Abstract
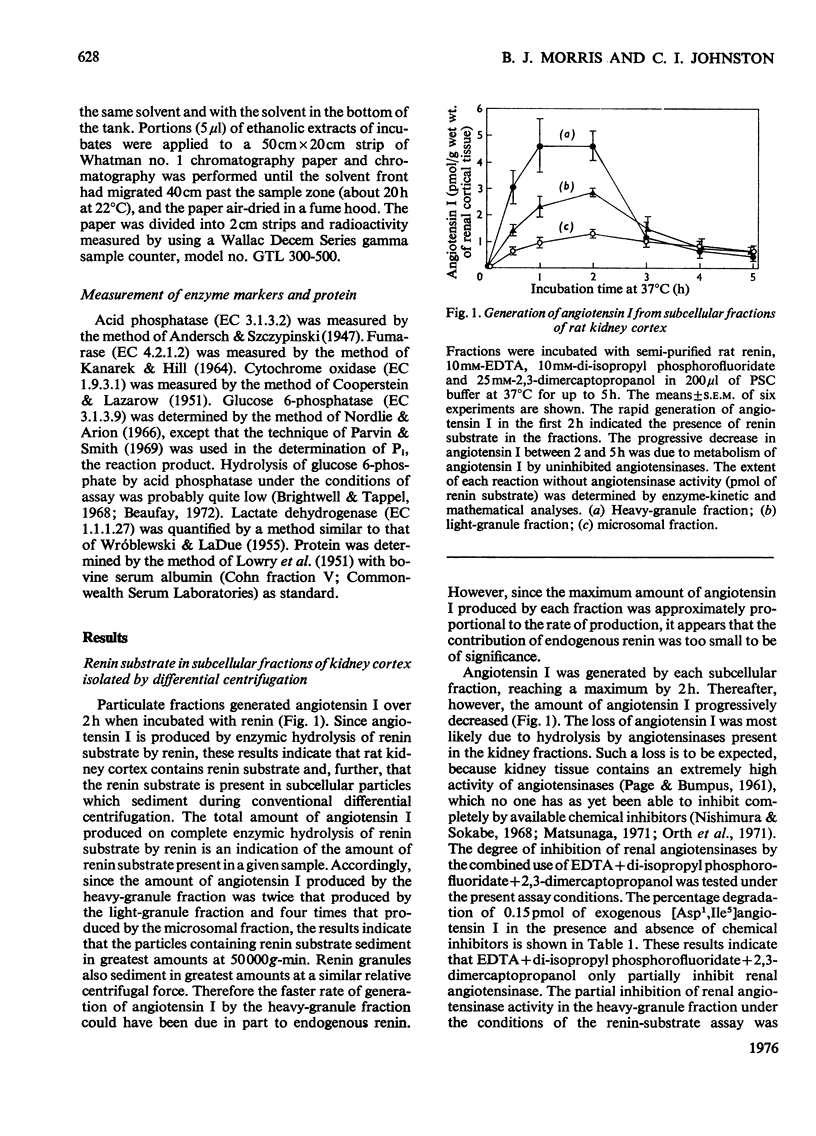
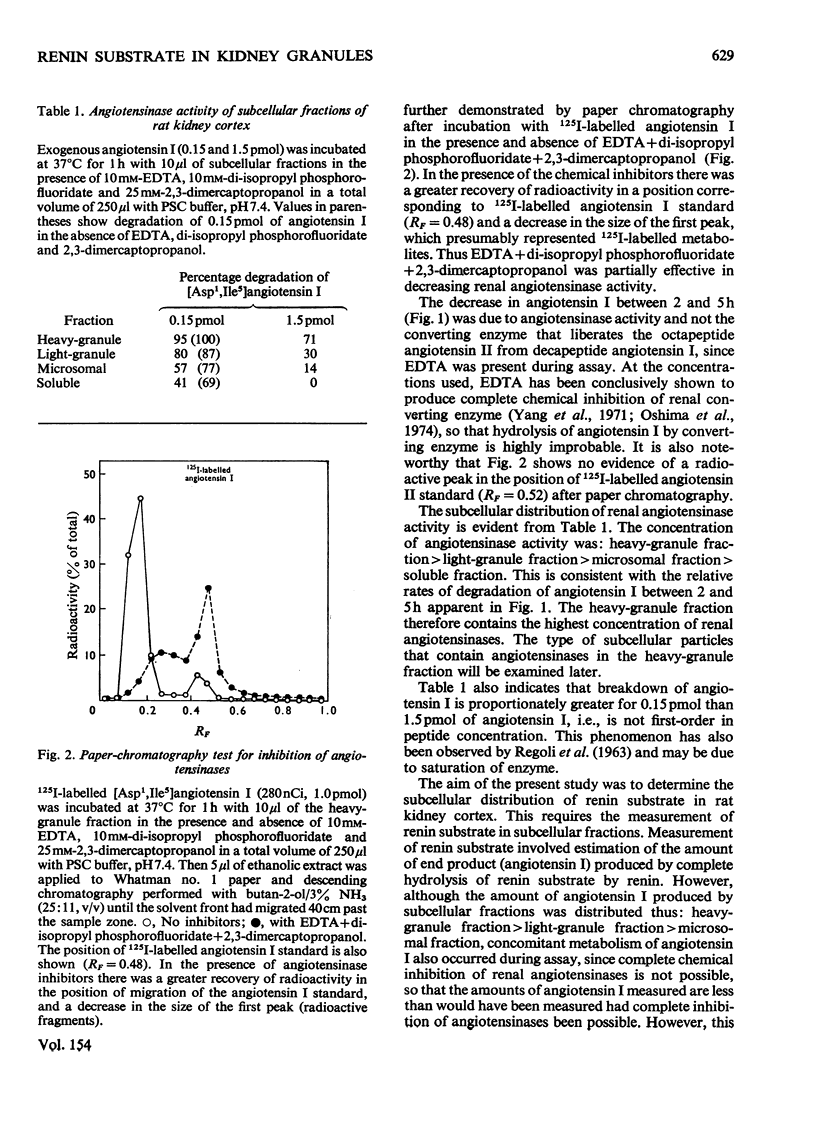
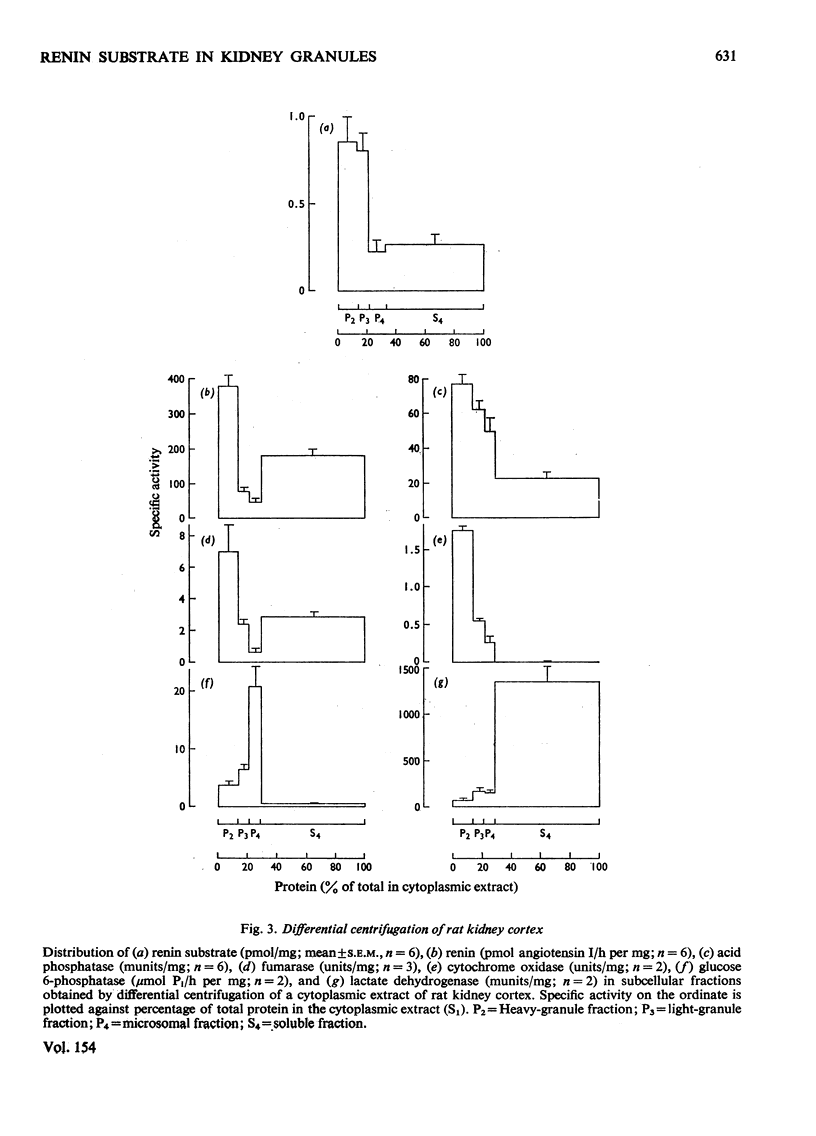
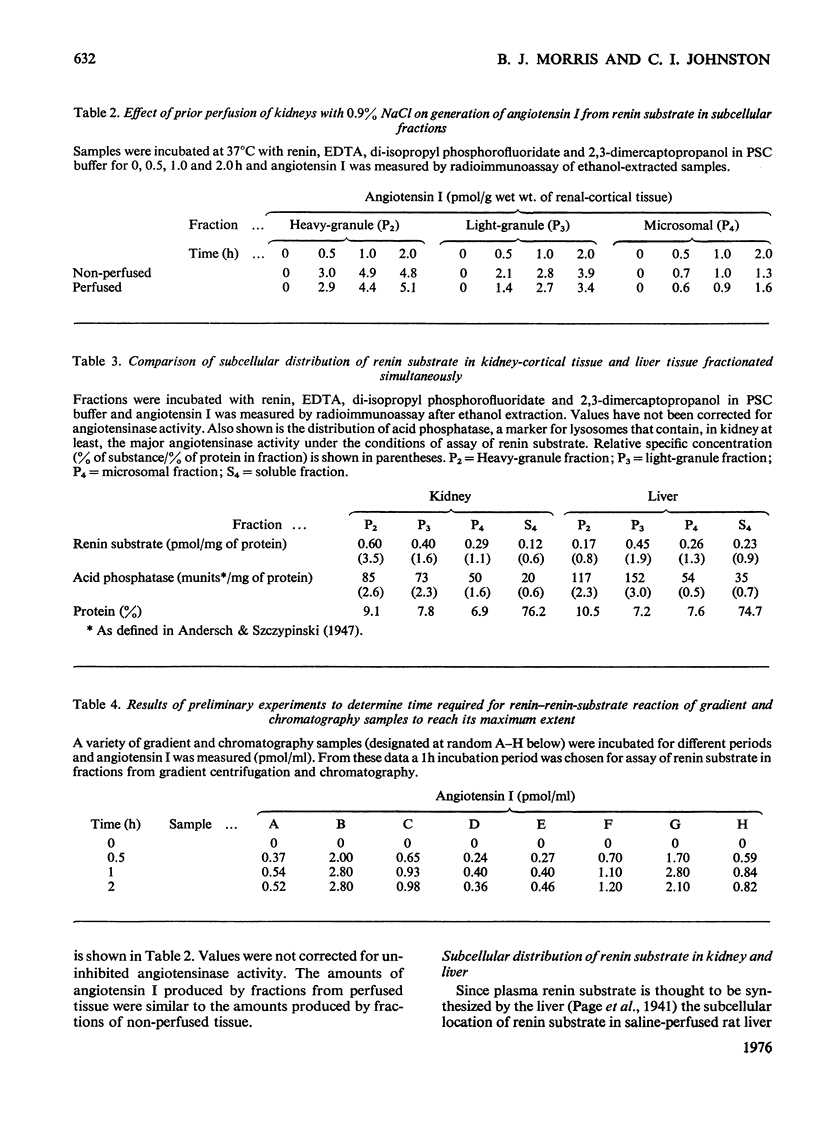
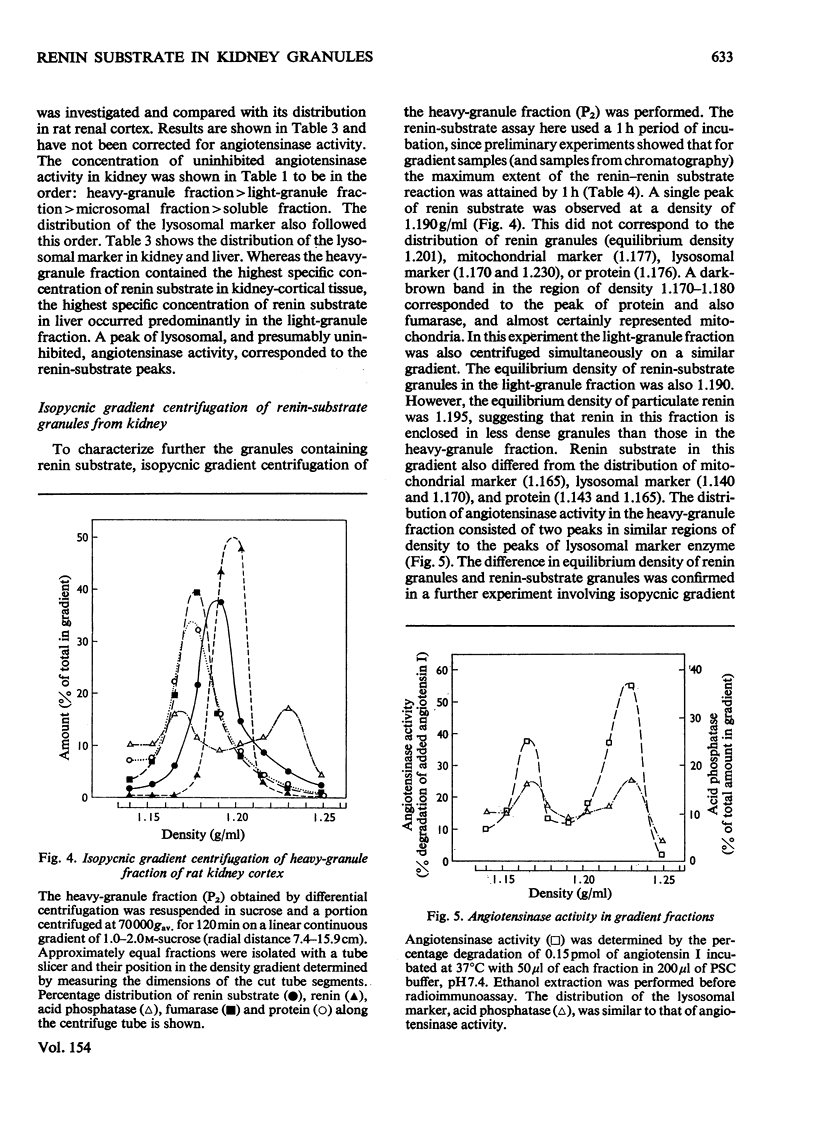
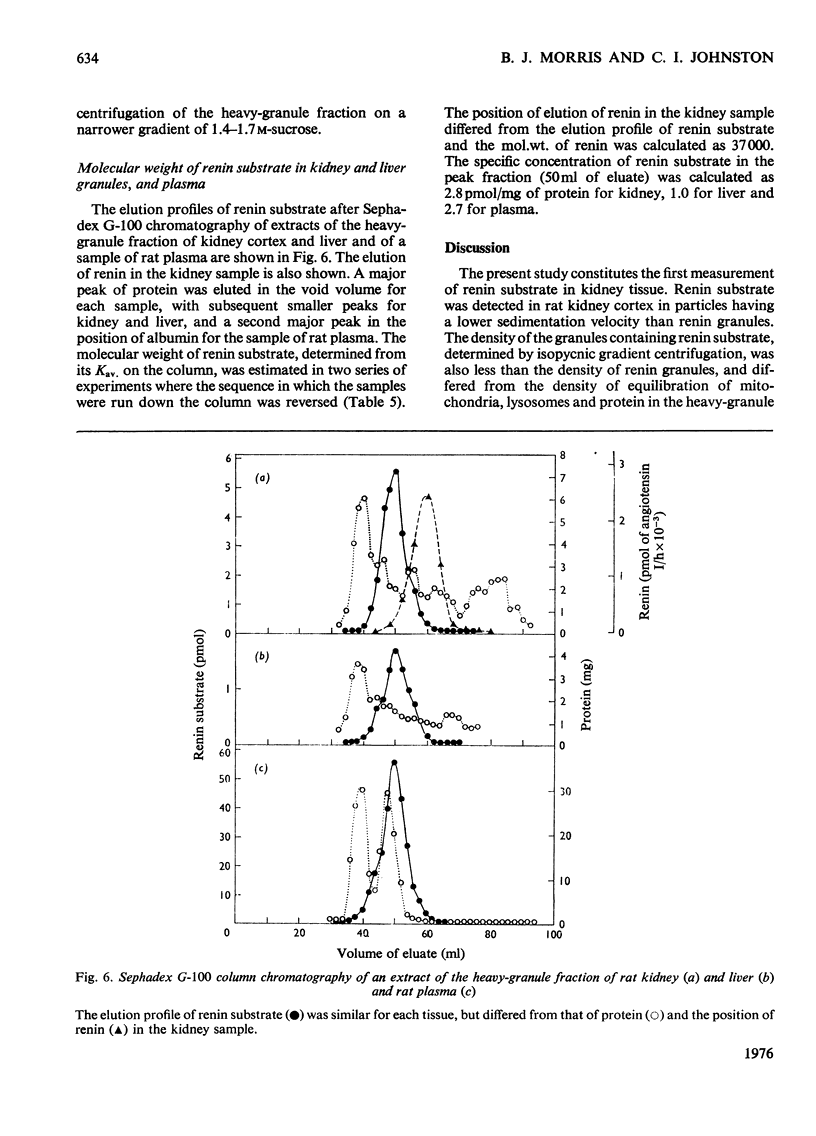
1. Subcellular fractions of rat kidney cortex generated angiotensin I continuously over 2h when incubated at 37degreesC with rat renin, indicating the presence of renin substrate within cells in the renal cortex. 2. Renin substrate was located in highest specific concentration in particulate fractions. The particles containing renin substrate had a sedimentation velocity slightly lower than mitochondria and renin granules but greater than the microsomal fraction. 3. Isopycnic gradient centrifugation indicated a density of 1.190g/ml for the particles containing renin substrate, compared with 1.201 for renin granules, 1.177 for mitochondria, and 1.170 and 1.230 for lysosomes in the heavy-granule fraction. 4. In the liver, renin substrate was also found in particles, but these had a lower sedimentation rate than those from the kidney. 5. The molecular weights of renin substrate in kidney and liver granules and rat plasma were similar, namely 61000-62000. 6. On the basis of these biochemical findings, a mechanism for the intrarenal production of angiotensin, incorporating a subcellular reaction scheme, is proposed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON N. G. Studies on isolated cell components. VIII. High resolution gradient differential centrifugation. