Abstract
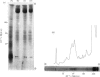
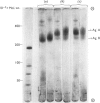
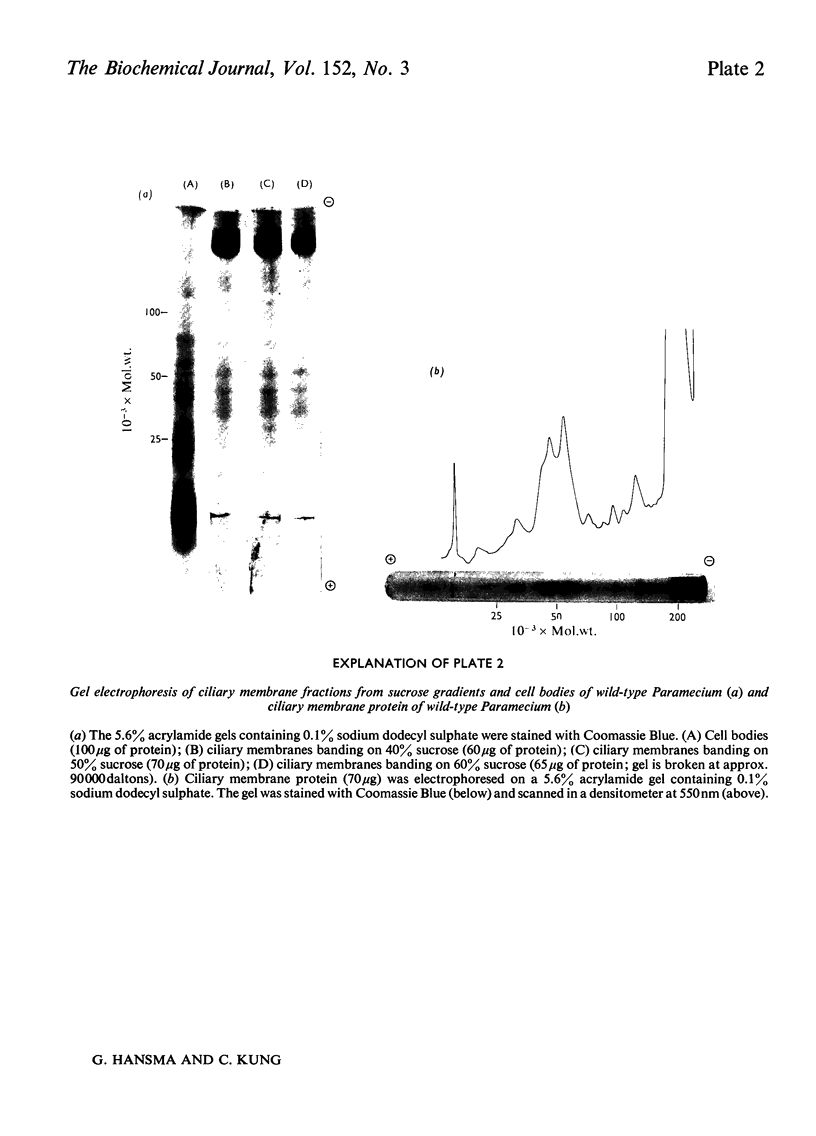
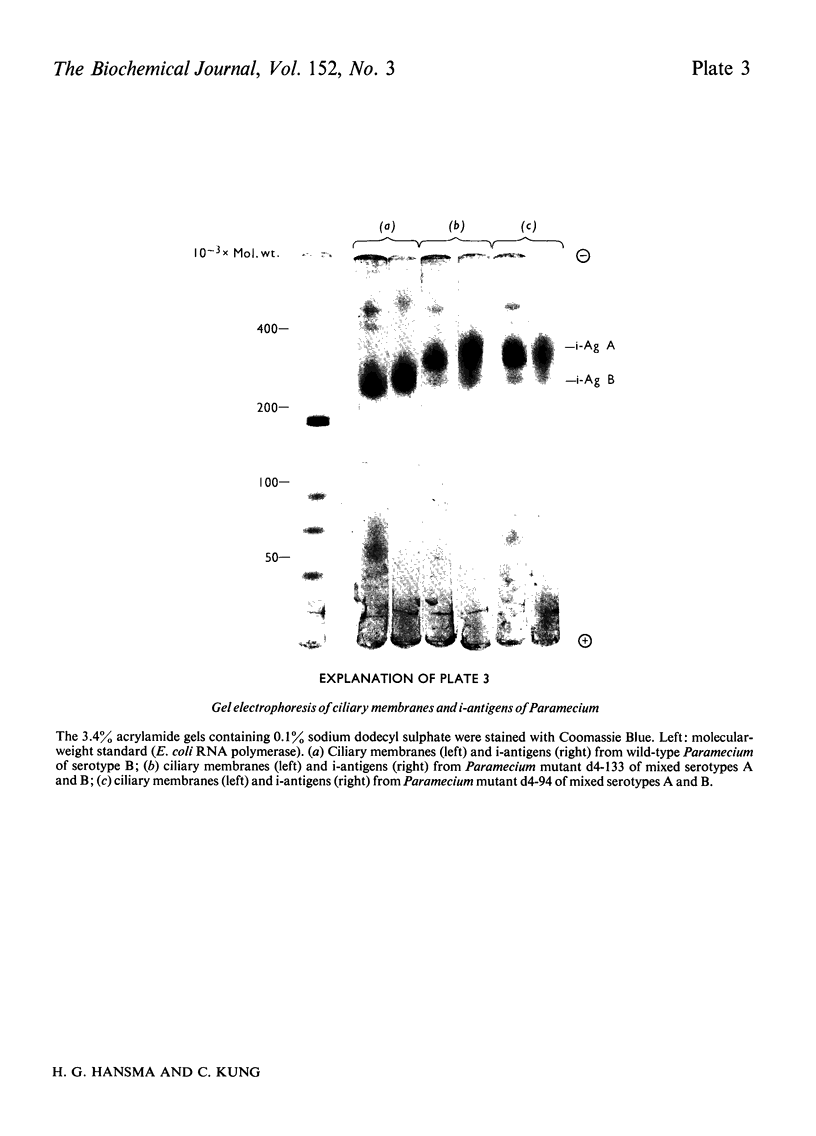
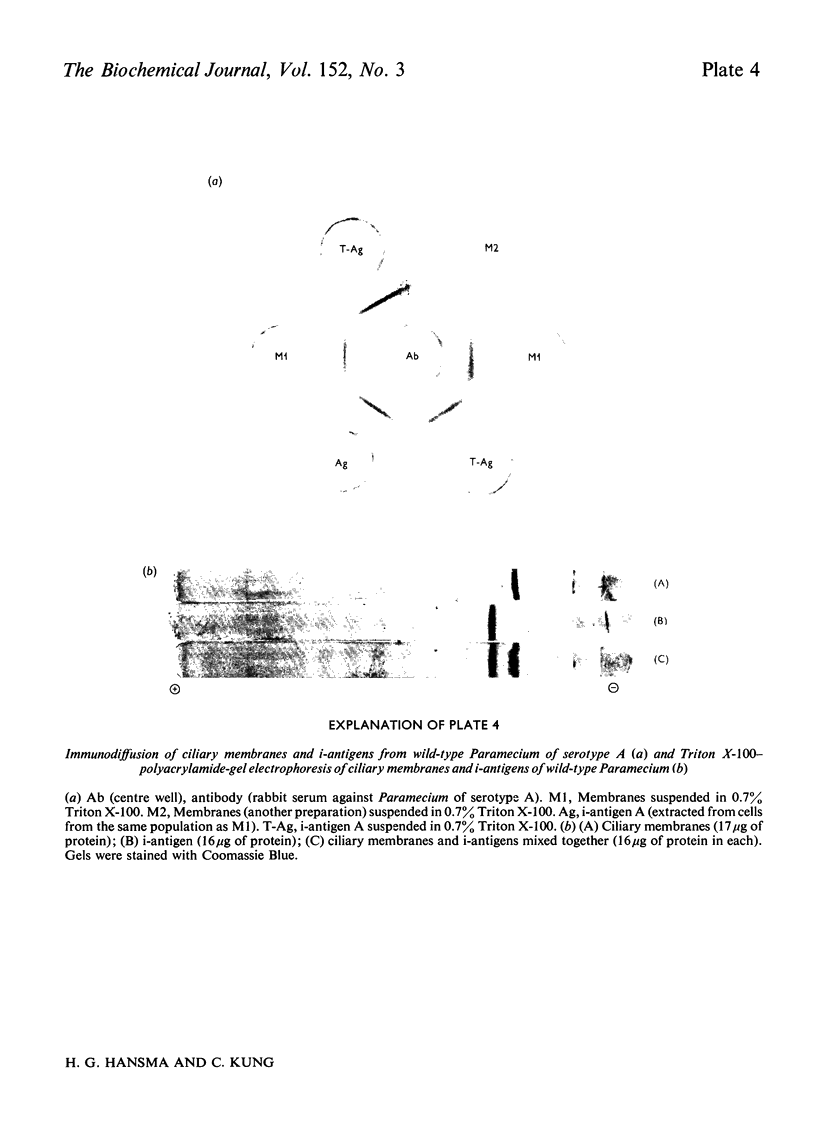
We have developed a procedure to isolate the ciliary membranes of Paramecium and have analysed the membrane proteins by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels containing either Triton X-100 or sodium dodecyl sulphate. The electrophoretic pattern on gels containing sodium dodecyl sulphate showed 12-15 minor bands of mol.wt. 25 000-150 000 and on major band of mol.wt. 200 000-300 000 that contained approximately three-quarters of the total membrane protein. 2. We present evidence that the major membrane protein is related to, but not identical with, the immobilization antigen (i-antigen), which is a large (250 000 mol.w.), soluble, surface protein of Paramecium. The similarity of the i-antigen and the major membrane protein was shown by immunodiffusion and by the electrophoretic mobilities in sodium dodecyl sulphate of these two proteins from Paramecium of serotypes A and B. The non-identity of these two proteins was shown by their different electrophoretic mobilities on Triton X-100 containing gels and their different solubilities. 3. We propose that the major membrane protein and the i-antigen have a precursor-product relationship.