Abstract
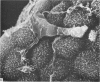
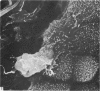
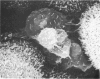
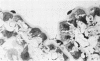
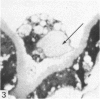
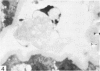
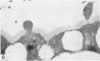
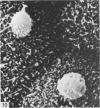
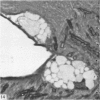
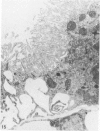
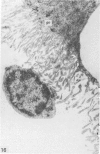
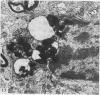
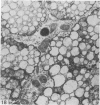
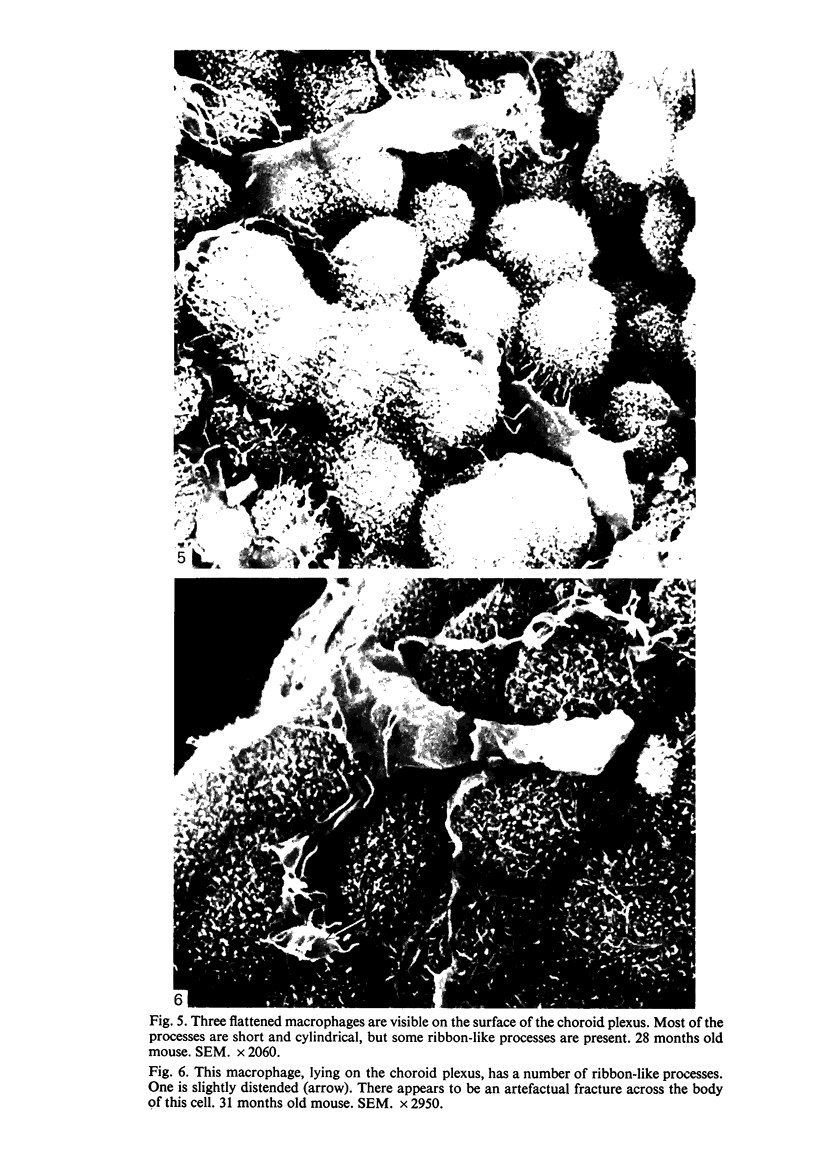
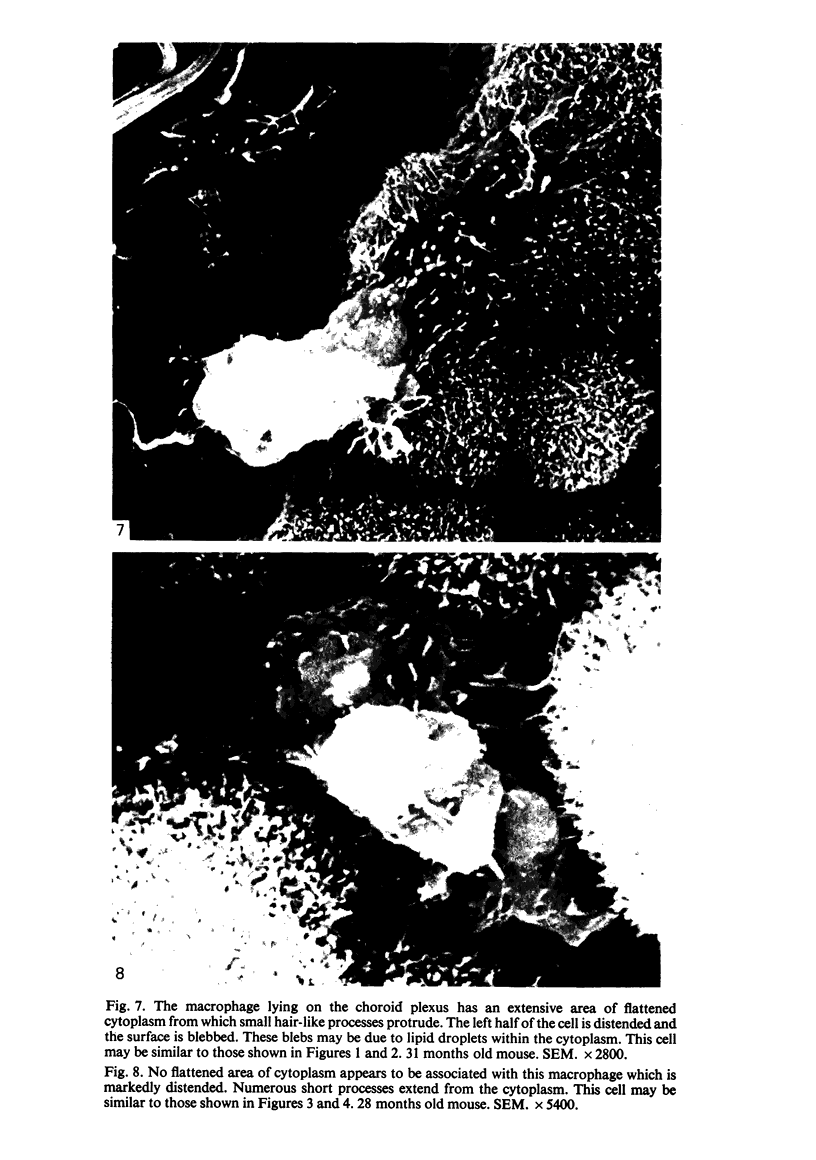
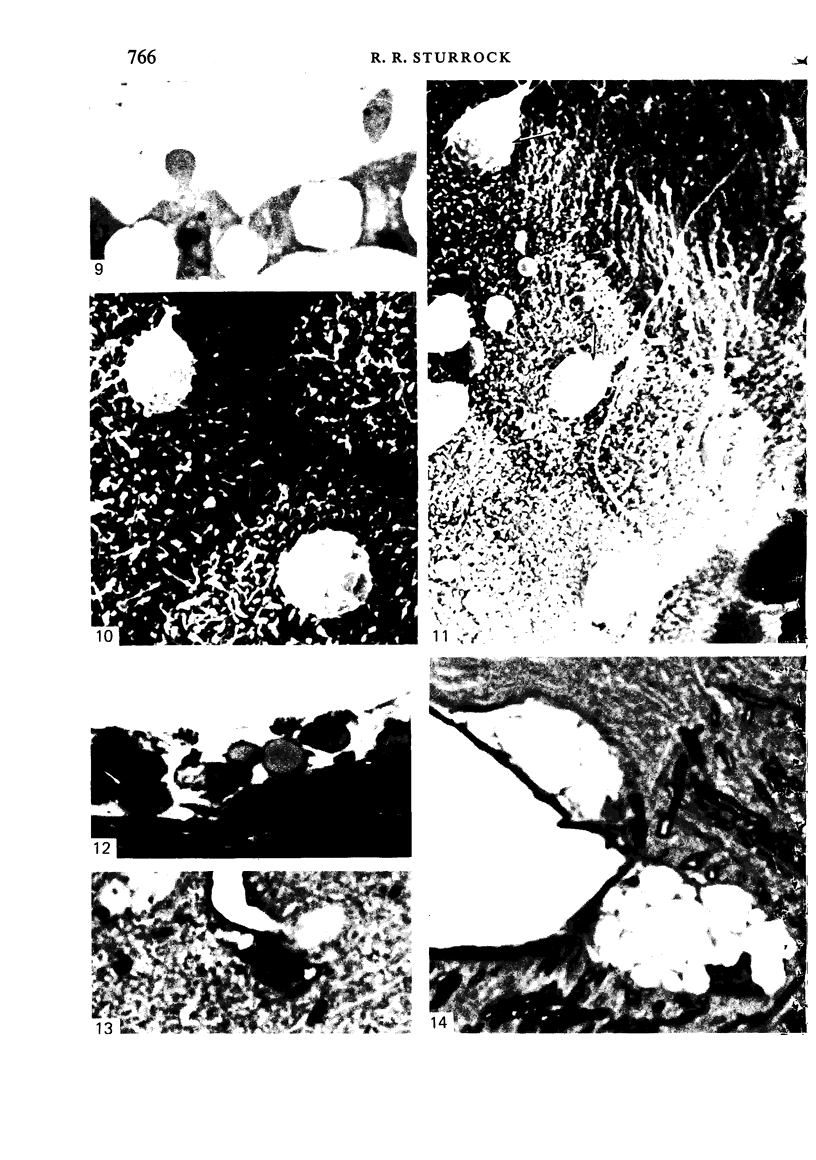
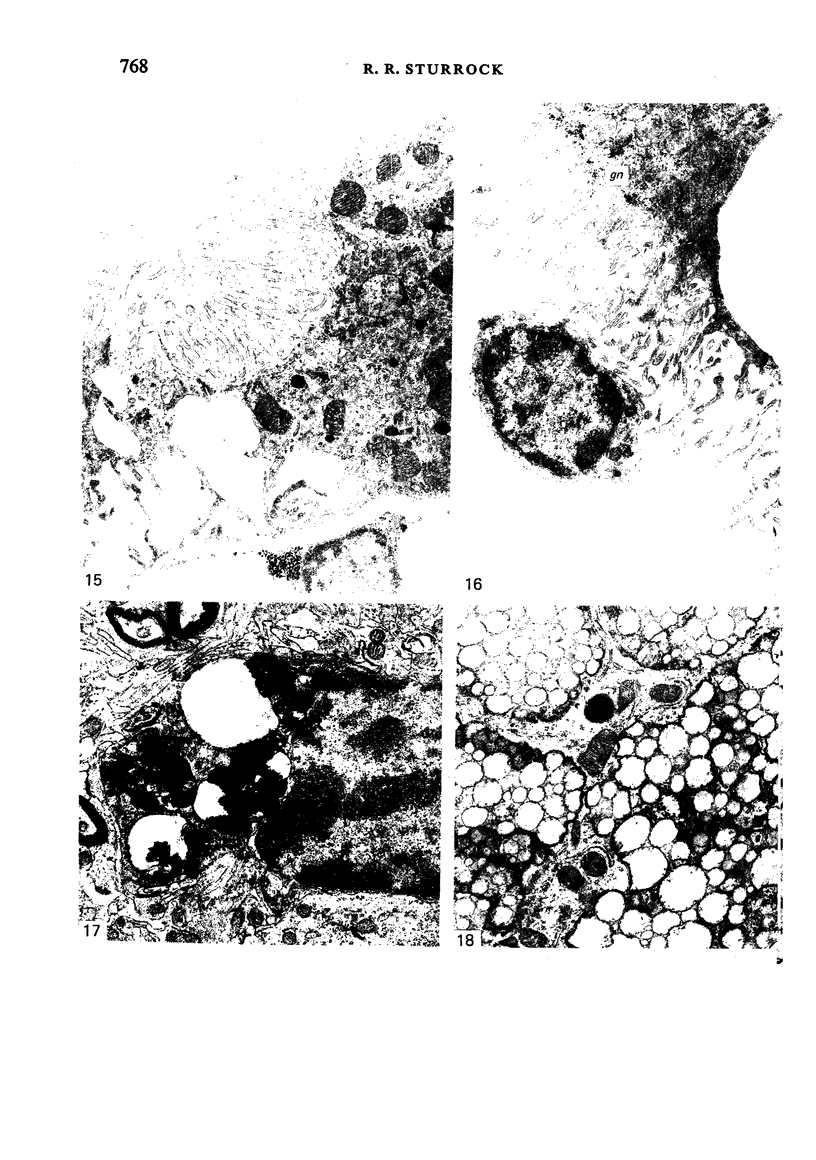
Intraventricular macrophages in the aged mouse brain (25-31 months) are found mainly on the surface of the choroid plexus. About half the population are flattened cells similar to those described by a number of authors in adult animals. The remainder are partially or completely distended due to the presence of varying amounts of lipid, either in the form of droplets or of foamy masses. These variations in shape are visible in the scanning electron microscope, as well as in semithin sections. The source of the lipid is unclear. It may result from passage of lipid into the cerebrospinal fluid from the ependyma, because many ependymal cells contain large lipid droplets. Alternatively, the lipid may be the result of phagocytosis of degeneration products of epithelial cells of the choroid plexus, either of complete cells, or of parts of cells extruded into the cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. J., Low F. N. The ependymal surface of the lateral ventricle of the dog as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Am J Anat. 1973 Aug;137(4):483–489. