Abstract
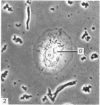
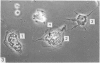
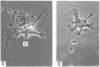
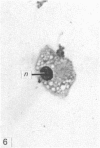
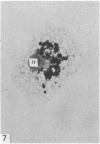
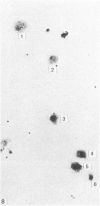
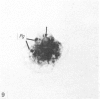
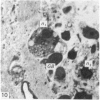
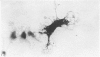
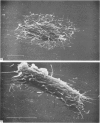
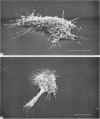
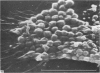
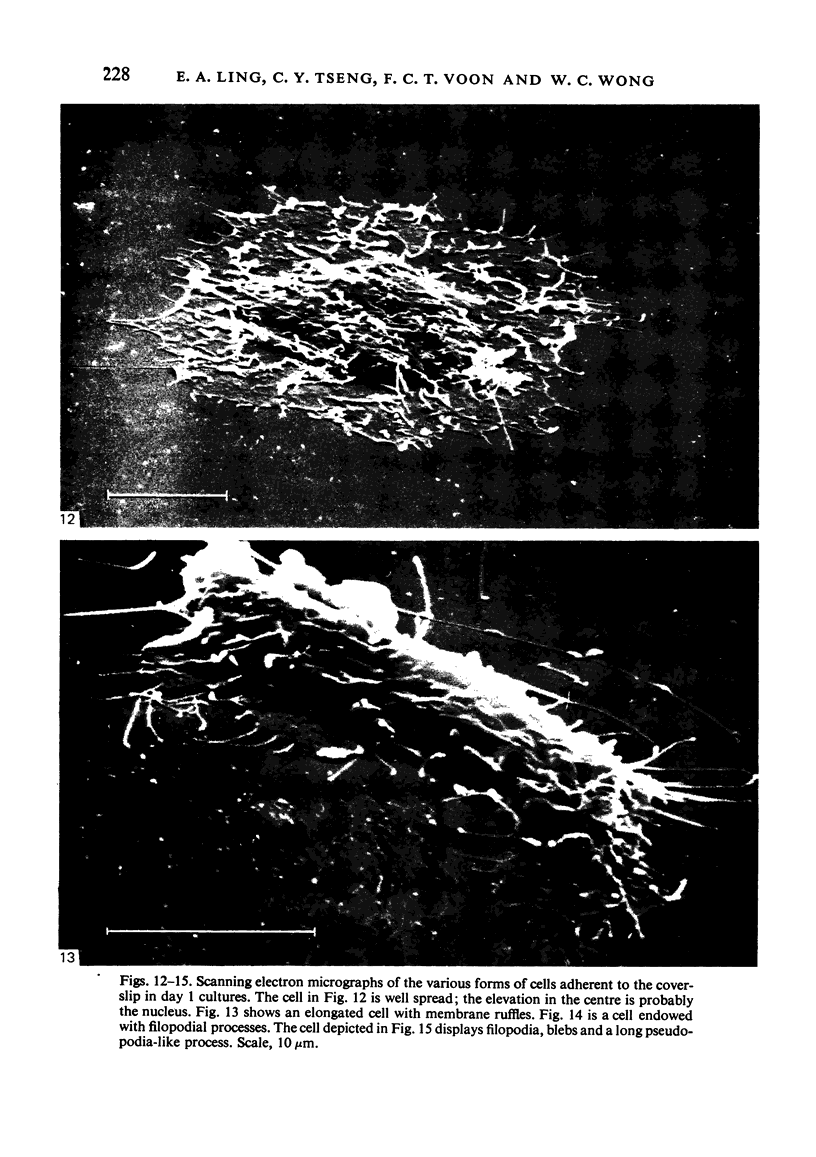
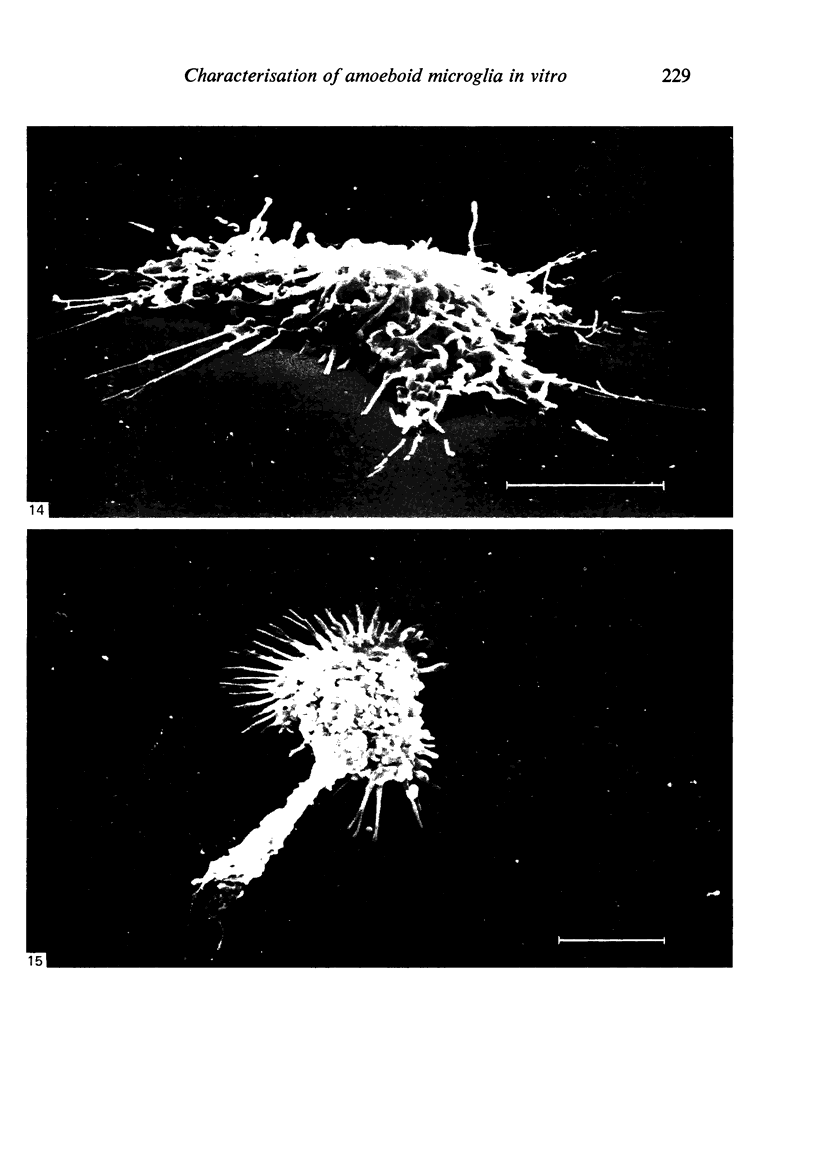
In phase contrast and scanning electron microscopy, diverse structural forms of cells tenaciously adherent to glass coverslips were observed in the culture of the corpus callosum and cavum septum pellucidum from postnatal rats. In day 1 culture, many of the cultured cells were round, with well spread peripheral cytoplasm which appeared homogeneous. Cell organelles aggregated mainly around the reniform or round nucleus. Some cells showed spinous projections. In day 3-5 culture, the cells became irregular, sending out long branching pseudopodial processes; often they displayed a vacuolated cytoplasm. The cultured cells were highly phagocytic, as shown by their uptake of colloidal carbon particles and latex beads, in light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. Cytochemical studies have shown that the cells were peroxidase-negative but were strongly positive for non-specific esterase, similar to the amoeboid microglial cells in the postnatal corpus callosum. On the basis of their structural features, both in phase contrast and scanning electron microscopy, experimental as well as cytochemical properties, it is concluded that the cells in the present culture are in fact amoeboid microglial cells which are active macrophages in the developing corpus callosum.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht R. M., Bleier R. Histochemical, functional, and structural features of isolated adherent supraependymal cells: characterization as resident mononuclear phagocytes. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleier R., Albrecht R. Supraependymal macrophages of third ventricle of hamster: morphological, functional and histochemical characterization in situ and in culture. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Aug 1;192(3):489–504. doi: 10.1002/cne.901920308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleier R., Siggelkow I., Albrecht R. Macrophages of hypothalamic third ventricle. I. Functional characterization of supraependymal cells in situ. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 May;41(3):315–329. