Summary
Introduction
Lassa fever (LF), a public health problem of great importance endemic in West Africa, is an acute and sometimes fatal viral haemorrhagic disease which leads to mortality. The current study assessed the knowledge, attitude and practice of Lassa fever prevention among adults in Bali Local Government Area, Taraba State, Nigeria.
Methods
Descriptive study design and Cross sectional study design was used for this study. A simple and systematic random sampling technique was used to draw samples of 399 participants for the study. A structured questionnaire was used for data collection after being validated and its reliability tested. The data collected was analysed using frequencies, percentage the hypotheses were tested using Data analysis was done using SPSS version 21, frequency, mean standard deviation, and chi square were performed to ascertain the value of the variables the hypotheses were tested using chi-square statistics at ≤ 0.05 level of significance.
Results
Findings from the study revealed that 75% of the respondents had knowledge of the Lassa fever and the preventive practices. It was also shown that about 66.7% were aware of the varied preventive measures at their disposal. The study further shows that 56% had positive attitudes that could affect their practice of preventive measures of Lassa fever. The acceptability level according to this study was very high (89%) among the adults of Bali L.G.A in Taraba state.
Conclusions
The study therefore, recommends that there should be a call for educational intervention to improve the knowledge of Lassa fever among community members in Bali LGA this will help towards its preventive practices. This is based on the expectation that good knowledge of Lassa fever can reduce the rate and spread of the Infection.
Keywords: Knowledge, Practice, Attitude, Lassa fever prevention, Nigeria
Introduction
It have been documented that the earliest cases of Lassa fever were thought to have occurred between 1920 and 1950, in Nigeria, Sierra Leone and Central African Republic and perhaps in other West African countries [8]. However, the disease became recognized and named in 1960 after two missionary nurses died and a third suffered a grave apparently communicable febrile systemic illness while working in Nigeria. The index patient was working in a mission hospital in Lassa town, Borno State, North-Eastern Nigeria when she fell critically ill and was transferred to Evangel Hospital, Jos Plateau State (now Bingham University Teaching Hospital, Jos) where she subsequently died. The second nurse, who was a staff of Evangel Hospital, cared for the index patient on presentation and she later developed comparable symptoms like the index case culminating in her death days later.
Lassa fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic illness caused by Lassa virus, a member of the virus family “Arenaviridae”. The disease is endemic in various West African countries including Nigeria where Lassa fever virus infections rate per annum is estimated at 100,000 to 300,000 with approximately 5,000 deaths [17]. Outbreaks of the disease have been reported in various parts of Nigeria since it was first reported in 1969 with the worst outbreak recorded in 2012 where 623 cases including 70 deaths were reported from 19 out of 36 states, and case fatality rate put at 37.9% [31].
The interaction between man and his environment is a major aspect to be considered in understanding the epidemiology of diseases. The transmission of Lassa fever is closely related to environmental factors intricately woven around the vector, the rodent Mastomysnatalensis [42, 39]. Other environmental factors such as overcrowding, poor food and personal hygiene and poor housekeeping are implicated in the transmission of the Lassa virus (Public Health Agency of Canada, 2011) [43]. Exposed food items, consumption of uncooked, poorly cooked and inadequately reheated foods are also important risk considerations.
In 2012, there were 1,723 cases and 112 deaths in Nigeria. Last year, 12 people died out of 375 infected, according to the Nigeria Center for Disease Control. Nigeria had an outbreak of Lassa fever in the year 2012 with 1,723 cases, 112 deaths, 201 laboratory-confirmed cases, and a case fatality rate of 6.50 [11, 21]. Between January 1 and April 15, 2018, 1,849 suspected cases have been reported from 21 states (Abia, Adamawa,Anambra, Bauchi, Benue, Delta, Ebonyi, Edo, Ekiti, Federal Capital Territory, Gombe, Imo, Kaduna, Kogi, Lagos, Nasarawa, Ondo, Osun, Plateau, Rivers, and Taraba). Out of these, 413 patients were confirmed with Lassa fever, nine were classified as suspected, 1,422 tested negative, and the remaining five laboratory results were pending. Of the 413 confirmed and the nine probable Lassa fever cases, 114 deaths were reported (case fatality rate for confirmed cases is 25.4% and for confirmed and probable cases combined is 27%). As of April, 27 health care workers in seven states (Abia, Benue, Ebonyi, Edo, Kogi, Nasarawa, and Ondo) have been infected since January 1, 2018, eight of whom have died [21].
Taraba State is one of the three high burdened states with frequent occurrences of Lassa fever outbreaks [37]. Abakaliki Local Government Area (LGA) had the highest proportion of confirmed Lassa fever cases during the 2018 and 2019 outbreaks in the State [41]. Researches carried out in places around the country have revealed that knowledge of the disease is deficient among many and inadequate among quite a large population making it hard for people to prevent the incident of an outbreak [24-26, 30]. In response to the poor knowledge of the public, the federal government put up various measures to prevent further spread of the diseases and treatment when it occurs. Such measures are the enhancement of disease surveillance, social health education through mass media, increased the number of diagnostic centers from 6 to 12, and also inaugurated a 15-member multisectoral Lassa fever Eradication Committee charged with fashioning and implementing the multifaceted response strategies against the outbreak [33, 40].
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
Lassa fever being a highly contagious disease endemic in West Africa, including Nigeria and Taraba state [25, 38] needs a robust public measures including early detection, effective treatment and widespread education on prevention to control its spread and mitigate its impact. The overall regional and global risks are through its primary mode of transmission through contact with food or household items contaminated with rat excreta. Due to drying of food items along high ways and outside houses over the night, constant burning of bushes, poor hygiene practices, and overcrowding in homes which causes logging of baggages and properties these give rise to these rats gaining entrance into the houses, all these factors put together may facilitate the increase in rodent man contact or contamination of food source by infected mastomys rat, it is against this background that the researcher have designed this study todetermine knowledge, attitude, practice of Lassa fever prevention among adult of Bali LGA.
Materials and Methods
POPULATION OF THE STUDY
It comprised of all adult in Bali L.G.A where the sample for the study was drawned. The current estimated number of adults 18 yrs and above 176,634 was derived by the researcher accordingto Bali Local government Commission.
STUDY AREA
Taraba state was carved out from the then defunct Gongola state (now Adamawa state) on the 27th August 1991, by the then Military Administration of General Ibrahim Babangida. The state derived its name from one of the three major rivers in the state and it has a land area of 59400 square kilometers with the headquarter situated in Jalingo. The state is made up of 16 local government areas namely, Ardo Kola, Bali, Jalingo, Zing, Yorro, Lau, Karim Lamido, Wukari, Ibi, Gassol, Gashaka, Sardauna, Kurmi, Donga, Takum, Ussa L.G.A. Bali L.G.A being the main study area for this study is situated in the north central part of the state with headquarter in Bali town about 50 km from Jalingo as shown in Figure 1. It was created in 1976 with population estimated to be 208,935 people at the 2006 census and comprising of Fulani, Mumuye, Jukun, Chamba and other ethnic groups. Bali has a latitude of 8.1554˚ North and longitude 10.9685˚ East. Christianity and Islam are the major religions practiced in Bali L.G.A.
