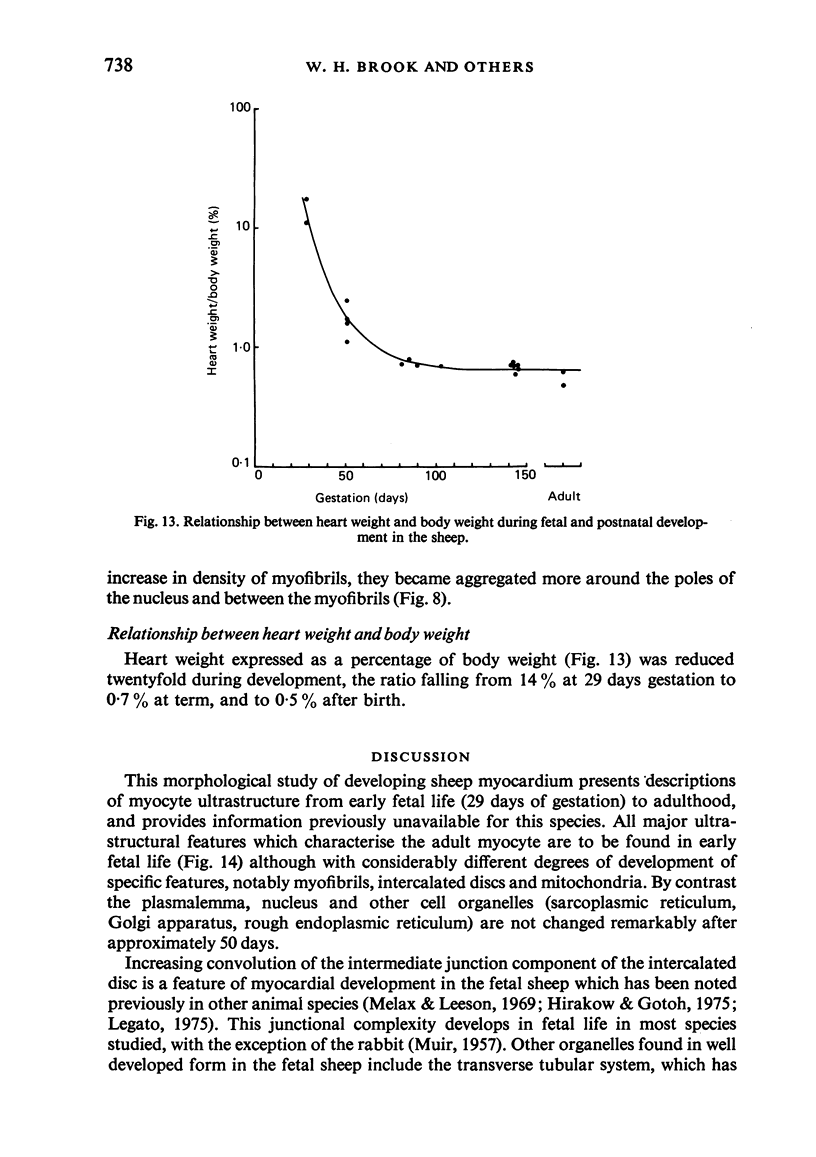
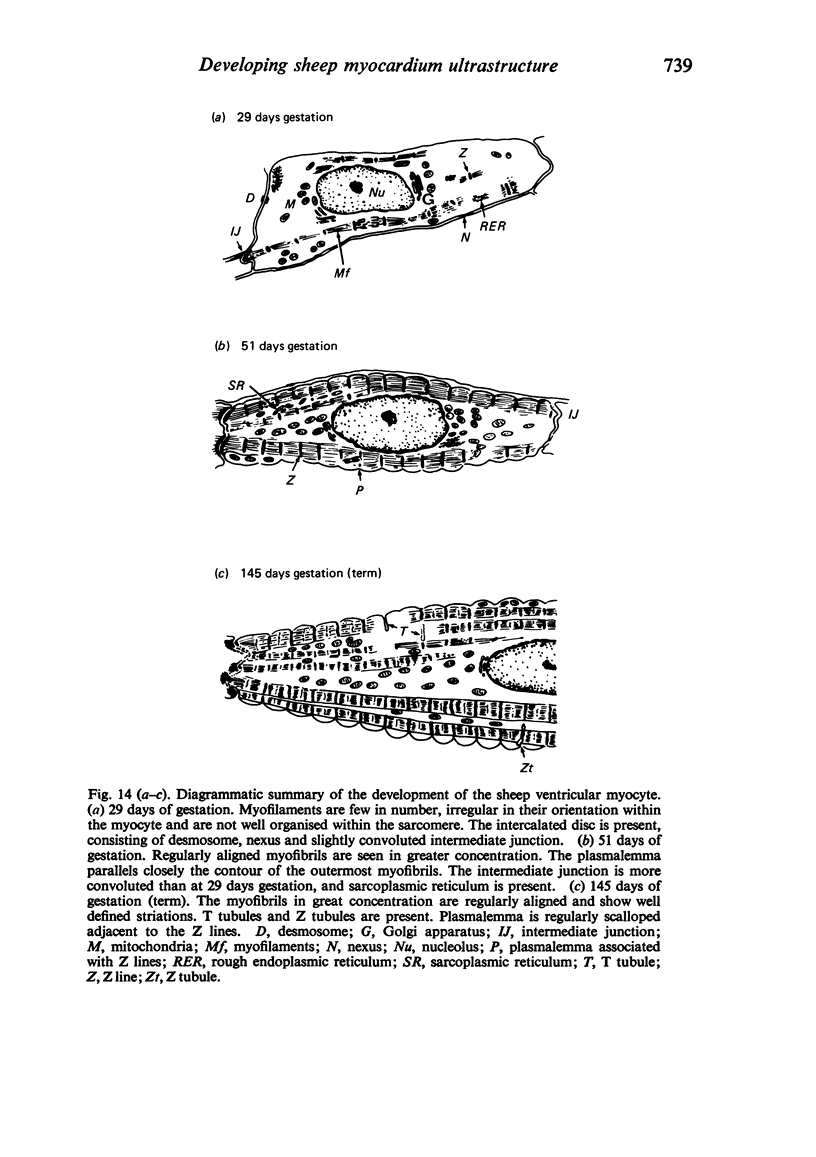
Abstract
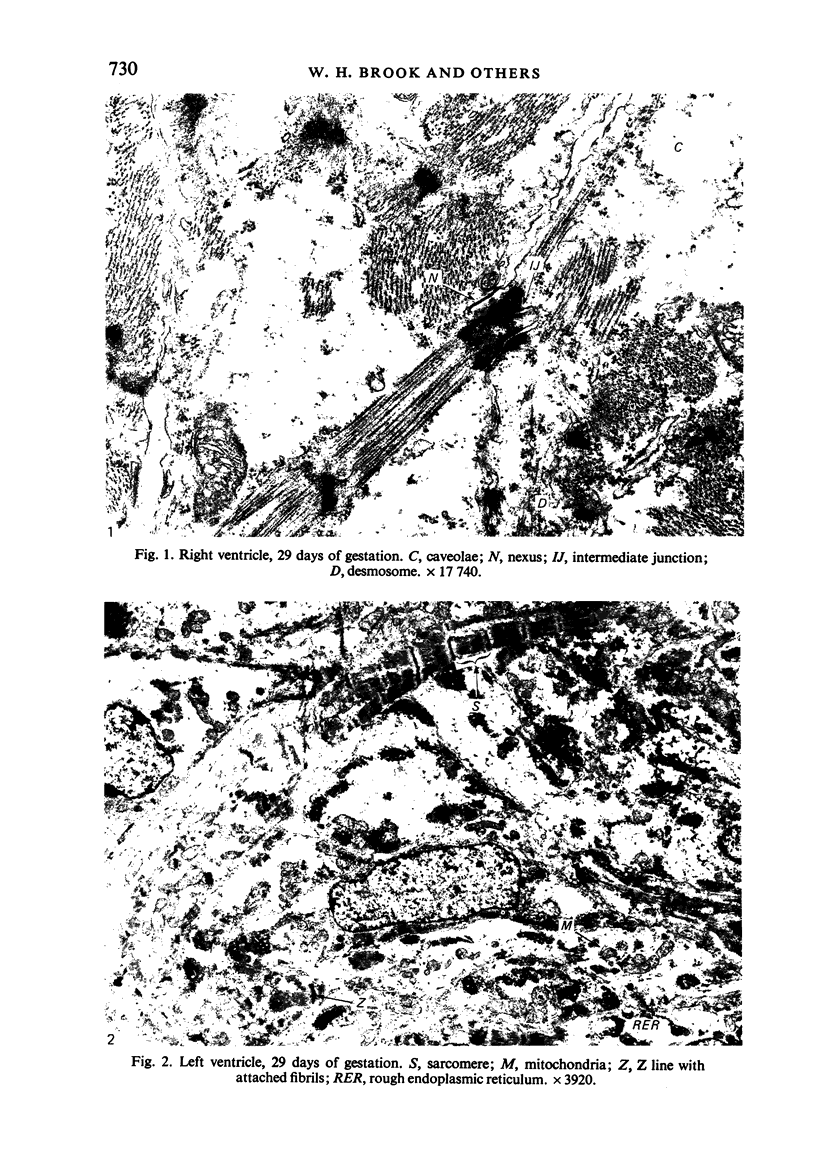
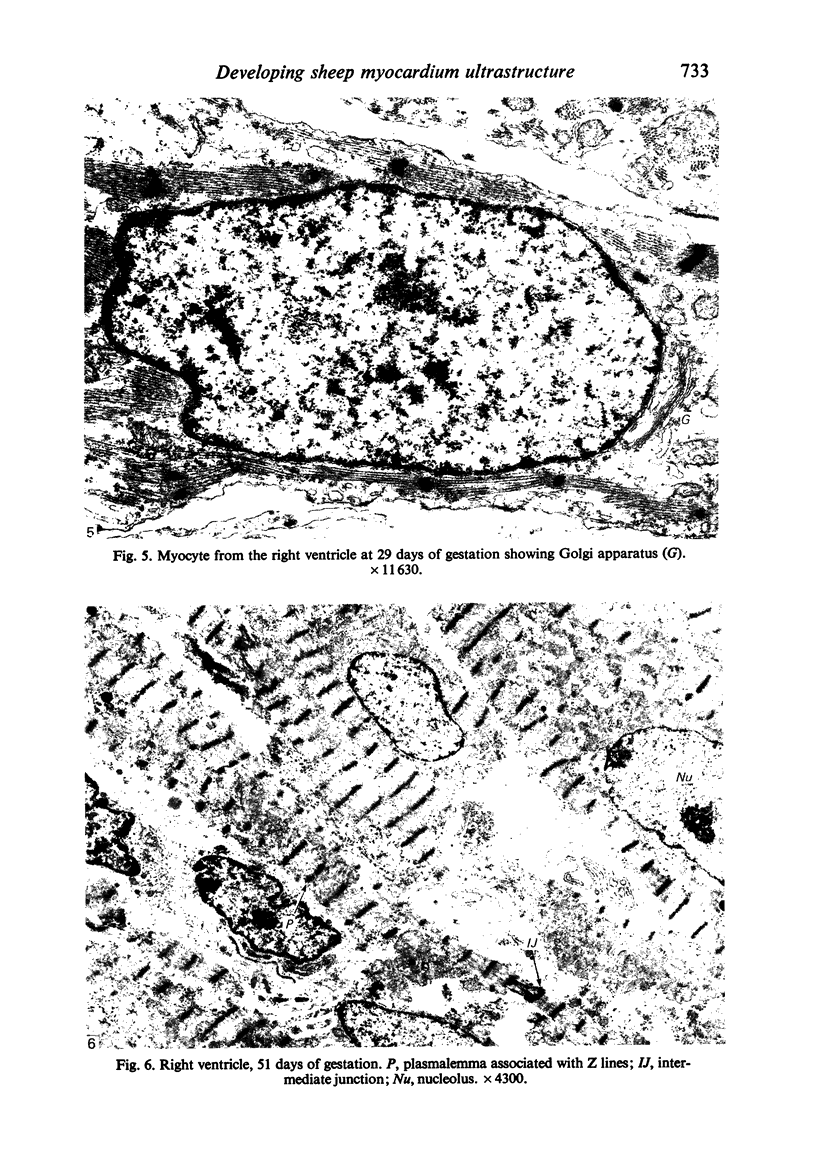
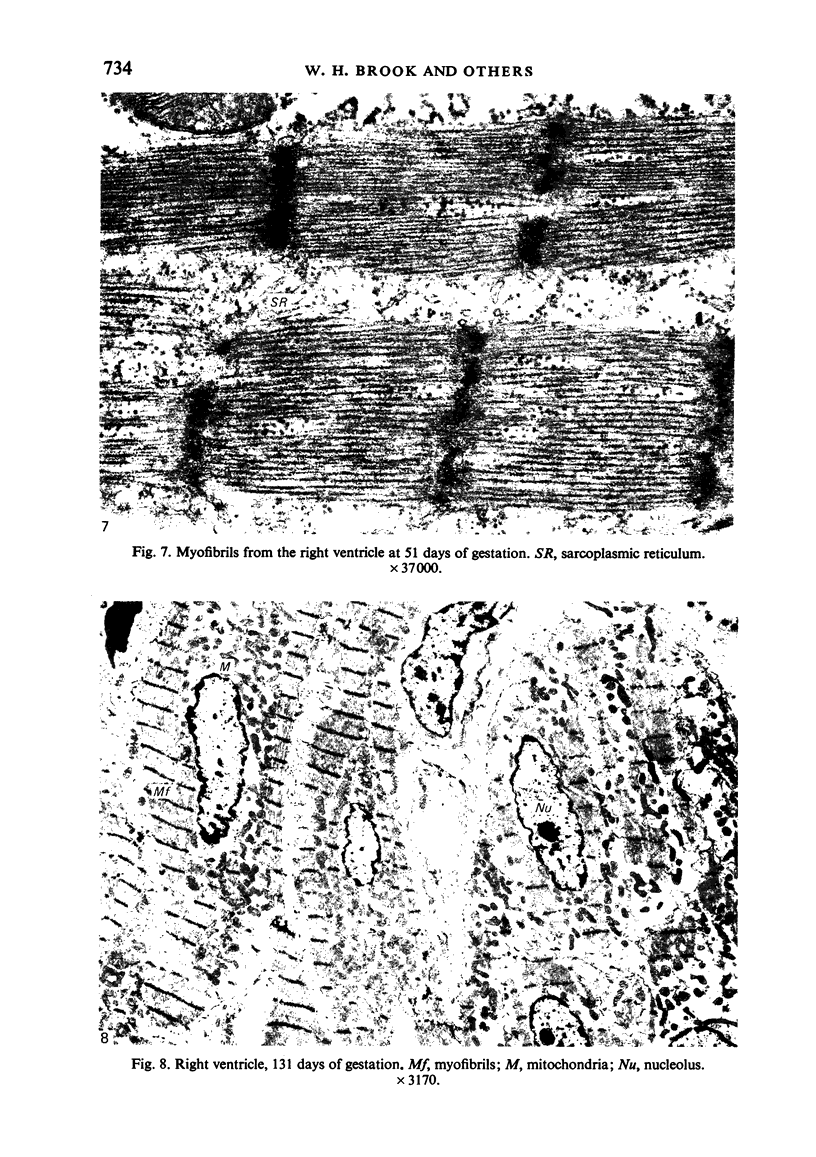
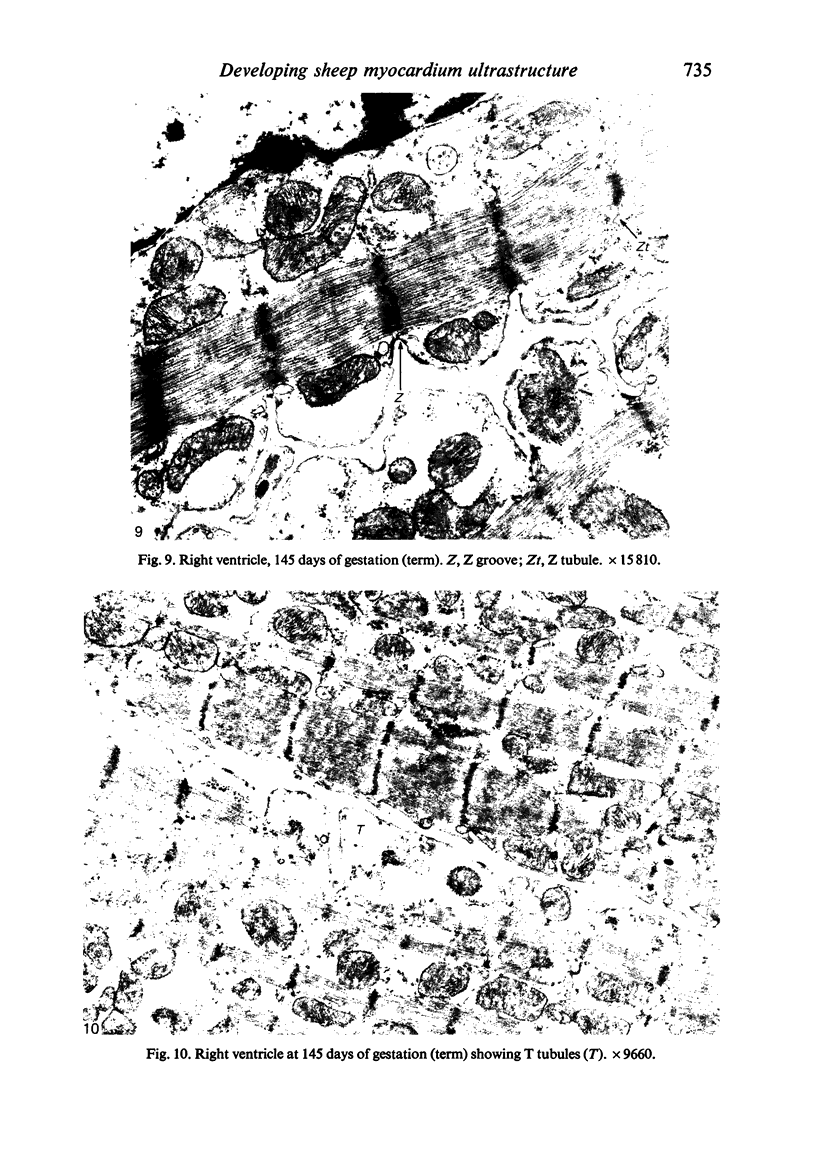
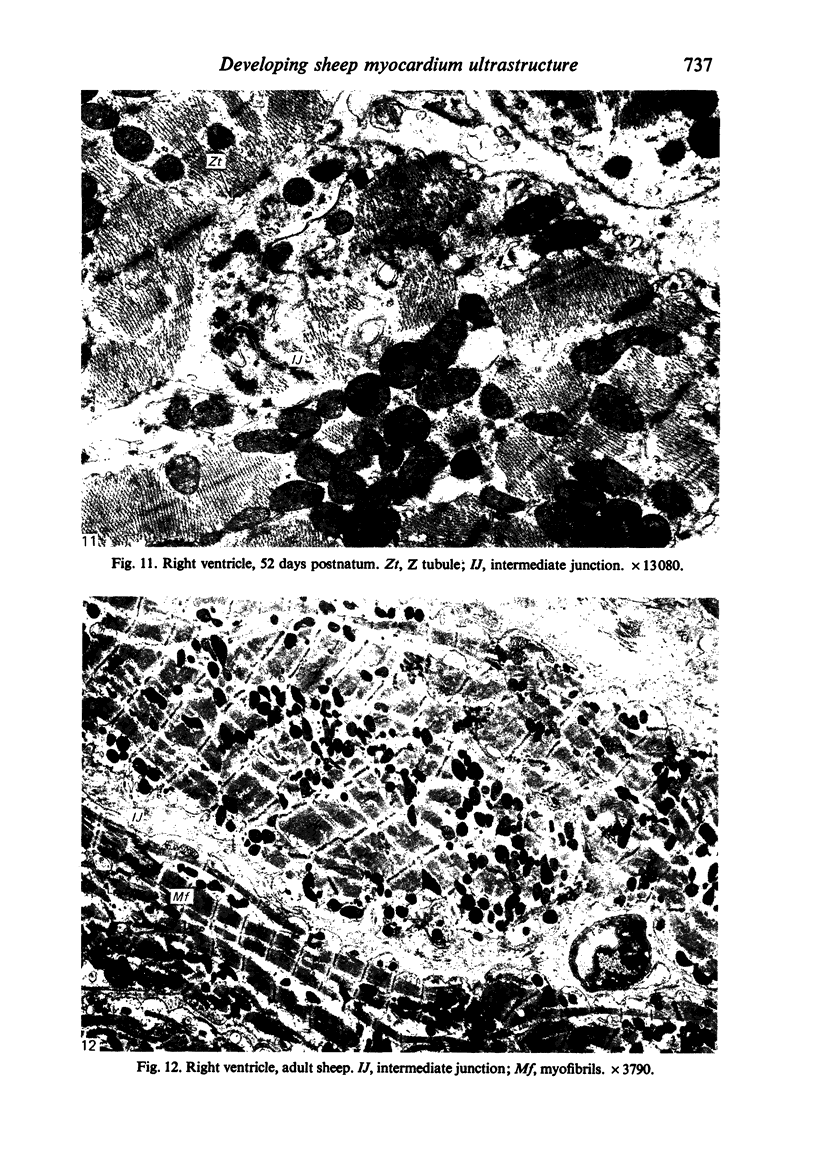
The ultrastructure of the developing fetal lamb myocardium was studied in a series of animals spanning 29 days of gestation to term, and compared with newborn and adult animals. All major ultrastructural features which characterise the adult myocyte were found in early fetal life, although with considerably different degrees of development of specific features. Notably, myofibrils at 29 days of gestation are sparse and show little organisation. With advancing gestation