Abstract
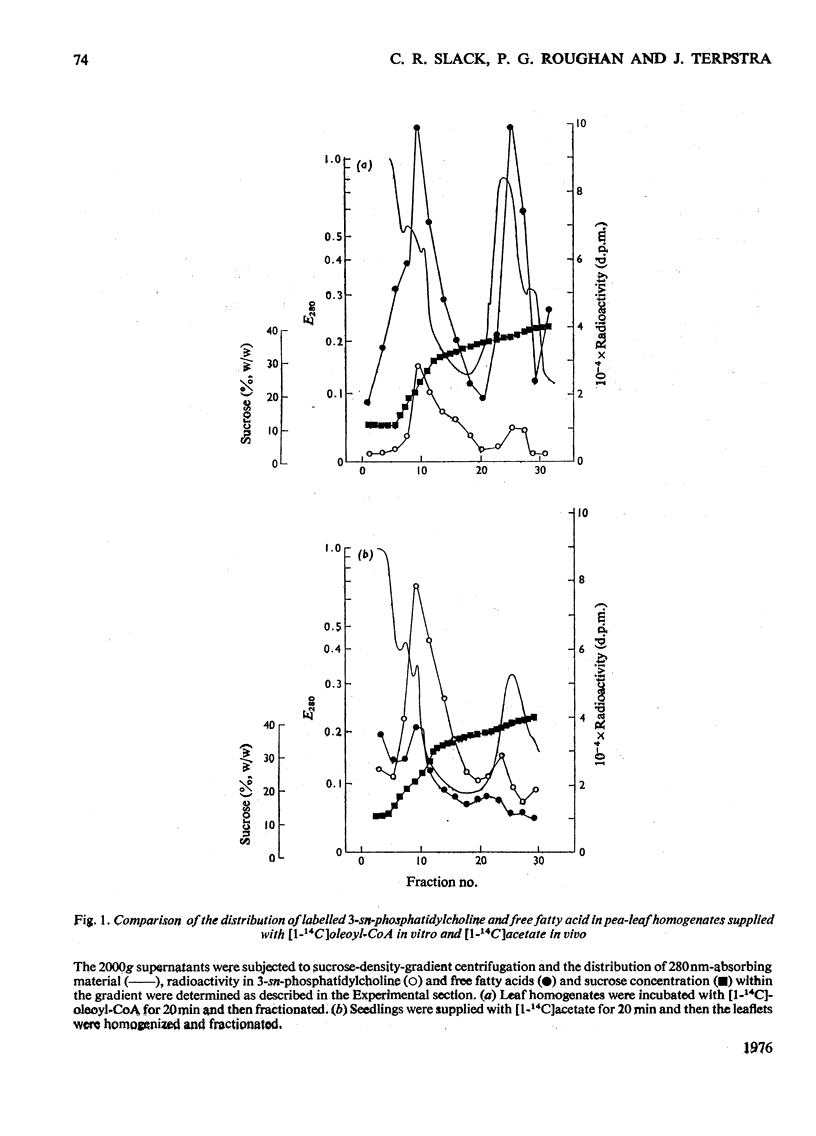
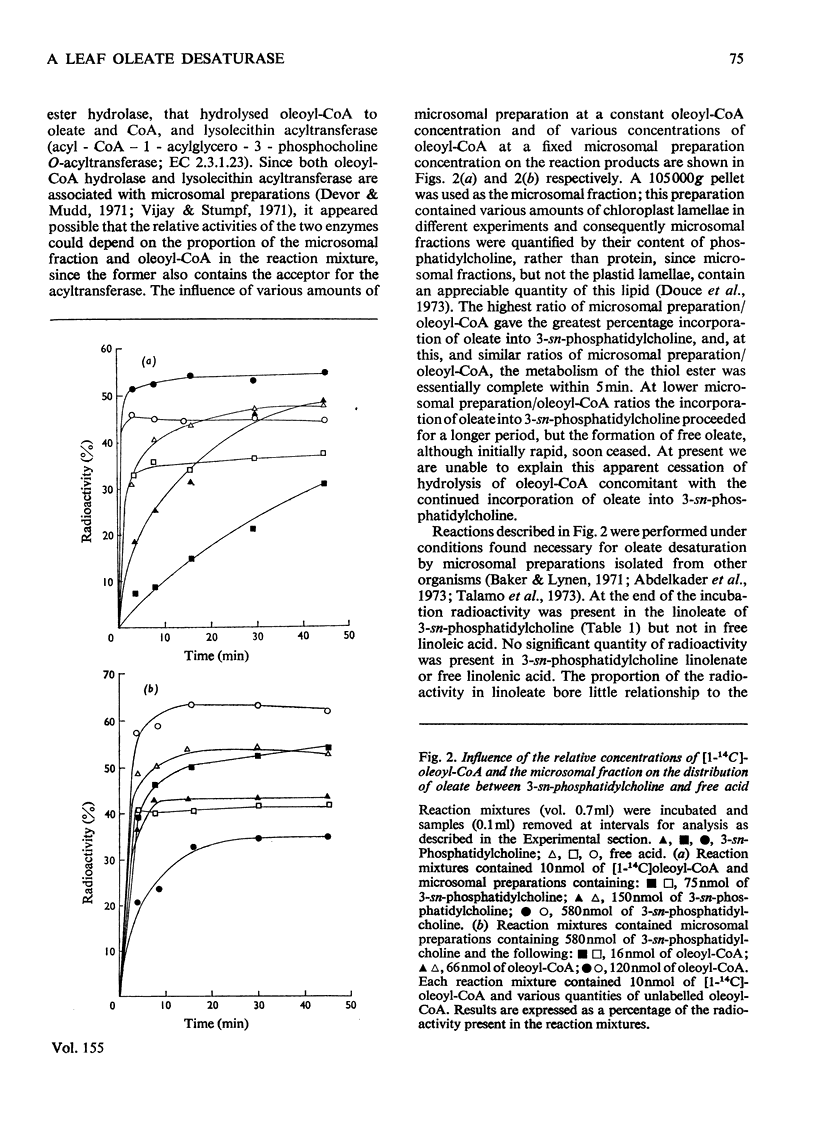
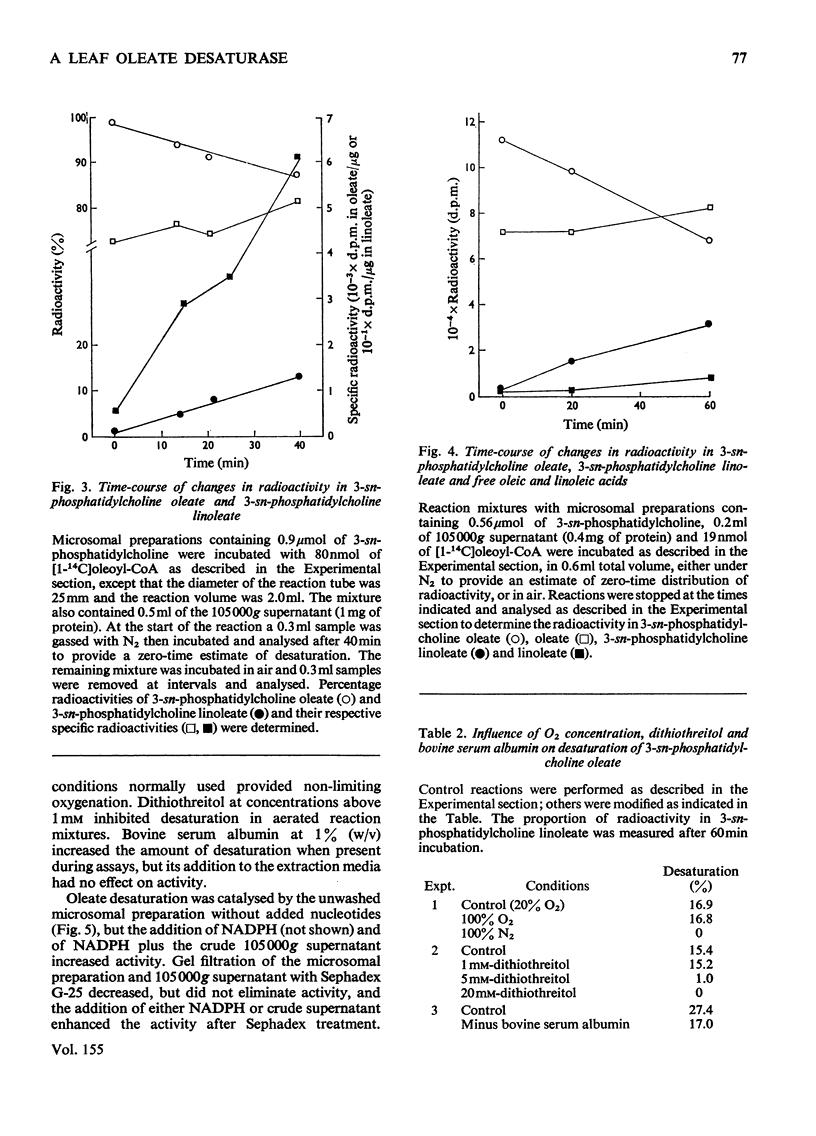
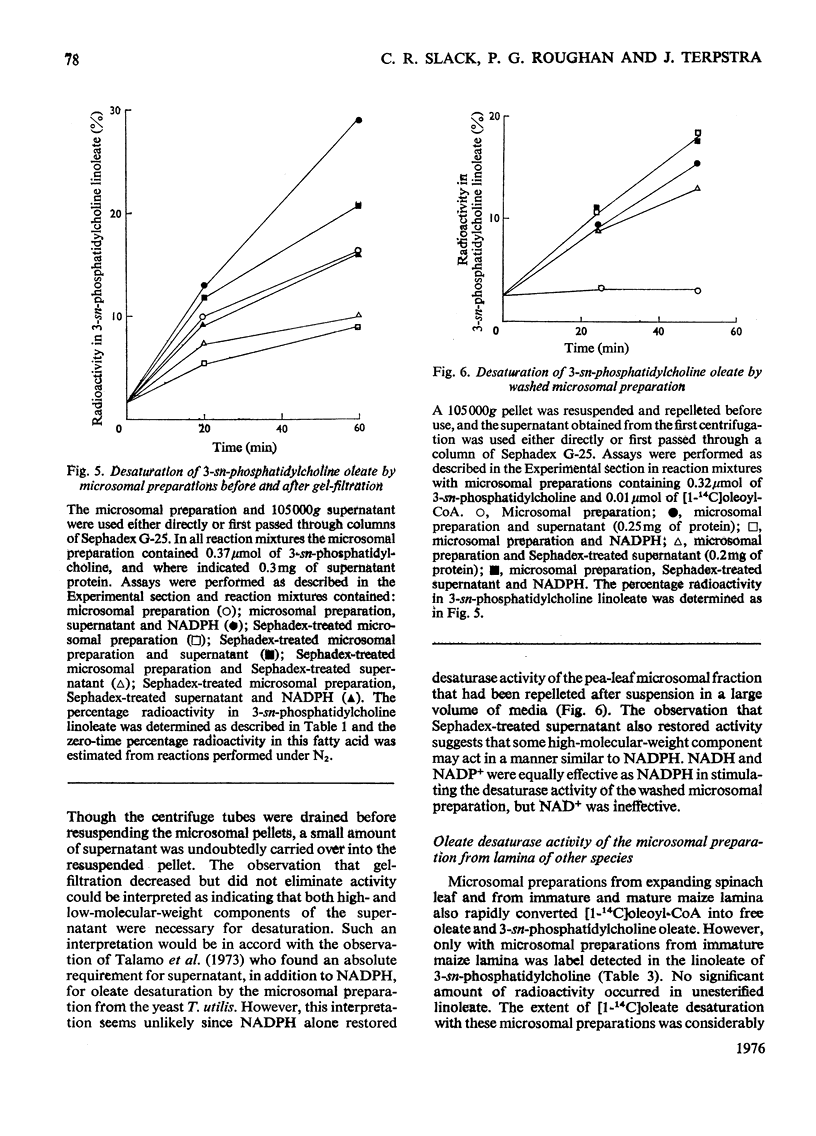
1. When [1-14C]oleoyl-CoA was incubated with a pea-leaf homogenate oleate was both incorporated into microsomal 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine and released as the unesterified fatty acid. The proportion of oleate incorporated into this phospholipid was dependent on the relative amounts of thiol ester and microsomal preparation present in reactions. 2. At the concentrations of microsomal preparation and [14C]oleoyl-CoA used to study oleate desaturation the metabolism of the thiol ester was essentially complete after 5 min incubation, but the loss of label from 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine oleate and the concomitant increase in radioactivity in the linoleate of this phospholipid proceeded at approximately linear rates over a 60 min period. The kinetics of labelling of unesterified linoleate was consistent with the view that this labelled fatty acid was derived from 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine. 3. Oleate desaturation required oxygen and with unwashed microsomal fractions was stimulated either by NADPH or by the 105 000g supernatant. Washed microsomal preparations did not catalyse desaturation, but actively was restored by the addition of NADPH, 105 000G supernatant or Sephadex-treated supernatant. NADPH could be replaced by NADH or NADP+, but not by NAD+. 