Abstract
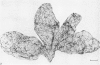
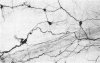
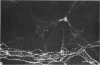
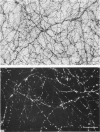
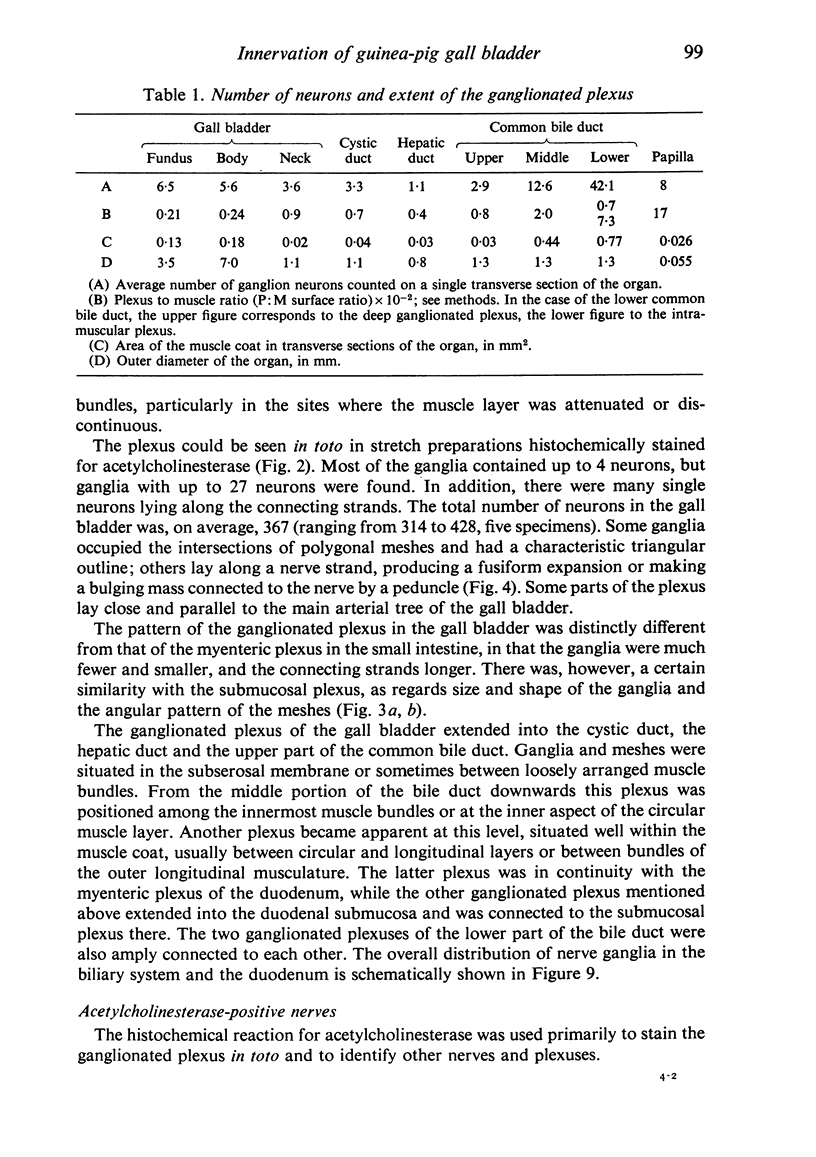
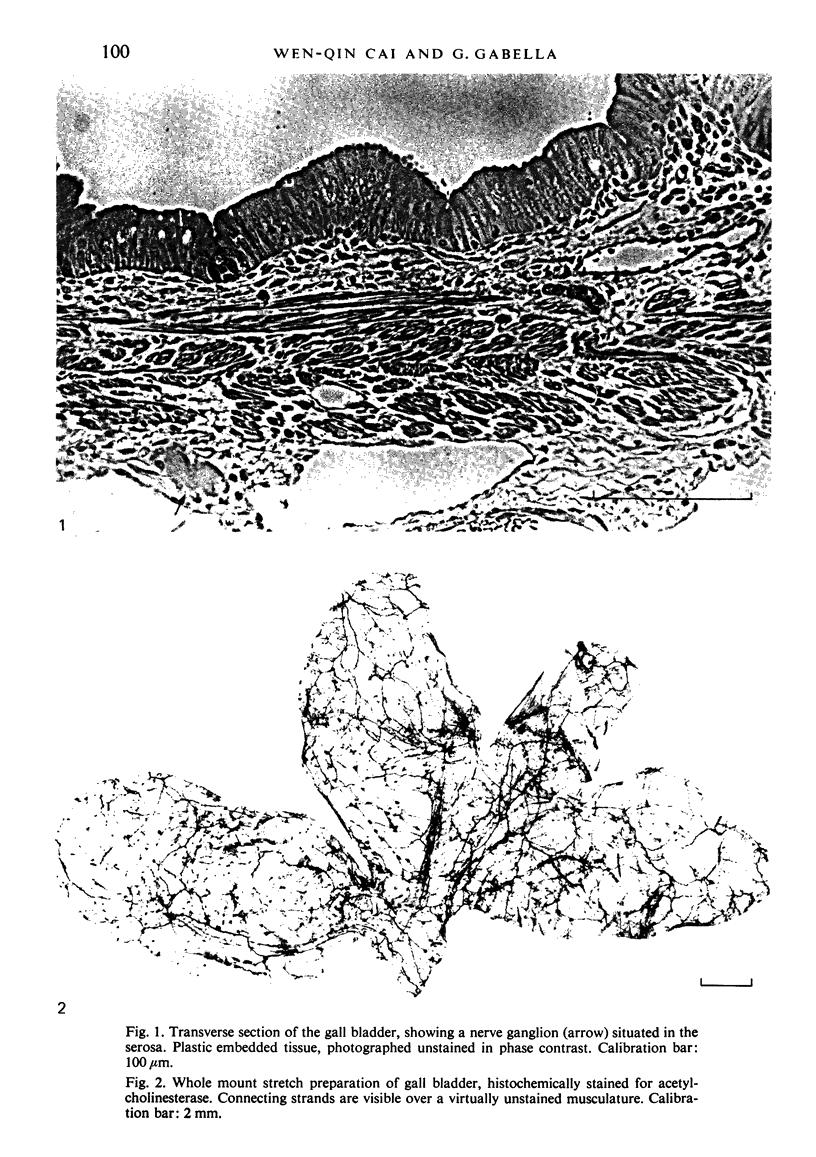
The innervation of the gall bladder and the biliary pathways was studied in guinea-pigs by means of histochemical methods for catecholamines and for acetylcholinesterase on whole mount preparations, on cryostat sections and on sections of plastic-embedded tissues. The gall bladder contains on average 367 neurons in a ganglionated plexus which lies at the outer surface of the muscle coat. The overall appearance of this plexus is rather similar to that of the submucosal plexus of the duodenum. From the gall bladder the plexus extends into the cystic duct, the hepatic duct and the common bile duct, but from the middle portion of the common bile duct downwards, it is positioned at or near the inner surface of the muscle coat. Concurrently with the marked increase in muscle thickness in the lower parts of the common bile duct, another ganglionated plexus appears, which is truly intramuscular. The latter plexus is highly developed, lies usually between longitudinal and circular muscle and resembles in appearance the myenteric plexus of the duodenum, with which it is in continuity. Throughout the biliary system, the extent of the ganglionated plexus is roughly related to the extent of the musculature. An exchange of adrenergic fibres between the ganglionated plexus and perivascular nerves is observed in the gall bladder. Another nerve plexus, without ganglia but rich in adrenergic and acetylcholinesterase-positive fibres, lies between the mucosa and the muscle coat. Very few nerve fibres run into the musculature of the gall bladder. On the other hand, in the thick musculature of the lower portion of the common bile duct, several intramuscular nerve fibres are found.
