Abstract
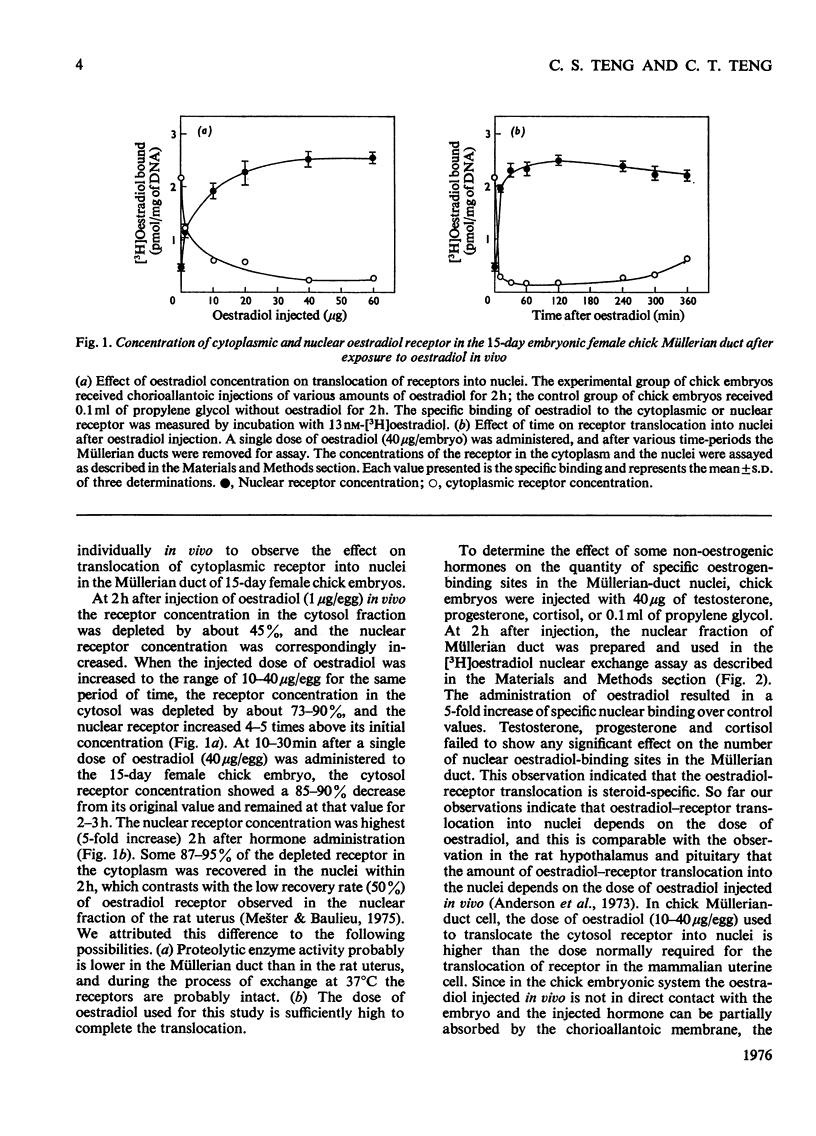
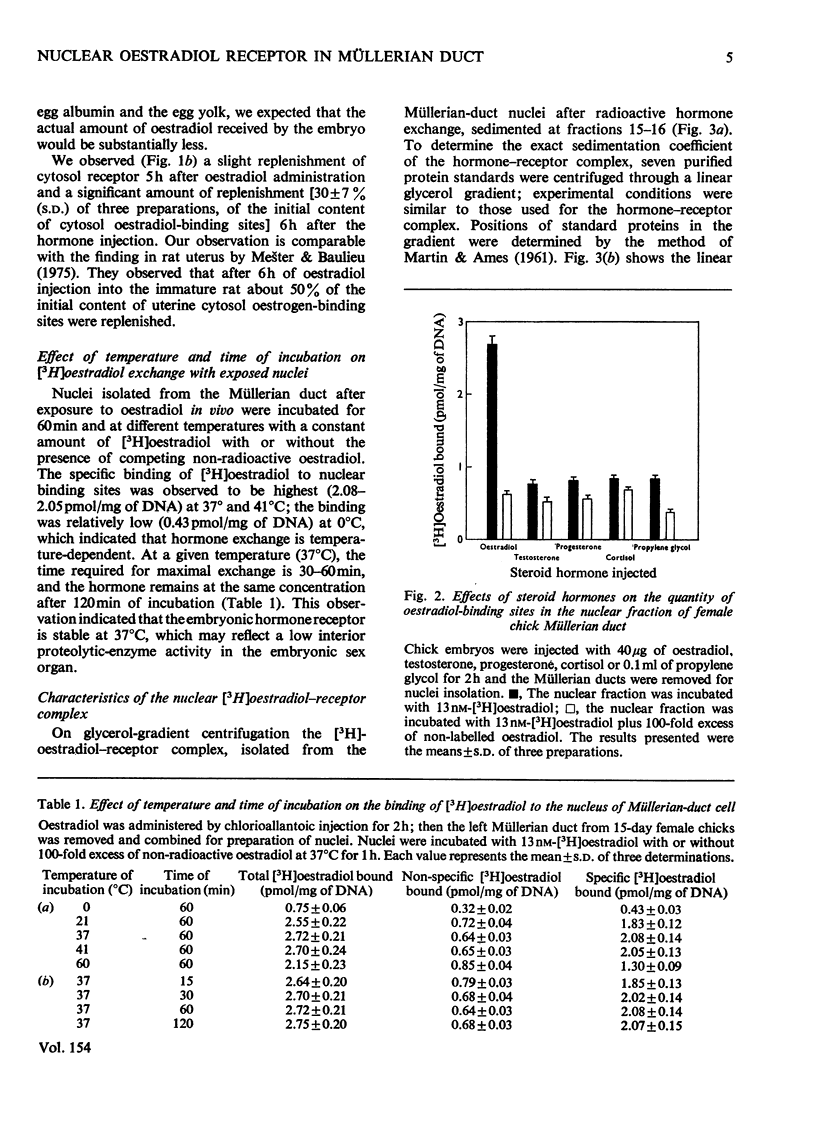
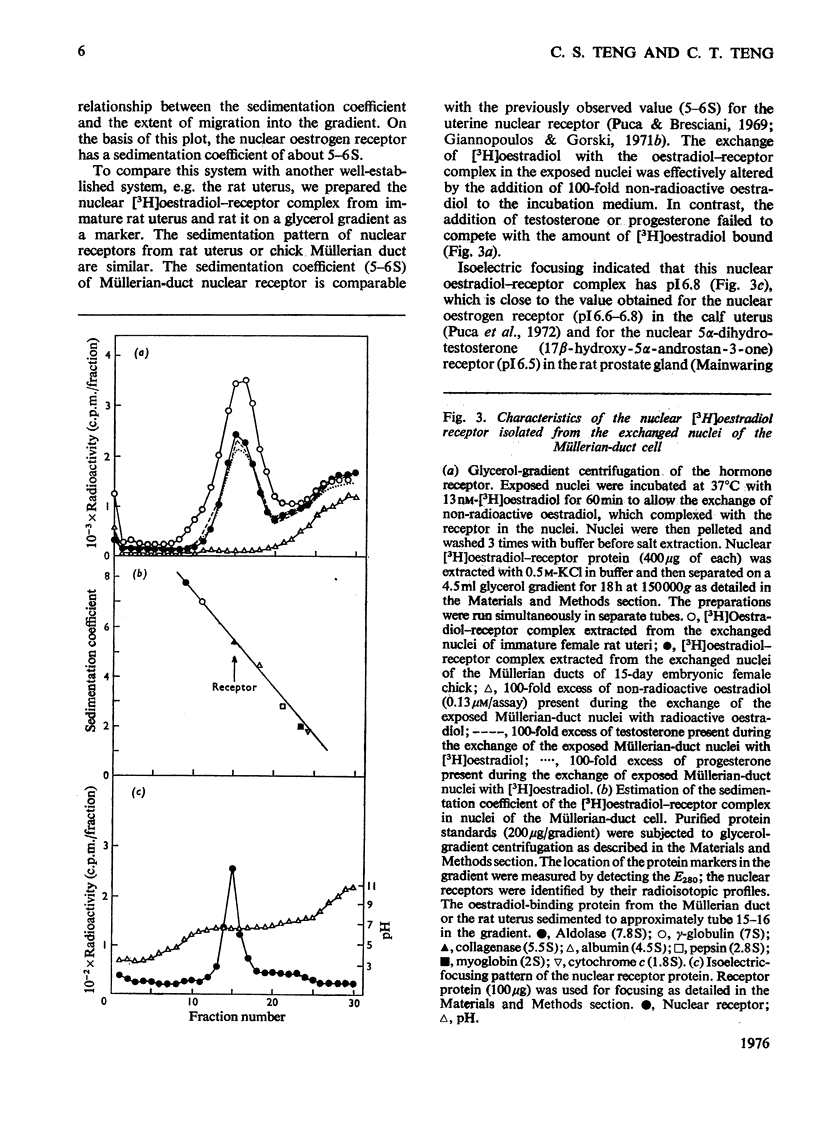
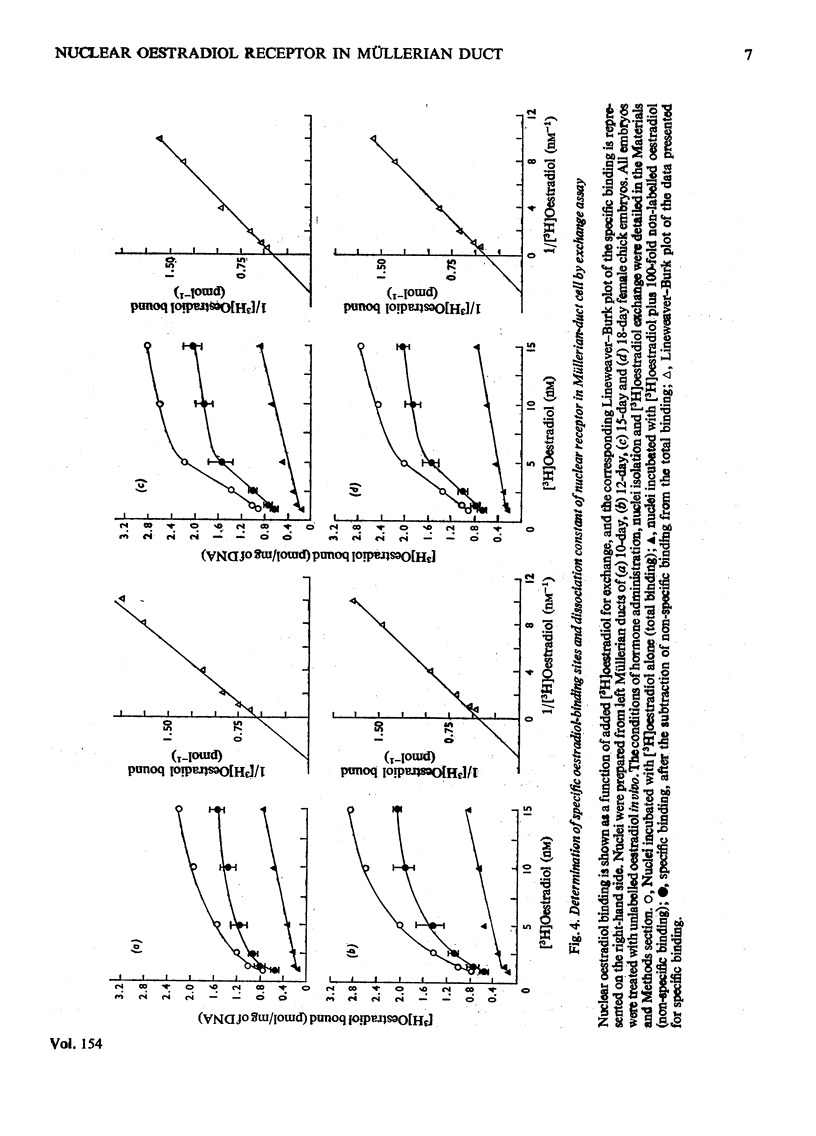
After oestradiol administration in vivo, 87-95% of the initial concentration of oestradiol receptor in the cytoplasm of the embryonic-chick Müllerian-duct cell was translocated into the nucleus. The process of translocation depends on the amount of oestardiol administered in vivo. At 6 h after oestradiol administration in vivo, about 30% replenishment of the initial content of the cytosol receptor was observed in the cytoplasm. The Müllerian-duct nuclei, after exposure to non-radioactive oestradiol, exhibit saturable exchange with [3H]oestradiol in vitro. The exchange of oestradiol is temperature- and time-dependent. The optimal temperature and time for exchange are 37-41 degrees C and 2h respectively. The [3H]oestradiol-receptor complex extracted from the exchanged nuclei is present in 5-6S form, and its isoelectric point is 6.8. The number of nuclear oestradiol-binding sites of the developing Müllerian duct are 1.66, 2.22, 2.63, and 2.50 pmol/mg of DNA respectively for embryos of 10, 12, 15 and 18 days. The dissociation constants of the nuclear oestradiol receptor of the four observed developmental stages range from 3.0 to 3.1 nM.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. N., Peck E. J., Jr, Clark J. H. Nuclear receptor estrogen complex: accumulation, retention and localization in the hypothalamus and pituitary. Endocrinology. 