Abstract
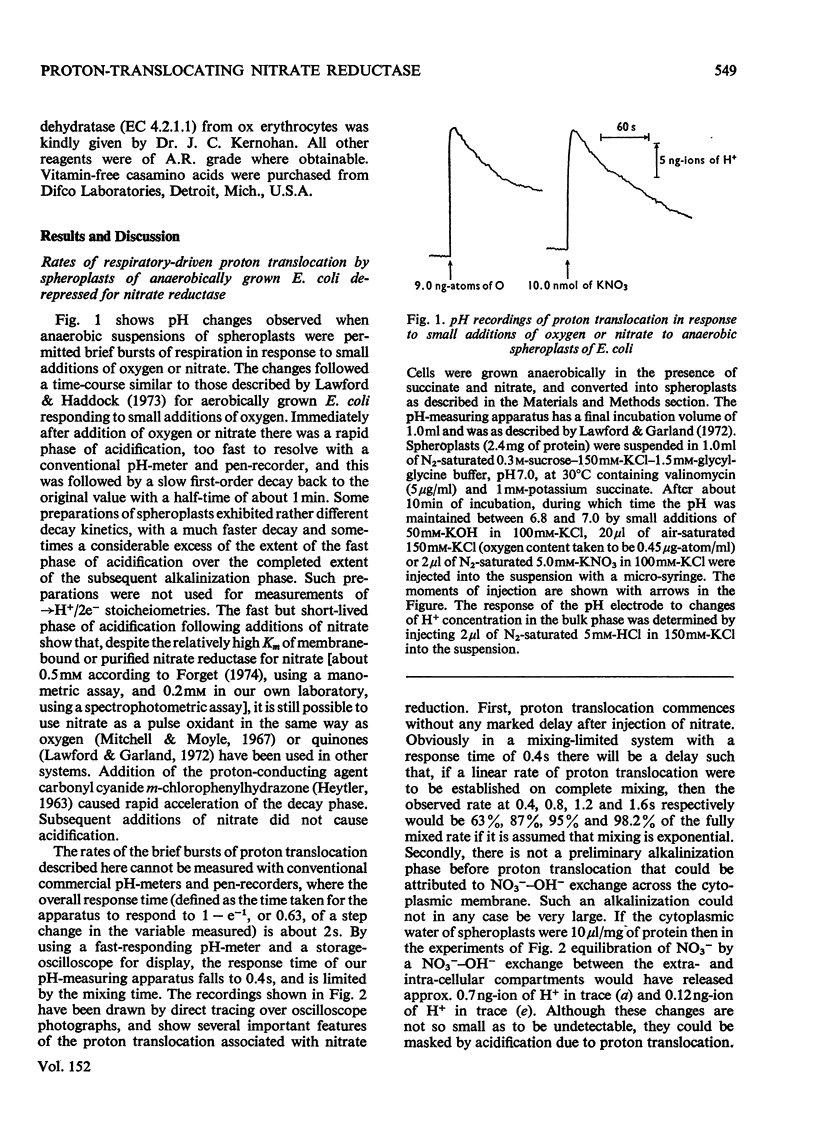
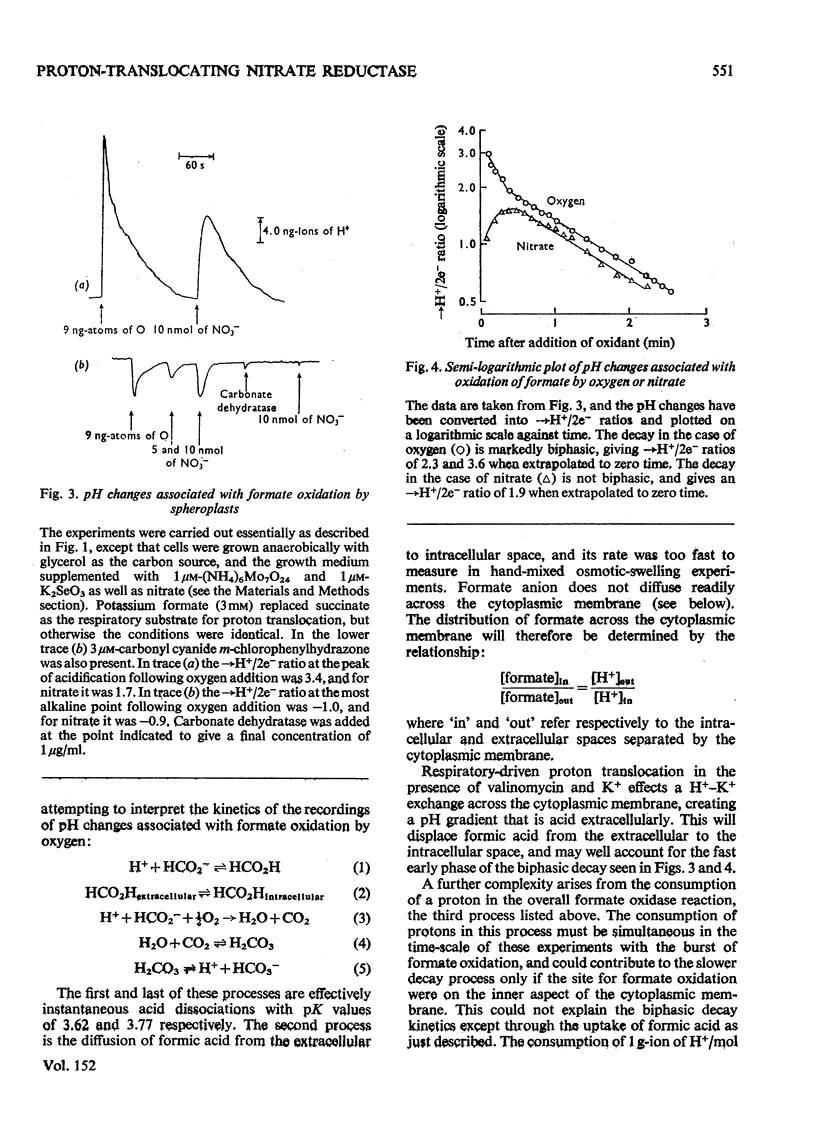
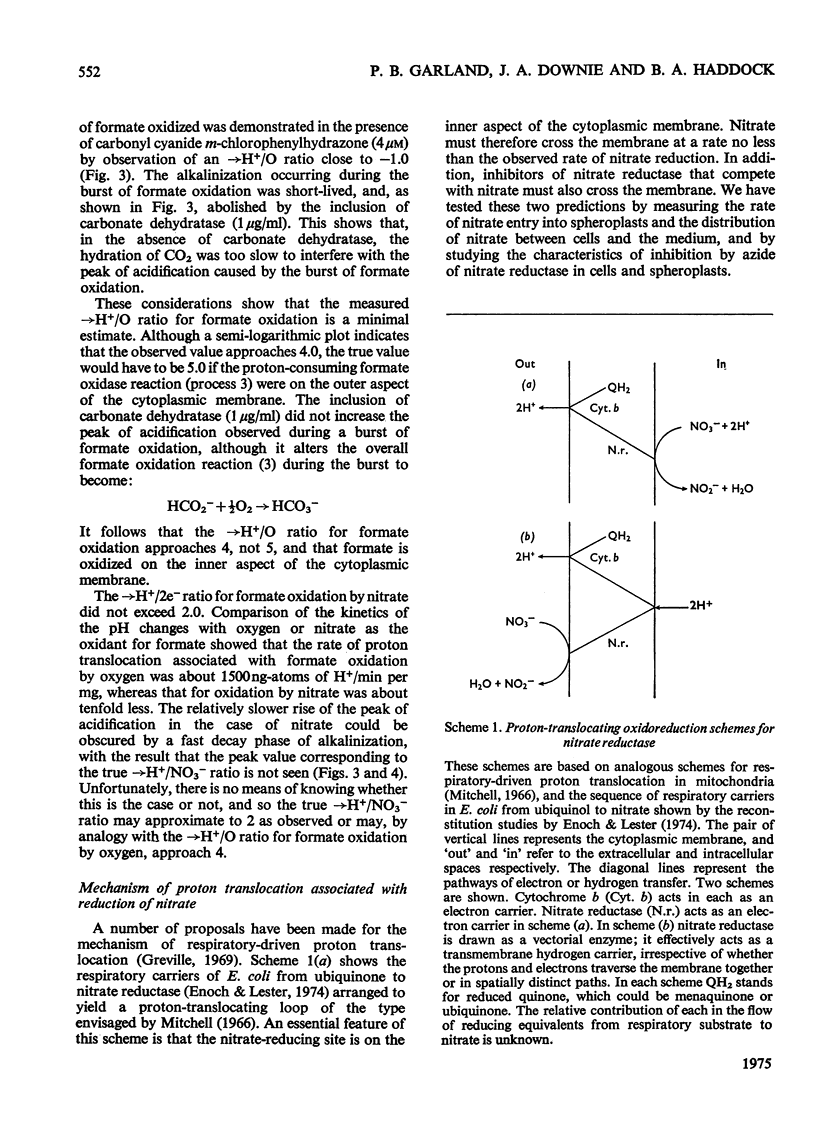
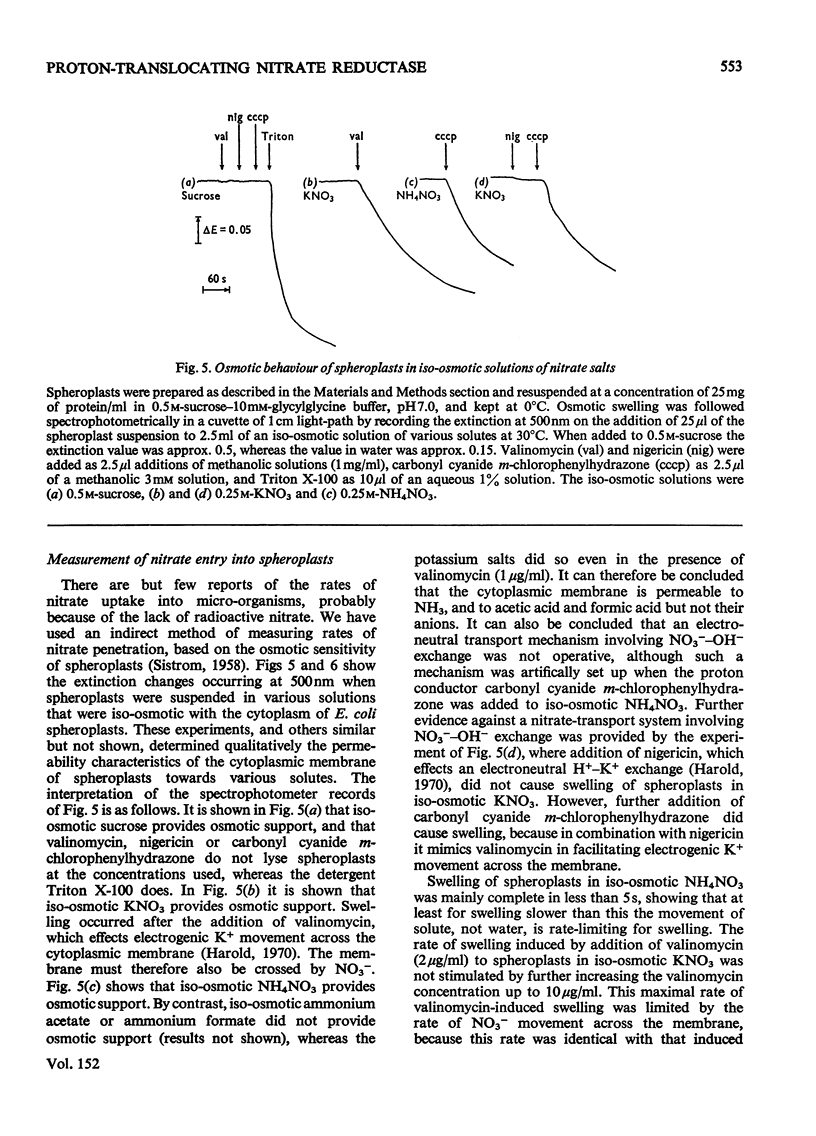
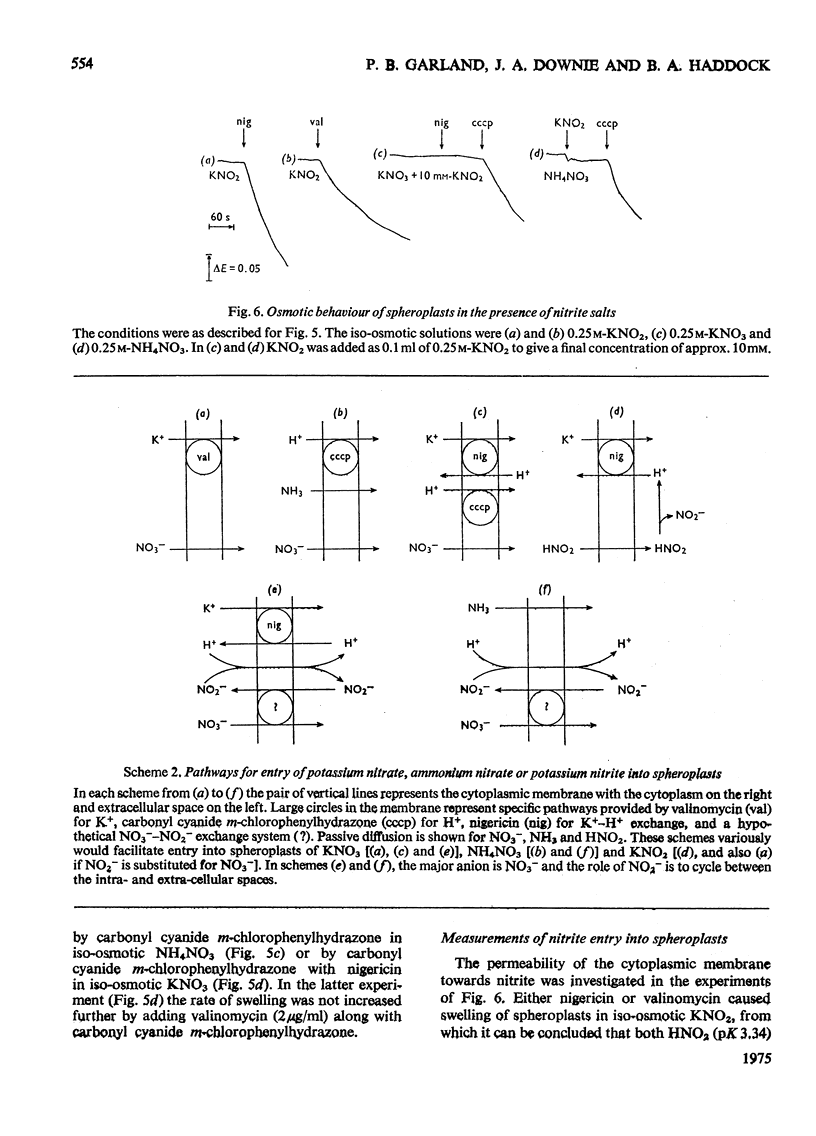
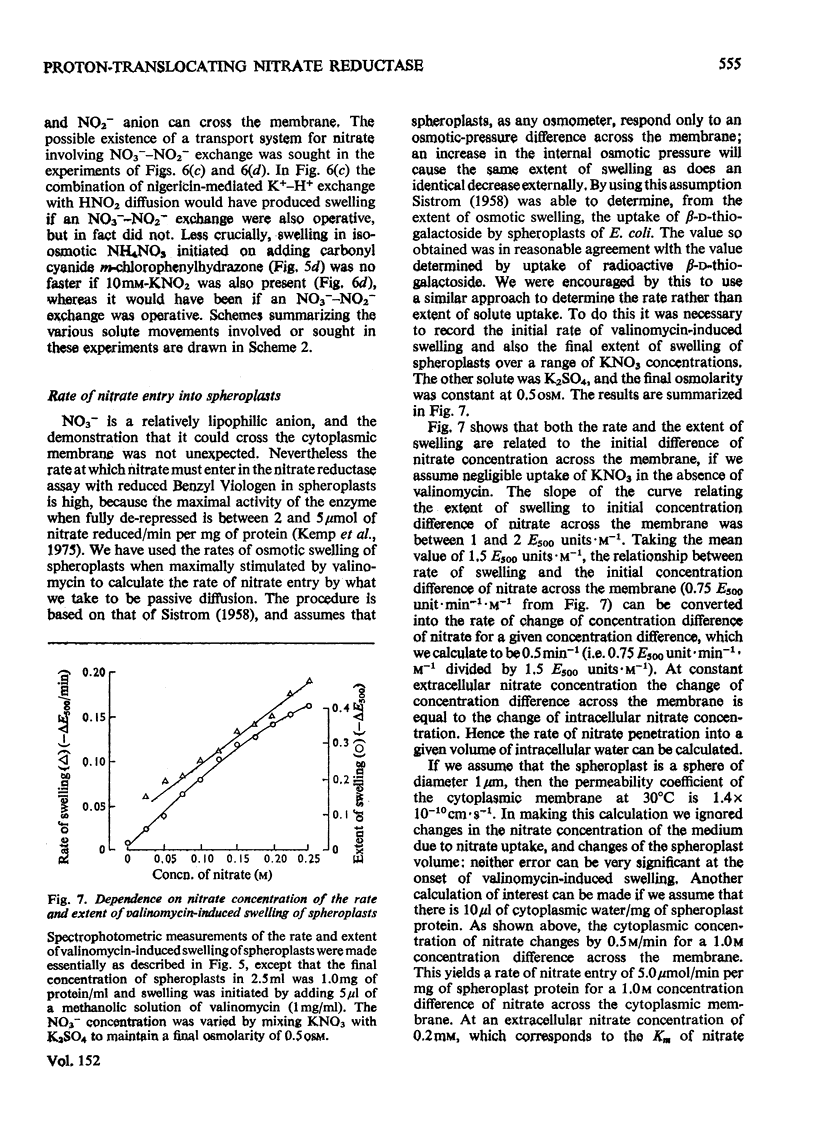
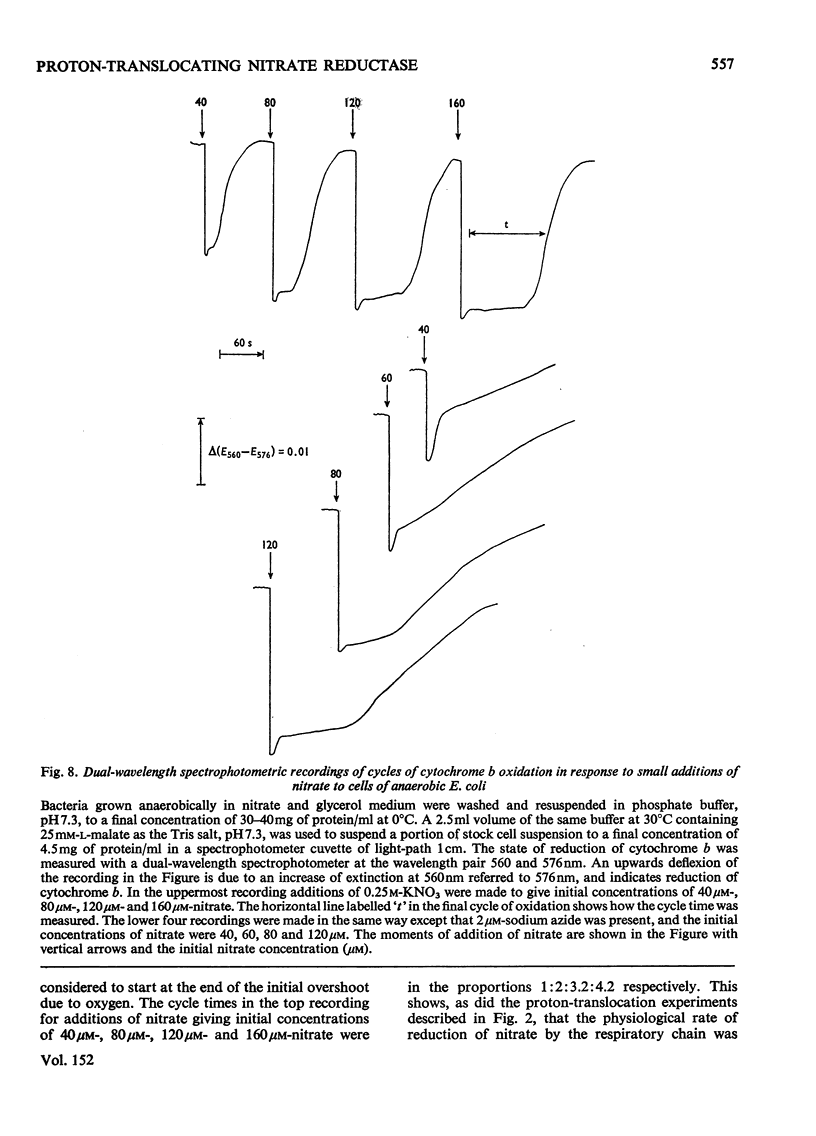
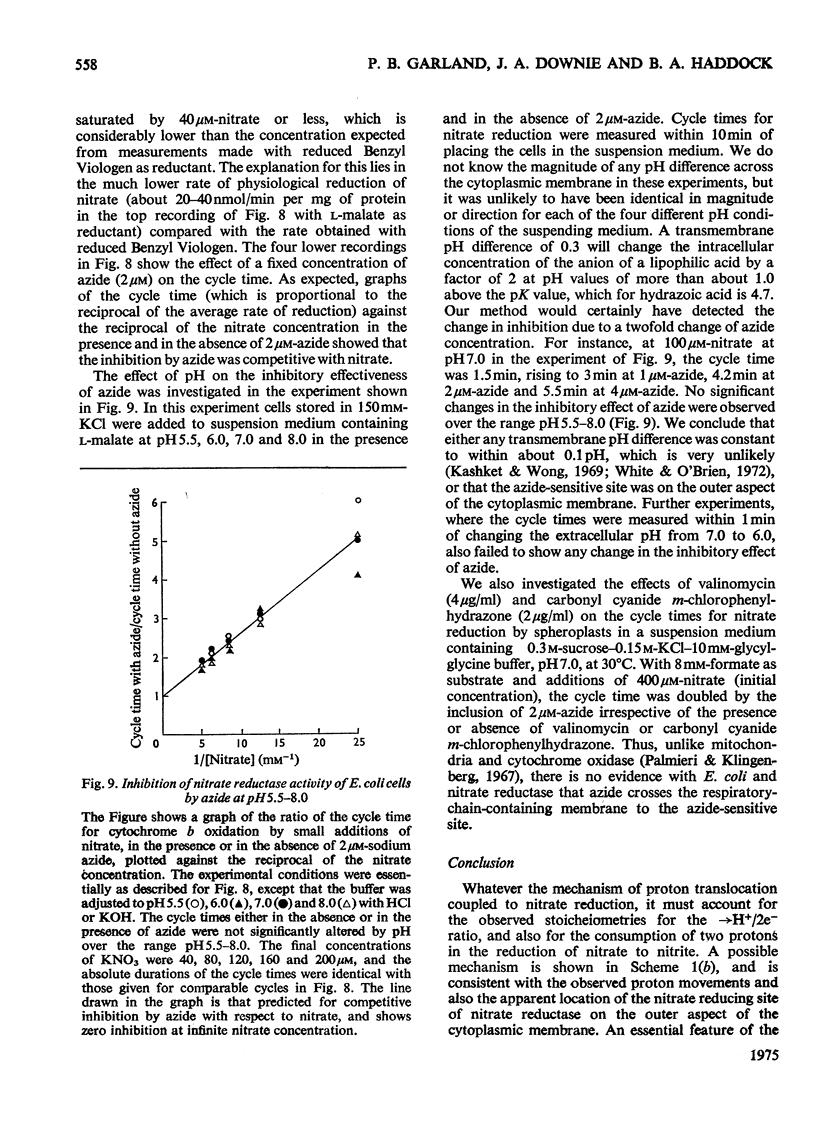
Stoicheometries and rates of proton translocation associated with respiratory reduction of NO3- have been measured for spheroplasts of Escherichia coli grown anaerobically in the presence of NO3-. Observed stoicheiometries [leads to H+/NO3- ratio; P. Mitchell (1966) Chemiosmotic Coupling in Oxidative and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation, Glynn Research, Bodmin] were approx. 4 for L-malate oxidation and approx. 2 for succinate, D-lactate and glycerol oxidation. Measurements of the leads to H+/2e- ratio with formate as the reductant and oxygen or NO3- as the oxidant were complicated by pH changes associated with formate uptake and CO2 formation. Nevertheless, it was possible to conclude that the site of formate oxidation is on the inner aspect of the cytoplasmic membrane, that the leads to H+/O ratio for formate oxidation is approx. 