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198205000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleier R. Surface fine structure of supraependymal elements and ependyma of hypothalamic third ventricle of mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Jun 15;161(4):555–567. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhles W. C., Jr Studies on mononuclear phagocyte progenitor cells: morphology of cells and colonies in liquid culture of mouse bone marrow. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Apr;25(4):363–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn P., Albrecht R., Bleier R. Macrophages of hypothalamic third ventricle. II. Immunological characterization of supraependymal cells in culture. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 May;41(3):330–336. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198205000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I., Sarmiento J. Nascent microglia in the developing brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;50(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00688537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. Cytogenesis and pathology of neuroglia and microglia. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;168(4):271–278. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(80)80269-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knyszynski A., Leibovich S. J., Skutelsky E., Danon D. Macrophages from unstimulated, mineral oil and thioglycollate-stimulated mice: a comparative study of surface anionic sites and phagocytosis of "old" red blood cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Sep;24(3):205–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake E. S., Wright M. J., Myrvik Q. N. Differences in surface morphology of alveolar macrophages attached to glass and to millipore filters: a scanning electron microscope study. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Jun;17(6):370–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake E. S., Wright M. J. Variations on the form of attachment of rabbit alveolar macrophages to various substrata as observed by scanning electron microscopy. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Apr;25(4):417–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. K., Shieh J. Y., Ling E. A., Wong W. C. Labelling of amoeboid microglial cells in the supraventricular corpus callosum following the application of horseradish peroxidase in the cerebrum and spinal cord in rats. J Anat. 1983 Mar;136(Pt 2):367–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Kaur C., Wong W. C. Light and electron microscopic demonstration of non-specific esterase in amoeboid microglial cells in the corpus callosum in postnatal rats: a cytochemical link to monocytes. J Anat. 1982 Sep;135(Pt 2):385–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Light and electron microscopic demonstration of some lysosomal enzymes in the amoeboid microglia in neonatal rat brain. J Anat. 1977 Jul;123(Pt 3):637–648. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Some aspects of amoeboid microglia in the corpus callosum and neighbouring regions of neonatal rats. J Anat. 1976 Feb;121(Pt 1):29–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastruct and origin of epiplexus cells in the telencephalic choroid plexus of postnatal rats studied by intravenous injection of carbon particles. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Feb;26(2):106–117. doi: 10.1177/26.2.24068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabarra B., Cavelier J. F., Dry M., Dimitriu A. Scanning electron microscopic studies of activated macrophages in the mouse. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Nov;24(5):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehmichen M. Enzyme-histochemical differentiation of neuroglia and microglia: a contribution to the cytogenesis of microglia and globoid cells. Review of the literature. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;168(4):344–373. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(80)80272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P., Pinto J., Hanifin J. M. Surface morphology of human mononuclear phagocytes during maturation and phagocytosis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Aug;48(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stensaas L. J., Reichert W. H. Round and amoeboid microglial cells in the neonatal rabbit brain. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;119(2):147–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00324517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A semithin light microscopic, transmission electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of macrophages in the lateral ventricle of mice from embryonic to adult life. J Anat. 1979 Aug;129(Pt 1):31–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng C. Y., Ling E. A., Wong W. C. Scanning electron microscopy of amoeboid microglial cells in the transient cavum septum pellucidum in pre- and postnatal rats. J Anat. 1983 Mar;136(Pt 2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh R. J., Brawer J. R., Lin P. S. Supraependymal cells in the third ventricle of the neonatal rat. Anat Rec. 1978 Feb;190(2):257–269. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]