Fig. 1.
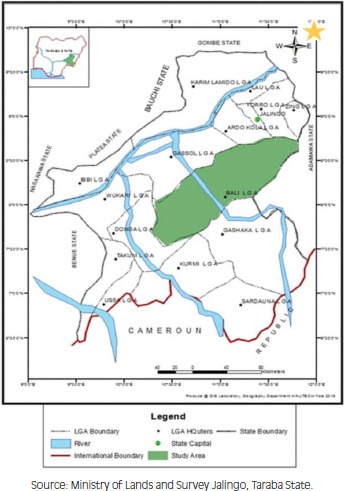
Map of Taraba state showing Bali LGA.
SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATION
Sample size was derived using Taro Yamane’ formula for finite population.
Using Taro Yamane’ formula for finite population.
The Yamane sample size states that:
| n = N/ (1+N (e) 2) |
Where: n signifies sample size
N signifies the population size under study (176,634)
e signifies the margin error (it could be 0.10, 0.05 or 0.01)
| n =176,634/ (1+176,634 (0.05) 2) n = 176,634/ (1+34,486(0.0025) n =176,634/ (1+441.59) n =176,634/ 441.59 n = 399 |
SAMPLING TECHNIQUE
Multi-stage sampling method was used for this study.
IN STAGE ONE: SELECTION BY CLUSTER
The communities in Bali L.G.A was clustered along existing twenty traditional communities which includes Bali A, Bali B, Mai hula, Sabin dale, Gazabu, Jatau, Sansani, Mayokam, Bakundi, Pangri, Sarkindawa, Ardo tinba, Badokoshi, Aka, Daniya, Dakka, Garba chede, Maigoge, Bayire, Sabon gida.
IN STAGE TWO: SELECTION OF COMMUNITIES PROPORTIONATELY
Simple random sampling technique by (balloting without replacement) was used to select both rural and semi-urban communities. Six rural communities were selected which were, Gazabu, Jatau, Sansani, Mayokam, Dakka, Sabon gida and four semi-urban communities were selected which included Bali A, Bayire, Pangri, Bali B. The proportional sample size for each of the selected communities were obtained.
STAGE FOUR: SELECTION OF HOUSE-HOLD
This stage involved the selection of the households by systematic random sampling technique. The determined sampling interval for each of the selected communities was employed where 5 was the interval for each selection. The researcher located the centre of each selected communities, divided it into four sections, randomly selected one sector, located the centre of that sector and spun a pen to determine the direction to begin the sampling. The first respondent (head of house hold) sampled was selected by simple random sampling by balloting without replacement. Sampling intervals were obtained for the various communities and it was maintained until the desired number of households was gotten. This was done for three weeks until the desired sample size of 399 respondents was achieved. Written informed consents were obtained from the participants.
VALIDITY OF INSTRUMENTS
The Instrument for data collection was a self-structured questionnaire which was drafted under supervision then went for validation by three experts in the field of Public health, two from Imo state and one from Taraba state. Correction made was used to finalize the instrument for content relevance and appropriateness of language.
RELIABILITY OF THE INSTRUMENT
The questionnaire was administered to 20 respondents with similar characteristics to those in the target population. The reliability of the instrument was tested using Chrombach Alpha Coefficient of Reliability test, and a coefficient of (r = 0.84) was deemed reliable.
DATA COLLECTION
A pretested self-structured survey questionnaire was used for data collection, containing closed-ended questions with 4 sections. Section A is the demographic variables of the respondent which is age, gender, marital status, level of education, occupation and religion. Section B contains 10 questions to ascertain their level of knowledge of Lassa fever. Section C contains questions on attitude towards Lassa fever with 10. Section D are the Lassa fever prevention practices which contains 24 questions after being validated and its reliability tested. The questionnaire had a total of 50 closed ended questions on a study on knowledge, attitude and practice of Lassa fever prevention among adults in Bali Local Government Area Taraba State.
DATA ANALYSIS
Data analysis was performed in IBM-SPSS Statistics version 23. Initial analysis involved construction of frequency distribution and manipulations. The average number of responses was used to compute the overall knowledge and preventive practices in each case and such scores were used to establish a cut-off point scoring 1 per point for each correct answer which were 10 questions, where 7 to 10 is graded as high knowledge, 4-6 as moderate knowledge and below 4 as poor knowledge as well as for the occurrence of preventive practices. The correct answers are indicated on table 4.2 with *. Chi square test (χ2) was used to test for significant association between the factors and the knowledge or preventive practices. Fisher exact test was conducted at 2 by 2 table where chi-square test assumptions were hard to meet. Statistical tests were performed at 5% level of significant and probability value (p ≤ 0.05) was used to interpret significance.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Ethical approval to undertake the study was obtained from Research and Ethics Committee of Taraba State Ministry of Health Jalingo, Nigeria. The participants were briefed on the objectives of the study, and their oral and written consent was also obtained before proceeding with the research. It is a descriptive cross-sectional survey, which is a type of design where the researcher does not alter the exposure status but measures the outcome and the exposure(s) in the population under observation. This design was successfully used in related studies of [26, 31].
Results
Table I, shows the demographic status of respondents in Bali LGA, a total of 399 participants were involved in the study but 385 recorded, majority of the participants were within ages 38-47 years 83 (21.6%) and 196 (50.9%) of the respondents are female, Majority of the respondents are married, 231 (60%). In terms of educational attainment, Majority attended secondary education 154 (40%). The participants cut across all religio us faith, 126 (32.7%) are of the Islamic faith, while majority were of the Christian faith with farming as their major occupation.
Tab. I.