4, and that the leads to H+/NO3- ratio is greater than 2. Measurements of the rate of NO3- penetration into osmotically sensitive spheroplasts demonstrated an electrogenic entry of NO3- anion. The permeability coefficient for nitrate entry at 30 degrees C was between 10(-9) and 10(-10) cm- s(-1). The calculated rate of nitrate entry at the concentration typically used for the assay of nitrate reductase (EC 1.7.99.4) activity was about 0.1% of that required to support the observed rate of nitrate reduction by reduced Benzyl Viologen. Measurements of the distribution of nitrate between the intracellular and extracellular spaces of a haem-less mutant, de-repressed for nitrate reductase but unable to reduce nitrate by the respiratory chain, showed that, irrespective of the presence or the absence of added glucose, nitrate was not concentrated intracellularly. Osmotic-swelling experiments showed that the rate of diffusion of azid anion across the cytoplasmic membrane is relatively low in comparison with the fast diffusion of hydrazoic acid. The inhibitory effect of azide on nitrate reductase was not altered by treatments that modify pH gradients across the cytoplasmic membrane. It is concluded that the nitrate-reducing azide-sensitive site of nitrate reductase is located on the outer aspect of the cytoplasmic membrane. The consequences of this location for mechanisms of proton translocation driven by nitrate reduction are discussed, and lead to the proposal that the nitrate reductase of the cytoplasmic membrane is vectorial, reducing nitrate on the outer aspect of the membrane with 2H+ and 2e- that have crossed from the inner aspect of the membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Hirata H., Harold F. M. Accumulation of lipid-soluble ions and of rubidium as indicators of the electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1405–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. H., Danchin A., Grunberg-Manago M. Denaturation of UGA suppressor tRNA-Trp from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell J. B. The oxidation of citrate, isocitrate and cis-aconitate by isolated mitochondria. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj0900225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. A. The size of nitrate reductase in Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):691–694. doi: 10.1042/bst0030691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. Effects of molybdate, tungstate, and selenium compounds on formate dehydrogenase and other enzyme systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1032-1040.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The role of a novel cytochrome b-containing nitrate reductase and quinone in the in vitro reconstruction of formate-nitrate reductase activity of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget P. The bacterial nitrate reductases. Solubilization, purification and properties of the enzyme A of Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYTLER P. G. uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation by carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazones. I. Some characteristics of m-Cl-CCP action on mitochondria and chloroplasts. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:357–361. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A. The reconstitution of oxidase activity in membranes derived from a 5-aminolaevulinic acid-requiring mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):877–884. doi: 10.1042/bj1360877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P., Mitchell P. Effect of membrane potential on equilibrium poise between cytochrome a and cytochrome c in rat liver mitochondria. J Bioenerg. 1970 Jun;1(1):45–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01516088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Brice J. M., Downs A. J., Drozd J. W. Bacterial respiration-linked proton translocation and its relationship to respiratory-chain composition. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wong P. T. The intracellular pH of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford H. G., Garland P. B. Proton translocation coupled to quinone reduction by reduced nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide in rat liver and ox heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1029–1044. doi: 10.1042/bj1301029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford H. G., Haddock B. A. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):217–220. doi: 10.1042/bj1360217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Anaerobic cytochrome b1 in Escherichia coli: association with and regulation of nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1111-1116.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Synthesis of nitrate reductase components in chlorate-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1117-1121.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Jones C. W. Oxidative phosphorylation in bacteria which contain different cytochrome oxidases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):144–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri F., Klingenberg M. Inhibition of respiration under the control of azide uptake by mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jun;1(4):439–446. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Herrera J., Showe M. K., DeMoss J. A. Nitrate reductase complex of Escherichia coli K-12: isolation and characterization of mutants unable to reduce nitrate. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1291-1297.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. On the physical state of the intracellularly accumulates substrates of beta-galactoside-permease in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Micrococcus denitrificans. J Bioenerg. 1971 Sep;1(3):309–323. doi: 10.1007/BF01516290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synthesis and sideedness of membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase (EC1.7.99.4) in Escherichia coli lacking cytochromes. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):329–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. C., PARDEE A. B. Regulation of flavin synthesis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:283–303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I., Mitchell P. Proton-coupled beta-galactoside translocation in non-metabolizing Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg. 1972 Aug;3(5):445–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01516082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., O'Brien W. M. The buffer value and transmembrane potential of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):780–785. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


