Abstract
Injections of phenylalanine increased a 2.5-fold in 9 h the hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase activity of 6-day-old or adult rats that had been pretreated (24h earlier) with p-chlorophenylalanine; without such pretreatment, phenylalanine did not raise the enzyme concentration. This difference is paralleled by the much greater extent to which the injected phenylalanine accumulated in livers of the pretreated compared with the normal animals. The hormonal induction of hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase activity obeyed different rules: an injection of cortisol was without effect on adult livers but caused a threefold rise in phenylalanine hydroxylase activity of immature ones, both without and after pretreatment with p-chlorophenylalanine. In the latter instance, the effects of cortisol, and of phenylalanine were additive. Actinomycin inhibited the cortisol- but not the substrate-induced increase of phenylalanine hydroxylase, whereas puromycin inhibited both. The results indicate that substrate and hormone, two potential positive regulators of the amount of the hepatic (but not the renal) phenylalanine hydroxylase, act independently by two different mechanisms. The negative effector, p-chlorophenylalanine, also appears to interact with the synthetic (or degradative) machinery rather than with the existing phenylalanine hydroxylase molecules: 24h were required in vivo for an 85% decrease to ensue, and no inhibition occurred in vitro when incubating the enzyme with p-chlorophenylalanine or with liver extracts from p-chlorophenylalanine-treated rats.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayling J. E., Pirson W. D., al-Janabi J. M., Helfand G. D. Kidney phenylalanine hydroxylase from man and rat. Comparison with the liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):78–85. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIVEN M., KNOX W. E. The independence of hydrocortisone and tryptophan inductions of tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jul;234(7):1787–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvalle J. A., Greengard O. The regulation of phenylalanine hydroxylase in rat tissues in vivo. The maintenance of high plasma phenylalanine concentrations in suckling rats: a model for phenylketonuria. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):613–618. doi: 10.1042/bj1540613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDLAND R. A., KRAKOWSKI M. C., WAISMAN H. A. Effect of age, sex, and nutrition on liver phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in rats. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jan;202:145–148. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDLAND R. A., KRAKOWSKI M. C., WAISMAN H. A. INFLUENCE OF AMINO ACIDS ON RAT LIVER PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE ACTIVITY. Am J Physiol. 1964 Feb;206:341–344. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., FEIGELSON P. A difference between the modes of action of substrate and hormonal inducers of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase. Nature. 