Distribution of respondent by socio-economic characteristics of adults in Bali LGA.
| Variables | Frequency (F) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| 18–27 | 69 | 17.9 |
| 28–37 | 61 | 15.8 |
| 38–47 | 83 | 21.6 |
| 48–57 | 66 | 17.1 |
| 58-67 | 41 | 10.6 |
| 68-77 | 17 | 4.4 |
| 78 and above | 48 | 12.5 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 196 | 50.9 |
| Male | 189 | 49.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Marital Status | ||
| Divorced | 15 | 3.9 |
| Married | 231 | 60.0 |
| Separated | 32 | 8.3 |
| Single | 81 | 21.0 |
| Widowed | 26 | 6.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Educational level | ||
| No formal education | 79 | 20.5 |
| Primary | 83 | 21.6 |
| Secondary | 154 | 40.0 |
| Tertiary | 69 | 17.9 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Occupation | ||
| Applicant | 19 | 5.0 |
| Business/Trading | 75 | 19.5 |
| Farming | 126 | 32.7 |
| Public/CivilService | 99 | 25.7 |
| Student | 66 | 17.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Religion | ||
| Christianity | 177 | 46.0 |
| Islam | 126 | 32.7 |
| Traditional worshiper | 82 | 21.3 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
Table II Present the knowledge of the respondents on Lassa fever prevention. Their knowledge were poor 48.3% as indicated that more than half of the respondents don’t know that Lassa fever is a severe disease caused by germ virus, 105 (27.3%) believed that Lassa fever is gotten from eating too much oil. The respondents that are aware that the incubation period of Lassa fever ranges from 1-7 days although are very few, although 175 (45.5%) stated that one can be infected with Lassa fever due to handling food and household items contaminated with rat’s faeces and urine. Few were of the opinion that the Lassa fever can be spread through sitting close to an infected person. About 107 (27.8%) affirmed that the disease can cause bleeding and death if not immediately handled. According to 230 (85.8%) of respondents, Lassa fever can be avoided by eliminating rat from the environment, proper environmental hygiene, and protecting food from being contaminated.
Tab. II.
Distribution of respondents by knowledge of Lassa fever prevention.
| Variables | Frequency (F) | Percent (%) | Correct answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| What is Lassa fever | |||
| A severe illness caused by germ | 126 | 32.7 | * |
| Another form of malaria | 99 | 25.7 | |
| Disease caused by eating too Much oil | 105 | 27.3 | |
| Fever caused by evil spirit | 55 | 14.3 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| Lassa fever vector | |||
| Monkey | 53 | 13.8 | |
| Mosquito | 97 | 25.2 | |
| None of the above | 28 | 7.3 | |
| Rat | 207 | 53.8 | * |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| How can Lassa fever be contacted | |||
| Eating over-cooked cow meat | 85 | 22.1 | |
| Items contaminated with rat’s faeces and urine | 175 | 45.5 | * |
| None of the above | 48 | 12.5 | |
| Prolonged mosquito bites | 77 | 20.0 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| Early Signs and symptoms of Lassa fever except | |||
| Cough | 73 | 19.0 | |
| Fever | 157 | 40.8 | |
| Headache | 58 | 15.1 | |
| Vomiting | 97 | 25.2 | * |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| Lassa fever can be prevented through except? | |||
| Eliminating mosquitoes | 55 | 14.3 | * |
| Eliminating rat in the environment | 150 | 39.0 | |
| Proper environmental sanitation | 92 | 23.9 | |
| Protecting food from being contaminated | 88 | 22.9 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| Community ways of controlling Lassa fever | |||
| All of the above | 39 | 10.1 | * |
| Good environmental hygiene | 140 | 36.4 | |
| Keeping cats at home | 85 | 22.1 | |
| Storing grains and food stuffs in rodent-proof containers | 121 | 31.4 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| How can Lassa fever spread | |||
| Contact with the body fluid of infected person | 117 | 30.4 | * |
| Shaking hand | 75 | 19.5 | |
| Sitting close to infected person | 137 | 35.6 | |
| Taking the infected person to hospital | 56 | 14.5 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| What to do one Lassa fever is suspected | |||
| Seek health care immediately | 180 | 46.8 | * |
| Try self-medication first | 90 | 23.4 | |
| Visit a spiritualist | 51 | 13.2 | |
| Watch the situation for sometimes | 64 | 16.6 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| Lassa fever can cause | |||
| All of the above | 68 | 17.7 | * |
| Bleeding | 107 | 27.8 | |
| Death | 137 | 35.6 | |
| Facial swelling | 73 | 19.0 | |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
| How long it takes signs and symptoms to manifest | |||
| 1-7 days | 94 | 24.4 | |
| 21-28 days | 104 | 27.0 | |
| 30-60 days | 66 | 17.1 | |
| 7-21 days | 121 | 31.4 | * |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 | |
Table III shows distribution of respondents by correct knowledge of Lassa Fever Prevention responses Overall knowledge in each case and scores were used to establish a cut-off point scoring 1 per point for each question which were 10 questions, where 7 to 10 is graded as high knowledge 4-6 as moderate knowledge and below 4 as poor knowledge. The classification of knowledge based on High, moderate and poor in percentage is shown in Figure 2 which was determined by scoring the highest score to the correct response and a lower number to a wrong answer. The general average of the total score was calculated to determine the cut-off score (3.24). The average scores of individual scores was also determined.
Tab. III.
Distribution of Respondents by correct knowledge of Lassa Fever Prevention responses.
| Variables | Correct | InCorrect | Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | % | F | % | F | % | |
| What is Lassa fever? | 126 | 32.7 | 259 | 67.3 | -133 | -34.6 |
| Lassa fever vector? | 207 | 53.8 | 178 | 46.2 | 29 | 7.6 |
| How can Lassa fever be contacted? | 175 | 45.5 | 210 | 54.5 | -35 | -9.0 |
| Signs and symptoms of Lassa fever? | 157 | 40.8 | 228 | 59.2 | -71 | -18.4 |
| Lassa fever can be prevented through? | 331 | 86.0 | 54 | 14.0 | 277 | 71.9 |
| Community ways of controlling Lassa fever? | 261 | 67.8 | 124 | 32.2 | 137 | 35.6 |
| How can Lassa fever spread? | 117 | 30.4 | 268 | 69.6 | -151 | -39.2 |
| What to do when Lassa fever is suspected? | 180 | 46.8 | 205 | 53.2 | -25 | -6.4 |
| Lassa fever can cause? | 244 | 63.4 | 141 | 36.6 | 103 | 26.8 |
| How long it takes signs and symptoms to manifest? | 121 | 31.4 | 264 | 68.6 | -143 | -37.2 |
Fig. 2.
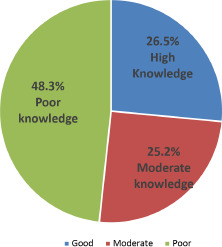
Level of knowledge of respondents about Lassa fever.
Table IV, showed that more than half of the respondents strongly agreed and agreed that anyone can be infected with Lassa fever, 29.6% and 33.5% strongly agreed and agreed respectively that Lassa fever is not a spiritual attack. Very few respondents were of the opinion strongly that environmental sanitation can limit rats in the environment, 36.9% of the respondents believed that Lassa fever can best be treated randomly and argued that it can be best treated by the native doctors. Negative and positive attitude was determined by scoring the highest score to the most positive attitude response and a lowest score to the most negative attitude, the general average of the total score was calculated to determine the cut-off score (2.8). The average scores of individual scores was also determined. Figure 3 showed the respondents’ percentage level of attitude towards Lassa fever (Score > 2.8 = negative attitude; score ≥ 2.8 = positive attitude).
Tab. IV.