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benzer T. I., Raftery M. A. Partial characterization of a tetrodotoxin-binding component from nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3634–3637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. Bioelectric control of ciliary activity. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):473–481. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Characterization and partial purification of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
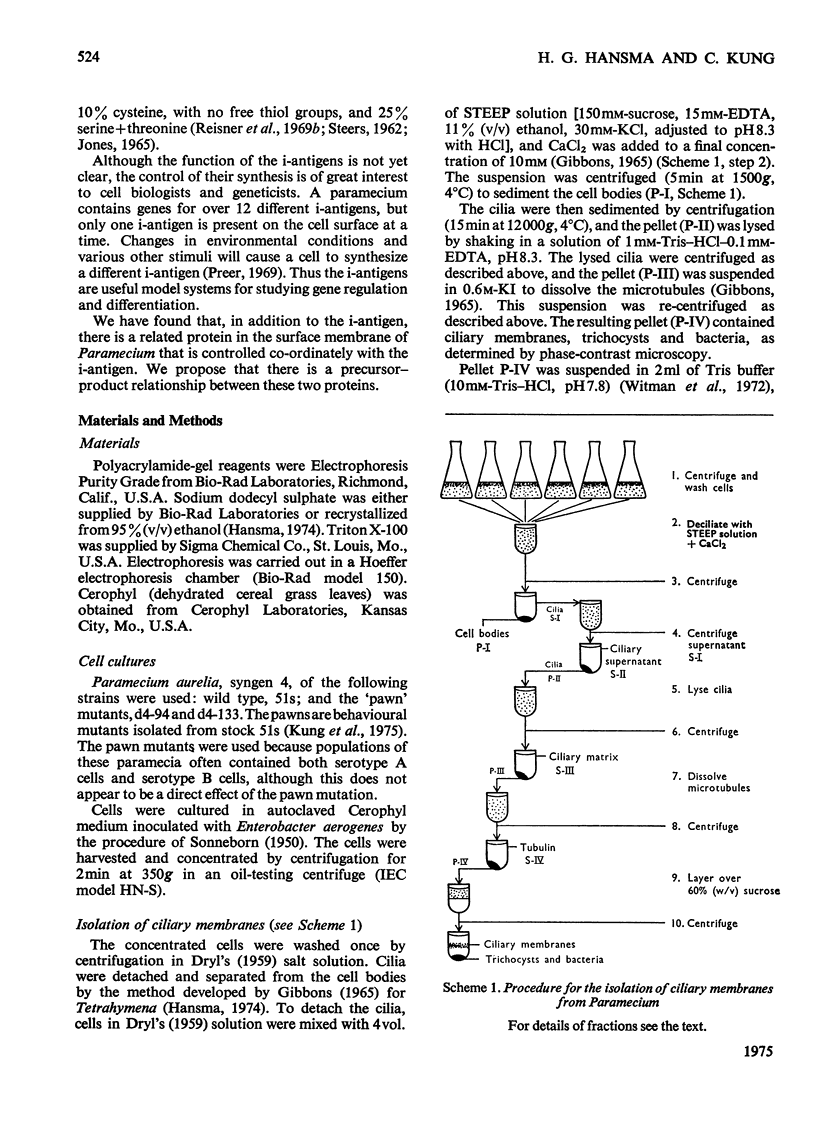
- Gibbons I. R. Chemical dissection of cilia. Arch Biol (Liege) 1965;76(2):317–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. Polypeptide components of an excitable plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6091–6094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:731–752. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G. The immobilization antigen of Paramecium aurelia is a single polypeptide chain. J Protozool. 1975 May;22(2):257–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES I. G. STUDIES ON THE CHARACTERIZATION AND STRUCTURE OF THE IMMOBILIZATION ANTIGENS OF PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:17–23. doi: 10.1042/bj0960017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D. Excitable membranes. Nature. 