Abstract
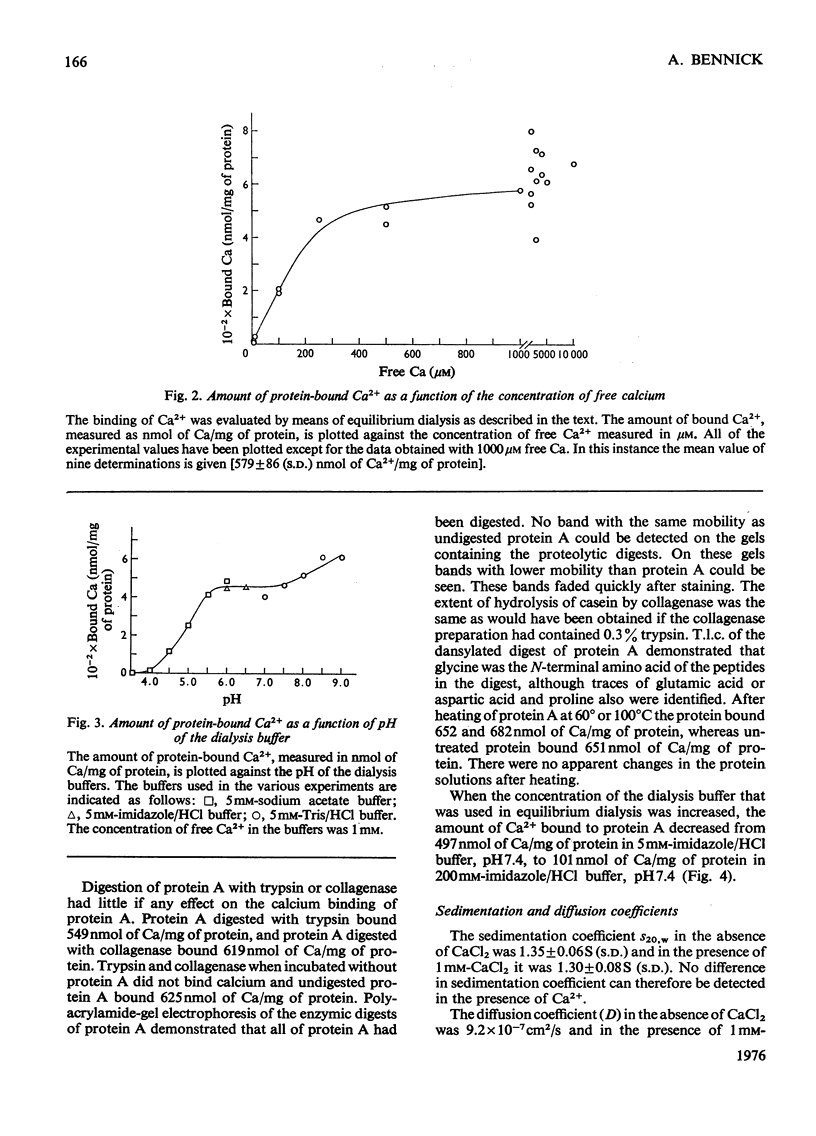
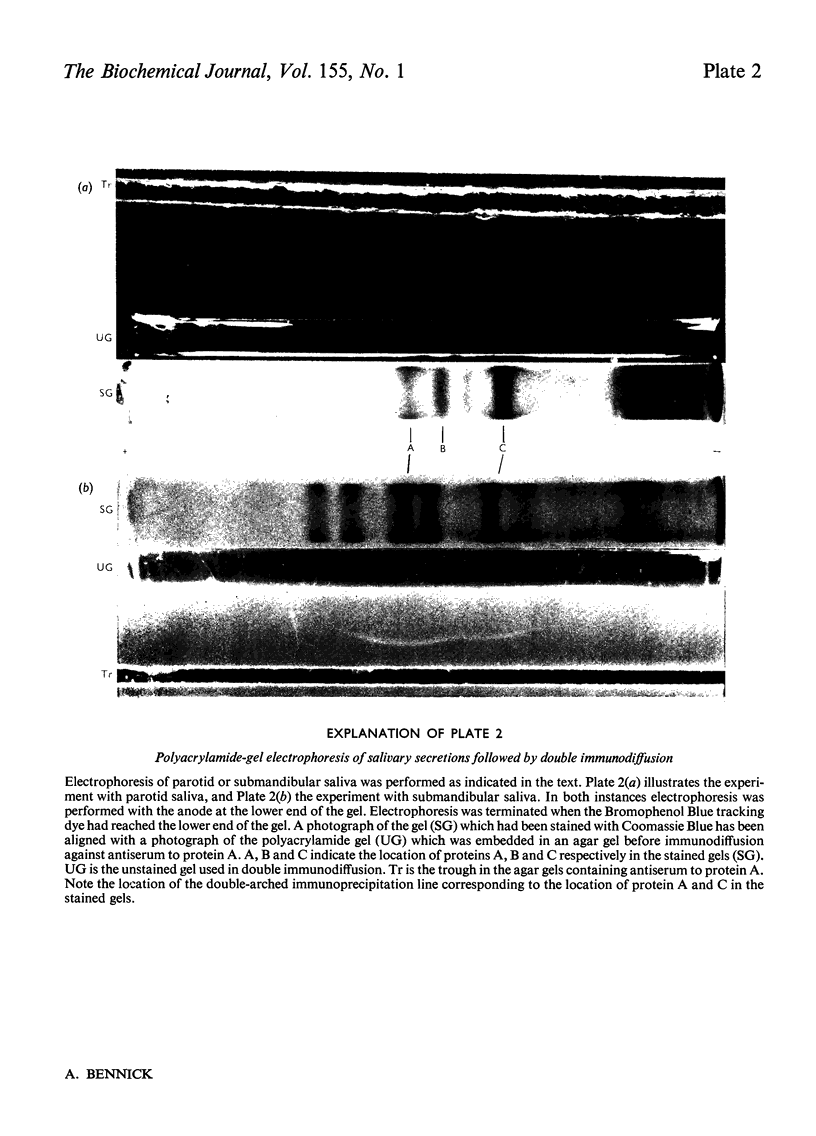
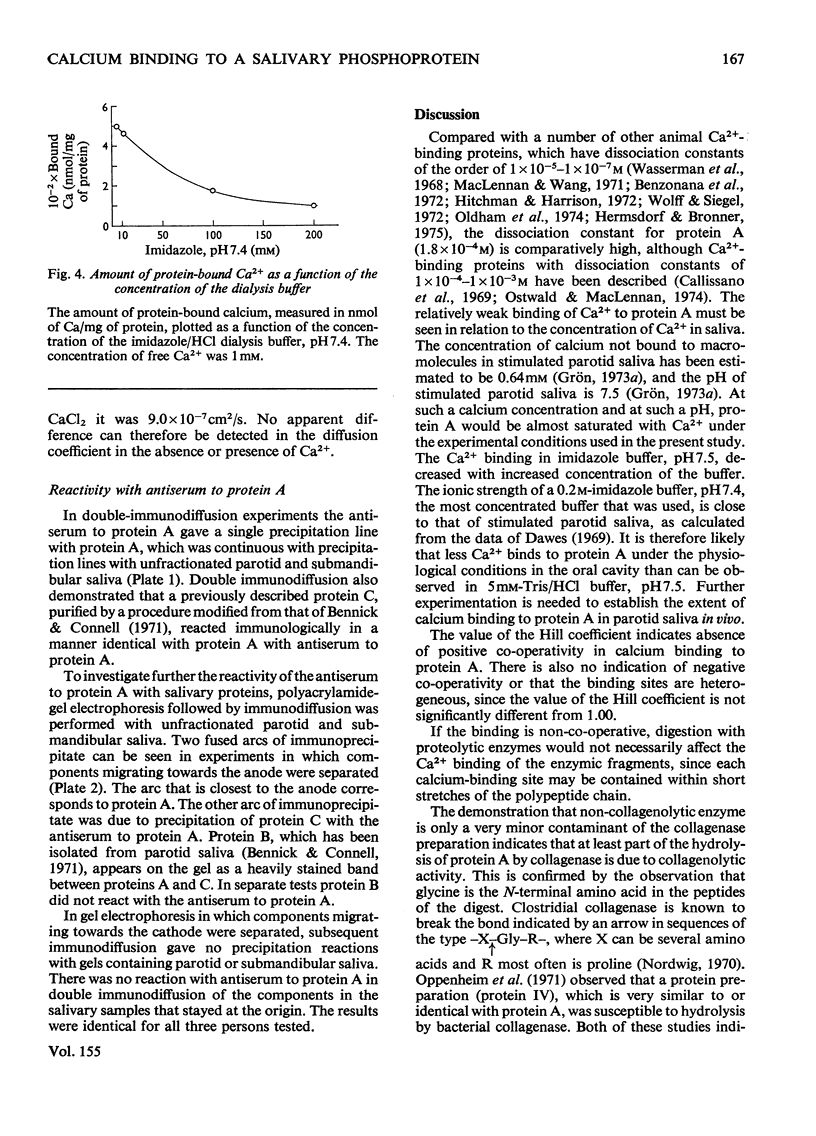
The binding of Ca2+ to a previously described phosphoprotein from human parotid saliva, protein A [Bennick (1975) Biochem J. 145, 557-567] was studied by means of equilibrium dialysis. In 5 mM-Tris/HC1 buffer, pH7.5, protein A bound 664nmol of Ca/mg of protein. Km was determined to be 181 muM and the binding of Ca2+ to the protein was non-co-operative. The binding of Ca2+ apparently occurs to side-chain carboxyl groups in the protein, but protein phosphate is of minor if any importance in calcium binding. Hydrolysis of protein A by trypsin and collagenase or heating of the protein at 60 degrees or 100 degrees C did not affect Ca2+ binding. The Ca2+ binding decreases with increased concentration of the dialysis buffer and on the addition of SrCl2, or MgCl2 or MnCl2 to the dialysis buffer. Protein A does not aggregate in the presence of Ca2+, since the s20,w was identical when determined in the presence (1.30S) and absence (1.35S) of CaCl2. By use of a specific antiserum to protein A it was found that protein C [Bennick & Connell (1971) Biochem. J. 123, 455-464] and perhaps minor related components cross-reacted with protein A. No other salivary proteins showed immunological similarity. Proteins A and C were also present in submandibular saliva. The possible functions of protein A are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrens G., Lücke H. The effects of stimulation and time of day on the calcium concentrations in human parotid and submandibular saliva. Caries Res. 1972;6(2):148–155. doi: 10.1159/000259786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arneberg P. Partial characterization of five glycoprotein fractions secreted by the human parotid glands. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Oct;19(10):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E. A., Oppenheim F. G. Genetic polymorphism of proline-rich human salivary proteins. Science. 1973 Jun 8;180(4090):1067–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4090.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characteristics of a phosphoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1450557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Connell G. E. Purification and partial characterization of four proteins from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1230455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzonana G., Capony J. P., Pechere J. F. The binding of calcium to muscular parvalbumins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boat T. F., Wiesman U. N., Pallavicini J. C. Purification and properties of the calcium-precipitable protein in submaxillary saliva of normal and cystic fibrosis subjects. Pediatr Res. 1974 May;8(5):531–539. