Abstract
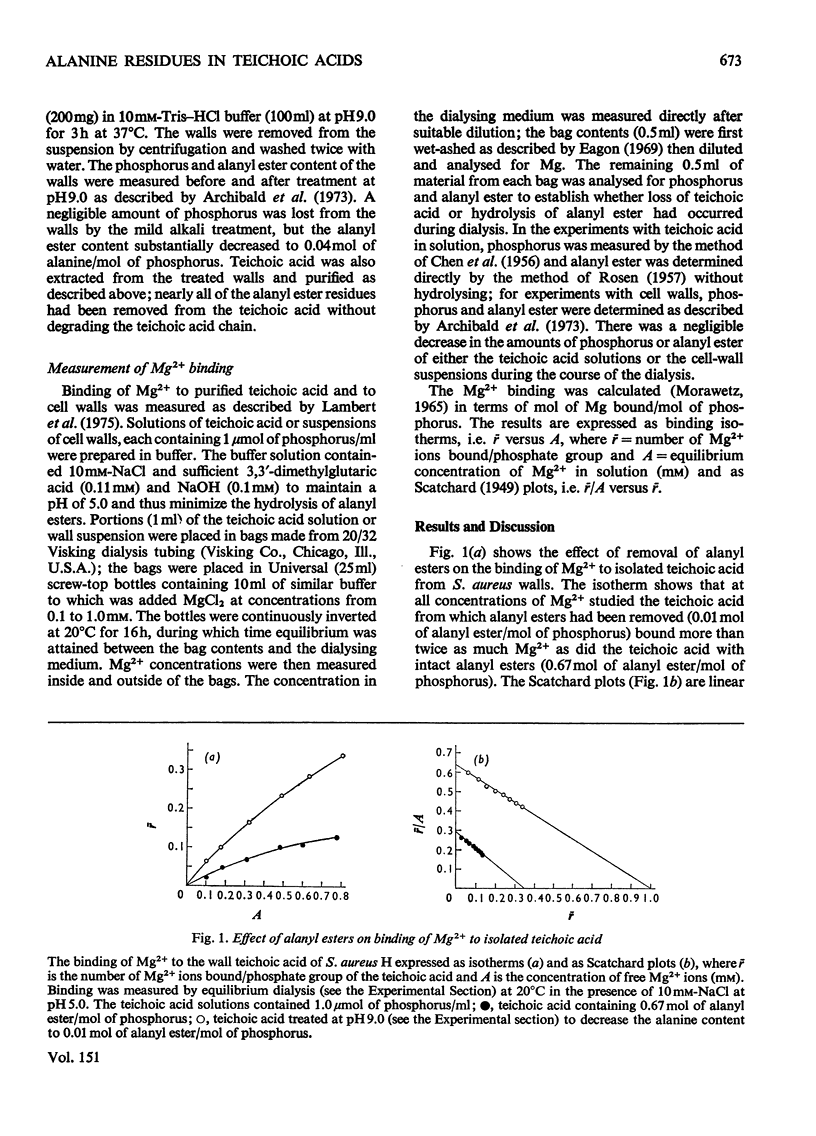
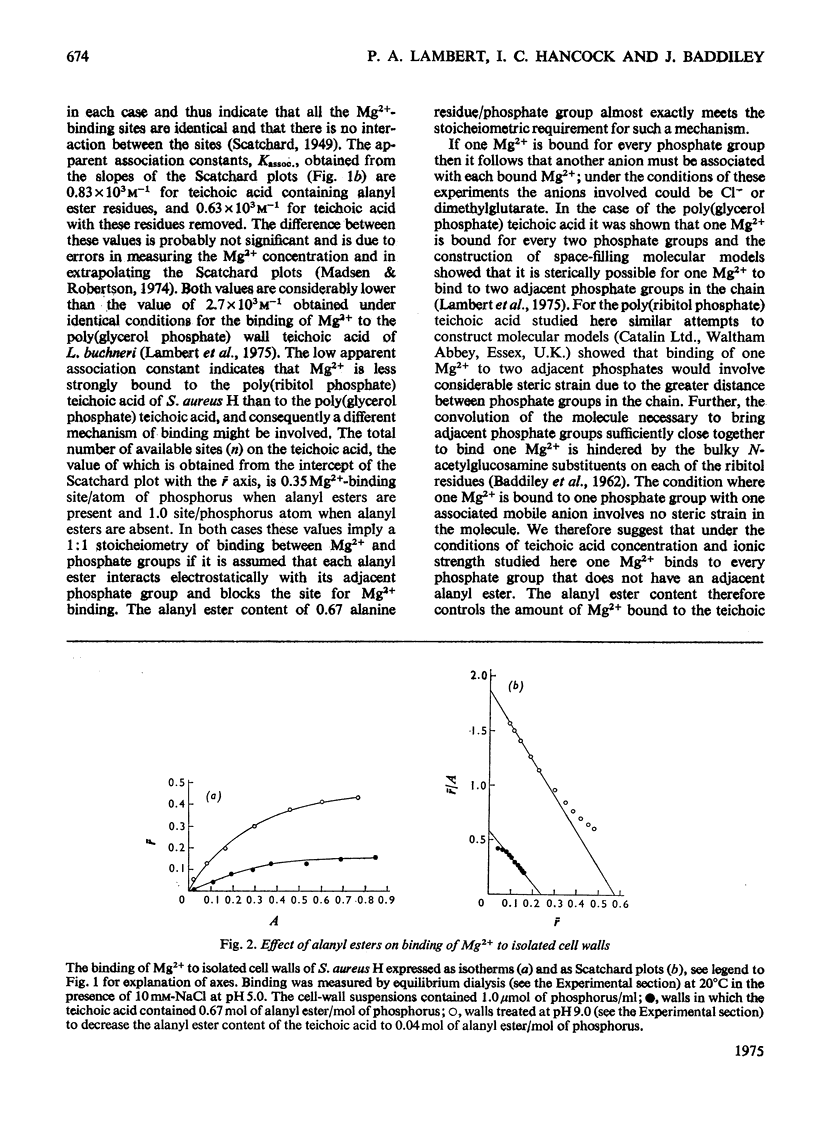
The binding of Mg2+ to the ribitol teichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus H walls was examined by equilibrium dialysis in solution and in the intact wall; the influence of alanyl ester groups on binding was determined. In solution the ribitol polymer had a lower affinity than did a glycerol teichoic acid and bound Mg2+ in the ratio Mg2+/P of 1:1. The presence of alanyl ester residues caused a decrease in the amount of cations bound in stoicheiometric proportion to the ratio Ala/P, but the affinity constant was unaltered. It is concluded that in solution the ribitol teichoic acid binds Mg2+ univalently to phosphate groups and univalently to a counter-ion. In the intact wall the binding of Mg2+ was different. The affinity constant was higher and resembled that of a glycerol teichoic acid. It is concluded that Mg2+ forms bridges across phosphate groups in teichoic acid chains lying adjacent to each other in the wall. The effect of alanyl esters was similar to that in solution, but Scatchard plots were not linear at low concentrations of Mg2+ where it was shown that the difference in affinities between walls with and without alanyl ester residues was much greater than it was at higher concentrations of Mg2+. Thus at very low concentrations of Mg2+ effective binding to the wall is markedly improved by loss of alanyl ester residues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Heptinstall S. The alanine ester content and magnesium binding capacity of walls of Staphylococcus aureus H grown at different pH values. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADDILEY J., BUCHANAN J. G., RAJBHANDARY U. L., SANDERSON A. R. Teichoic acid from the walls of Staphylococcus aureus H. Structure of the N-acetylglucosaminyl-ribitol residues. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:439–448. doi: 10.1042/bj0820439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J., Hancock I. C., Sherwood P. M. X-ray photoelectron studies of magnesium ions bound to the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Nature. 1973 May 4;243(5401):43–45. doi: 10.1038/243043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J. Teichoic acids in cell walls and membranes of bacteria. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:35–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Doyle R. J., Morgenstern M. Organization of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.726-734.