Abstract
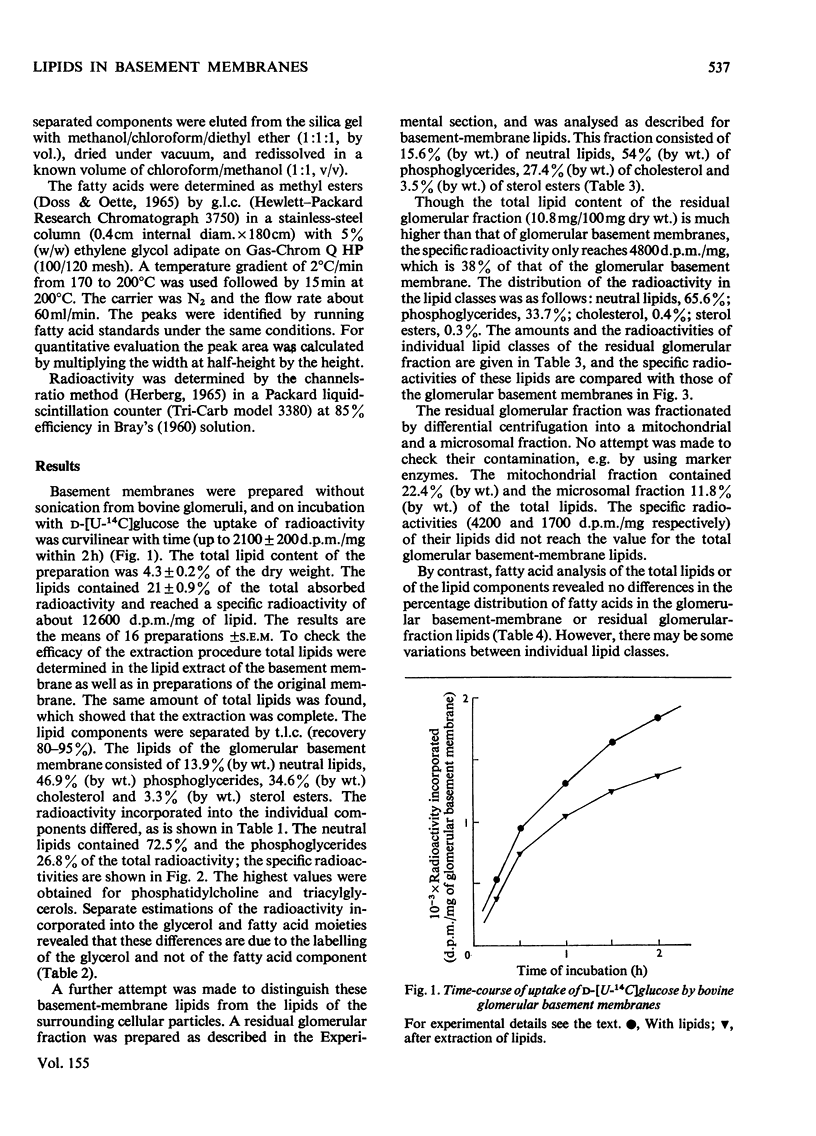
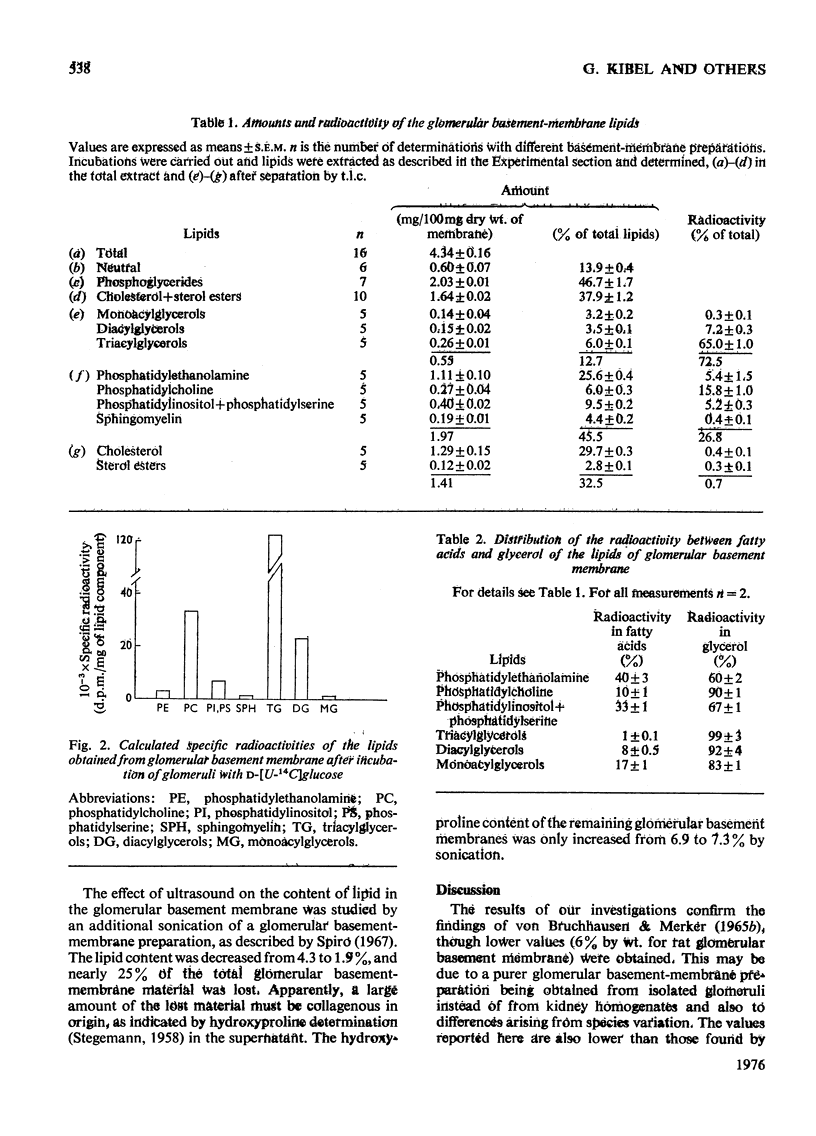
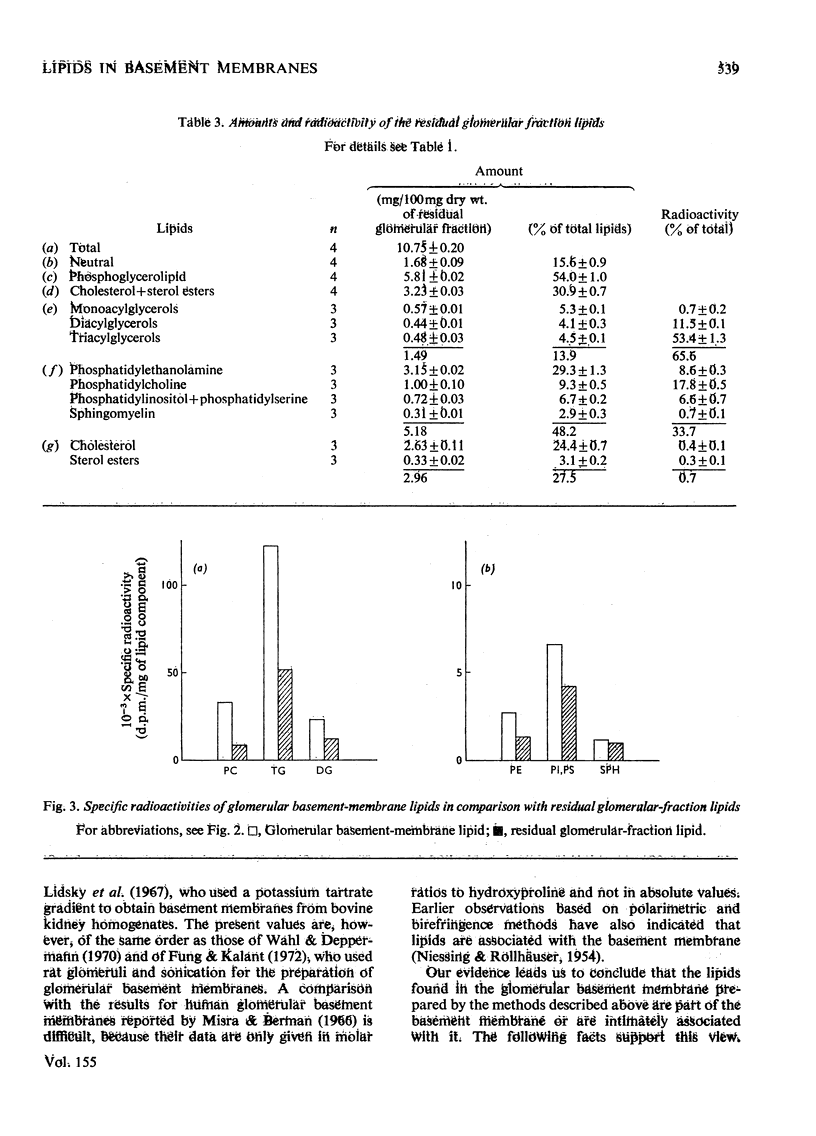
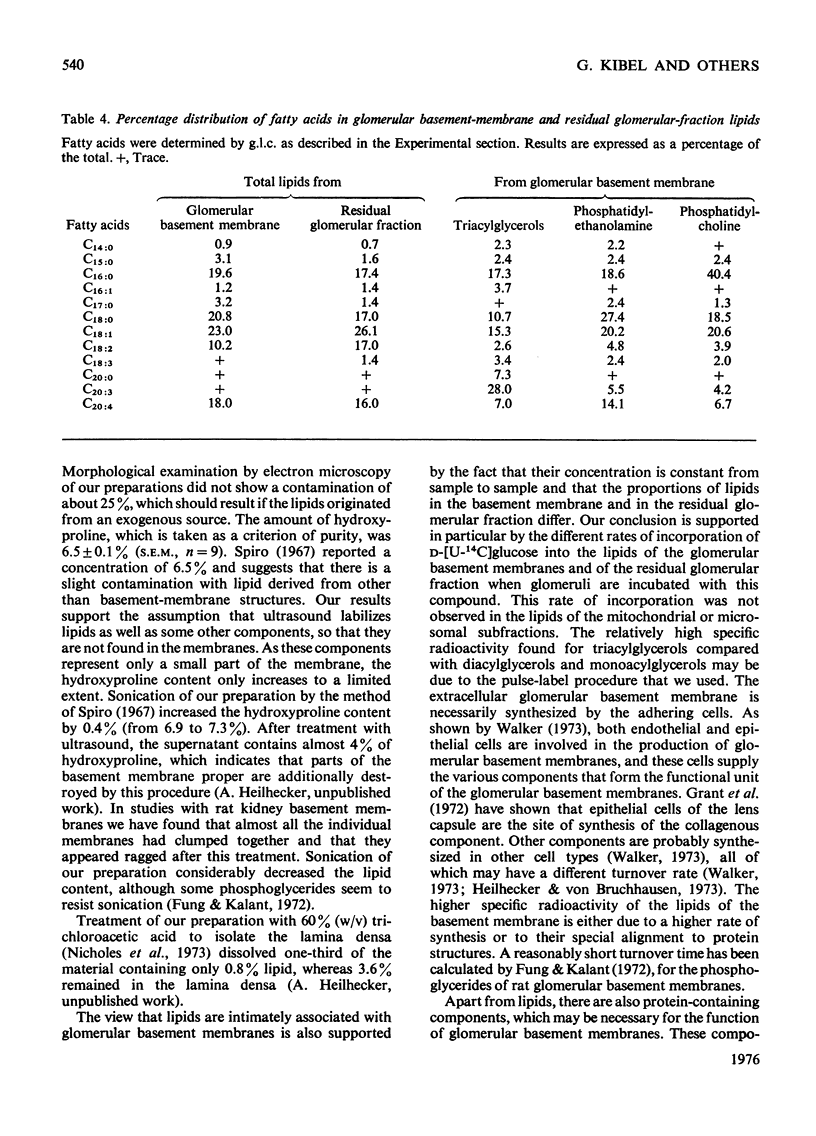
1. After incubation of bovine glomeruli with D-[U-14C]glucose, about 21% of the total radioactivity is found in lipid extracts of glomerular basement membranes. 2. The concentration of lipids in glomerular basement membranes (4.3% of dry wt.) is lower than in the residual glomerular particles (10.8% of dry wt.). The concentrations of neutral lipids (13.9%), phospholipids (46.7%) and cholesterol (37.9%) in the total lipid extract of the glomerular basement membranes, however, differ from those in the residual glomerular particles (15.6, 54.0 and 30.9% respectively). Though residual glomerular particles show a higher lipid content, the radioactivity in this fraction only amounts to 38% of that found in the glomerular basement membranes. 3. The specific radioactivity of total glomerular basement-membrane lipids (12 600 d.p.m./mg) is about 4 times as high as that of the glomerular basement membranes. The specific radioactivities of the individual lipid components, however, differ. The highest values are found for phosphatidylcholine and triacylglycerols. The largest proportion of the radioactivity is found in the glycerol of the glycerides. The radioactivity in the fatty acids is much less and does not differ significantly in the various classes of lipids. 4. G.1.c. of methyl esters of the fatty acids does not reveal a clear difference between the fatty acid compositions of glomerular basement membranes and residual glomerular particles. 5. Treatment of glomerular basement-membrane preparations with ultrasound, the generally used procedure for glomerular basement-membrane preparations, drastically decreases the lipid content of glomerular basement membranes. 6. It is concluded that lipids are associated with the basement membranes. Further, the comparatively high radioactive labelling suggests that glomerular basement-membrane lipids may be an interesting class of substances for further pathological studies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES G. A., MORGAN C., HSU K. C., RIFKIND R. A., SEEGAL B. C. Electron microscopic studies of experimental nephritis with ferritin-conjugated antibody. The basement membranes and cisternae of visceral epithelial cells in nephritic rat glomeruli. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:929–936. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSSEL L., LISEWSKI G., MOHNIKE G. [Electron microscopic and clinical studies in diabetic glomerulosclerosis]. Klin Wochenschr. 1959 Oct 1;37:1005–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF01483208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doss M., Oette K. Schnellmethode zur Darstellung von Fettsäuremethylestern für die gaschromatographische Analyse. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1965 Aug;3(4):125–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., WISSIG S. L., PALADE G. E. Glomerular permeability. I. Ferritin transfer across the normal glomerular capillary wall. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:47–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C. P., West D. Complete separation of lipid classes on a single thin-layer plate. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):324–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung K. K., Kalant N. Phospholipid of the rat glomerular basement membrane in experimental nephrosis. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):733–741. doi: 10.1042/bj1290733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gang N. F., Kalant N. Nephrotoxic serum nephritis. I. Chemical, morphologic, and functional changes in the glomerular basement membrane during the evolution of nephritis. Lab Invest. 1970 Jun;22(6):531–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekle D., Bruchhausen F., Fuchs G. Porenäquivalentradien isolierter Basalmembranen der Ratternniere nach Einwirkung von Aminonucleosid. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;290(3):250–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00363129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. E., Harwood R., Williams I. F. The biosynthesis of basement-membrane collagen by isolated rat glomeruli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. E., Kefalides N. A., Prockop D. J. The biosynthesis of basement membrane collagen in embryonic chick lens. II. Synthesis of a precursor form by matrix-free cells and a time-dependent conversion to chains in intact lens. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3545–3551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. O., Lundbaek K., Olsen T. S., Orskov H. Kidney lesions in rats with severe long term alloxan diabetes. 3. Glomerular ultrastructure. Lab Invest. 