Full text
PDF


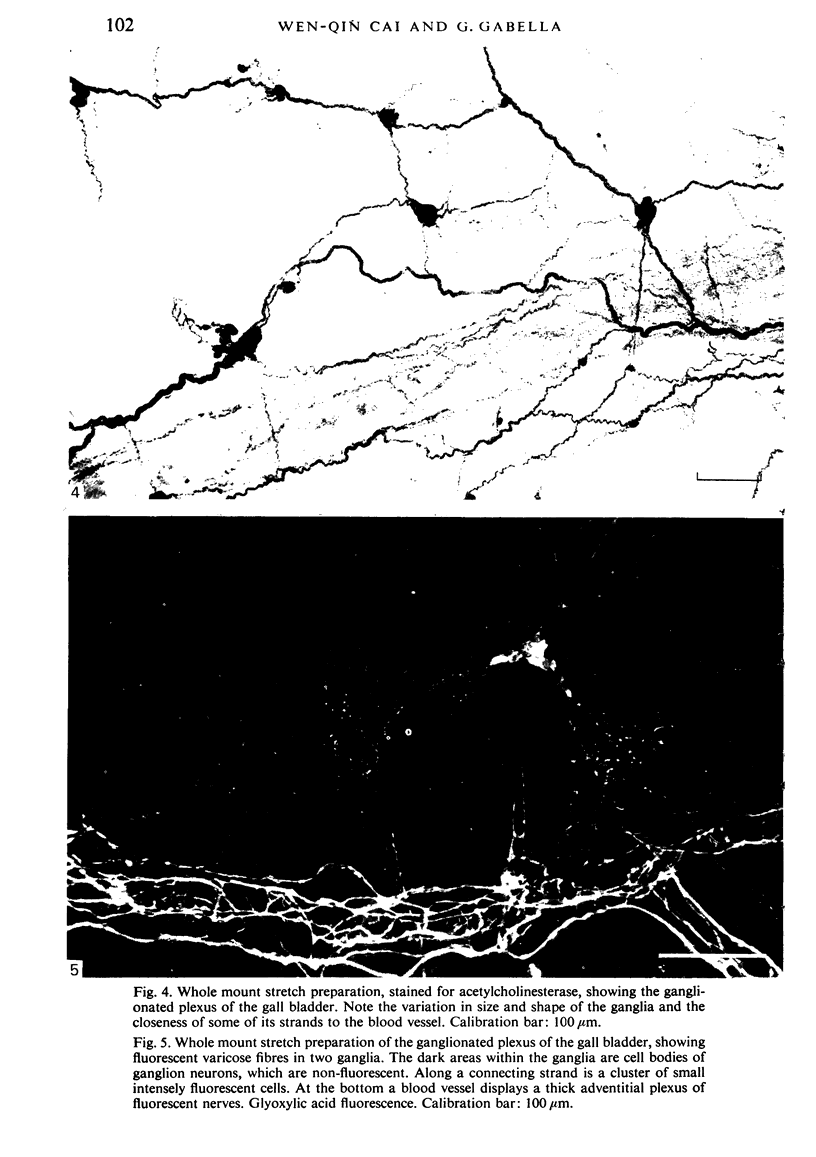
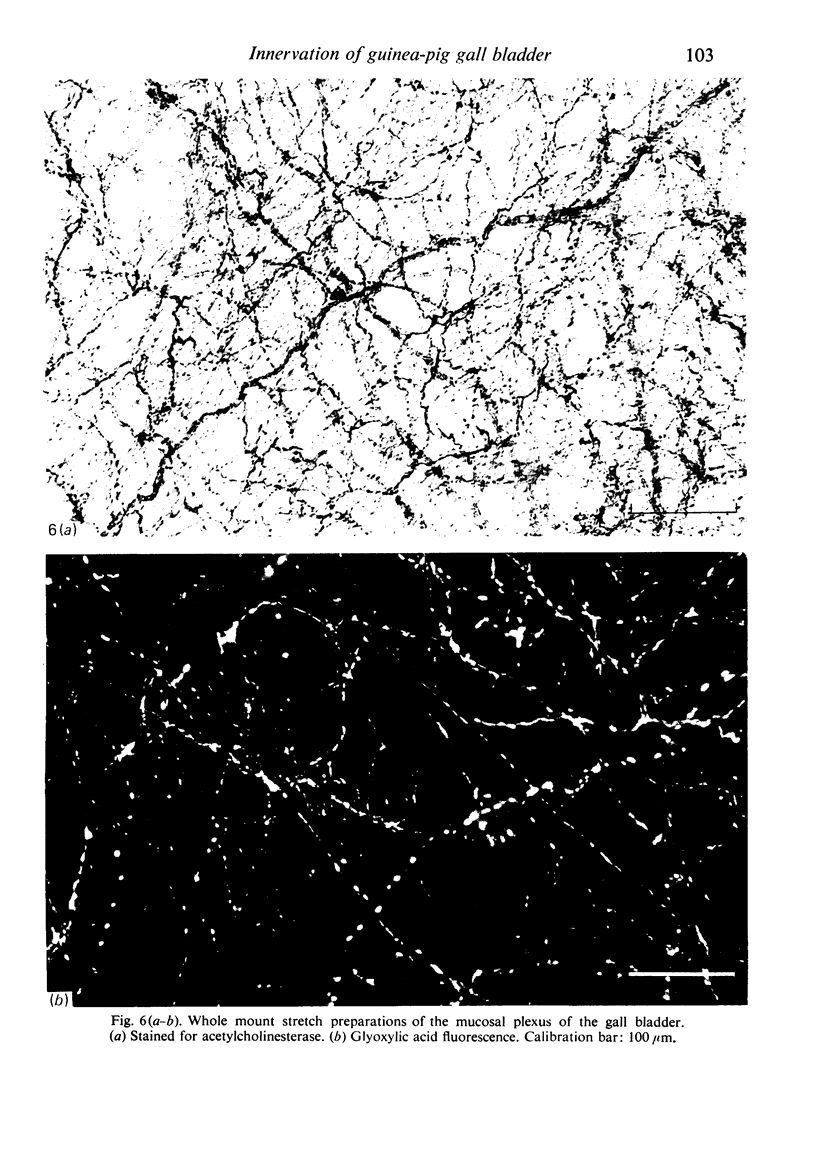
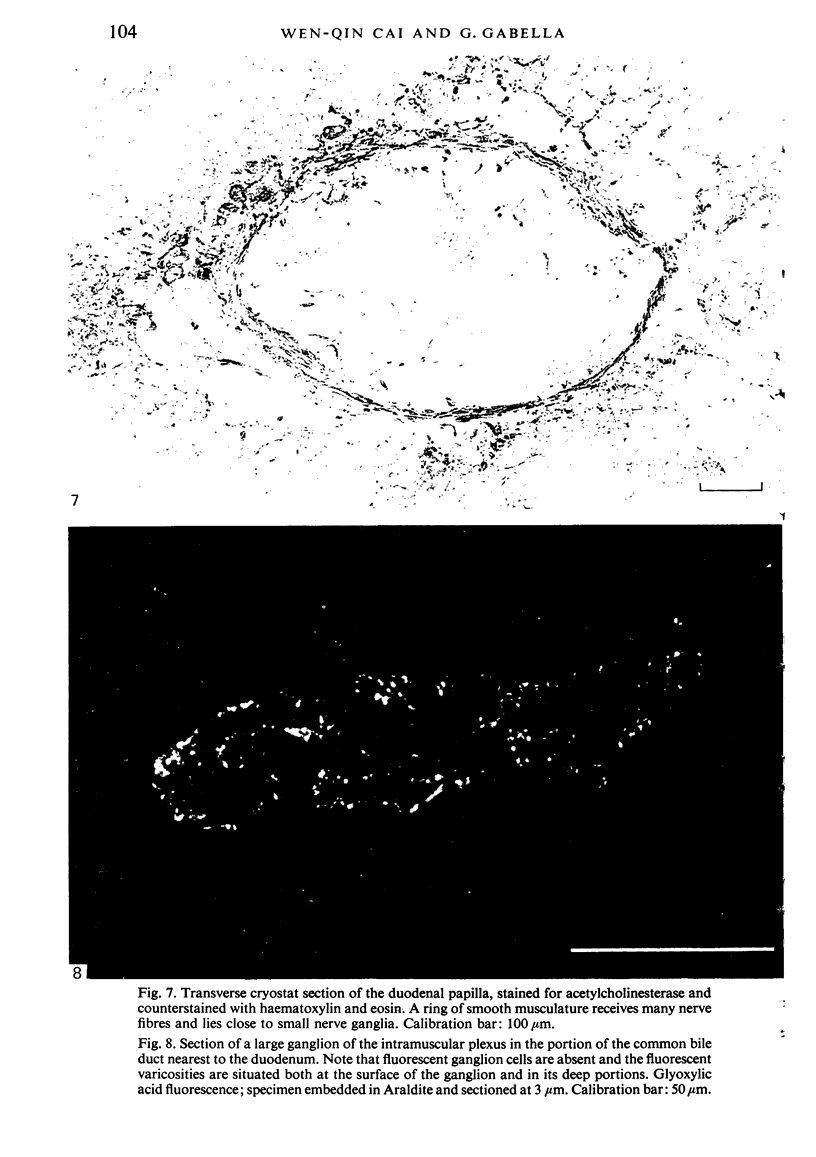

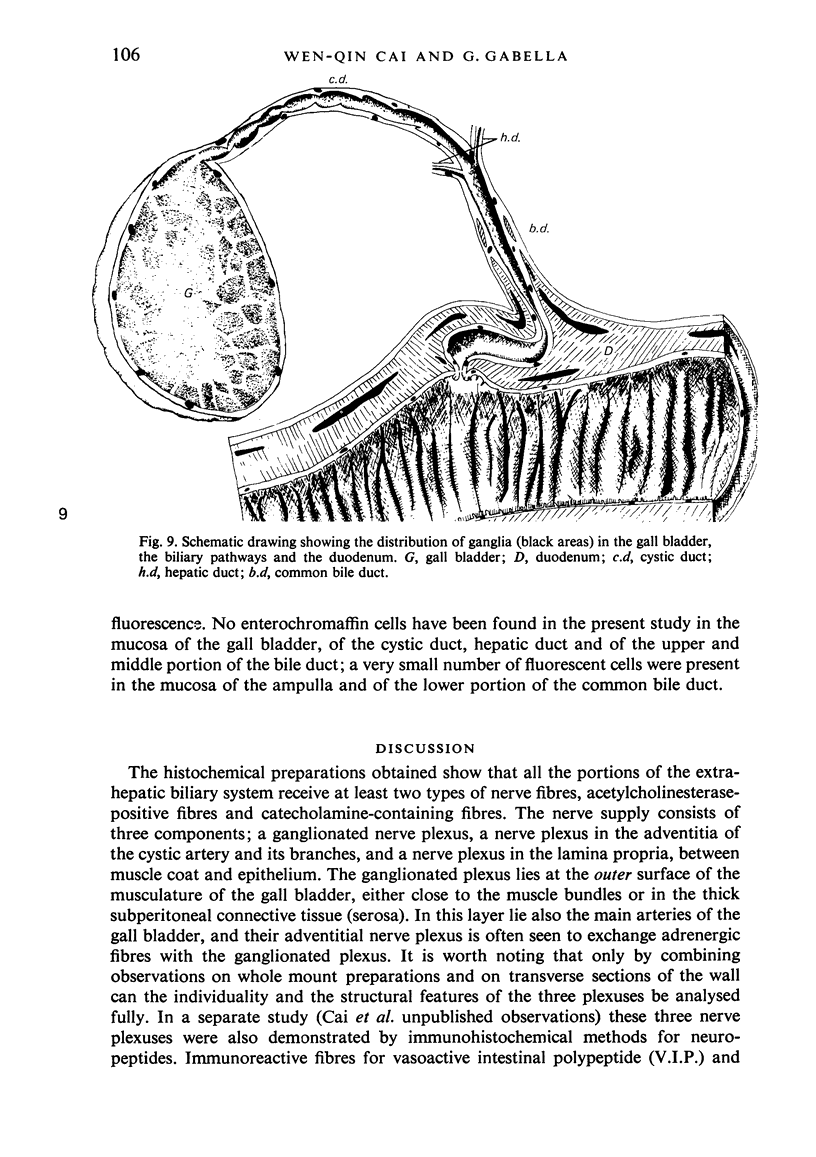



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgarten H. G., Lange W. Extrinsic adrenergic innervation of the extrahepatic biliary duct system in guinea-pigs, cats and rhesus monkeys. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969 Sep 22;100(4):606–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00344379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J. S., Al-Hassani M., Crowe R., Burnstock G. The non-adrenergic, inhibitory innervation of the guinea-pig gallbladder. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Oct 18;377(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00584372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
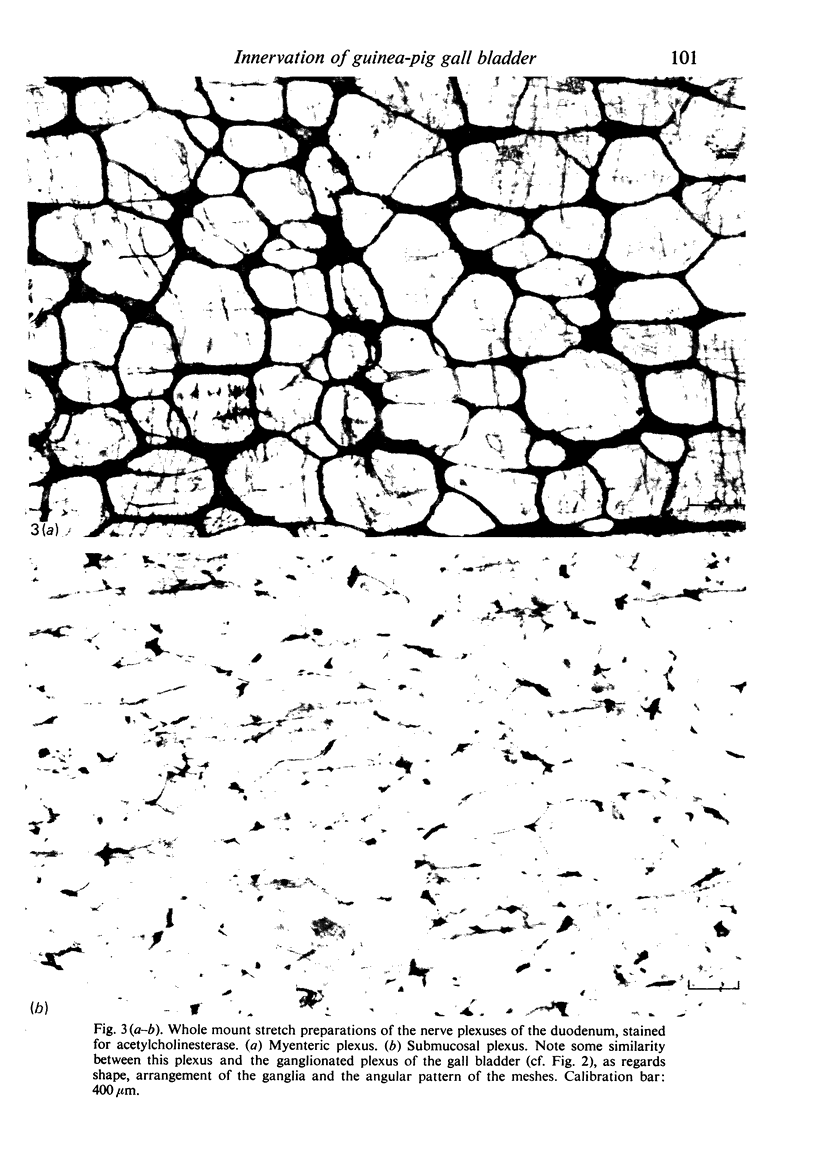
- Gabella G. Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;59:129–193. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grapulin G., Ottolenghi A., Fagiolo U., Vecellio A. Studio sull'innervazione terminale delle vei biliari extraepatiche del cane. 3. L'innervazione adrenergica al microscopio a florescenza prima e dopo la resezione delle vie afferenti vegetative. Arch De Vecchi Anat Patol. 1968 Jul;51(3):785–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn M. Histological and histochemical observations on the myenteric and submucous plexuses of mammals. J Anat. 1968 Jan;102(Pt 2):223–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K. Adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the supraduodenal common bile duct. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978 Aug;70(2):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K. Cholinesterase histochemistry of the innervation of the smooth muscle sphincters around the terminal intramural part of the ductus choledochus in the cat and the dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):278–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K. Cholinesterases of the gall bladder. Histochemistry. 1977 Feb 1;50(4):337–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00507127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K., Penttilä O. Adrenergic innervation of the human gall bladder. Histochemistry. 1977 Dec 7;54(3):209–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00492243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K., Rechardt L. Adrenergic innervation of the choledocho-duodenal junction of the cat and the dog. Histochemie. 1973 Mar 26;34(4):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00306304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K. Structure and innervation of the choledocho-duodenal junction. Ann Chir Gynaecol Suppl. 1976;192:3–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindvall O., Björklund A. The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemistry. 1974 Apr 22;39(2):97–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00492041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onda M., Miyazaki T. [The adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of gallbladder and extrahepatic biliary duct system in the cat and human. Part I. Experimental study: fluorescence histochemical and histochemical study concerning intrinsic innervation of the biliary duct system in the cat (author's transl)]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1980 May;77(5):768–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland S. D. The intrinsic innervation of the gall bladder in Macaca rhesus and Cavia porcellus. J Anat. 1966 Apr;100(Pt 2):261–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansy M. F., Innes D. L., Martin J. S., Kendall F. M. An evaluation of neural influences on the sphincter of oddi in the dog. Am J Dig Dis. 1974 May;19(5):423–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01255606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlin T., Axelsson H., Schiebler T. H., Winckler J. Light and electron microscopic observations of the autonomic innervation of the mouse gallbladder mucosa. A histochemical, cytochemical, and secretory study. Histochemistry. 1977 Aug 1;53(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00498486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]