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Helman J. R., Streips U. N. Distribution of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G. Cell wall-associated inorganic substances from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Feb;15(2):235–236. doi: 10.1139/m69-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C., Tempest D. W. Influence of culture pH on the content and composition of teichoic acids in the walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):395–402. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Collins-Thompson D. L., Shah B. G. Relationship between loss of magnesium and loss of salt tolerance after sublethal heating of Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1153–1158. doi: 10.1139/m74-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A., Duckworth M., Baddiley J. Loss of D-alanine during sublethal heating of Staphylococcus aureus S6 and magnesium binding during repair. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The interaction of magnesium ions with teichoic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1490519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen B. W., Robertson J. S. Improved parameter estimates in drug-protein binding studies by non-linear regression. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;26(10):807–813. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb09177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W. The influence of growth-limiting substrate and medium NaCl concentration on the synthesis of magnesium-binding sites in the walls of Bacillus subtilis var. niger. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):325–331. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky T. J., Chan M., Himes R. H., Akagi J. M. Effect of temperature on the growth and cell wall chemistry of a facultative thermophilic Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.858-865.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayman M. K., MacLeod R. A. Interaction of Mg-2+ with peptidoglycan and its relation to the prevention of lysis of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):650–659. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.650-659.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabyj B. M., Panos C. Teichoic acid of a stabilized L-form of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):934–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.934-942.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