Distribution of Respondent based on attitude towards Lassa Fever Prevention.
| Variables | Frequency (N) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Anybody no matter the socio-economic status can be Infected with Lassa fever | ||
| Strongly Agree | 127 | 33.0 |
| Agree | 127 | 33.0 |
| Strongly disagree | 30 | 7.8 |
| Disagree | 101 | 26.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Lassa fever is not as a result of spiritual attack | ||
| Strongly Agree | 114 | 29.6 |
| Agree | 129 | 33.5 |
| Strongly disagree | 45 | 11.7 |
| Disagree | 97 | 25.3 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Environmental sanitation limits the presence of rats in the Environment | ||
| Strongly Agree | 114 | 29.6 |
| Agree | 136 | 35.3 |
| Strongly disagree | 27 | 7.0 |
| Disagree | 108 | 28.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Absence of rat in the house is a preventive measure for Lassa fever | ||
| Strongly Agree | 114 | 29.6 |
| Agree | 129 | 33.5 |
| Strongly disagree | 45 | 11.7 |
| Disagree | 97 | 25.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Body fluid of anyone who is suffering from Lassa fever should be avoided | ||
| Strongly Agree | 116 | 30.1 |
| Agree | 132 | 34.3 |
| Strongly disagree | 30 | 7.8 |
| Disagree | 107 | 27.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Treatment of Lassa fever should be prompt to reduce the risk of death | ||
| Strongly Agree | 102 | 26.5 |
| Agree | 144 | 37.4 |
| Strongly disagree | 35 | 9.1 |
| Disagree | 104 | 27.0 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Lassa fever is not a death sentence | ||
| Strongly Agree | 113 | 29.4 |
| Agree | 130 | 33.8 |
| Strongly disagree | 45 | 11.7 |
| Disagree | 97 | 25.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Lassa fever should be managed in the health facility by trained health personnel | ||
| Strongly Agree | 114 | 29.6 |
| Agree | 129 | 33.5 |
| Strongly disagree | 45 | 11.7 |
| Disagree | 97 | 25.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Those who have Lassa fever should not be stigmatized | ||
| Strongly Agree | 103 | 26.8 |
| Agree | 144 | 37.4 |
| Strongly disagree | 42 | 10.9 |
| Disagree | 96 | 24.9 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Lassa fever is a very serious illness | ||
| Strongly Agree | 114 | 29.6 |
| Agree | 129 | 33.5 |
| Strongly disagree | 45 | 11.7 |
| Disagree | 97 | 25.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
Fig. 3.
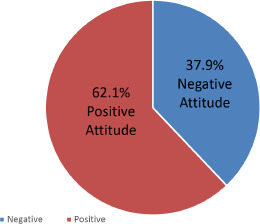
Attitude Level of respondents about Lassa Fever.
Table V reveled 32.7% of the respondents are of the opinion that Lassa fever can be prevented by good food protection policy, 36.6% believed that fruits are to be washed thoroughly with water before eating, and half of the respondent said the best way to safe guard your food items from Lassa fever is by eradicating rat and by regular environmental sanitation practice.
Tab. V.
Distribution of respondents by their practice.
| Variables | Frequency (N) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Safeguards your food items in the house | ||
| Always | 124 | 32.2 |
| Never | 131 | 34.0 |
| Sometimes | 130 | 33.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| How can you safe guard your food items from rats | ||
| Covering food items properly | 126 | 32.7 |
| Nothing | 37 | 9.6 |
| Rat poison | 76 | 19.7 |
| Using rat gum | 103 | 26.8 |
| Using rat trap | 43 | 11.2 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| How often do you carry out environmental sanitation | ||
| Once a month | 57 | 14.8 |
| Once in a week | 103 | 26.8 |
| Once in three week | 103 | 26.8 |
| Once in two week | 122 | 31.7 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| How do you store your household refuse | ||
| Covered container | 225 | 58.4 |
| Open container | 57 | 14.8 |
| Standard refuse bin | 103 | 26.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes fruits thoroughly with water before eating | ||
| Always | 141 | 36.6 |
| Never | 51 | 13.2 |
| Sometimes | 193 | 50.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Why do you wash fruits thoroughly before eating | ||
| 51 | 13.2 | |
| I do not wash fruits before eating | 82 | 21.3 |
| No reason | 60 | 15.6 |
| To kill germs that can cause disease | 94 | 24.4 |
| To make it look appetizing | 98 | 25.5 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| If you do not wash fruits thoroughly before eating,why | ||
| 334 | 86.8 | |
| I wash fruits thoroughly before eating | 12 | 3.1 |
| It is not necessary to wash fruits before eating | 16 | 4.2 |
| No reason | 9 | 2.3 |
| Water is not available for washing | 14 | 3.6 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Do you cook your food very well before eating | ||
| Never | 20 | 5.2 |
| Always | 65 | 16.9 |
| Sometimes | 300 | 77.9 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Why do you cook your food very well before eating | ||
| I do not cook my food very well before eating | 88 | 22.9 |
| No reason | 64 | 16.6 |
| To kill germs that can cause disease | 109 | 28.3 |
| To make the food delicious | 104 | 27.0 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Why don’t you cook your food very well before eating | ||
| I cook my food very well before eating | 370 | 96.1 |
| I enjoy food that is not cooked to tender | 7 | 1.8 |
| No reason | 4 | 1.0 |
| To save cooking fuel | 4 | 1.0 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes your hands with soap and water or ash and water after visiting the toilet | ||
| Always | 164 | 42.6 |
| Never | 21 | 5.5 |
| Sometimes | 200 | 51.9 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes your hands with soap and water or ash and water before eating food | ||
| Always | 127 | 33.0 |
| Never | 38 | 9.9 |
| Sometimes | 220 | 57.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes your hands with soap and water or ash and water when you return home | ||
| Always | 127 | 33.0 |
| Never | 38 | 9.9 |
| Sometimes | 220 | 57.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes your hands with soap and water or ash and water after attending to a sick person | ||
| Always | 118 | 30.6 |
| Never | 38 | 9.9 |
| Sometimes | 229 | 59.5 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Washes your hands with soap and water or ash and water after handling dirt/garbage | ||
| Always | 107 | 27.8 |
| Never | 38 | 9.9 |
| Sometimes | 240 | 62.3 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| How long does your single session of hand washing last | ||
| 20 | 5.2 | |
| 10-120 seconds and above seconds | 78 | 20.3 |
| 15-19 seconds | 6 | 1.6 |
| 20 seconds and above | 109 | 28.3 |
| 5-9 seconds | 82 | 21.3 |
| Less than 5 seconds | 90 | 23.4 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| What do you use in drying your hands after washing | ||
| Dryer | 24 | 6.2 |
| Hand towel | 95 | 24.7 |
| Handkerchief | 100 | 26.0 |
| Old clothes | 79 | 20.5 |
| Paper napkin | 87 | 22.6 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Do you hunt for rats or other rodents? | ||
| Always | 31 | 8.1 |
| Never | 281 | 73.0 |
| Sometimes | 73 | 19.0 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Do you eat raw meat or other rodents? | ||
| Never | 306 | 79.5 |
| Sometimes | 79 | 20.5 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| If you eat rat meat or other rodents, how do you prepare it for eating? | ||
| 306 | 79.5 | |
| Boiling | 21 | 5.5 |
| Roasting | 58 | 15.1 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Assists friends or family members who are ill in their activities of daily living? | ||
| Always | 141 | 36.6 |
| Never | 37 | 9.6 |
| Sometimes | 207 | 53.8 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Have assisted in caring for friends or family members who have Lassa fever? | ||
| No | 385 | 100.0 |
| Will you assist in caring for a friend or a family member whom you are aware has lassa fever | ||
| No | 75 | 19.5 |
| Yes | 310 | 80.5 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
| Do you seek health care from the health facility promptly | ||
| Always | 83 | 21.6 |
| Never | 7 | 1.8 |
| Sometimes | 295 | 76.6 |
| Total | 385 | 100.0 |
Table V also shows that very few respondents cook their food very well before eating on a daily basis. With 28.3% believing that it kills germs when food are prepared very well before eating. 4.2% washes their hands always with soap and water after visiting the toilet, 33.0% washes their hands before eating while very few don’t as shown in Table V. Not many take 20 seconds and above for a single session of hand washing as well as using handkerchief to dry off their hands after washing. A good number of respondents do not hunt for rat or other rodents and do not also eat raw meat or even rodent. Half of the respondents sometimes assist friends and family members who are ill in their activities of daily living as all respondent have never assisted friends or family members who have Lassa fever. Not many always seek health care from the health facility promptly. Good and poor practice was determined by scoring the highest score to the most good practice response and a lowest score to the most poor practice, the general average of the total score was calculated to determine the cut-off score (2.5). The average scores of individual scores was also determined. Figure 4 shows the percentage level of Lassa fever preventive practices by the respondent (Score > 2.5 = negative practice; score ≥ 2.5 = positive practice).
