Abstract
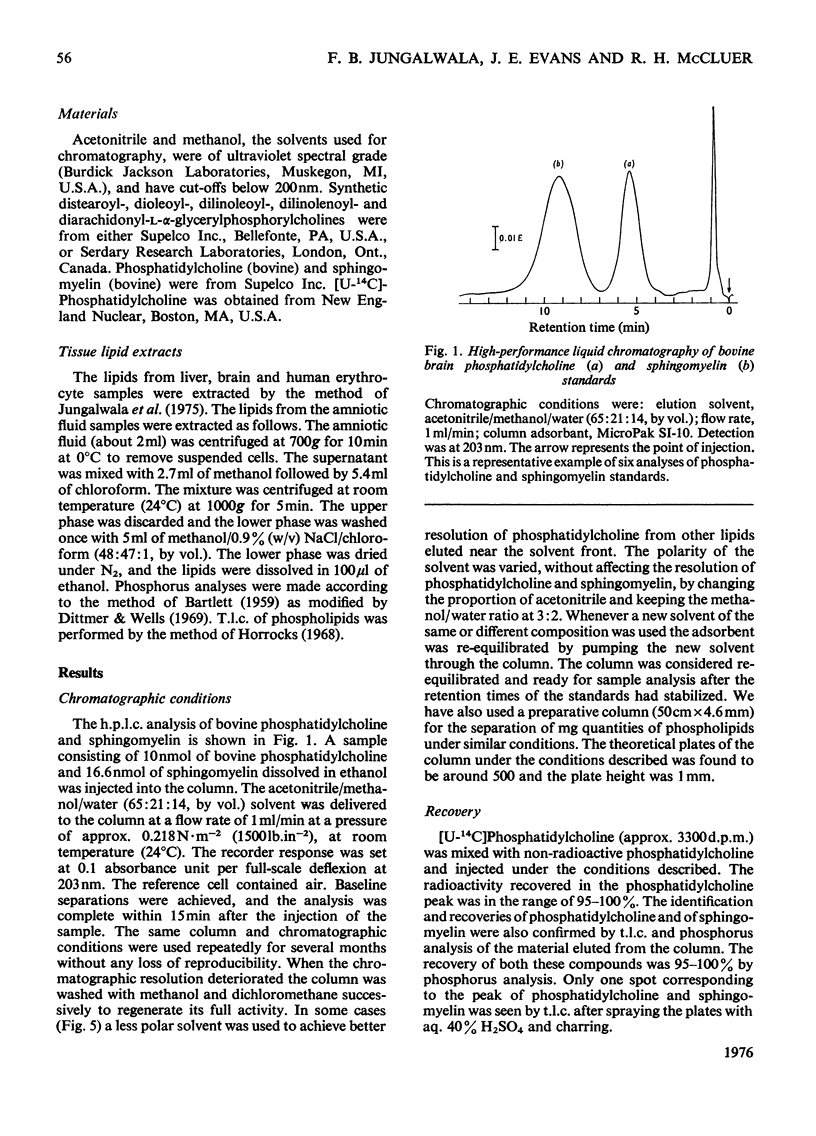
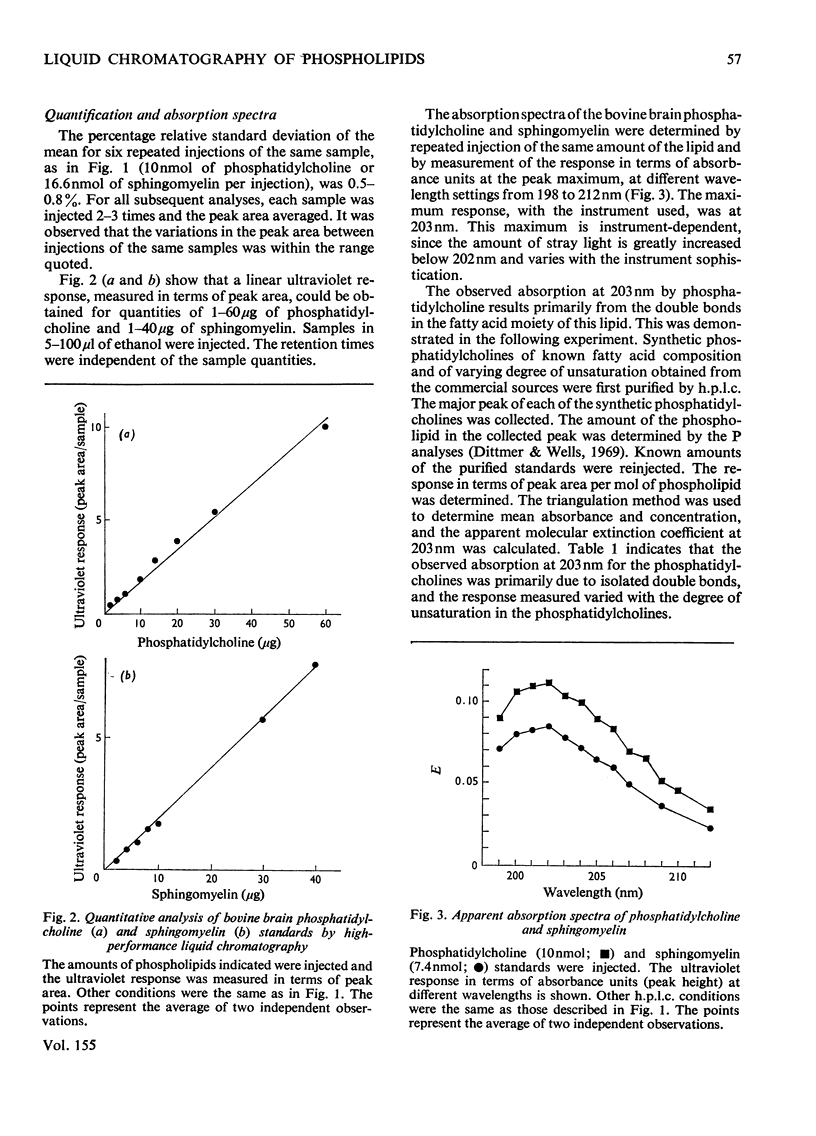
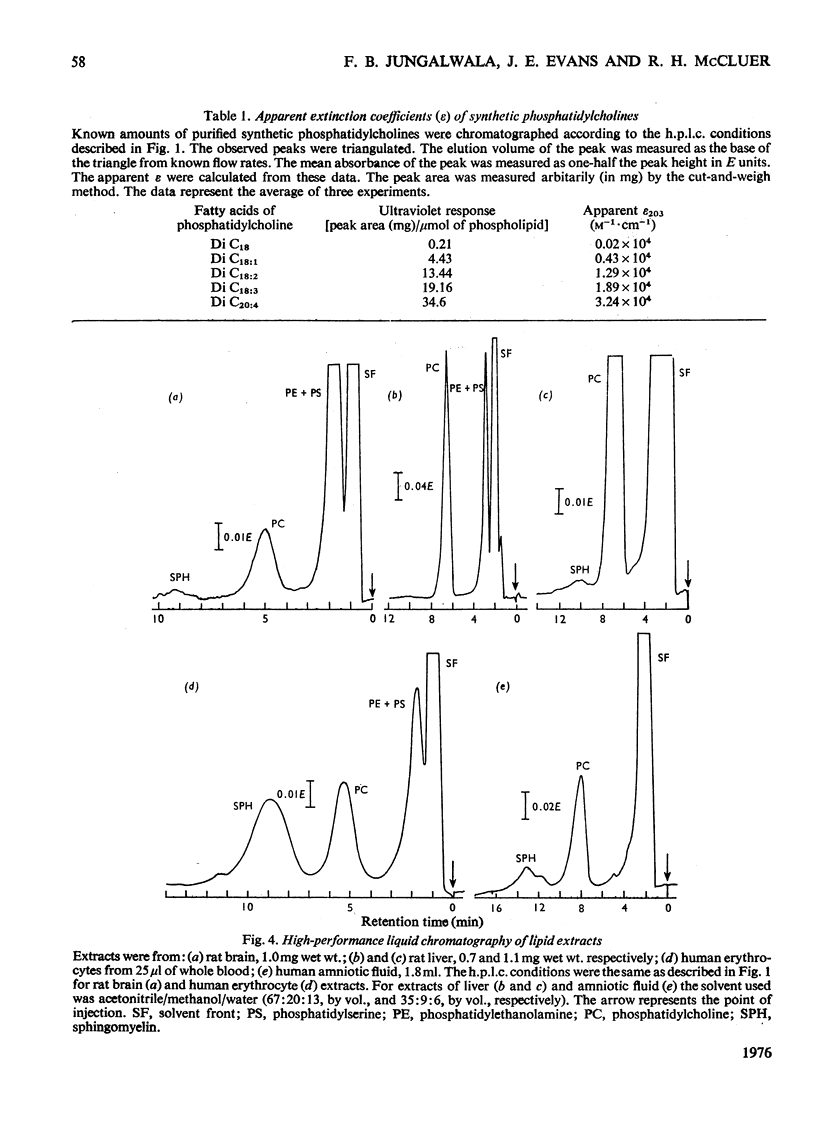
A sensitive method for the separation of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin by high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis is described. The elution of the phospholipids from a microparticulate (10 mum) silica-gel chromatographic column was monitored with an ultraviolet spectromonitor at 203 nm. Acetonitrile/methanol/water (65:21:14, by vol.) was used as the solvent. It was shown by using synthetic phosphatidylcholines of knowm fatty acid composition and of varying degree of unsaturation that the absorption at 203 nm was primarily due to the isolated double bonds and the response measured varied with the degree of unsaturation. Approx. 1 nmol of phosphatidylcholine, containing at least one double bond per molecule, can be detected. The amounts of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin could be determined by high-performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet absorption if the apparent extinction coefficient of the material analyzed was established. Alternatively, peaks were collected and the phospholipids were determined by the analysis of phosphorus. The analysis of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin present in the lipid extracts from animal tissues, blood and amniotic fluids were made without interference from other phospholipids or ultraviolet-absorbing material. The method described here is complementary to the high-performance liquid chromatographic method described previously for the analysis of ethanolamine-containing phosphoglycerides and serine-containing phosphoglycerides [Jungalwala, Turel, Evans and McCluer (1975) Biochem. J. 145, 517-526].
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Norton W. T. The characterization of sphingolipids from neurons and astroglia of immature rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Nov;23(5):1025–1036. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb10755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrocks L. A. The alk-1-enyl group content of mammalian myelin phosphoglycerides by quantitative two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Turel R. J., Evans J. E., McCluer R. H. Sensitive analysis of ethanolamine- and serine-containing phosphoglycerides by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):517–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1450517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murawski U., Egge H., Zilliken F. Quantitative Bestimmung dünnschichtchromatographisch getrennter Lipide aus Serum und Gewebe durch UV-Absorptionsmessung in Remission. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1974 Oct;12(10):464–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer H. G., Neuhoff V. Fluorometric microdetermination of phospholipids on the cellular level. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Jul;352(7):913–926. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