1967 Dec;17(6):675–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel E., Geyer G. Experimentelle Untersuchungen an der glomerulären Basalmembran in der Niere der Maus. Anat Anz. 1967;120(1):84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURTZ S. M., FELDMAN J. D. Experimental studies on the formation of the glomerular basement membrane. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Feb;6:19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURTZ S. M. The electron microscopy of the developing human renal glomerulus. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Apr;14(2):355–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Biochemical properties of human glomerular basement membrane in normal and diabetic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Winzler R. J. The chemistry of glomerular basement membrane and its relation to collagen. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):702–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANNIGAN R., BLAINEY J. D., BREWER D. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE DIFFUSE GLOMERULAR LESION IN DIABETES MELLITUS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO EARLY CHANGES. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky M. D., Sharp J. T., Rudee M. L. Studies on acellular bovine glomeruli. Isolation, chemical composition, and demonstration of collagen with an unusual hydroxylysine: hydroxyproline ratio. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):491–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R. P., Berman L. B. Studies on glomerular basement membrane. 1. Isolation and chemical analysis of normal glomerular basement membrane. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):705–710. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R. P., Berman L. B. Studies on glomerular basement membrane. 3. Effects of steroid on membrane chemistry and its protein permeability. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):666–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIESSING K., ROLLHAUSER H. Uber den submikroskopischen Bau des Grundhäutchens der Hirnkapillaren. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1954;39(4):431–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholes B. K., Krakower C. A., Greenspon S. A. The chemically isolated lamina densa of the renal glomerulus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1316–1321. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEGEMANN H. Mikrobestimmung von Hydroxyprolin mit Chloramin-T und p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyd. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1958;311(1-3):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on the renal glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and chemical composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenes W. Endoplasmatisches Retikulum und "Sekretkörper" in Glomerulum-Epithel der Säugerniere. Ein morphologischer Beitrag zum Problem der Basalmembran-Bildung. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;78(4):561–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNIER R. L., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. Studies of the human fetal kidney. I. Development of the glomerulus. J Pediatr. 1962 May;60:754–768. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Deppermann D. Untersuchungen zur Pathogenese der diabetischen Mikroangiopathie. II. Die chemische Zusammensetzung der glomerulären Basalmembran der Ratte. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 Jun 1;48(11):653–658. doi: 10.1007/BF01493809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Krezdorn W., Deppermann D. Untersuchungen zur Pathogenese der diabetischen Mikroangiopathie. I. Isolierung von Nierenglomerula und glomerulären Basalmembranen. Durchführung und Prinzip der Method. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 Jun 1;48(11):650–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01493808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. The origin, turnover and removal of glomerular basement-membrane. J Pathol. 1973 Jul;110(3):233–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., Michael A. F. Human glomerular basement membrane. Preparation and composition. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 15;9(19):3837–3846. doi: 10.1021/bi00821a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bruchhausen F., Merker H. J. Gewinnung und morphologische Charakterisierung einer Basalmembranfraktion aus der Nierenrinde der Ratte. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1965 Jun 1;251(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bruchhausen F. Zur Biosynthese der Basalmembran. Die Verwertung von Prolin nd Glucose zum Aufbau von Bestandteilen der glomerulären Basalmembran in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;268(1):83–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