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001370410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleier R., Albrecht R. Supraependymal macrophages of third ventricle of hamster: morphological, functional and histochemical characterization in situ and in culture. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Aug 1;192(3):489–504. doi: 10.1002/cne.901920308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleier R. Surface fine structure of supraependymal elements and ependyma of hypothalamic third ventricle of mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Jun 15;161(4):555–567. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. J., McCarthy L. E., Borison H. L. Electron microscopic study of the epiplexus (Kolmer) cells of the cat choroid plexus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;110(4):471–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00330099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Wang I. W., Oppenheim R. W. Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. I. A light and electron microscopic study of naturally occurring and induced cell loss during development. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;177(1):33–57. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi F., Marini D. The surface fine structure of the walls of cerebral ventricles and of choroid plexus in cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;123(1):82–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00337675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. W. Supraependymal cells in recesses of the monkey third ventricle. Am J Anat. 1973 Apr;136(4):533–539. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001360410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. W. Supraependymal cells: light and transmission electron microscopy extends scanning electron microscopic demonstration. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):502–507. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim M. Z., Al-Wirr M. E., Bahuth N. The mast cells of the mammalian central nervous system. III. Ultrastructural characteristics in the adult rat brain. Acta Anat (Basel) 1979;104(2):134–154. doi: 10.1159/000145062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. A., Gwyn D. G., Morrison C. M. The fine structure of the ventricular surface of the area postrema of the cat, with particular reference to supraependymal structures. Am J Anat. 1978 Oct;153(2):273–290. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001530207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastruct and origin of epiplexus cells in the telencephalic choroid plexus of postnatal rats studied by intravenous injection of carbon particles. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastructure and mode of formation of epiplexus cells in the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):555–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noack W., Dumitrescu L., Schweichel J. U. Scanning and electron microscopical investigations of the surface structures of the lateral ventricles in the cat. Brain Res. 1972 Nov 13;46:121–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. The surface fine structure of the choroid plexus and ependymal lining of the rat lateral ventricle. J Neurocytol. 1974 Mar;3(1):99–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01111935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. E., Krobisch-Dudley G., Paull W. K., Kozlowski G. P., Ribas J. The primate median eminence. I. Correlative scanning-transmission electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Sep 16;162(1):61–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00223262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. E., Sladek J. R., Jr Age related changes in the endocrine hypothalamus: I. Tanycytes and the blood-brain-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Neurobiol Aging. 1981 Summer;2(2):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(81)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A developmental study of epiplexus cells and supraependymal cells and their possible relationship to microglia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Sep-Oct;4(5):307–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of the embryonic mouse telencephalon. J Anat. 1982 Jan;134(Pt 1):25–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A semithin light microscopic, transmission electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of macrophages in the lateral ventricle of mice from embryonic to adult life. J Anat. 1979 Aug;129(Pt 1):31–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. Microglia in the prenatal mouse neostriatum and spinal cord. J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):499–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R., Smart I. H. A morphological study of the mouse subependymal layer from embryonic life to old age. J Anat. 1980 Mar;130(Pt 2):391–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh R. J., Brawer J. R., Lin P. S. Supraependymal cells in the third ventricle of the neonatal rat. Anat Rec. 1978 Feb;190(2):257–269. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]