Fig. 4.
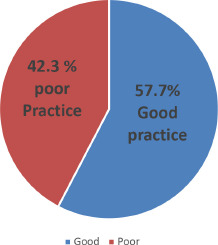
Level of Practice of respondents of Lassa fever prevention..
Table VI Shows a cross tabulation of the socio-demographic characteristics of respondents and their knowledge about Lassa fever, results shows a significant relationship between age, gender, marital status, educational status, occupation and religion of respondents and their knowledge about Lassa fever (p-value = < 0.001, 0.042, < 0.001, 0.031, 0.039 and < 0.001 respectively).
Tab. VI.
Association between socio-demographic characteristics and knowledge.
| Variables | Knowledge | Total | X2 | p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good | Moderate | Poor | |||||
| Age | 18–27 | 17(24.6) | 14(20.3) | 38(55.1) | 69 | 445.668 | < 0.001 |
| 28–37 | 15(24.6) | 14(23.0) | 32(52.5) | 61 | |||
| 38–47 | 22(26.8) | 23(28.0) | 37(45.1) | 82 | |||
| 48–57 | 11(16.7) | 15(22.7) | 40(60.6) | 66 | |||
| 58-67 | 21(36.8) | 21(36.8) | 15(26.3) | 57 | |||
| 68-77 | 0(0.0) | 1(100.0) | 0(0.0) | 1 | |||
| 78 and above | 16(32.7) | 9(18.4) | 24(49.0) | 49 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Gender | Female | 52(26.5) | 41(20.9) | 103(52.6) | 196 | 625.793 | 0.042 |
| Male | 50(26.5) | 56(29.6) | 83(43.9) | 189 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Marital Status | Divorced | 3(21.4) | 4(28.6) | 7(50.0) | 14 | 427.683 | < 0.001 |
| Married | 67(28.9) | 55(23.7) | 110(47.4) | 232 | |||
| Separated | 9(28.1) | 5(15.6) | 18(56.3) | 32 | |||
| Single | 16(19.8) | 24(29.6) | 41(50.0) | 81 | |||
| Widowed | 7(26.9) | 9(34.6) | 10(38.5) | 26 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Educational Status | No formal education | 20(25.3) | 19(24.1) | 40(50.6) | 79 | 523.816 | 0.031 |
| Primary | 26(31.3) | 18(21.7) | 39(47.0) | 83 | |||
| Secondary | 37(24.0) | 40(26.0) | 77(50.0) | 154 | |||
| Tertiary | 19(27.5) | 20(29.0) | 30(43.5) | 69 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Occupation | Applicant | 4(21.1) | 3(15.8) | 12(63.2) | 19 | 550.973 | 0.039 |
| Business/Trading | 15(19.7) | 21(27.6) | 40(52.6) | 76 | |||
| Farming | 29(23.2) | 39(31.2) | 57(45.6) | 125 | |||
| Public/CivilService | 44(44.4) | 17(17.2) | 38(38.4) | 99 | |||
| Student | 10(15.2) | 17(25.8) | 39(59.1) | 66 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Religion | Christianity | 45(25.4) | 43(24.3) | 89(50.3) | 177 | 421.790 | < 0.001 |
| Islam | 40(28.4) | 36(25.5) | 65(46.1) | 141 | |||
| Traditional worshiper | 17(25.4) | 18(26.9) | 32(47.8) | 67 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
Table VII shows the association between the socio demographic characteristics of respondents and their attitude toward Lassa fever disease, results shows a significant relationship between the respondents attitude, educational status and occupation of the respondents (p-value = < 0.001, < 0.001 and 0.049 respectively). No significant relationship was established between attitude and respondents gender, marital status and religion (p-value = 0.201, 0.131 and 0.501 respectively).
Tab. VII.
Association between socio-demographic characteristics and attitude.
