Abstract
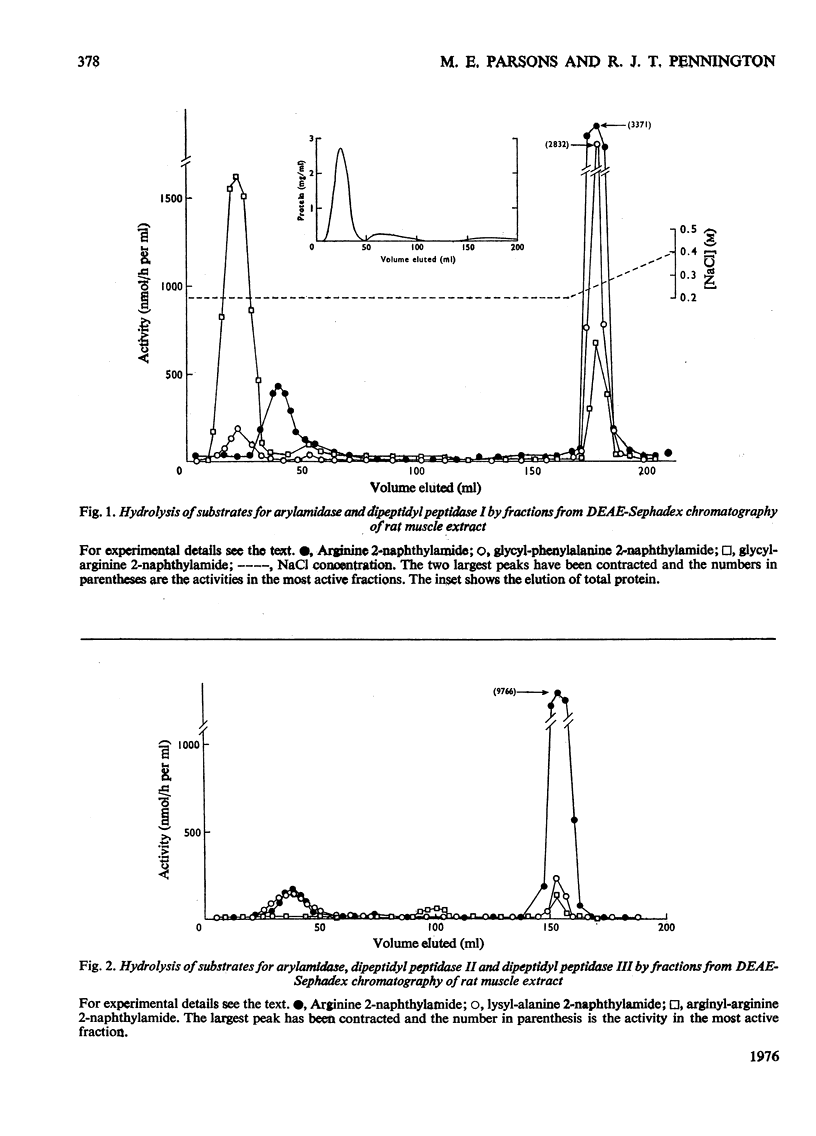
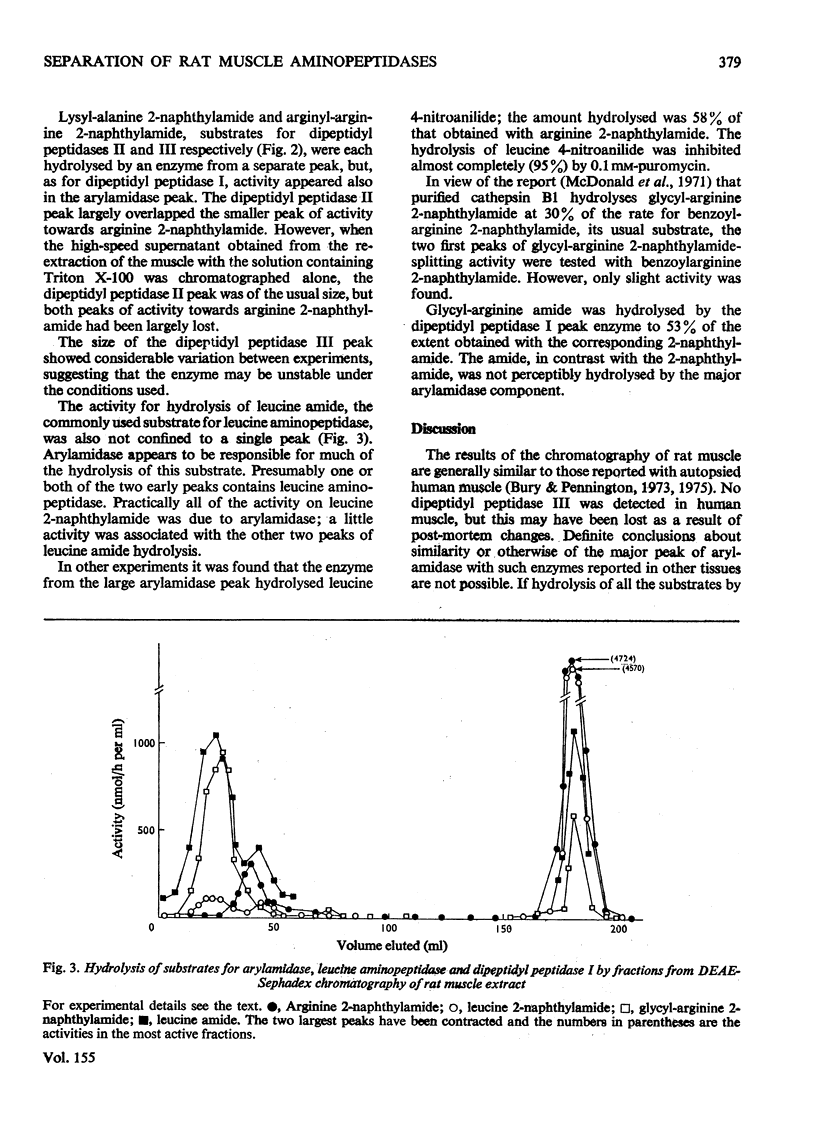
By means of chromatography on DEAE-Sephadex, two arylamidases (hydrolysing L-arginine 2-naphthylamide) and three dipeptidyl peptidases (hydrolysing dipeptide 2-naphthylamides) were distinguished in extracts of rat muscle. However, the arylamidase from the larger peak also hydrolysed the dipeptide 2-naphthylamides. Glycyl-L-arginine amide, an alternative substrate for dipeptidyl peptidase I, was not hydrolysed by arylamidase. L-Leucine amide was hydrolysed by an enzyme, presumed to be leucine aminopeptidase, from a separate peak, but was also hydrolysed by arylamidase. Arylamidase, dipeptidyl peptidase III and most of the leucine aminopeptidase could be extracted from the muscle with a neutral salt solution, but dipeptidyl peptidase I was extracted only in the presence of Triton X-100; dipeptidyl peptidase II showed an intermediate extraction behaviour.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behal F. J., Asserson B., Dawson F., Hardman J. A study of human tissue aminopeptidase components. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma J. M., Gruber M. Intracellular distribution of cathepsin B and cathepsin C in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bury A. F., Pennington R. J. Hydrolysis of diepptide 2-naphthylamides by human muscle enzymes. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;145(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1450413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R., BAUDHUIN P. Distribution of enzymes between subcellular fractions in animal tissues. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1962;24:291–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470124888.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S., Perry M. Pituitary arylamidases and peptidases. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3679–3686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felicetti D., Gründig C. A., Hanson H. Zum Verhalten von Glyzyl-D-leuzin und L-Leuzinamid spaltenden Enzymaktivitäten in Rohhomogenaten aus menschlichen Nieren und Rattennieren auf Sephadex G 200. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;26(3):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu V. K., Mäkinn K. K., Glenner G. G. Characterization of aminopeptidase B: substrate specificity and affector studies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jun;114(3):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R. L., Sanders W. J. Leucine aminopeptidase in extracts of swine muscle. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):827–832. doi: 10.1042/bj1000827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren E., Roos G. Plasma membrane-bound and lysosomal isozymes of amino acid naphthylamidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 17;358(1):208–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks N., Datta R. K., Lajtha A. Partial resolution of brain arylamidases and aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2882–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Ellis S., Reilly T. J. Properties of dipeptidyl arylamidase I of the pituitary. Chloride and sulfhydryl activation of seryltyrosyl-beta-naphthylamide hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1494–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Reilly T. J., Ellis S. A chloride-activated dipeptidyl-beta-naphthylamidase of the pituitary gland. Life Sci. 1965 Sep;4(17):1665–1668. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Reilly T. J., Zeitman B. B., Ellis S. Dipeptidyl arylamidase II of the pituitary. Properties of lysylalanyl-beta-naphthylamide hydrolysis: inhibition by cations, distribution in tissues, and subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):2028–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan D. J. Inhibition of the indophenol reaction in the spectrophotometric determination of ammonia. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):59–61. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON E. K., HSIAO S. H., KEPPEL A. STUDIES ON DIPEPTIDASES AND AMINOPEPTIDASES. I. DISTINCTION BETWEEN LEUCINE AMINOPEPTIDASE AND ENZYMES THAT HYDROLYZE L-LEUCYL-BETA-NAPHTHYLAMIDE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3611–3620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGSON D., SELIGSON H. A microdiffusion method for the determination of nitrogen liberated as ammonia. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Aug;38(2):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Brecher A. S. Brain aminoacyl arylamidase. Further purification of the soluble bovine enzyme and studies on substrate specificity and possible active-site residues. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 29;9(20):4008–4017. doi: 10.1021/bi00822a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Ninjoor V., Dowd D. M., Tappel A. L. Cathepsin B2 measurement by sensitive fluorometric ammonia analysis. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanha-Perttula T., Hopsu V. K., Sonninen V., Glenner G. G. Cathepsin C activity as related to some histochemical substrates. Histochemie. 1965 Jul 27;5(2):170–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00285511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


