Abstract
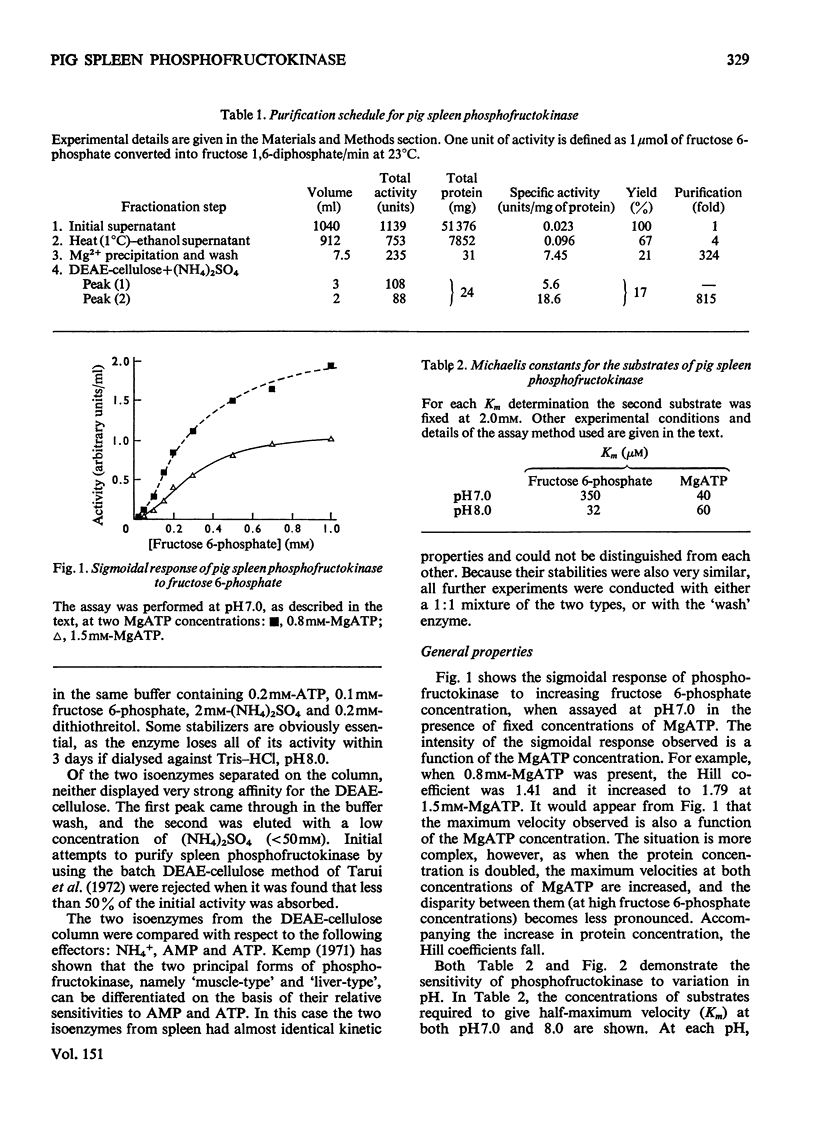
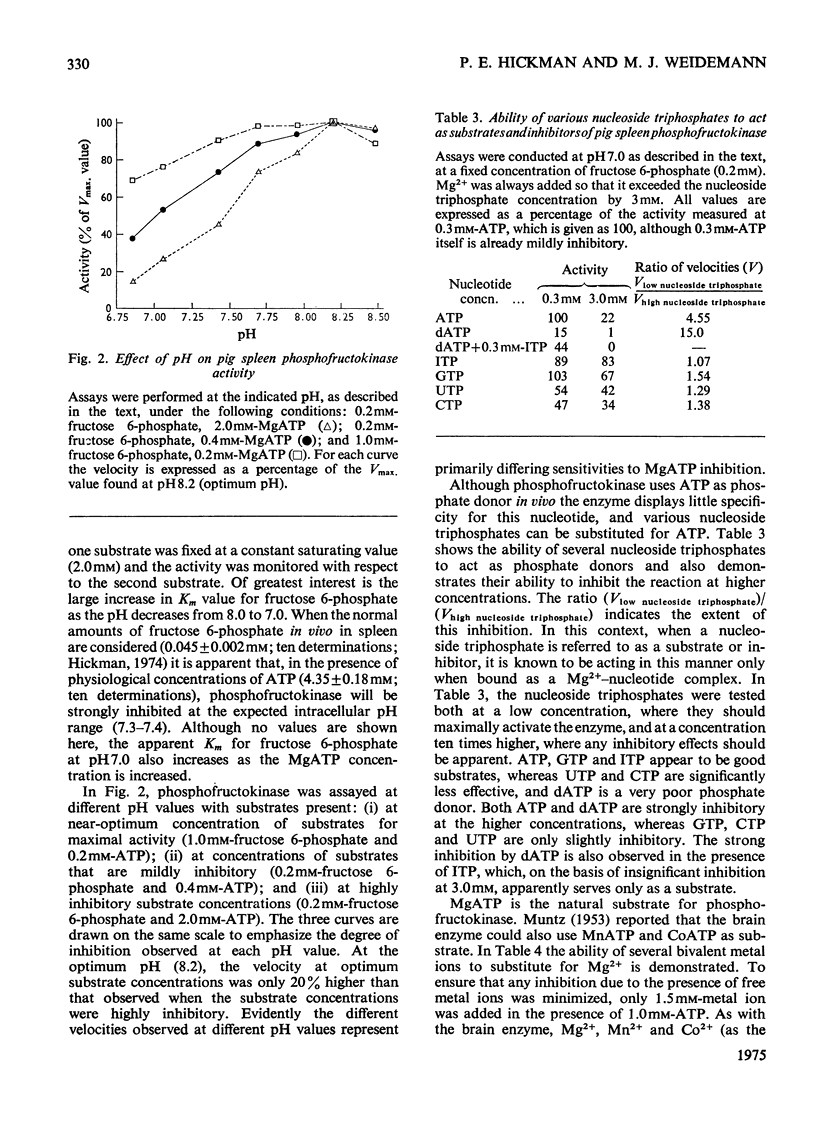
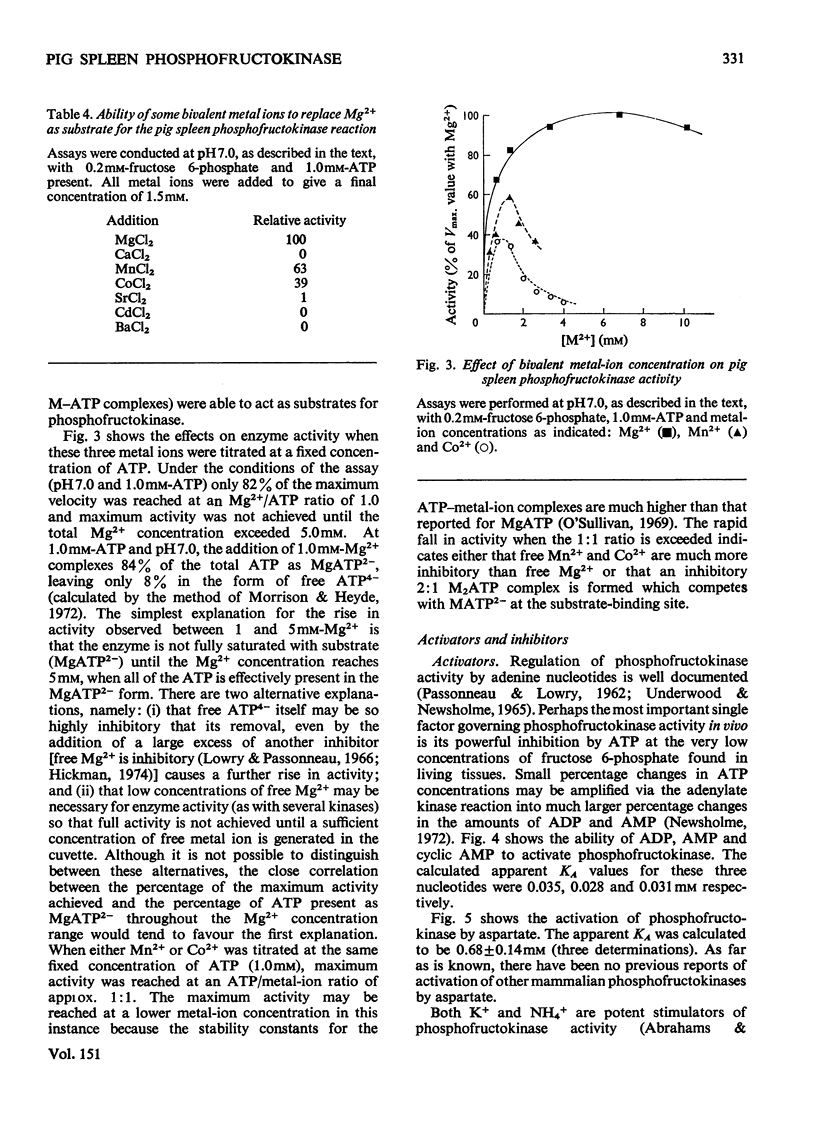
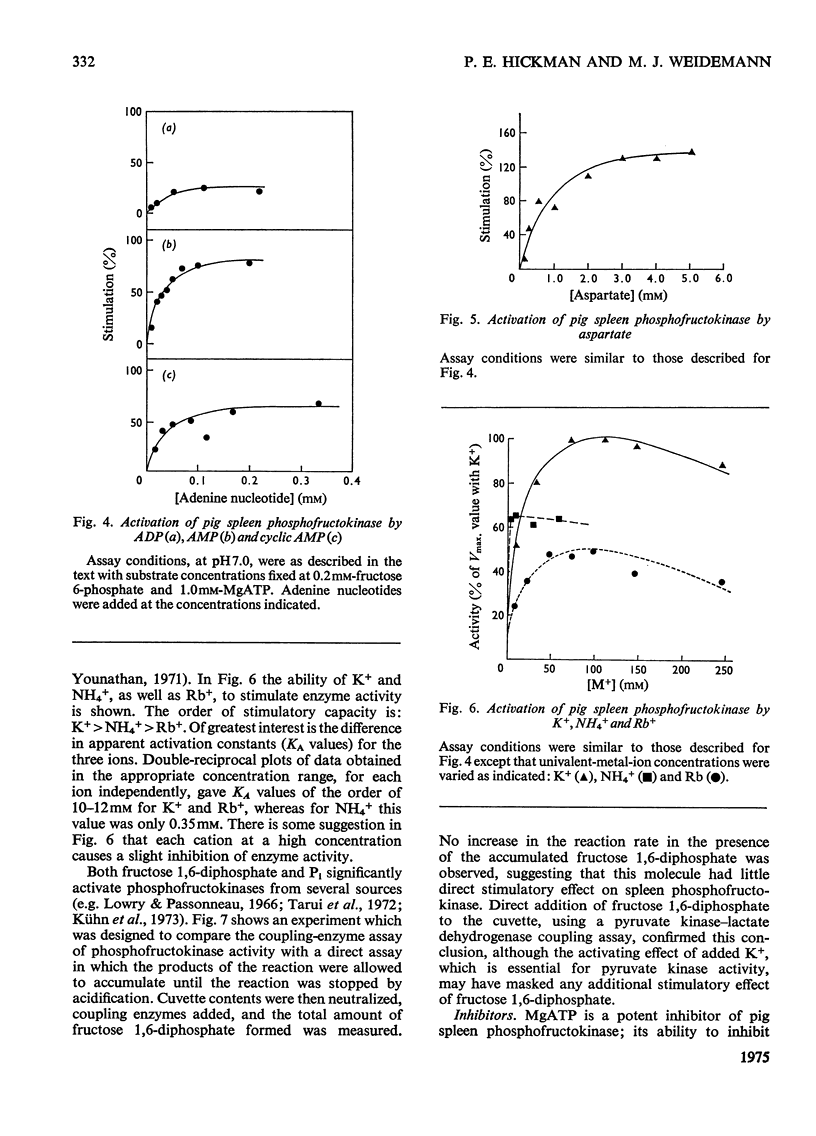
Pig spleen phosphofructokinase has been purified 800-fold with a yield of 17%. Two isoenzymes that appear to be kinetically identical can be separated by DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. In common with the enzyme from other mammalian sources, the spleen enzyme has a pH optimum of 8.2. At pH 7.0 it displays sigmoidal kinetics with respect to fructose 6-phosphate concentration but its co-operative behaviour is very dependent on pH, protein concentration and the concentration of MgATP. MgGTP and MgITP can replace MgATP as phosphate donors but, unlike MgATP, these nucleotides do not cause significant inhibition. Mn2+ and Co2+ (as the metal ion-ATP complexes) act as cofactors and in the free form are far more inhibitory than free Mg2+. The spleen enzyme responds to a wide variety of potential effector molecules: ADP, AMP, cyclic AMP, aspartate, NH4+, fructose 6-phosphate, fructose 1,6-diphosphate and Pi all act as either activators or protectors, whereas Mg-ATP, Mg2+, citrate, phosphoenol-pyruvate and the phosphoglucerates are inhibitors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams S. L., Younathan E. S. Modulation of the kinetic properties of phosphofructokinase by ammonium ions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2464–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum A. L., Gumaa K. A., McLean P. The distribution of hepatic metabolites and the control of the pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in animals of different dietary and hormonal status. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):617–663. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman P. E., Weidemann M. J. Modulation of phosphofructokinase activity by positive effectors. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G., Krebs E. G. Binding of metabolites by phosphofructokinase. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):423–434. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G. Rabbit liver phosphofructokinase. Comparison of some properties with those of muscle phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzanowski J., Matschinsky F. M. Regulation of phosphofructokinase by phosphocreatine and phosphorylated glycolytic intermediates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):816–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata N., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. Multiple forms of phosphofructokinase in rat tissues and rat tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn B., Jacobasch G., Rapoport S. M. Identity of sulfate and phosphate activation of the phosphofructokinase from erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jan 15;38(3):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING K. H., MARCUS F., LARDY H. A. PURIFICATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1893–1899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B., Rowland L. P., Bank W. J. Physical and kinetic properties of human phosphofructokinase from skeletal muscle and erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3823–3831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Passonneau J. V. Kinetic evidence for multiple binding sites on phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2268–2279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNTZ J. A., HURWITZ J. The effect of ammonium ions upon isolated reactions of the glycolytic scheme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jun;32(1):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNTZ J. A. Partial purification and some properties of brain phosphofructokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour T. E., Ahlfors C. E. Studies on heart phosphofructokinase. Some kinetic and physical properties of the crystalline enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2523–2533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey T. H., Deal W. C., Jr Unusual, metabolite-dependent solubility properties of phosphofructokinase. The basis for a new and rapid purification from liver, kidney, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. A kinetic analysis of coupled enzyme assays. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2782–2786. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F., Heyde E. Enzymic phosphoryl group transfer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):29–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Sugden P. H. The apparent inhibition of phosphofrunctokinase by reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide: a problem of coupled-enzyme assays. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(4):787–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1190787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A. The regulation of phosphofructokinase in muscle. Cardiology. 1971;56(1):22–34. doi: 10.1159/000169338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASSONNEAU J. V., LOWRY O. H. Phosphofructokinase and the Pasteur effect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Feb 20;7:10–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. C., Fall L., Walton G. M., Atkinson D. E. Interaction between energy charge and metabolite modulation in the regulation of enzymes of amphibolic sequences. Phosphofructokinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4041–4045. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter D., Weidemann M. J. Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in lymphoid tissue. Quantitative aspects of [U-14C]glucose oxidation by rat spleen slices. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):583–594. doi: 10.1042/bj1480583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarui S., Kono N., Uyeda K. Purification and properties of rabbit erythrocyte phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1138–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi B., Danforth W. H. Effect of pH on the kinetics of frog muscle phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):4110–4112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. Y., Kemp R. G. Isozymes of rabbit phosphofructokinase. Electrophoretic and immunochemical studies. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):785–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD A. H., NEWSHOLME E. A. PROPERTIES OF PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE FROM RAT LIVER AND THEIR RELATION TO THE CONTROL OF GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:868–875. doi: 10.1042/bj0950868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Oyama H. Rat thymocyte phosphofructokinase: some kinetic properties compared with those of muscle phosphofructokinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 19;284(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve P. D., Haghshenass M., Krevans J. R. Intracellular pH of the human lymphocyte. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1099–1102. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