| Variable | Attitude | Total | X2 | p-values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | |||||
| Age | 18–27 | 29 (42.0) | 40 (58.0) | 69 | 551.618 | < 0.001 |
| 28–37 | 41 (67.2) | 20 (32.8) | 61 | |||
| 38–47 | 19 (23.2) | 63 (76.8) | 82 | |||
| 48–57 | 50 (75.8) | 16 (24.2) | 66 | |||
| 58-67 | 5 (8.8) | 52 (91.2) | 57 | |||
| 68-77 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 | |||
| 78 and above | 1 (2.0) | 48 (98.0) | 49 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
| Gender | Female | 102 (52.0) | 94 (48.0) | 196 | 4579.69 | 0.201 |
| Male | 44 (23.3) | 145 (76.7) | 189 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
| Marital Status | Divorced | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | 14 | 9306.36 | 0.131 |
| Married | 91 (39.2) | 141 (60.8) | 232 | |||
| Separated | 17 (53.1) | 15 (46.9) | 32 | |||
| Single | 30 (37.0) | 51 (63.0) | 81 | |||
| Widowed | 5 (19.2) | 21 (80.8) | 26 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
| Educational Status | No formal education | 41 (51.9) | 38 (48.1) | 79 | 465.233 | < 0.001 |
| Primary | 25 (30.1) | 58 (69.9) | 83 | |||
| Secondary | 74 (48.1) | 80 (51.9) | 154 | |||
| Tertiary | 6 (8.7) | 63 (91.3) | 69 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
| Occupation | Applicant | 19 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 19 | 463.892a | 0.049 |
| Business/Trading | 22 (28.9) | 54 (71.1) | 76 | |||
| Farming | 36 (28.8) | 89 (71.2) | 125 | |||
| Public/Civil Service | 42 (42.4) | 57 (57.6) | 99 | |||
| Student | 27 (40.9) | 39 (59.1) | 66 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
| Religion | Christianity | 82 (46.3) | 95 (53.7) | 177 | 43201.9a | 0.501 |
| Islam | 45 (31.9) | 96 (68.1) | 141 | |||
| Traditional worshiper | 19 (28.4) | 48 (71.6) | 67 | |||
| Total | 146 | 239 | 385 | |||
Table VIII shows a cross tabulation between knowledge and attitude and knowledge and practice of respondents about Lassa fever. Association was established between knowledge and attitude (p = 0.023) and knowledge and practice (p = 0.033).
Tab. VIII.
Association of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Lassa Fever Prevention.
| Variable | Knowledge | Total | X2 | p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good | Moderate | Poor | |||||
| Attitude | Negative | 21 (14.4) | 43 (29.5) | 82 (56.2) | 146 | 6342.62 | 0.023 |
| Positive | 81 (33.9) | 54 (22.6) | 104 (43.5) | 239 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
| Practice | Good | 59 (26.6) | 54 (24.3) | 109 (49.1) | 222 | 8646.21 | 0.033 |
| Poor | 43 (26.4) | 43 (26.4) | 77 (47.2) | 163 | |||
| Total | 102 | 97 | 186 | 385 | |||
HYPOTHESES TESTING
In this study, two null Hypotheses were tested to determine which of the predictor variables produced greater influence on the outcome variable of knowledge and attitudes in the prevention of Lassa fever disease. Chi-square analysis was used in conducting this test at 0.05 level of significance. Decision rule applied was that if p ≤ 0.05, then the Null Hypotheses will be rejected in favor of alternative hypotheses and if p ≥ 0.05, then the Null Hypotheses will be accepted and the alternative rejected.
Ho: 1.
There is no significant relationship between knowledge and attitude of Lassa fever prevention among adults of Bali L.G.A in Taraba state
HA: 1.
As suggested by our results (see Table VIII) a significant relationship between knowledge and attitude of Lassa fever prevention among adults of Bali L.G.A in Taraba state was identified (p = 0.033)
Ho: 2.
There is no significant relationship between knowledge and practice of Lassa fever prevention among adults of Bali L.G.A in Taraba state.
HA: 2.
Results from this study shown above, a p-value of 0.023 less than statistically significant differences at 0.05 level of significance. The null hypothesis is therefore rejected and the alternate hypothesis accepted.
Therefore, we conclude by saying there is a significant relationship between attitudes and the prevention/control of Lassa fever infection among adults of Bali L.G.A in Taraba state.
Discussion
SUMMARY OF MAIN RESULTS
Various knowledge variables were used to test their knowledge of the subject matter. Such variables definition of Lassa fever causes of Lassa fever, transmission of Lassa fever, vectors of Lassa fever, incubation and signs/symptoms of Lassa fever. 48.3% of the respondents had a poor knowledge; few of them (26.5%) still had good knowledge of the subject under consideration. These findings are definitely not in line with a study carried out in Nigeria to determine the outbreak of Lassa fever disease [27, 36]. They observed from their study that most of the respondents had high knowledge about the Lassa fever infection especially urban settlers which has been able to help them to adopt some preventive measures against frequent outbreaks. Also NCDC, [38] noted get the fact, get the factual and correct information on Lassa fever from social media, radio, television and newspaper; be knowledgeable about how to response to outbreak. This helps minimize fear and will curtail the spread of the infection.
Various attitudes were identified from this study which may have effects on either the outbreak or the spread of Lassa fever disease in a given community. 62.1% of the respondents believed that they are at risk of developing the disease Lassa fever irrespective of their status, race, sex and religious background. This agrees with the findings of [4] in a study titled knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding Lassa fever disease among adults in endemic and non-endemic countries of Liberia. They find out that majority of the respondents in their study believed they are at risk of getting LF; with 52% (231/442) in the non-endemic counties. Also 63.1% of the respondents believed that the disease is not as a result of spiritual attack and that environmental sanitation can greatly limit the occurrence of the disease [4]. However with the poor knowledge of Lassa fever observed among the studied group the overall preventive practices seems to be high 57.7%. Lassa fever preventive practices were also found to be low (45.2%) Findings of this study are in conformity with 51% poor practice toward Lassa fever in a descriptive survey research design done by Abdulkadir and Mohammed in North-Eastern part of Nigeria [22], but the result of the findings are in consistent with66.4% good preventive practices in a descriptive cross-sectional study design by Ossai et al.(2020) [23]. The differences in these results could be as a result of different available information about Lassa fever in the areas, and also the location of the study area towards exposure of information about Lassa fever. The study observed that high-risk behaviours and attitudes emanating from societal beliefs among community and households’ members have been long associated with the transmission of infectious diseases.
GENERALIZABILITY
Given the specific characteristics of the study population in Bali Local Government Area, the generalizability of the results may be restricted to similar communities in Taraba State due to comparable socio-economic characteristics. However, to assess the applicability of these findings more broadly, further research involving diverse population is recommended.
LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
On carrying this study, the researcher had limited scope, limited generalizability with different cultural norms and demographics,some of the respondent were reluctant and needed close guide in answering the questionnaire; it took the researcher extra time and effort to stay with respondents to ensure proper filling of the questionnaire.
IMPLICATION
The study is believed to have made impact towards informing health policies and strategies at state and national level to improve better surveillance system, community development which can lead to increased awareness towards better preventive practices, the findings of the research can also be used to develop training programs for health care providers in the state towards response to Lassa fever outbreak. It can be used for intervention that address and modify risk behaviors.
Conclusions
Lassa fever virus outbreak, a poverty-related infectious diseases outbreak remains a public health threat and burden on vulnerable populations in West Africa and Nigeria in particular. Robust and sustainable leadership commitment and investment of all stakeholders and affected communities in Lassa fever outbreaks prevention and containment is crucial and requires strengthening integrated Lassa fever outbreak surveillance quality data gathering to support evidence data sharing, contextual local and regional outbreak early warning alert, preparedness and response systems. Collaborative ‘One Health’ approach operational research is needed in understanding spatio-geographical risk factors patterns, reservoir(s) mapping and phylogenetic in guiding evidence-based, appropriately tailored, timely integrated programs, strategic interventions and implementation against the zoonotic disease epidemics and pandemics threats in Nigeria. Moreover, fostering local community to regional re-merging and emerging epidemics and pandemics data sharing, coordinated invasive pathogens epidemiology surveillance and early warning indicators metrics capacity building, monitoring and evaluation is crucial for timely and quality risk communication and operational research.