1973 Sep;93(3):711–717. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-3-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J., Clark J. H., Peck E. J., Jr Oestrogen and nuclear binding sites. Determination of specific sites by ( 3 H)oestradiol exchange. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):561–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1260561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. H., Anderson J., Peck E. J., Jr Receptor-estrogen complex in the nuclear fraction of rat uterine cells during the estrous cycle. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G., Gorski J. Estrogen receptors. Quantitative studies on transfer of estradiol from cytoplasmic to nuclear binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2524–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G., Gorski J. Estrogen-binding protein of the rat uterus. Different molecular forms associated with nuclear uptake of estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2530–2536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guichard A., Cedard L., Haffen K. Aspect comparatif de la synthèse de stéroïdes sexuels par les gonades embryonnaires de poulet à differents stades du développement (étude en culture organotypique à partir de précurseurs radioactifs. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1973 Feb;20(1):16–28. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(73)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Desombre E. R., Hurst D. J., Kawashima T., Jungblut P. W. Estrogen-receptor interactions in target tissues. Arch Anat Microsc Morphol Exp. 1967;56(3):547–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING R. J., GORDON J., INMAN D. R. THE INTRACELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF OESTROGEN IN RAT TISSUES. J Endocrinol. 1965 Apr;32:9–15. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0320009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. B., Gordon J. The localization of [6,7-3H]oestradiol-17-beta in rat uterus. J Endocrinol. 1966 Apr;34(4):431–437. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0340431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainwaring W. I., Irving R. The use of deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose chromatography and isoelectric focusing for the characterization and partial purification of steroid-receptor complexes. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):113–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1340113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Dynamics of oestrogen-receptor distribution between the cytosol and nuclear fractions of immature rat uterus after oestradiol administration. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):617–623. doi: 10.1042/bj1460617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohla S., DeSombre E. R., Jensen E. V. Tissue-specific stimulation of RNA synthesis by transformed estradiol-receptor complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):661–667. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Bresciani F. Association constant and specificity of oestradiol-receptor interaction. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):745–747. doi: 10.1038/223745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Nola E., Sica V., Bresciani F. Estrogen-binding proteins of calf uterus. Interrelationship between various forms and identification of a receptor-transforming factor. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4157–4165. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G., Gorski J. Estrogen receptors in the rat uterus. Studies on the interaction of cytosol and nuclear binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1097–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. S., Teng C. T. Studies on sex-organ development. Ontogeny of cytoplasmic oestrogen receptor in chick Müllerian duct. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):191–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1500191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Hamilton T. H., Tata J. R. The isolation of enzymically active nuclei from the rat heart and uterus. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):766–770. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


