Abstract
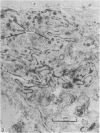
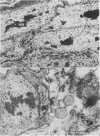
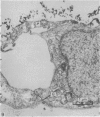
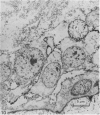
The permeability of the skin of fetal rats between 14 and 21 days of intrauterine life was investigated by injecting lanthanum nitrate solution subepidermally and by exposing the external surface of other fetuses to the same solution. Up to the age of 18 days, the epidermis was freely permeable from the basal surface and lanthanum entered junctional complexes between periderm cells. After 18 days, the limit of permeation corresponded to the level at which membrane-coating granules were released into the intercellular spaces. At all ages, permeation from the outer surface was limited to the junctional complexes between the periderm cells covering the epidermis throughout fetal life. Damage to the periderm at early ages resulted in complete penetration of the epidermis by lanthanum. It was concluded that, prior to secretion of the epidermal permeability barrier at 18 days, the periderm was the principal barrier to permeation by lanthanum.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer F. W. Differentiation and keratinization of fetal rat skin. II. Ultrastructural study of the epidermis in vivo and in vitro. Dermatologica. 1972;145(1):17–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville M. A. Observations on epidermal differentiation in the fetal rat. Am J Anat. 1968 Jul;123(1):147–164. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001230107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Hostetter T. H., Humes H. D. Glomerular permselectivity: barrier function based on discrimination of molecular size and charge. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):F455–F460. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.6.F455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Brown B. E., Fritsch P., Goerke J., Gray G. M., White R. J. Localization and composition of lipids in neonatal mouse stratum granulosum and stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Nov;73(5):339–348. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12550377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Friend D. S. The permeability barrier in mammalian epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):180–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M. Lipids and the epidermal permeability barrier. Arch Dermatol Res. 1981;270(1):95–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00417155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., McNutt N. S., Friend D. S. Membrane alterations during cornification of mammalian squamous epithelia: a freeze-fracture, tracer, and thin-section study. Anat Rec. 1977 Dec;189(4):577–594. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091890404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBMAN A. I. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF A SMALL CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURE IN RAT ORAL EPITHELIUM. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:491–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITHIOF L., WERSAELL J. A HIGHLY ORDERED STRUCTURE IN KERATINIZING HUMAN ORAL EPITHELIUM. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Apr;12:371–379. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotow T., Hashimoto P. H. Graded differences in tightness of ependymal intercellular junctions within and in the vicinity of the rat median eminence. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Sep;76(3):293–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Gross B. G., DiBella R. J., Lever W. F. The ultrastructure of the skin of human embryos. IV. The epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1966 Oct;47(4):317–335. doi: 10.1038/jid.1966.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. F. Membrane-coating granules. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;59:97–127. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61661-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. F. Ultrastructural changes in contents of membrane-coating granules after extrusion from epithelial cells of hamster cheek pouch. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Feb 24;187(2):323–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00224374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook K. A. Human epidermal embryogenesis. Int J Dermatol. 1979 Jun;18(5):329–356. doi: 10.1111/ijd.1979.18.5.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavker R. M. Membrane coating granules: the fate of the discharged lamellae. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Apr;55(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATOLTSY A. G., PARAKKAL P. F. MEMBRANE-COATING GRANULES OF KERATINIZING EPITHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1965 Feb;24:297–307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.24.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENEFEE M. G. The differentiation of keratin-containing cells in the epidermis of embryo mice. Anat Rec. 1955 Jun;122(2):181–191. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordquist R. E., Olson R. L., Everett M. A. The transport, uptake, and storage of ferritin in human epidermis. Arch Dermatol. 1966 Oct;94(4):482–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odland G. F., Holbrook K. The lamellar granules of epidermis. Curr Probl Dermatol. 1981;9:29–49. doi: 10.1159/000403343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuplein R. J., Blank I. H. Permeability of the skin. Physiol Rev. 1971 Oct;51(4):702–747. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.4.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuplein R. J. Permeability of the skin: a review of major concepts. Curr Probl Dermatol. 1978;7:172–186. doi: 10.1159/000401285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner E., Wolff K. Die Permeabilität des epidermalen Intercellularraumes für kleinmolekulares protein. Ergebnisse elektronenmikroskopisch-cytochemischer Untersuchungen mit Peroxidase als Markierungssubstanz. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1969;235(1):78–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Simionescu M., Palade G. E. Differentiated microdomains on the luminal surface of the capillary endothelium. I. Preferential distribution of anionic sites. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):605–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier C. A., Hopps R. M. A study of the permeability barrier in epidermis and oral epithelium using horseradish peroxidase as a tracer in vitro. Br J Dermatol. 1976 Aug;95(2):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb00814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier C. A., Johnson N. W. Permeability of oral mucosa. Br Med Bull. 1975 May;31(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier C. A., Rooney L. The permeability of keratinized and nonkeratinized oral epithelium to lanthanum in vivo. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Feb;54(2):286–295. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier C. A. The permeability of keratinized and nonkeratinized oral epithelium to horseradish peroxidase. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Apr;43(1):160–177. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. W., Zelickson A. S. Embryology of the epidermis: ultrastructural aspects. 1. Formation and early development in the mouse with mammalian comparisons. Acta Derm Venereol. 1975;55(3):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. W., Zelickson A. S. Embryology of the epidermis: ultrastructural aspects. II. Period of differentiation in the mouse with mammalian comparisons. Acta Derm Venereol. 1975;55(5):321–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. W., Zelickson A. S. Embryology of the epidermis: ultrastructural aspects. III. Maturation and primary appearance of dendritic cells in the mouse with mammalian comparisons. Acta Derm Venereol. 1975;55(6):431–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]