there is an increasing number of myofibrils and the development of well defined striations. Thus, at term, the fetal tissue is not substantially different from the adult myofibril in the appearance of sarcomere structure. The observation of contractile tissue paucity and disorder in early fetal lamb myocardium is difficult to reconcile with available physiological data, which show an extraordinary pumping performance of the heart in vivo, and requires further investigation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anversa P., Olivetti G., Loud A. V. Morphometric study of early postnatal development in the left and right ventricular myocardium of the rat. I. Hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and binucleation of myocytes. Circ Res. 1980 Apr;46(4):495–502. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.4.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko K. J. Observations on the ultrastructure of developing myocardium of rat embryos. J Morphol. 1976 Nov;150(3):681–709. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Dewar J., Tynan M., Ward R. Post-natal developmental changes in the length-tension relationship of cat papillary muscles. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):95–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann M. A., Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M. Factors affecting changes in the neonatal systemic circulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:371–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAK L. V., BURKE J. F. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF HUMAN EMBRYONIC MYOCARDIUM. Anat Rec. 1964 Aug;149:623–649. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091490408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR A. R. An electron microscope study of the embryology of the intercalated disc in the heart of the rabbit. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Mar 25;3(2):193–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melax H., Leeson T. S. Fine structure of developing and adult intercalated discs in rat heart. Cardiovasc Res. 1969 Jul;3(3):261–267. doi: 10.1093/cvr/3.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivetti G., Anversa P., Loud A. V. Morphometric study of early postnatal development in the left and right ventricular myocardium of the rat. II. Tissue composition, capillary growth, and sarcoplasmic alterations. Circ Res. 1980 Apr;46(4):503–512. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon C. A., Friedman W. F., Sybers H. D. Scanning electron microscopy of fetal and neonatal lamb cardiac cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1976 Nov;8(11):853–862. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(76)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan D. J., Cullen M. J., Tynan M. J. Postnatal ultrastructural changes in the cat myocardium: a morphometric study. Cardiovasc Res. 1977 Nov;11(6):536–540. doi: 10.1093/cvr/11.6.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan D. J., Cullen M. J., Tynan M. J. Qualitative and quantitative observations on ultrastructural changes during postnatal development in the cat myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Nov;11(11):1173–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(79)80004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolich J. J., Stratford B. F., Maloney J. E., Ritchie B. C. Postnatal development of the epithelium of larynx and trachea in the rat: scanning electron microscopy. J Anat. 1977 Dec;124(Pt 3):657–673. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Kizu A., Bugaisky L. Cardiac hypertrophy: its characteristics as a growth process. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Oct 22;44(5):941–946. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]