4. Microsomal fractions from mature and immature maize lamina and expanding spinach leaves also rapidly incorporated oleate from ([14C]oleoyl-CoA into 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine, but desaturation of 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine oleate was detected only with microsomal preparations from immature maize lamina. 5. It is proposed that leaf microsomal preparations posses an oleate desaturase for which 3-sn-phosphatidylcholine oleate is either the substrate or an immediate precursor of the substrate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelkader A. B., Cherif A., Demandre C., Mazliak P. The oleyl-coenzyme-A desaturase of potato tubers. Enzymatic properties, intracellular localization and induction during "aging" of tuber slices. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 3;32(1):155–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N., Lynen F. Factors involved in fatty acyl CoA desaturation by fungal microsomes. The relative roles of acyl CoA and phospholipids as substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):200–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devor K. A., Mudd J. B. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine by enzyme preparations from spinach leaves. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce R., Holtz R. B., Benson A. A. Isolation and properties of the envelope of spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7215–7222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN P., VAGELOS P. R. The specificity of triglyceride synthesis from diglycerides in chicken adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2620–2623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurr M. I., Robinson M. P., James A. T. The mechanism of formation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by photosynthetic tissue. The tight coupling of oleate desaturation with phospholipid synthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Eur J Biochem. 1969 May 1;9(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T., Lord J. M., Beevers H. Lecithin synthesis during microbody biogenesis in watermelon cotyledons. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T., Lord J. M., Beevers H. The origin and turnover of organelle membranes in castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):61–65. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. W., Safford R. Conversion of lipids to fatty alcohols and lysolipids by NaBH4. Chem Phys Lipids. 1973 Oct;11(3):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(73)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughan P. G. Phosphatidyl choline: Donor of 18-carbon unsaturated fatty acids for glycerolipid biosynthesis. Lipids. 1975 Oct;10(10):609–614. doi: 10.1007/BF02532725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughan P. G. Turnover of the glycerolipids of pumpkin leaves. The importence of phosphatidylcholine. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj1170001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C. R., Roughan P. G. The kinetics of incorporation in vivo of (14C)acetate and (14C)carbon dioxide into the fatty acids of glycerolipids in developing leaves. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;152(2):217–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1520217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamo B., Chang N., Bloch K. Desaturation of oleyl phospholipid to linoleyl phospholipid in Torulopsis utilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2738–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay I. K., Stumpf P. K. Fat metabolism in higher plants. XLVI. Nature of the substrate and the product of oleyl coenzyme A desaturase from Carthamus tinctorius. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaire P. J., Kekwick R. G. The synthesis of fatty acids in avocado mesocarp and cauliflower bud tissue. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):425–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1460425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


