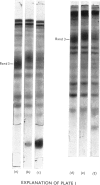
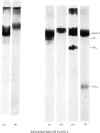
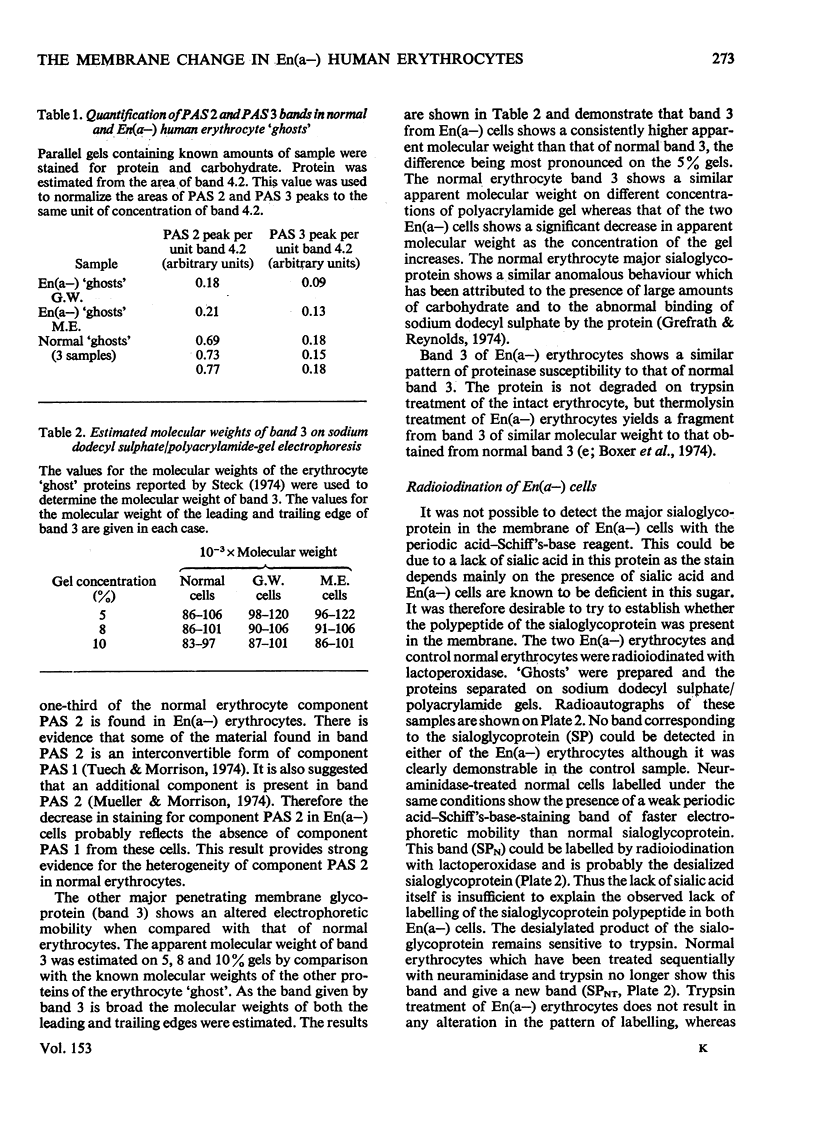
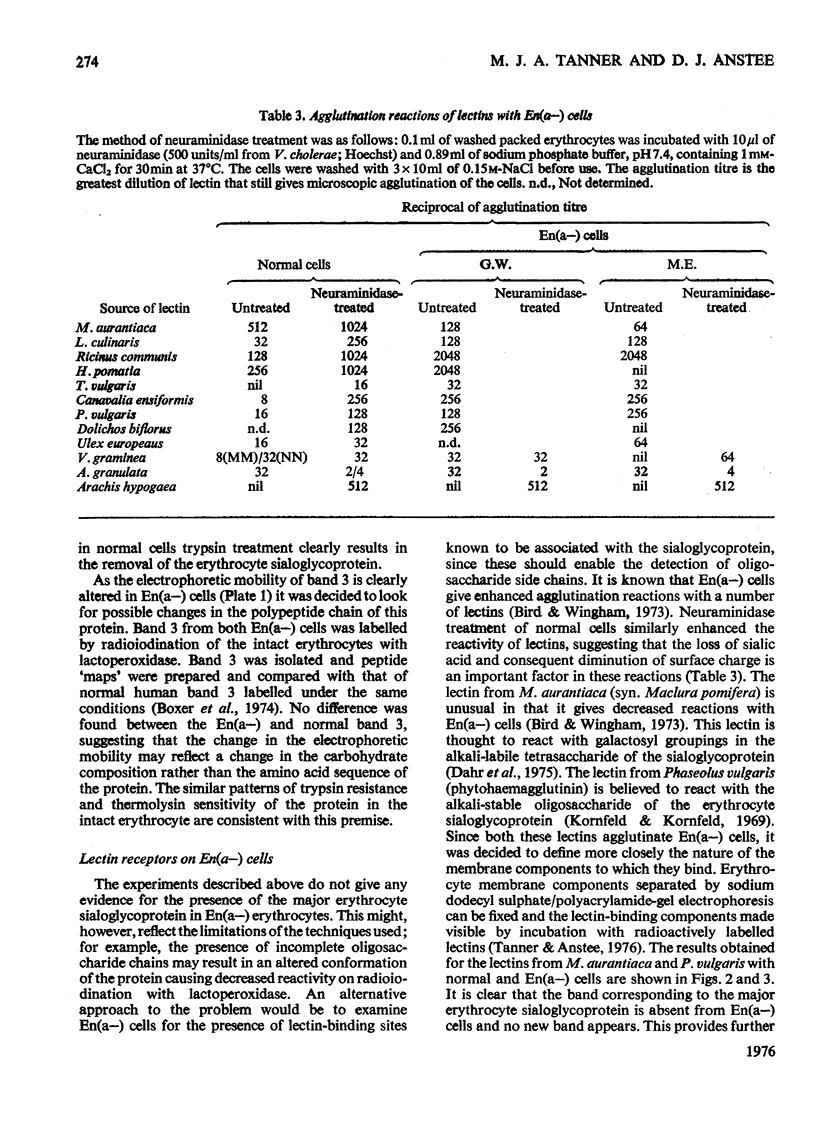
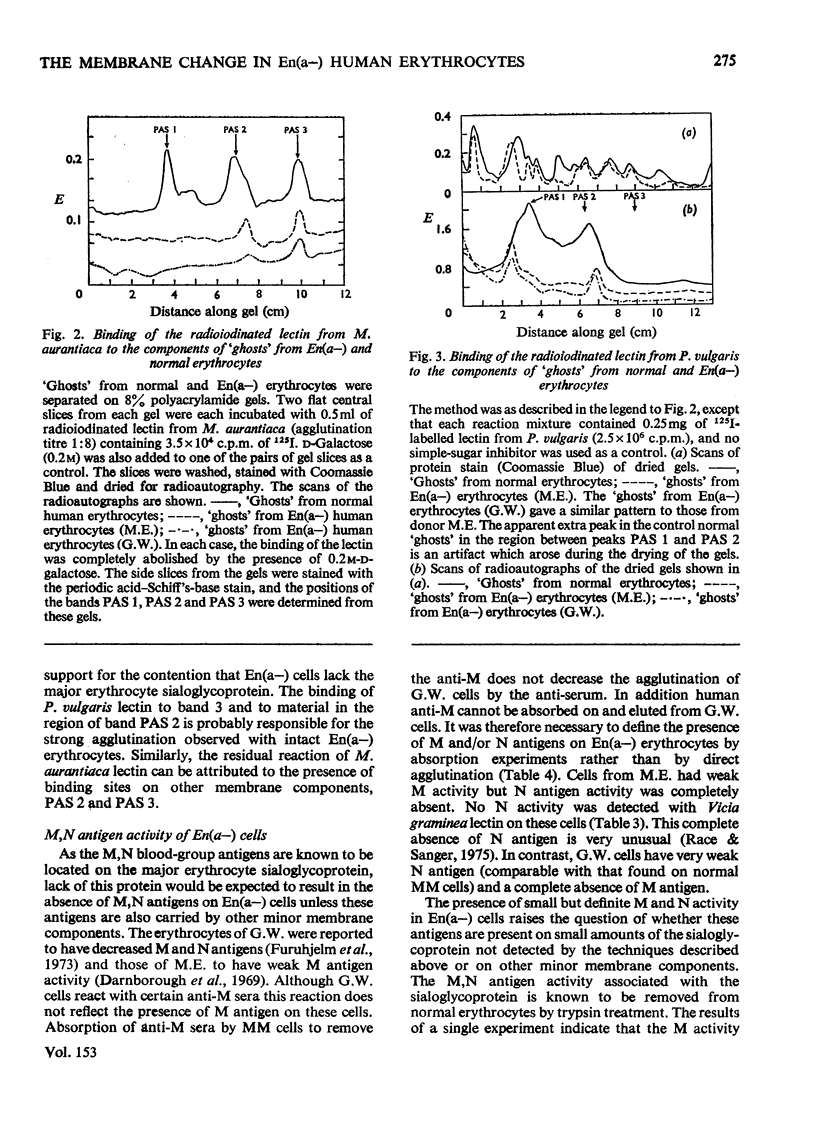
Abstract
We investigated the membrane of En(a-) human erythrocytes as part of a study of the structure and biochemical function of the surface glycoproteins of the mammalian cell. 2. En(a-) erythrocytes were selected because they have more extensive changes at the cell surface than any other known erythrocyte variant. 3. Our results show that in En(a-) erythrocytes: (a) the major membrane sialoglycoprotein is lacking; (b) the other major membrane-penetrating glycoprotein (band 3) has an altered electrophoretic mobility. 4. The apparent clinical normality of En(a-) cells suggests that the change in band 3 may compensate for the loss of the membrane sialoglycoproteins. It is clear that a viable erythrocyte can exist despite the absence of one of its major surface components.
Full text
PDF
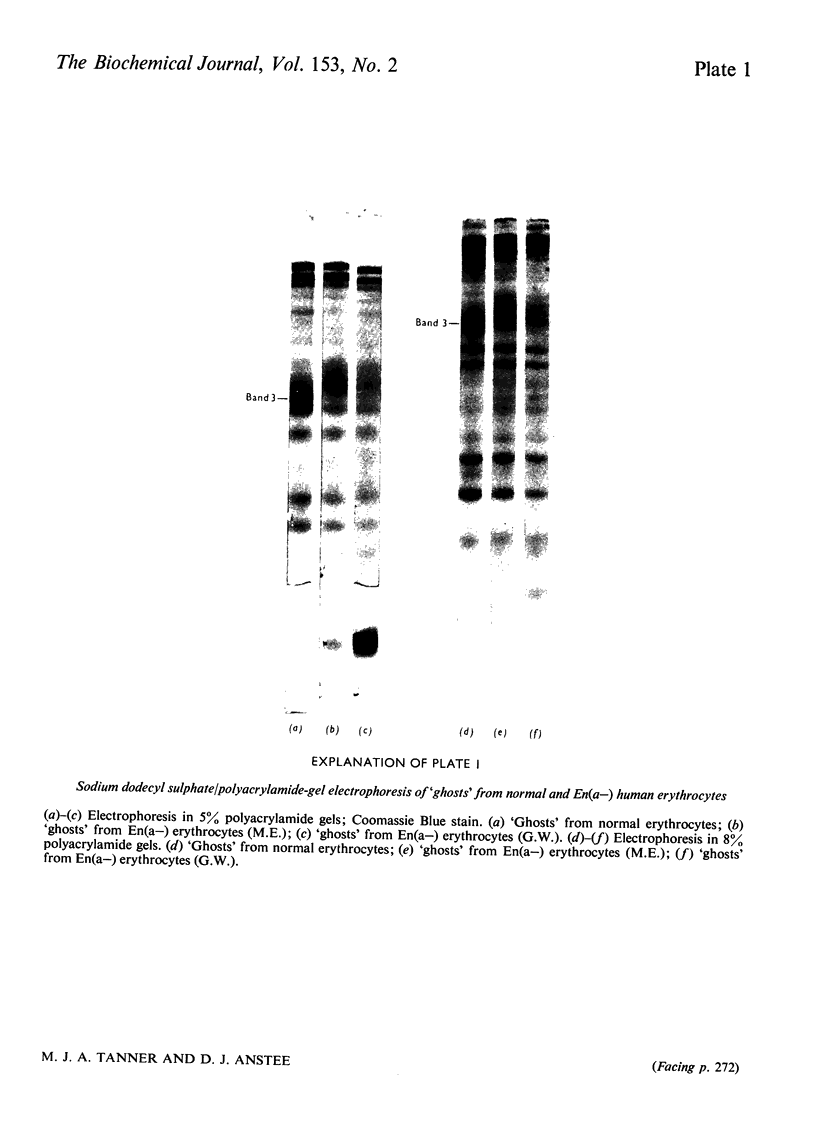



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstee D. J., Pardoe G. I. Structural aspects of heterologous blood-group-P1 substance. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):149–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. W., Wingham J. The action of seed and other reagents on En(a-) erythrocytes. Vox Sang. 1973 Jan;24(1):48–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb03856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer D. H., Jenkins R. E., Tanner M. J. The organization of the major protein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):531–534. doi: 10.1042/bj1370531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Membrane structure: some general principles. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):622–629. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. I. Localization of disulfonic stilbene binding sites in proteins involved in permeation. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):207–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Uhlenbruck G., Bird G. W. Further characterization of some heterophile agglutinins reacting with alkali-labile carbohydrate chains of human erythrocyte glycoproteins. Vox Sang. 1975;28(2):133–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1975.tb02751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnborough J., Dunsford I., Wallace J. A. The Ena antigen and antibody a genetical modification of human red cells affecting their blood grouping reactions. Vox Sang. 1969 Oct;17(4):241–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb00395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durocher J. R., Payne R. C., Conrad M. E. Role of sialic acid in erythrocyte survival. Blood. 1975 Jan;45(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhjelm U., Myllylä G., Nevanlinna H. R., Nordling S., Pirkola A., Gavin J., Gooch A., Sanger R., Tippett P. The red cell phenotype En(a-) and anti-Ena: serological and physicochemical aspects. Vox Sang. 1969 Oct;17(4):256–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhjelm U., Nevanlinna H. R., Pirkola A. A second Finnish En(a-) propositus with anti-Ena. Vox Sang. 1973;24(6):545–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1973.tb03498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. The molecular weight of the major glycoprotein from the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3913–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard I. K., Sage H. J., Stein M. D., Young N. M., Leon M. A., Dyckes D. F. Studies on a phytohemagglutinin from the lentil. II. Multiple forms of Lens culinaris hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Marchesi V. T. Studies on the major sialoglycoprotein of the human red cell membrane. Isolation and characterization of tryptic glycopeptides. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3131–3138. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. E., Tanner J. A. The major human erythrocyte membrane protein. Evidence for an S-shaped structure which traverses the membrane twice and contains a duplicated set of sites. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;147(3):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj1470393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON C. R., MARSON A. THE USE OF THROMBIN TO ACCELERATE COAGULATION FOR BLOOD-BANKING PROCEDURES. Vox Sang. 1965 May-Jun;10:346–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb01400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T. J., Morrison M. The transmembrane proteins in the plasma membrane of normal human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7568–7573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. P., Nicolson G. L. Freeze-etch localization of concanavalin A receptors to the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghost membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 23;363(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. A method for the direct demonstration of the lectin-binding components of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1530265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuech J. K., Morrison M. Human erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins: a study of interconversion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):352–360. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]