1972 Sep 1;239(5366):29–32. doi: 10.1038/239029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klett R. P., Fulpius B. W., Cooper D., Smith M., Reich E., Possani L. D. The acetylcholine receptor. I. Purification and characterization of a macromolecule isolated from Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6841–6853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Dearborn D. G., Wright P. L. Lipophosphonoglycan of the plasma membrance of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Isolation from whole amoebae and identification of the water-soluble products of acid hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3335–3341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung C., Chang S. Y., Satow Y., Houten J. V., Hansma H. Genetic dissection of behavior in paramecium. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):898–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macindoe H., Reisner A. H. Adsorption titration as a specific semi-quantitative assay for soluble and bound Paramecium serotypic antigen. Aust J Biol Sci. 1967 Feb;20(1):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREER J. R., Jr Studies on the immobilization antigens of Paramecium. II. Isolation. J Immunol. 1959 Oct;83:378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A. Isolation of acetylcholine receptor-- -bungarotoxin complexes from Torpedo californica electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Rowe J., Macindoe H. M. The largest known monomeric globular proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;188(2):196–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Rowe J., Sleigh R. W. Concerning the tertiary structure of the soluble surface proteins of Paramecium. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4637–4644. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satow Y., Kung C. Genetic dissection of active electrogenesis in Paramecium aurelia. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):69–71. doi: 10.1038/247069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Shore B. Some physical and chemical studies on two polypeptide components of high-density lipoproteins of human serum. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3396–3403. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steers E., Jr Electrophoretic Analysis of Immobilization Antigens of Paramecium aurelia. Science. 1961 Jun 23;133(3469):2010–2011. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3469.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Carlson K., Berliner J., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas flagella. I. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of microtubules, matrix, membranes, and mastigonemes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):507–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]