BS, Wu WJ, Ho CH, et al. An innovative nonpharmacological intervention combined with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia increased patient global improvement in pain and satisfaction after major surgery. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:1033–42. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S131517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sfakianakis MZ, Karteraki M, Panayiota K, Christaki O, Sorrou E, Chatzikou V, et al. Effect of music therapy intervention in acute postoperative pain among obese patients. Int J Caring Sci. 2017;10:937. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Soliman H, Mohamed S. Effects of zikr meditation and jaw relaxation on postoperative pain, anxiety and physiologic response of patients undergoing abdominal surgery. J Biol Agriculture Healthc. 2013;3:23–38. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ramesh C, Pai VB, Patil N, Nayak BS, George A, George LS, et al. Effectiveness of massage therapy on post-operative outcomes among patients undergoing cardiac surgery: A systematic review. Int J Nurs Sci. 2015;2:304–12. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Beiranvand S, Noparast M, Eslamizade N, Saeedikia S. The effects of religion and spirituality on postoperative pain, hemodynamic functioning and anxiety after cesarean section. Acta Med Iran. 2014;52:909–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Özer N, Karaman ÖzlüZ, Arslan S, Günes N. Effect of music on postoperative pain and physiologic parameters of patients after open heart surgery. Pain Manag Nurs. 2013;14:20–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nilsson U, Rawal N. A comparison of intra-operative or postoperative exposure to music--a controlled trial of the effects on postoperative pain. Anaesthesia. 2003;58:699–703. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2003.03189_4.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yusuf A, Iswari MF, Sriyono S, Yunitasari E. The effect of combination of spiritual deep breathing exercise therapy on pain and anxiety in postoperative nonpatological orthopedic fracture patients. Eur Asian J Bio Sci. 2020;14:1625–31. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang HL, Keck JF. Foot and hand massage as an intervention for postoperative pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2004;5:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2004.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zaslansky R, Rothaug J, Chapman CR, Bäckström R, Brill S, Fletcher D, et al. PAIN OUT: The making of an international acute pain registry. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:490–502. doi: 10.1002/ejp.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mwanza E, Gwisai RD. Knowledge on nonpharmacological methods of pain management among nurses at Bindura Hospital, Zimbabwe. Pain Res Treat. 2019;2019:2703579. doi: 10.1155/2019/2703579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Andrews-Cooper IN, Kozachik SL. How patient education influences utilization of nonpharmacological modalities for persistent pain management: An integrative review. Pain Manag Nurs. 2020;21:157–64. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2019.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller TA. Health literacy and adherence to medical treatment in chronic and acute illness: A meta-analysis. Patient Educ Couns. 2016;9:1079–86. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2016.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