1961 Apr 29;190:446–447. doi: 10.1038/190446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., SMITH M. A., ACS G. Relation of cortisone and synthesis of ribonucleic acid to induced and developmental enzyme formation. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1548–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O. TRYPTOPHAN ANALOGUES AND THE MECHANISM OF INDUCTION OF RAT-LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE, IN VIVO. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 1;85:492–494. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O. Enzymic differentiation in mammalian tissues. Essays Biochem. 1971;7:159–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Sahib M. K., Knox W. E. Developmental formation and distribution of arginase in rat tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90465-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O. The quantitative regulation of specific proteins in animal tissues; words and facts. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1967;8(2):81–96. doi: 10.1159/000458182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
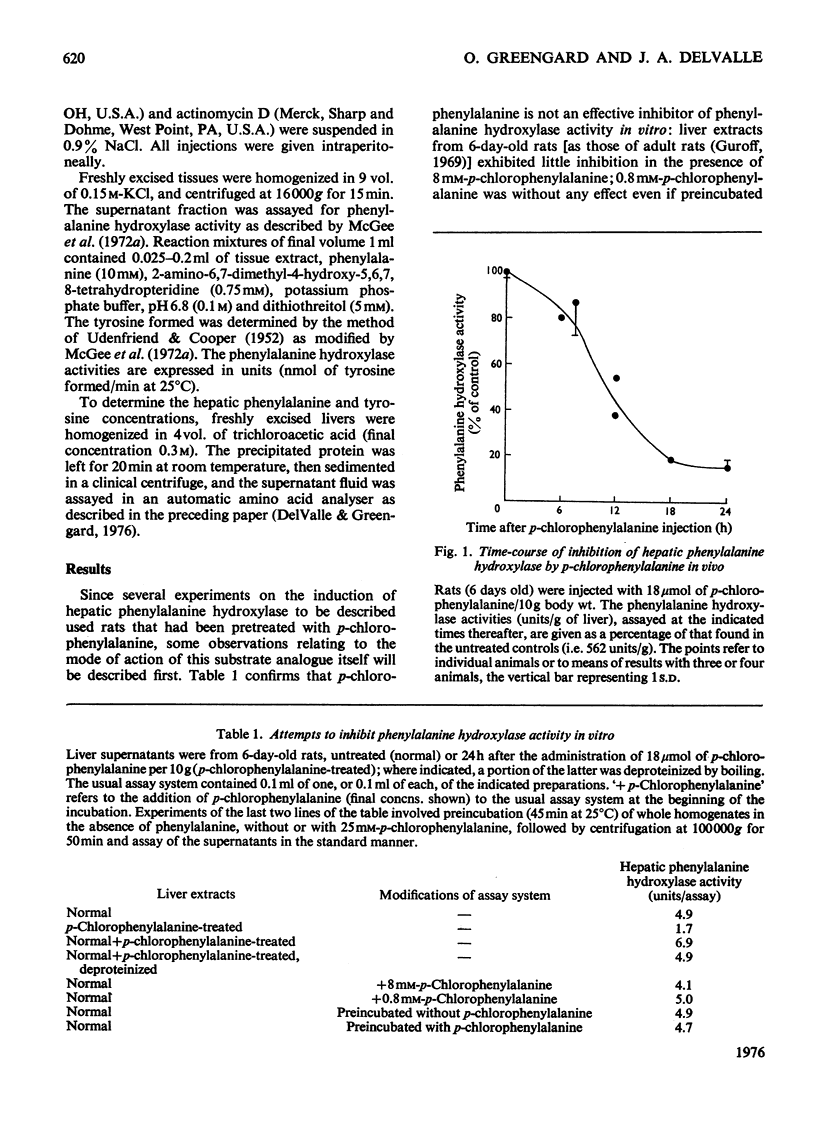
- Guroff G. Irreversible in vivo inhibition of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by p-chlorophenylalanine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):610–611. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gál E. M., Millard S. A. The mechanism of inhibition of hydroxylases in vivo by p-chlorophenylalanine: the effect of cycloheximide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 13;227(1):32–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
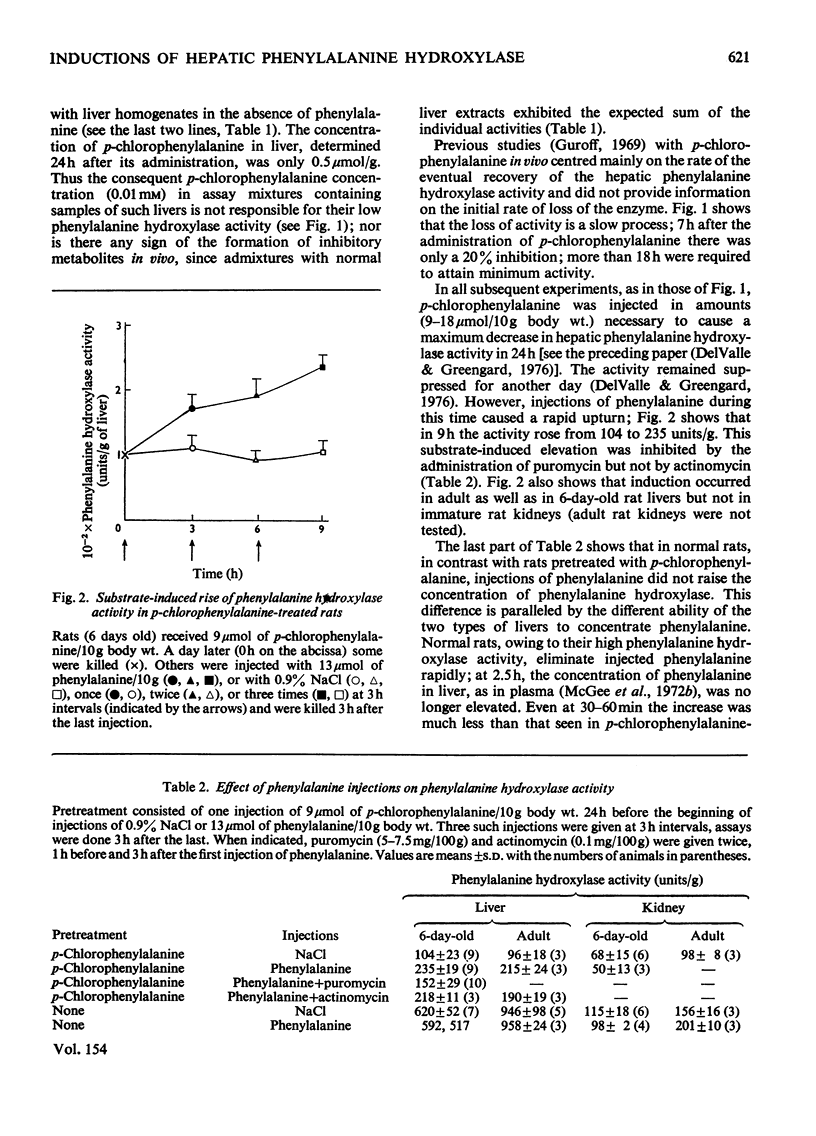
- Herzfeld A., Greengard O. Endocrine modification of the developmental formation of ornithine aminotransferase in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4894–4898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox W. E., Piras M. M. Tryptophan pyrrolase of liver. 3. Conjugation in vivo during cofactor induction by tryptophan analogues. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2959–2965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. M., Greengard O., Knox W. E. Liver phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in relation to blood concentrations of tyrosine and phenylalanine in the rat. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(4):675–680. doi: 10.1042/bj1270675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. M., Greengard O., Knox W. E. The quantitative determination of phenylalanine hydroxylase in rat tissues. Its developmental formation in liver. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(4):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1270669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., McClure D., Shiman R. p-Chlorphenylalanine effect on phenylalanine hydroxylase in hepatoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1132–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., COOPER J. R. The chemical estimation of tyrosine and tyramine. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


