Abstract
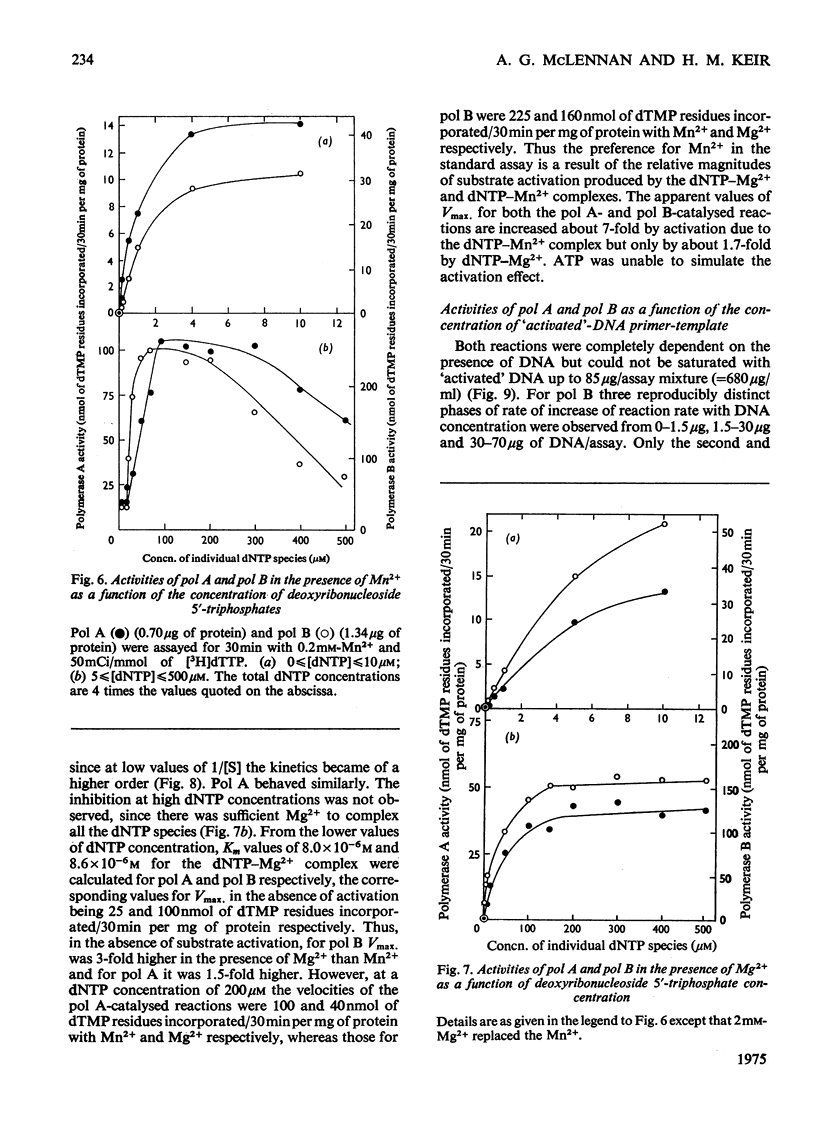
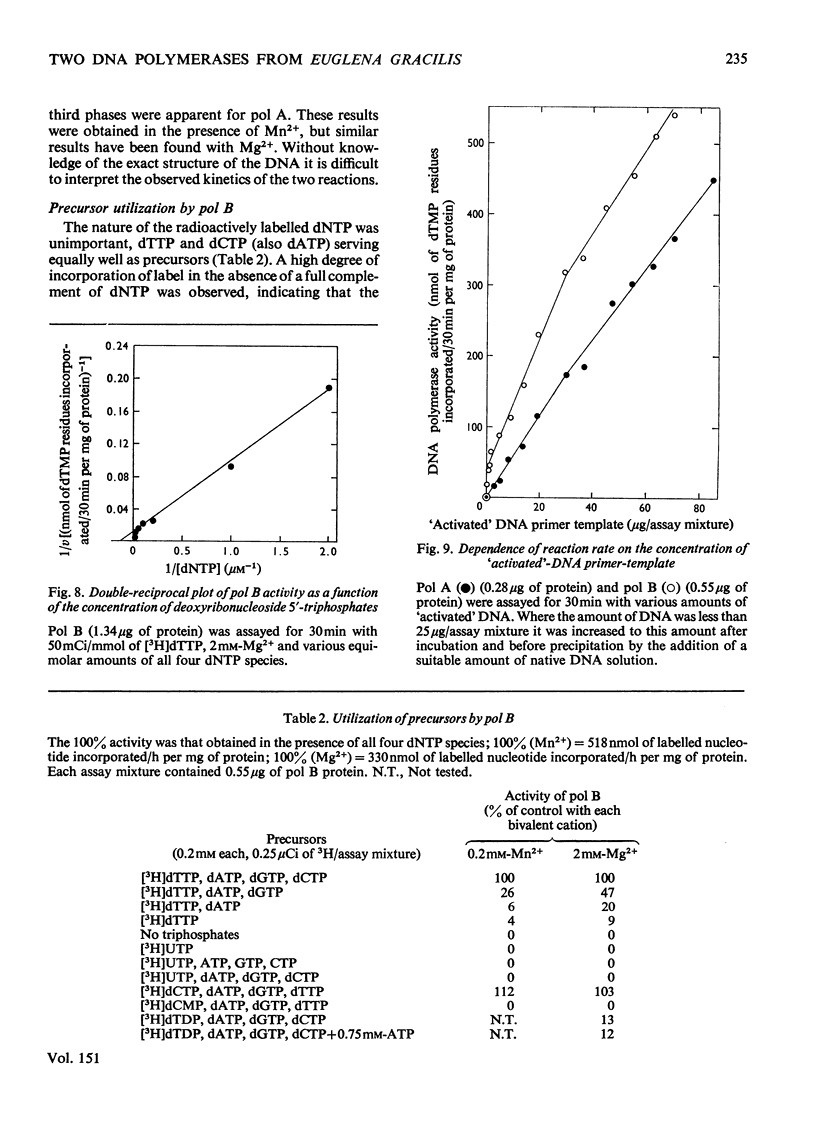
Two DNA polymerases of high molecular weight, pol A (mol.wt. 190 000) and pol B (mol.wt. 240 ooo), have been purified 6300-fold and 1600-fold respectively from an extramitochondrial supernatant of a bleached strain of Euglena gracilis. They have very similar requirements when assayed with an 'activated'-DNA primer-template [the optimum conditions of pH and ionic (K+ and Mn2+) composition being 7.2, 25 mM and 0.2 mM respectively]. 0.2 mM-Mn2+ was about 1.5-2-fold as effective as 2 mM-Mg2+, owing to substrate activation by deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphates in the presence of Mn2+. Km values for the triphosphates in the absence of activation were about 10(-6)M with Mn2+ and 8 X 10(-6) M with Mg2+ for both enzymes. They were inhibited to the same extent by N-ethylmaleimide, novobiocin and o-phenanthroline, but differed in their chromatographic behaviour on DEAE-cellulose and in their electrophoretic mobilities on polyacrylamide gel. No evidence was found for the existence in these cells of a DNA polymerase of low molecular weight, but there were indications that a third enzyme of high molecular weight might exist.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkering-Kuylaars S. A., Campagnari F. Purification of a DNA polymerase from calf thymus nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):526–538. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Downey K. M., So A. G. Bone marrow cytoplasmic deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Variation of pH and ionic environment as a possible control mechanism. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4378–4384. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Downey K. M., So A. G. Metabolic regulation of cytoplasmic DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):205–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. K., Costello P. A., Keir H. M. Dexyribonucleic acid polymerases of BHK-21/C13cells. Relationship to the physiological state of the cells, and to synchronous indution of synthesis of deoxyribonuleic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):233–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1450233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. K., Keir H. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of BHK-21/C13 cells. Partial purification and characterization of the enzymes. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):215–224. doi: 10.1042/bj1450215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crerar M., Pearlman R. E. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Purification and properties of the major activity in exponentially growing cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3123–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Kornberg A. Conversion of the M13 viral single strand to the double-stranded replicative forms by purified proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):3999–4005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht N. B., Davidson D. The presence of a common active subunit in low and high molecular weight murine DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 17;51(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman W. B. The presence of an exonuclease in highly purified DNA polymerase from bakers' yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):42–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer A. M., Hesslewood I. P., Johnston I. R. The occurrence of multiple activities in the high-molecular-weight DNA polymerase fraction of mammalian tissues. A preliminary study of some of their properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):487–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. A., Unrau P., Banks G. R., Holliday R. A temperature sensitive DNA polymerase mutant of Ustilago maydis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 7;242(114):14–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio242014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Eisenstadt J. M. Ribonucleic acids from the mitochondria of bleached Euglena gracilis Z. I. Isolation of mitochondria and extraction of nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Kitron N. Letter: Cytoplasmic DNA polymerase: polymeric forms and their conversion into an active monomer resembling nuclear DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from nuclei of sea urchin embryos. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 10;244(7):1672–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan A. G., Keir H. M. DNA polymerases of Euglena gracilis: heterogeneity of molecular weight and subunit structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):223–237. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan A. G., Keir H. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of Euglena gracilis. Primer-template utilization of and enzyme activities associated with the two deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of high molecular weight. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):239–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1510239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momparler R. L., Rossi M., Labitan A. Partial purification and properties of two forms of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):285–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönherr O. T., Wanka F. An investigation of DNA polymerase in synchronously growing Chlorella cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 25;232(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedwick W. D., Wang T. S., Korn D. Purification and properties of nuclear and cytoplasmic deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5026–5033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Mildvan A. S., Loeb L. A. Zinc in DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Tamir I., Loeb L. A., Mildvan A. S. The mechanism of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of the role of metals. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6784–6794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Muller R., Weissbach A. The dissimilitude of the low and high molecular weight deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2991–2992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. C. Effect of novobiocin on DNA-dependent DNA polymerases from developing rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A., Cummings D. J. DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities from Paramecia macronuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 20;378(2):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait R. C., Harris A. L., Smith D. W. DNA repair in Escherichia coli mutants deficient in DNA polymerases I, II and-or 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):675–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait R. C., Smith D. W. Roles for E. coli DNA polymerases I, II, and 3 in DNA replication. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):116–119. doi: 10.1038/249116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead E. The regulation of enzyme activity and allosteric transition. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:321–397. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(70)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Wintersberger E. Studies on deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases from yeast. 1. Parial purification and properties of two DNA polymerases from mitochondria-free cell extracts. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONEDA M., BOLLUM F. J. DEOXYNUCLEOTIDE-POLYMERIZING ENZYMES OF CALF THYMUS GLAND. I. LARGE SCALE PURIFICATION OF TERMINAL AND REPLICATIVE DEOXYNUCLEOTIDYL TRANSFERASES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3385–3391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Kondo T., Ando T. Multiple molecular species of cytoplasmic DNA polymerase from calf thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 24;353(4):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


