Abstract
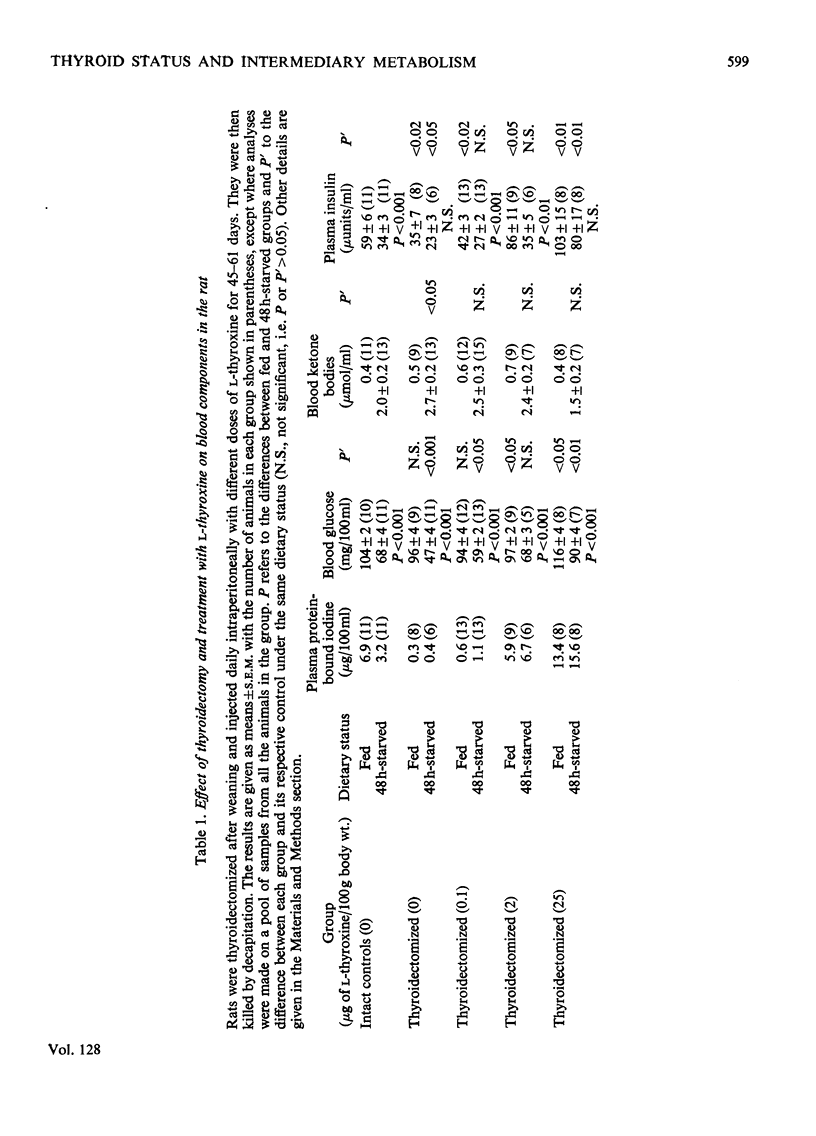
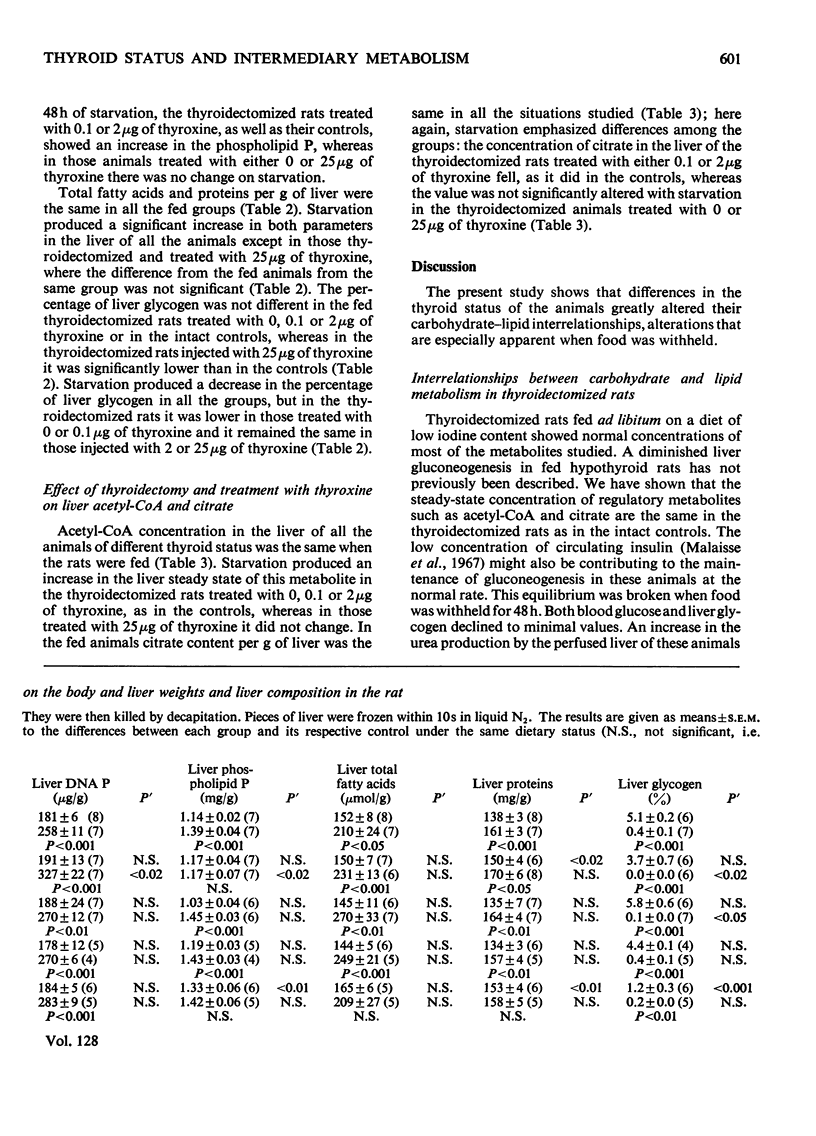
1. Thyroidectomized rats injected daily with 0, 0.1, 2 or 25μg of l-thyroxine/100g body wt. were compared with intact controls. In plasma, the protein-bound iodine was decreased in the rats given the 0 or 0.1μg doses and increased in those given the 25μg dose. 2. Blood glucose decreased in those given 2μg and was augmented in those given 25μg, and ketone bodies were the same in all the groups. 3. Plasma insulin was lowest in the rats given the 0 or 0.1μg doses and was highest in those given the 2 or 25μg doses of thyroxine. 4. After 48h starvation, the decrease in blood glucose and increase in ketone bodies observed in all the groups was greatest in the group not supplemented with thyroxine. 5. Plasma insulin concentrations remained at the value for fed animals in the rats given the 25μg dose of thyroxine but decreased in the other groups. 6. In fed animals, concentrations of hepatic DNA P, citrate, total fatty acids and acetyl-CoA were similar in all the groups, and glycogen was low only in the rats given the 25μg dose of thyroxine. 7. After 48h starvation, liver DNA P, total fatty acids and acetyl-CoA increased in all the groups, except in the rats given the 25μg dose, where both total fatty acids and acetyl-CoA remained at the value for fed animals. Liver citrate did not change in the groups given the 0 or 25μg doses of thyroxine, but decreased in the other groups. 8. The results are discussed in relation to the regulation of intermediary metabolism in hypo- and hyper-thyroidism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENOTTI J., BENOTTI N. PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE, TOTAL IODINE, AND BUTANOL-EXTRACTABLE IODINE BY PARTIAL AUTOMATION. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., Goodman H. M. Metabolism of adipose tissue from normal and hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1968 Apr;82(4):860–864. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-4-860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler R., Wittels B. The effect of thyroxine on lipid and carbohdrate metabolism in the heart. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1326–1333. doi: 10.1172/JCI105439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. M. Interrelation of insulin activity and thyroid function. Am J Physiol. 1957 Feb;188(2):287–294. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.188.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe W. G. The colorimetric micro-determination of long-chain fatty acids. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):7–10. doi: 10.1042/bj0880007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELGEE N. J., WILLIAMS R. H. Effects of thyroid function on insulin-I131 degradation. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jan;180(1):13–15. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.180.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar del Rey F., Morreale de Escobar G., Jolin T., Lopez-Quijada C. Effects of small doses of thyroid hormones on thyroid weight in hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1968 Jul;83(1):41–50. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREINKEL N. Pathways of thyroid phosphorus metabolism; the phospholipids of sheep thyroid. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):327–333. doi: 10.1042/bj0680327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedland R. A., Krebs H. A. The effect of thyroxine treatment on the rate of gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):45P–45P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey H. M. Peripheral circulatory and metabolic consequences of thyrotoxicosis. II. Uptake of free fatty acids by the gracilis muscle in normal and thyrotoxic dogs. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1967;19(1):15–28. doi: 10.3109/00365516709093477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMBURGER J., SMITH R. W., Jr, MILLER J. M. EFFECTS OF EPINEPHRINE ON FREE FATTY ACID MOBILIZATION IN HYPERTHYROID AND HYPOTHYROID SUBJECTS. Metabolism. 1963 Sep;12:821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera E., Freinkel N. Internal standards in the estimation of acetyl-CoA in liver extracts. J Lipid Res. 1967 Sep;8(5):515–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera E., Freinkel N. Interrelationships between liver composition, plasma glucose and ketones, and hepatic acetyl-CoA and citric acid during prolonged starvation in the male rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):244–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera E., Knopp R. H., Freinkel N. Carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancy. VI. Plasma fuels, insulin, liver composition, gluconeogenesis, and nitrogen metabolism during late gestation in the fed and fasted rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2260–2272. doi: 10.1172/JCI106192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A. Bovine ketosis. Vet Rec. 1966 Feb 5;78(6):187–192. doi: 10.1136/vr.78.6.