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197405000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calissano P., Moore B. W., Friesen A. Effect of calcium ion on S-100, a protein of the nervous system. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4318–4326. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes C., Ong B. Y. Circadian rhythms in the concentrations of protein and the main electrolytes in human unstimulated parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Oct;18(10):1233–1242. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes C. The effects of flow rate and duration of stimulation on the condentrations of protein and the main electrolytes in human parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLSCH G., OSTERBERG R. The apparent acid ionization constants of some O-phosphorylated peptides and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2298–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. B., Fort A., Elliott A. L., Potts A. J. Circadian rhythms in human parotid saliva flow rate and composition. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Sep;18(9):1155–1173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gron P. Saturation of human saliva with calcium phosphates. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Nov;18(11):1385–1392. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gron P. The state of calcium and inorganic orthophosphate in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Nov;18(11):1365–1378. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Oppenheim F. G. The isolation from human parotid saliva of a further group of proline-rich proteins. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Aug;19(8):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I. The interaction of human parotid salivary proteins with hydroxyapatite. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Dec;18(12):1517–1529. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin R. I., Lippoldt R. E., Bilstad J., Edelhoch H. A zinc protein isolated from human parotid saliva. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermsdorf C. L., Bronner F. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from rat kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):553–561. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Calcium binding proteins in the duodenal mucosa of the chick, rat, pig, and human. Can J Biochem. 1972 Jul;50(7):758–765. doi: 10.1139/o72-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J., Robinovitch M., Iversen J., Kauffman D. L. The protein composition of rat parotid saliva and secretory granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):562–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Wong P. T. Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutzbauer H., Schulz G. V. Die Bestimmung der molekularen Konstanten von alpha-Amylase aus Humanspeichel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 22;102(2):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordwig A. Collagenolytic enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;34:155–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470122792.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham S. B., Fischer J. A., Shen L. H., Arnaud C. D. Isolation and properties of a calcium-binding protein from porcine parathyroid glands. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4790–4796. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Hay D. I., Franzblau C. Proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva. I. Isolation and partial characterization. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4233–4238. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostwald T. J., MacLennan D. H. Isolation of a high affinity calcium-binding protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):974–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy M. E., Buchwald B. M. A manual method of sequential Edman degradation followed by dansylation for the determination of protein sequences. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinovitch M. R., Keller P. J., Iversen J., Kauffman D. L. Demonstration of a class of proteins loosely associated with secretory granule membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 13;382(2):260–24b. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Jonsen J. The calcium-binding effect of a human salivary glycoprotein. Caries Res. 1967;1(4):343–348. doi: 10.1159/000259534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEYER L. H. Amylase content of separate salivary gland secretions of man. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Nov;9(3):453–455. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truelove E. L., Bixler D., Merritt A. D. Simplified method for collection of pure submandibular saliva in large volumes. J Dent Res. 1967 Nov-Dec;46(6):1400–1403. doi: 10.1177/00220345670460064301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L., STEIN E. A., SUMERWELL W. N., FISCHER E. H. Metal content of alpha-amylases of various origins. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2901–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Schramm M. Calcium and the exportable protein in rat parotid gland. Parallel subcellular distribution and concomitant secretion. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Taylor A. N. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windeler A. S., Jr, Shannon I. L. The effect of flow rate on parotid fluid calcium and protein levels. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Oct;11(10):1043–1045. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Siegel F. L. Purification of a calcium-binding phosphoprotein from pig brain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4180–4185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]