SUGGESTION FOR FURTHER STUDIES
Similar studies could be carried out in other LGA.A more elaborate research on environmental health education programmes should be undertaken to cover a wider geographical area of Taraba State.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the following persons for their unalloyed supports (ideas, questionnaire distribution interview arrangements) towards making this research successful. Dr. UM Chukwuocha, Joel K. Yakubu Dagah Bakari, CommrGoerge Dan Azumi Rafinkada, Takum, Justina Christopher, Fuhalah (Favour) Christopher, Pigweh Christopher, and Emmanuel Christopher. We equally appreciate Research and Ethics Committee of Taraba State Ministry of Health Jalingo, Nigeria for their support and guidance on gaining access to the communities in Bali Local Government Taraba State.
Funding
None.
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest.
Authors’ contributions
CN: Concept. SI: Methodology. BN: Proof Reading. LI: Formatting. GA: Data collection.
History
Received on March 14, 2024. Accepted on August 20, 2024.
Figures and tables
References
- [1].Adewuyi G M, Fowotade A, Adewuyi B T. Lassa Fever: Another Infectious Menace. Afr J Clin Exp Microbiol 2009;10:144-55. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajcem.v10i3.43407 10.4314/ajcem.v10i3.43407 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Blumberg L, Enria D, Bausch DG. Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers, In: Manson’s Tropical Diseases. Saunders 2014. [Google Scholar]
- [3].Dahmane A, van Griensven J, Van Herp M, Van den Bergh R, Nzomukunda Y, Prior J, Alders P, Jambai A, Zachariah R. Constraints in the diagnosis and treatment of Lassa Fever and the effect on mortality in hospitalized children and women with obstetric conditions in a rural district hospital in Sierra Leone. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2014;108:126-32. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/tru009. 10.1093/trstmh/tru009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Dolopei D, Amo-Addae M, Adewuyi P, Himiede W, Fulton S, Lawubah Woods O, Gbearr O, Deodeh V.K, Sanley A, Kullie M.W, Tamatia G, Muyan J, Gbabow L, Bunnah T.G, Sackie A, Duo H, Leyhen D, Paye E, Phebe T. Knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) regarding Lassa fever disease among adults in endemic and non-endemic Counties of Liberia, 2018: A Cross-sectional study. J Interv Epidemiol Public Health 2021;4:9. https://doi.org/10.11604/JIEPH.supp.2021.4.1.1081. 10.11604/JIEPH.supp.2021.4.1.1081 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Ireye F, Ejiyere H, Aigbiremolen A O, Famiyesin O E, Rowland-Udoh E A, Ogeyemhe C O, Okudo I, Onimisi AB. Knowledge, Attitude and Infection Prevention and Control Practices Regarding Lassa Fever among Healthcare Workers in Edo State, Nigeria. Int J Prev Treat 2019;8:21-7 https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ijpt.20190801.03. 10.5923/j.ijpt.20190801.03 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Haas WH, Breuer T, Pfaff G, Schmitz H, Kohler P, Asper M. Imported Lassa fever in Germany: Surveillance and management of contact persons. Clin Infect Dis 2003;36:1254-7. https://doi.org/10.1086/374853. 10.1086/374853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].McCormick JB, Fisher-Hoch SP. Lassa fever. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2002;262:75-109. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-56029-3_4. 10.1007/978-3-642-56029-3_4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Merson L, Bourner J, Jalloh S, Erber A, Salam AP, Flahault A, Olliaro PL. Clinical characterization of Lassa fever: A systematic review of clinical reports and research to inform clinical trial design. PLoSNegl Trop Dis 2021;15:e0009788. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0009788. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Mofolorunsho K C. Outbreak of lassa fever in Nigeria: Measures for prevention and control. Pan African Medical Jorunal 2016;23(210). https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2016.23.210. 10.11604/pamj.2016.23.210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Mylne AQ, Pigott DM, Longbottom J, Shearer F, Duda KA, Messina JP, Weiss DJ, Moyes CL, Golding N, Hay SI. Mapping the zoonotic niche of Lassa fever in Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2015;109:483-92. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/trv047. 10.1093/trstmh/trv047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Nigeria Centre for Disease Control. Experts Meet to Discuss Lassa Fever Control. Wkly Epidemiol Rep 2017:1-12. Available at: http://www.ncdc.gov.ng/reports/weekly (Accessed on: 5/09/2017).
- [12].Ogoina D. Lassa fever:A clinical and epidemiological review. Niger Delta Jorunal Medical Research 2015;1:16-22. [Google Scholar]
- [13].Ogboghodo EO, Adam VY, Omuemu VO, Okojie OH. Knowledge, Attitude and Preventive Practices Against Lassa Fever Among Residents in a Rural Community in Southern Nigeria. West Afr J Med 2019;36:165-71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Richmond JK, Baglole DJ. Lassa fever: epidemiology, clinical features, and social consequences. BMJ 2003;327:1271-5. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7426.1271. 10.1136/bmj.327.7426.1271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Tambo E, Ugwu EC, Ngogang JY. Need of surveillance response systems to combat Ebola outbreaks and other emerging infectious diseases in African countries. Infect Dis Poverty 2014;3:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-9957-3-29. 10.1186/2049-9957-3-29 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].WHO. Clinical Management of Patients with Viral Haemorrhagic Fever: A Pocket Guide for the Front-line Health Worker. Interim Emergency Guidance-Generic Draft For West African Adaptation 2014. Available at: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/130883/WHO_HSE_PED_AIP_14.05.pdf?sequence=2 (Accessed on: 14/08/2023).
- [17].WHO. Introduction to lassa fever managing infectious hazard 2015. Available at:https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/documents/emergencies/health-topics---lassa-fever/lassa-fever-introduction.pdf?sfvrsn=b1b96509_2&download=true (Accessed on: 01/7/2023).
- [18].WHO. IMAI District Clinician Manual: Hospital Care for Adolescentsand Adults. Guidelines for the Management of Common Illnesses with Limited Resources 2011. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/77751/1/9789241548281_Vol1_eng.pdf (Accessed on: 22/07/2023).
- [19].WHO NCDC. Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response in Nigeria. Abuja; March 2013. Available at: https://ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/docs/protocols/4_1476085948.pdf (Accessed on: 16/08/2023). [Google Scholar]
- [20].WHO CDC. Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response in the African Region. Brazzaville and Atlanta: 2010. Available at: https://www.afro.who.int/sites/default/files/2017-06/IDSR-Technical-Guidelines_Final_2010_0.pdf (Accessed on: 16/08/2023). [Google Scholar]
- [21].World Health Organization. Lassa fever-Nigeria. Disease Outbreak News 2018. Availableat: http://www.who.int/csr/don/20-april-2018-lassa-fever-nigeria/en/ (Accessed on: 5/07/2023).
