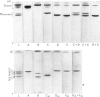
Abstract
1. The polypedtide chains that comprise the subunits of the tonofilaments, or th alpha-keratin component, of bovine epidermis were fractionated by combination of chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and preparative polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. 2. The seve polypeptide chains investigated had generalyy similar properties; all contained two residues per molecule of tryptophan and N-acetylserine was the common N-terminal amino acid residue. 3. On the basis of close similarities in alpha-helix content and amino acid composition, the polypeptide chains were classified into three distinct groups. Each group contained approximately one-third of the total polypeptides on a molar basis. The groups and designated polypeptides chain numbers were: group one, polypeptides 1a and 1b, which had moleculae weights of 58,000, contained about 25% alpha-helix, 86 glutamic acid and 8 cysteine residues per molecule, but which differed in net charge, extinction coefficients and tyrosine contents; group two, polypeptides 2, 3, and 4, which hadmolecular weights within thewithin the range of 52,00-56,000, contained about 48% alpha-helix, 54 glutamic acid and 6 cysteine residues per molecule, but which differed in extinction coefficients and tryosine contents; and group, polypeptides 5 and 6, which had molecular weights of 47000-48000, contained about 56% alpha-helix, 64 glutamic acid and 4 cysteine residues per molecule, but which differed in extinction coefficients and tyrosine contents...
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baden H. P., Bonar L. The alpha-fibrous proteins of epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Dec;51(6):478–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baden H. P., Goldsmith L. A., Fleming B. A comparative study of the physicochemical properties of human keratinized tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 18;322(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cotman C. W. Measurement of free electrophoretic mobility and retardation coefficient of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis. A method to validate molecular weight estimates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5856–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall S., Noack N., Wu M., Loewenberg J. R. A simple colorimetric method for determination of protein. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK F. H. C. Is alpha-keratin a coiled coil? Nature. 1952 Nov 22;170(4334):882–883. doi: 10.1038/170882b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaitonde M. K., Dovey T. A rapid and direct method for the quantitative determination of tryptophan in the intact protein. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):907–911. doi: 10.1042/bj1170907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehreke C. W., Nakamoto H., Zumwalt R. W. Gas-liquid chromatography of protein amino acid trimethylsilyl derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1969 Nov 25;45(1):24–51. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Peptides obtained by tryptic hydrolysis of performic acid-oxidized ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):623–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Rogers G. E. Differentiation of avian keratinocytes. Characterization and relationships of the keratin proteins of adult and embryonic feathers and scales. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):969–975. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. S., Goolsby S. P. A membrane filter assay for protein sulfhydryl groups. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):453–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPIENSKA-BLAUTH J., CHAREZINSKI M., BERBEC H. A new, rapid method of determining tryptophan. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jul;6:69–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. Compound helical configurations of polypeptide chains: structure of proteins of the alpha-keratin type. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):59–61. doi: 10.1038/171059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole T., Leach B. S., Fish W. W. Analysis of polypeptide molecular weights by electrophoresis in urea. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):596–607. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90272-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press E. M., Piggot P. J., Porter R. R. The N- and c-terminal amino acid sequences of the heavy chain from a pathological human immunoglobulin IgG. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):356–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0990356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Binding of dodecyl sulfate to proteins at high binding ratios. Possible implications for the state of proteins in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow D., Matoltsy A. G., Matoltsy M. N. Isolation and characterization of the helical regions of epidermal prekeratin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4820–4826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow D. The structure of prekeratin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1311–1316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rogers G. E. Characterization of the proteins of guinea-pig hair and hair-follicle tissue. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):759–771. doi: 10.1042/bj1350759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rogers G. E. In vitro studies on the synthesis of guinea pig hair keratin proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 23;312(2):403–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. The extraction and characterization of bovine epidermal alpha-keratin. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):39–48. doi: 10.1042/bj1490039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:121–282. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugel A. R., Chrambach A., Rodbard D. Fractionation and characterization of an oligomeric series of bovine keratohyalin by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):410–426. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]