Abstract
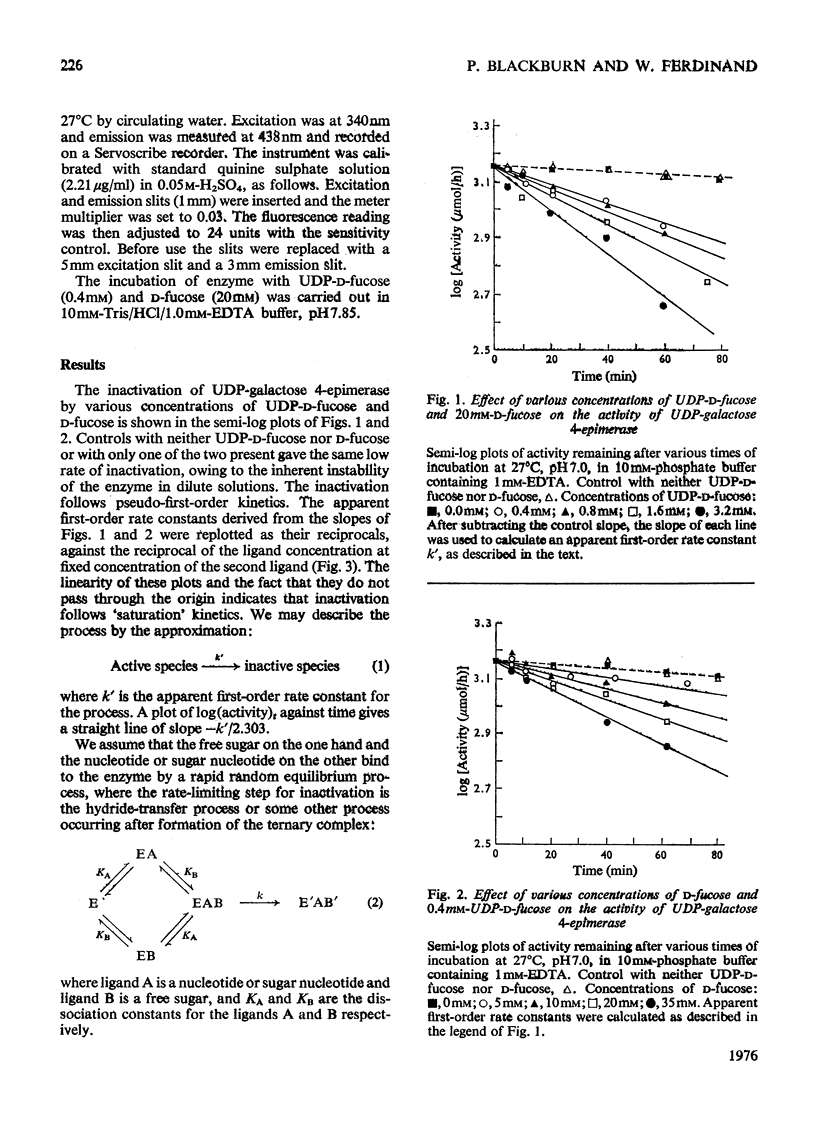
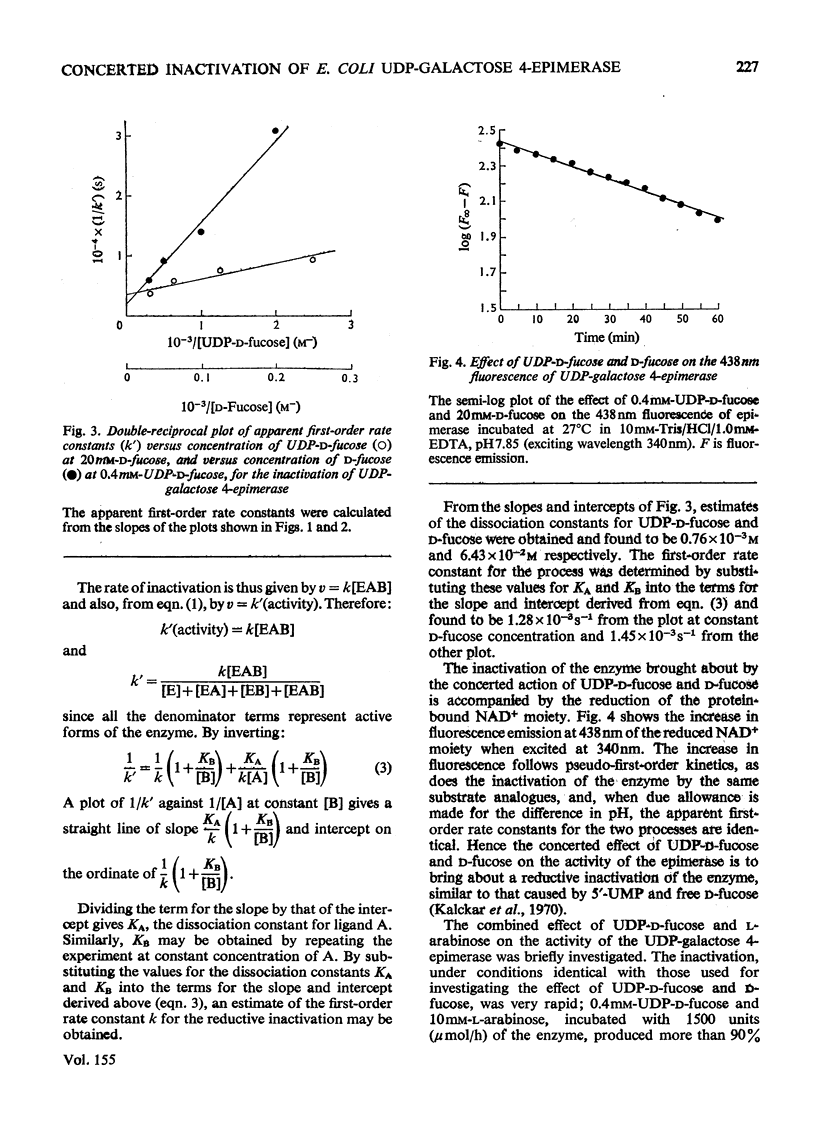
1. The combined effect of the sugar nucleotides UDP-D-fucose or UDP-D-glucuronic acid together with the free sugars D-fucose or L-arabinose is the inactivation of the Escherichia coli enzyme UDP-galactose 4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2). The sugar nucleotide or the free sugar alone or the sugar nucleotide plus 5'-Ump do not inactivate the enzyme. 2. The inactivation of the enzyme by its substrate UDP-D-glucose was not affected by the presence of free sugar. 3. In all cases the inactivation observed follows pseudo-first-order kinetics. 4. A comparison of various sugar nucleotides indicates that the hydroxymethyl group at position 6 of the sugar moiety of the natural substrates is important for substrate binding.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTIN G. M'ECANISMES R'EGULATEURS DANS LA BIOSYNTH'ESE DES ENZYMES DU M'ETABOLISME DU GALACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. II. LE D'ETERMINISME G'EN'ETIQUE DE LA R'EGULATION. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:183–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertland A., Bugge B., Kalckar H. M. Fluorescence enhancement of uridine diphosphagalactose 4-epimerase induced by specific sugars. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):280–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalckar H. M., Bertland A. U., 2nd, Bugge B. The reductive inactivation of UDPgalactose-4-epimerase from yeast and E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1113–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang U. G., Nolan L. D., Frey P. A. Uridine diphosphate galactose-4-epimerase. Uridine monophosphate-dependent reduction by alpha- and beta-D-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7099–7105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketley J. N., Schellenberg K. A. Substrate stereochemical requirements in the reductive inactivation of uridine diphosphate galactose 4-epimerase by sugar and 5'-uridine monophosphate. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):315–320. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuem G. L., Kirkwood S. The mechanism of action of the enzyme uridine diphosphoglucose 4-epimerase. Proof of an oxidation-reduction mechanism with direct transfer of hydrogen between substrate and the B-position of the enzyme-bound pyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7533–7543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin J. H., Salo W. L., Bevill R. D., Kirkwood S. A vacuum system for the synthesis of nucleotide sugars on a micro scale. Anal Biochem. 1965 Dec;13(3):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo W. L., Nordin J. H., Peterson D. R., Bevill R. D., Kirkwood S. The specificity of UDP-glucose 4-epimerase from the yeast Saccharomyces fragilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 5;151(2):484–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyama Y., Kalckar H. M. Specific tritium labeling of uridine diphosphogalactose 4-epimerase by D-(1- 3 H) galactose. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 4;11(1):36–40. doi: 10.1021/bi00751a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M., Blackburn P., Ferdinand W., Blackburn G. M. Competitive inhibition and substrate activity of uridine diphosphate 6-deoxygalactose for Escherichia coli uridine diphosphate galactose 4-epimerase. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):421–423. doi: 10.1042/bj1310421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON D. B., HOGNESS D. S. THE ENZYMES OF THE GALACTOSE OPERON IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF URIDINE DIPHOSPHOGALACTOSE 4-EPIMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2469–2481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