- [22].Abdulkadir S, Mohammed AS. Assessment of knowledge of Lassa fever among residents in North-Eastern Nigeria. Int J Health Scie Res 2019:197-202. [Google Scholar]
- [23].Ossai E.N., Onwe O.E., Okeagu N.P., Ugwuoru A., Laura, Eze T. K., Nwede A. S. Knowledge and preventive practices against Lassa fever among heads of households in Abakaliki metropolis Southeast Nigeria: A cross-sectional study. Proc Singap Healthc 2020;29:73-80. https://doi.org/10.1177/2010105819899120. 10.1177/2010105819899120 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Aigbiremolen AO, Duru CB, Awunor NS, Abejegah C, Abah SO, Asogun AD. Knowledge and application of infectious disease control measures among primary care workers in Nigeria: the Lassa fever example. Int J Basic, Appl Innov Res 2012;1:122-129. [Google Scholar]
- [25].Akinwumi AA, Ademola AO, Oladimeji A E, Abiodun O C, Oghenevo A G, Adebola A O, Olarewaju O P, Olayinka AA, Ojo B F. Knowledge of Lassa fever among students of a college of education: Call for inclusion in curriculum. J Adv Med Med Res 2016;16;1-8. https://doi.org/10.9734/BJMMR/2016/26857. 10.9734/BJMMR/2016/26857 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Akunne M O, Isah A, Anene-Okeke C G, Oguejiofor F A. Assessment of knowledge of Lassa fever infection among the undergraduate students of University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Enugu State, Nigeria. Int Res J Pharm Med Sci 2018;1:6-9. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2538556. 10.5281/zenodo.2538556 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Amoran O, Onwube O. Infection control and practice of standard precautions among healthcare workers in northern Nigeria. J Glob Infect Dis 2013;5;156-63. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-777X.122010. 10.4103/0974-777X.122010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2019, January). Lassa fever. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/index.html (Accessed on: 29/8/2023).
- [29].Fidelis C, Olajolumo J. Assessment of the level of knowledge and universal cross-infection control practices against Lassa fever among health workers in Sokoto, Nigeria: A hospital survey during Lassa fever outbreak in Nigeria. Int J Adv Med Health Res 2018;5:57-65. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJAMR.IJAMR_11_18. 10.4103/IJAMR.IJAMR_11_18 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Ighedosa SU., Asemota O, Aighewi IT., Odigie E A., Usifoh S F., Omorogbe C E., Asemota D O, Osaghae V G, Faboya T N E, Erahuyi O. Knowledge. Attitude and prevention practices of Lassa fever by staff of University of Benin, Benin City. Nigerian Soc Exp Biol J 2017;17:82-90. [Google Scholar]
- [31].Nwonwu E U, Alo C, Una A F, Madubueze U C, Eze I, Eze N C, Ogbonnaya L U, Akamike I C. Knowledge of Lassa fever and its determinants among traders in Izzi community in south-east Nigeria. Arch Curr Res Int 2018;13;1-9. https://doi.org/10.9734/ACRI/2018/39904. 10.9734/ACRI/2018/39904 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Ossai EN, Onwe OE, Okeagu NP, Ugwuoru AL, Eze TK, Nwede AS. Knowledge and preventive practices against Lassa fever among heads of households in Abakaliki metropolis, Southeast Nigeria: a cross-sectional study. Proc Singap Healthc 2020;29:73-80. https://doi.org/10.1177/2010105819899120. 10.1177/2010105819899120 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Reuben C R, Gyar S D. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of Lassa fever in and around Lafia, central Nigeria. Int J Public Health Epidemiol Res 2016;2:14-19. [Google Scholar]
- [34].Usifoh S F, Ighedosa S U, Aighewi I T, Asemota O D, Odigie E A, Faboya T. Impact of Lassa fever on the practice and consumption of stored food by University of Benin Community, in Benin City, Nigeria. J Community Med Prim Health Care. 2018;30:66-76. [Google Scholar]
- [35].World Health Organization (2017, July). Lassa fever: Key fact. Available at:https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lassa-fever (Accessed on: 20/07/2023).
- [36].World Health Organization. Lassa fever-Nigeria 2018. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/01-march-2018-lassa-fever-nigeria-en (Accessed on: 16/7/2023).
- [37].Nigeria Center for Disease Control. Press release: NCDC reviews Lassa fever outbreak response amidst reducing number of cases 2019. Available at: https://ncdc.gov.ng/news/164/press-release%3A-ncdc-reviews-lassa-fever-outbreak-response-amidst-reducing-number-of-cases (Accessed on: 7/10/2023).
- [38].Olayiwola J O, Bakarey A S. Epidemiological Trends of Lassa Fever Outbreaks and Insights for Future Control in Nigeria. Int J Trop Dis Health 2017;24:1-14. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJTDH/2017/32823. 10.9734/IJTDH/2017/32823 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Kelly JD, Barrie MB, Ross RA, Temple BA, Moses LM, Bausch DG. Housing equity for health equity: a rights-based approach to the control of Lassa fever in post-war Sierra Leone. BMC Int Health Hum Rights 2013;2:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-698X-13-2. 10.1186/1472-698X-13-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Wogu JO. Mass media awareness campaign and the prevention of the spread of Lassa fever in the rural communities of Ebonyi State, Nigeria: Impact evaluation. J Public Health Afr 2018. 21;9:882. https://doi.org/10.4081/jphia.2018.882. 10.4081/jphia.2018.882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Usuwa IS, Akpa CO, Umeokonkwo CD, Umoke M, Oguanuo CS, Olorukooba AA, Bamgboye E, Balogun MS. Knowledge and risk perception towards Lassa fever infection among residents of affected communities in Ebonyi State, Nigeria: implications for risk communication. BMC Public Health 2020;20:217. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-8299-3. 10.1186/s12889-020-8299-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Lecompte E, Fichet-Calvet E, Daffis S, Koulémou K, Sylla O, Kourouma F, Doré A, Soropogui B, Aniskin V, Allali B, Kouassi Kan S, Lalis A, Koivogui L, Günther S, Denys C, terMeulen J. Mastomysnatalensis and Lassa fever, West Africa. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:1971-4. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1212.060812. 10.3201/eid1212.060812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Muanya C. Poor hygiene,poverty, ignorance fuel Lassa Fever epidemic in Nigeria. The Guardian 2016. Available at: http://guardian.ng/sunday-magazine/poor-hygiene-poverty-ignorance-fuel-lassa-fever-epidemic-in-nigeria/ (Accessed on: 19/10/2023).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


