Abstract
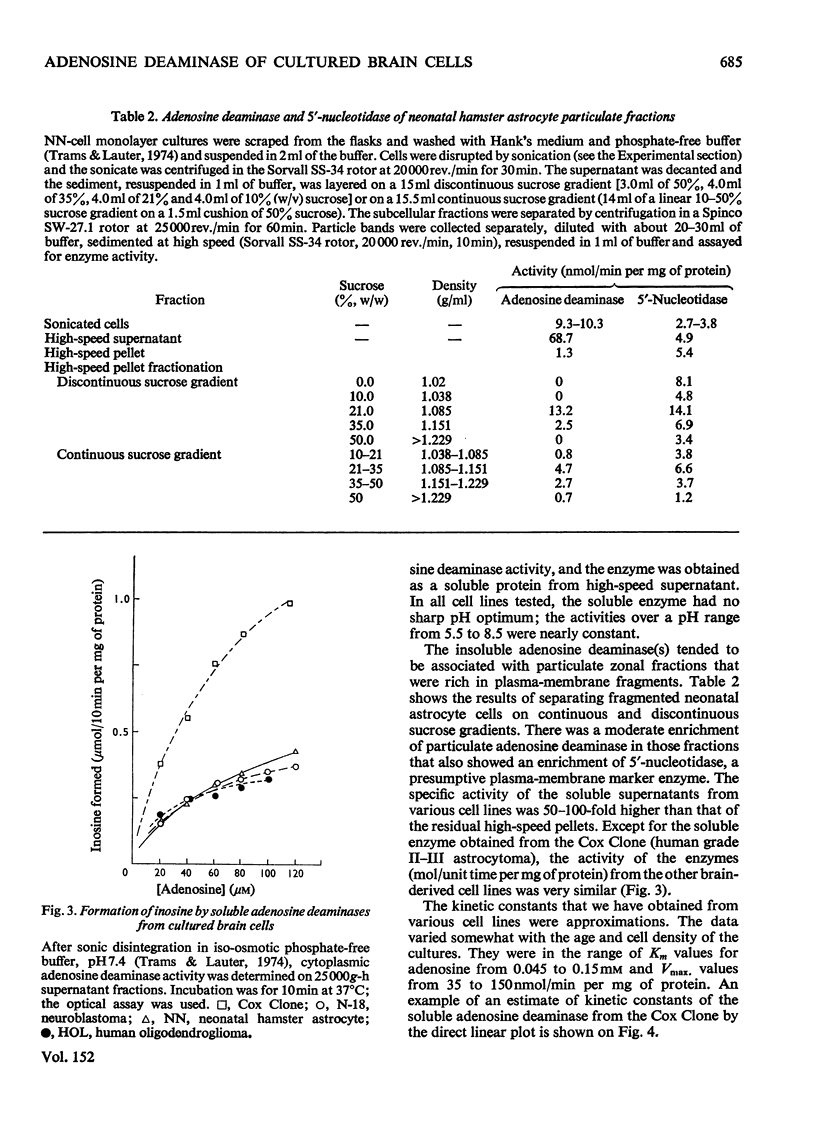
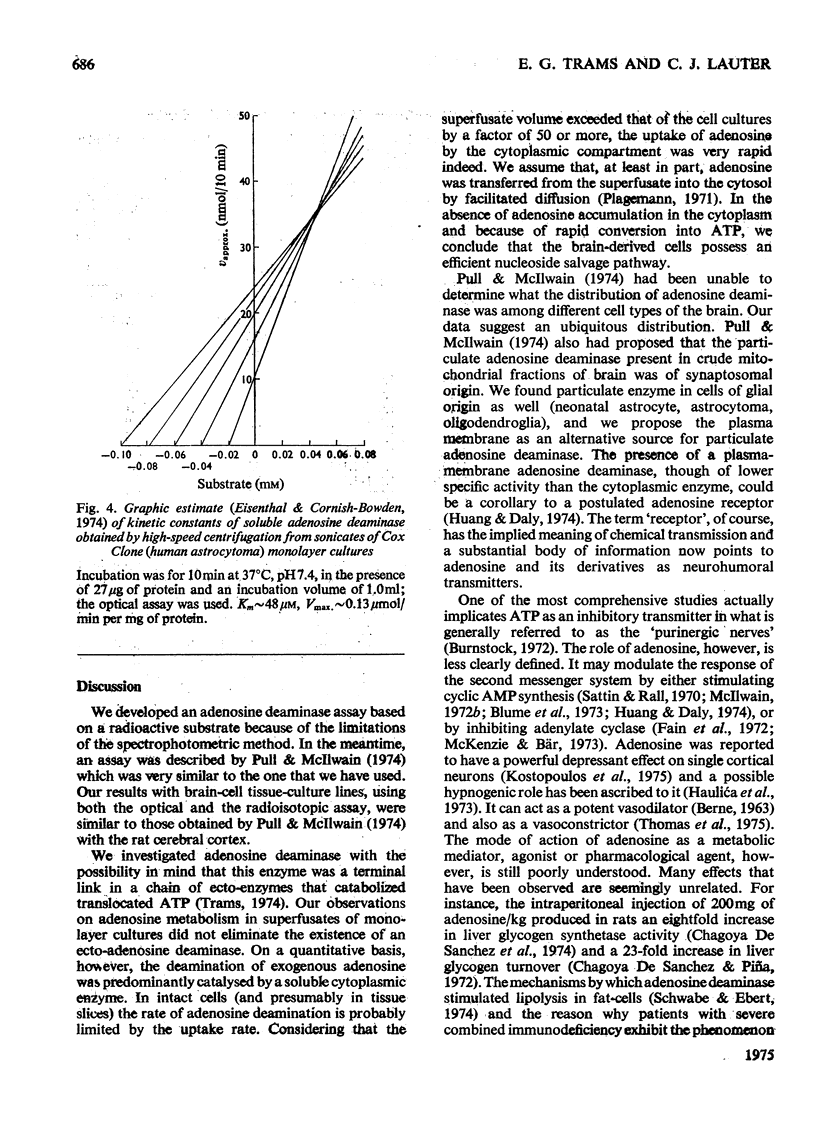
Two types of adenosine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.4) were found in cultured cells of central-nervous-system origin. The predominant and more active enzyme was obtained in soluble form from the cytosol of mouse neuroblastoma (N-18), neonatal hamster astrocytes (NN), human oligodendroglioma (HOL) and human astrocytoma (Cox Clone). Particulate adenosine deaminase was probably associated with the plasma membrane. When radioactive adenosine was added to superfusates of monolayer cultures it was rapidly converted into inosine and hypoxanthine. The metabolic conversion required adenosine uptake by the cells, a probable transition through the intracellular ATP pool(s) and a rapid excretion into the superfusate of the catabolic products. We discuss the evidence that points to adenosine and its derivatives as neurohumoral modulators of central-nervous-system function.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNE R. M. Cardiac nucleotides in hypoxia: possible role in regulation of coronary blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1963 Feb;204:317–322. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J., Dalton C., Sheppard H. Adenosine-mediated elevation of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate concentrations in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3099–3102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagoya de Sánchez V., Brunner A., Sánchez M. E., López C., Piña E. Utilization of adenosine as a tool in studies on the regulation of liver glycogen biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sanchez V. C., Piña E. Adenosine, a glucogenic and lipogenic compound. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 1;19(4):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Karnovsky M. L. Ecto-enzymes of the guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocyte. I. Evidence for an ecto-adenosine monophosphatase, adenosine triphosphatase, and -p-nitrophenyl phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7111–7120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. Nucleotide pyrophosphatase, a sialoglycoprotein located on the hepatocyte surface. Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):391–394. doi: 10.1038/250391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Pointer R. H., Ward W. F. Effects of adenosine nucleosides on adenylate cyclase, phosphodiesterase, cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation, and lipolysis in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6866–6872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haulică I., Ababei L., Brănişteanu D., Topoliceanu F. Letter: Preliminary data on the possible hypnogenic role of adenosine. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):1019–1020. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Daly J. W. Adenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in brain slices: potentiation by agents which inhibit uptake of adenosine. Life Sci. 1974 Feb 1;14(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Stefanovic V., Ciesielski-Treska J., Ebel A. ATPase activity at the cell surface of astroglia in culture. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):337–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80875-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. Regulatory significance of the release and action of adenine derivatives in cerebral systems. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(36):69–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. G., Bär H. P. On the mechanism of adenyl cyclase inhibition by adenosine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;51(3):190–196. doi: 10.1139/y73-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Gelfand E. W., Rosen F. S., Sanderson A., Hirschhorn R. Severe combined immunodeficiency and adenosine deaminase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1975 Apr 3;292(14):714–719. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197504032921402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pataki G. Thin-layer chromatography of nucleic acid bases, nucleosides, nucleotides and related compounds. 3. Separation of complex mixtures on cellulose layers. J Chromatogr. 1967 Jul;29(1):126–132. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92637-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Nucleotide pools of Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. I. Kinetics of incorporation of nucleosides into nucleotide pools and pool sizes during growth cycle. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):213–240. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Metabolism of ( 14 C)adenine and derivatives by cerebral tissues, superfused and electrically stimulated. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):965–973. doi: 10.1042/bj1260965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Rat cerebral-cortex adenosine deaminase activity and its subcellular distribution. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):37–41. doi: 10.1042/bj1440037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert W. H., Lauter C. J., Trams E. G. Inorganic pyrophosphatase in cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 29;370(2):556–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Ebert R. Stimulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation and lipolysis in fat cells by adenosine deaminase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;282(1):33–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00647401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Creveling C. R., Daly J. Stimulated formation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in cerebral cortex: synergism between electrical activity and biogenic amines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trams E. G. Evidence for ATP action on the cell surface. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):480–482. doi: 10.1038/252480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trams E. G., Lauter C. J. On the sidedness of plasma membrane enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):180–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