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Dec;9(3):446–459. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailie M. D., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Angiotensin II in arterial and renal venous plasma and renal lymph in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):119–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI106465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudouin M., Meyer P., Fermandjian S., Morgat J. L. Calcium release induced by interaction of angiotensin with its receptors in smooth muscle cell microsomes. Nature. 1972 Feb 11;235(5337):336–338. doi: 10.1038/235336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biava C., West M. Fine structure of normal human juxtaglomerular cells. I. General structure and intercellular relationships. Am J Pathol. 1966 Oct;49(4):679–721. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightwell R., Tappel A. L. Lysosomal acid pyrophosphatase and acid phosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Pernollet M. G., Meyer P., Fermandjian S., Fromageot P. Angiotensin receptors in smooth muscle cell membranes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):55–58. doi: 10.1038/newbio245055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkielman S., Nahmod V. E. In vitro production of angiotensin I by renal glomeruli. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1186–1188. doi: 10.1038/2221186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. H., Rostorfer H. H. Hepatic changes in renin substrate biosynthesis and alkaline phosphatase activity in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Aug;223(2):364–370. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Diaz A., Finkielman S., Nahmod V. E., Fischer-Ferraro C. Regulation of the in vitro synthesis of angiotensin I. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):793–795. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger P., Dahlheim H., Thurau K. Enzyme activities of the single juxtaglomerular apparatus in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):78–88. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Goldblatt H., Gipson E. C., Lewis L. Extraction, purification, and assay of human renin free of angiotensinase. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):739–749. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer K. G., Zschiedrich H., Rauh W., Orth H., Gross F. Reaction of endogenous renin with exogenous renin substrate within the isolate perfused rat kidney. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):796–799. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horky K., Rojo-Ortega J. M., Rodriguez J., Boucher R., Genest J. Renin, renin substrate, and angiotensin I-converting enzyme in the lymph of rats. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):307–311. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. I., Mendelsohn F. A., Doyle A. E. Metabolism of angiotensin II in sodium depletion and hypertension in humans. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):203–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANAREK L., HILL R. L. THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FUMARASE FROM SWINE HEART MUSCLE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4202–4206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahé P., Hofbauer K. G., Gross F. Effects of endogenous renin on the function of the isolated kidney. Life Sci I. 1970 Nov 15;9(22):1317–1320. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER A. F., PEART W. S. Renin and angiotensin-like activity in renal lymph. J Physiol. 1962 Mar;160:548–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckie B., Gavras H., McGregor J., McElwee G. The conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by rabbit glomeruli. J Endocrinol. 1972 Oct;55(1):229–230. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0550229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga M. Nature of lysosomal angiotensinase activity. Jpn Circ J. 1971 Mar;35(3):333–338. doi: 10.1253/jcj.35.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Lumbers E. R. The activation of renin in human amniotic fluid by proteolytic enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 7;289(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjetti A., Masson G. M. Hepatic origin of renin substrate. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;49(10):931–932. doi: 10.1139/y71-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura H., Sokabe H. Inhibition of angiotensinases in the rat plasma and kidney. Jpn Heart J. 1968 Sep;9(5):494–503. doi: 10.1536/ihj.9.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth H., Krahé P., Steigelmann C., Gross F. An improved method for the determination of renin in rat kidneys. Pflugers Arch. 1971;329(2):125–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00586987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima G., Gecse A., Erdös E. G. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme of the kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE I. H., BUMPUS F. M. Angiotensin. Physiol Rev. 1961 Apr;41:331–390. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin R., Smith R. A. Determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of labile organic phosphates. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jan;27(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., RINIKER B., BRUNNER H. The enzymatic degradation of various angiotensin II derivatives by serum, plasma or kidney homogenate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Jul;12:637–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIBKO S., TAPPEL A. L. RAT-KIDNEY LYSOSOMES: ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj0950731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, LENTZ K. E., HOCHSTRASSER H., KAHN J. R. The purification and partial characterization of several forms of hog renin substrate. J Exp Med. 1963 Jul;118:73–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THURAU K. RENAL HEMODYNAMICS. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:698–719. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurau K. W., Dahlheim H., Grüner A., Mason J., Granger P. Activation of renin in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus by sodium chloride in the tubular fluid at the macula densa. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Use of computers in pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1967 Jan-Feb;8(1):201–218. doi: 10.1002/cpt196781part2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Rutgeerts M. J., Wattiaux R. Lysosomes in rat-kidney tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 20;105(3):446–459. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Erdös E. G., Levin Y. Characterization of a dipeptide hydrolase (kininase II: angiotensin I converting enzyme). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


