Abstract
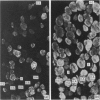
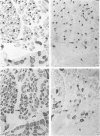
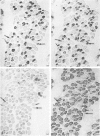
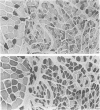
The middle ear muscles of several species of carnivores (cat, dog, fox, ferret and stone-marten) and some New World monkeys (Callithrix, Saimiri) and Old World monkeys (Cercopithecus, Macaca) were examined. The fibre type compositions of these muscles were determined by a combination of the standard histochemical myofibrillar ATPase method, and immunohistochemical techniques using myosintype-specific antisera. Immunohistochemically slow-tonic fibres were found in the stapedius muscles of only two carnivores, the ferret and stone-marten. In all the carnivores and the New World monkeys, tensor tympani muscle contained IIM, slow-tonic and slow-twitch fibres, but in the Old World monkeys it resembled stapedius muscle, and contained only Type I (slow-twitch) and IIA fibres. Thus, because all the species examined had IIM fibres in the jaw-closer muscles, this means that the common embryological origin of tensor tympani muscle and the jaw-closers does not necessarily result in tensor tympani muscle containing this fibre type even though IIM fibres occur only in first branchial arch muscles. This fact, together with other species differences in the fibre type composition of these muscles, shows that there is no typical composition of middle ear muscles in general, and suggests that the differences are related to very different functional requirements.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billeter R., Weber H., Lutz H., Howald H., Eppenberger H. M., Jenny E. Myosin types in human skeletal muscle fibers. Histochemistry. 1980;65(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00493174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormioli S. P., Sartore S., Vitadello M., Schiaffino S. "Slow" myosins in vertebrate skeletal muscle. An immunofluorescence study. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):672–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERULKAR S. D., SHELANSKI M. L., WHITSEL B. L., OGLE P. STUDIES OF MUSCLE FIBERS ON THE TENSOR TYMPANI OF THE CAT. Anat Rec. 1964 Jun;149:279–297. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernand V. S., Hess A. The occurrence, structure and innervation of slow and twitch muscle fibres in the tensor tympani and stapedius of the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):547–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello F., Carpenè E., Veggetti A., Rowlerson A., Jenny E. The tensor tympani muscle of cat and dog contains IIM and slow-tonic fibres: an unusual combination of fibre types. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):363–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00713043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell L. C., Carlson D. S., Brangwyn C. E. Lack of 'acid reversal' of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase in masticatory muscle fibres of rhesus monkeys. Histochem J. 1980 Mar;12(2):209–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01024551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierobon-Bormioli S., Sartore S., Libera L. D., Vitadello M., Schiaffino S. "Fast" isomyosins and fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Oct;29(10):1179–1188. doi: 10.1177/29.10.7028858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow D. H., Billeter R., Mascarello F., Carpenè E., Rowlerson A., Jenny E. No classical type IIB fibres in dog skeletal muscle. Histochemistry. 1982;75(1):53–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00492533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veggetti A., Mascarello F., Carpenè E. A comparative histochemical study of fibre types in middle ear muscles. J Anat. 1982 Sep;135(Pt 2):333–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]