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg B. A. Glucose metabolism in thyroid disease. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Sep;178(3):351–362. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1965.tb04279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein J. M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. Biochem Soc Symp. 1968;27:61–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., McCraw E. F. Effects of thyroid function upon insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):643–646. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menahan L. A., Wieland O. The role of endogenous lipid in gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis of perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):182–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering H., Gruber W. Determination of citrate with citrate lyase. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad S., Freedland R. A. Effect of thyroxine administration on enzymes associated with glucose metabolism in the liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Apr;124(4):1176–1178. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz J. L., Myerson R. M. The effects of triiodothyronine on some metabolic parameters of obese individuals. Blood C-14-glucose replacement rate, respiratory C-14-O-2, the pentose cycle, the biological half-life of T-3 and the concentration of T-3 in adipose tissue. Metabolism. 1967 Jan;16(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOW R. O. Development of obesity in force fed young thyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1951 Oct;49(4):522–529. doi: 10.1210/endo-49-4-522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Lambert A. E., Vecchio D., Renold A. E. Measurements of insulin activities in pancreas and serum of mice with spontaneous ("Obese" and "New Zealand Obese") and induced (Goldthioglucose) obesity and hyperglycemia, with considerations on the pathogenesis of the spontaneous syndrome. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):230–237. doi: 10.1007/BF01222200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szepsi B., Freedland R. A. Effect of thyroid hormones on metabolism IV. Comparative aspects of enzyme responses. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1054–1056. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. W. Effects of D- and L-thyroxine on enzymes in liver and adipose tissue of rats. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):378–383. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


