Abstract
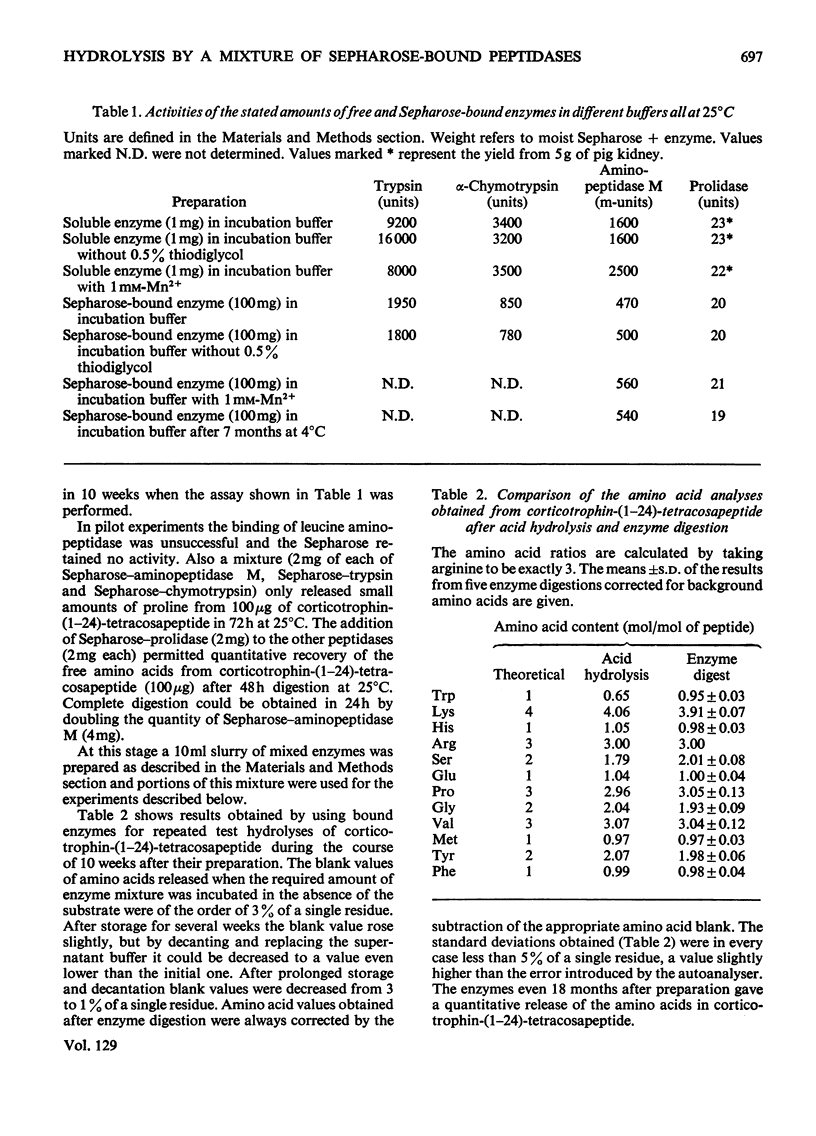
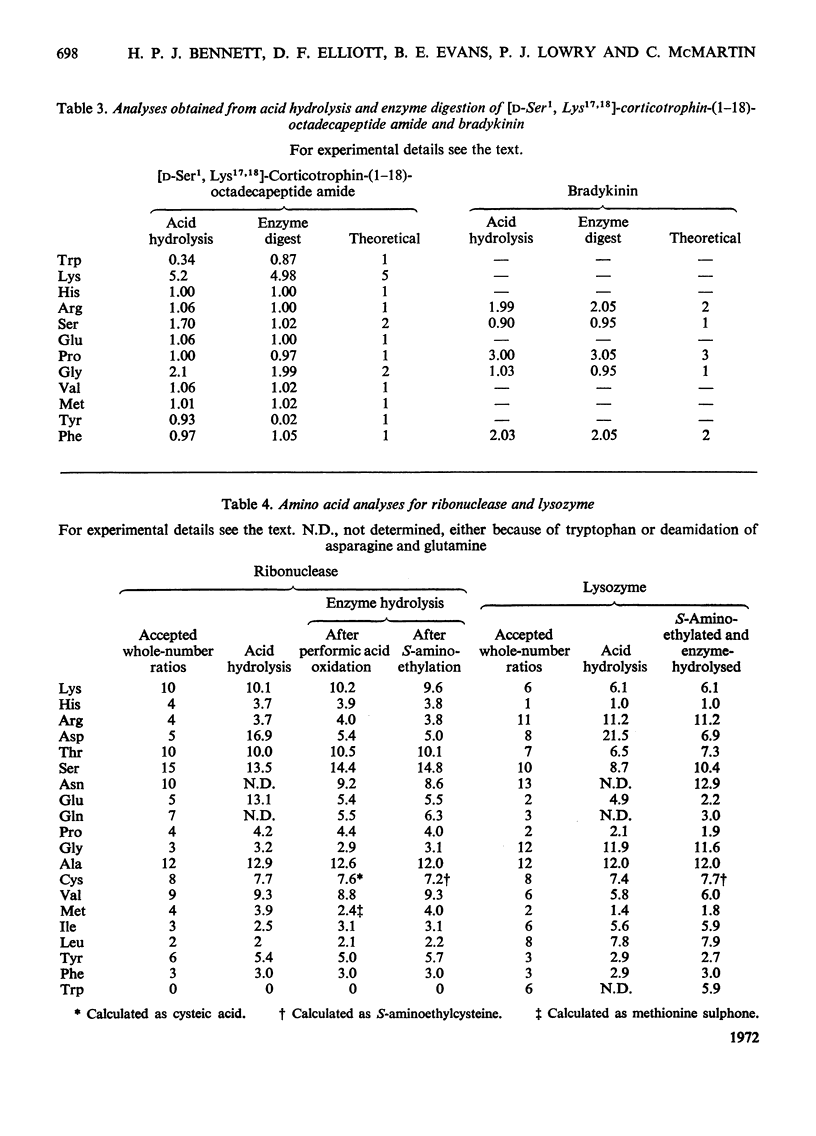
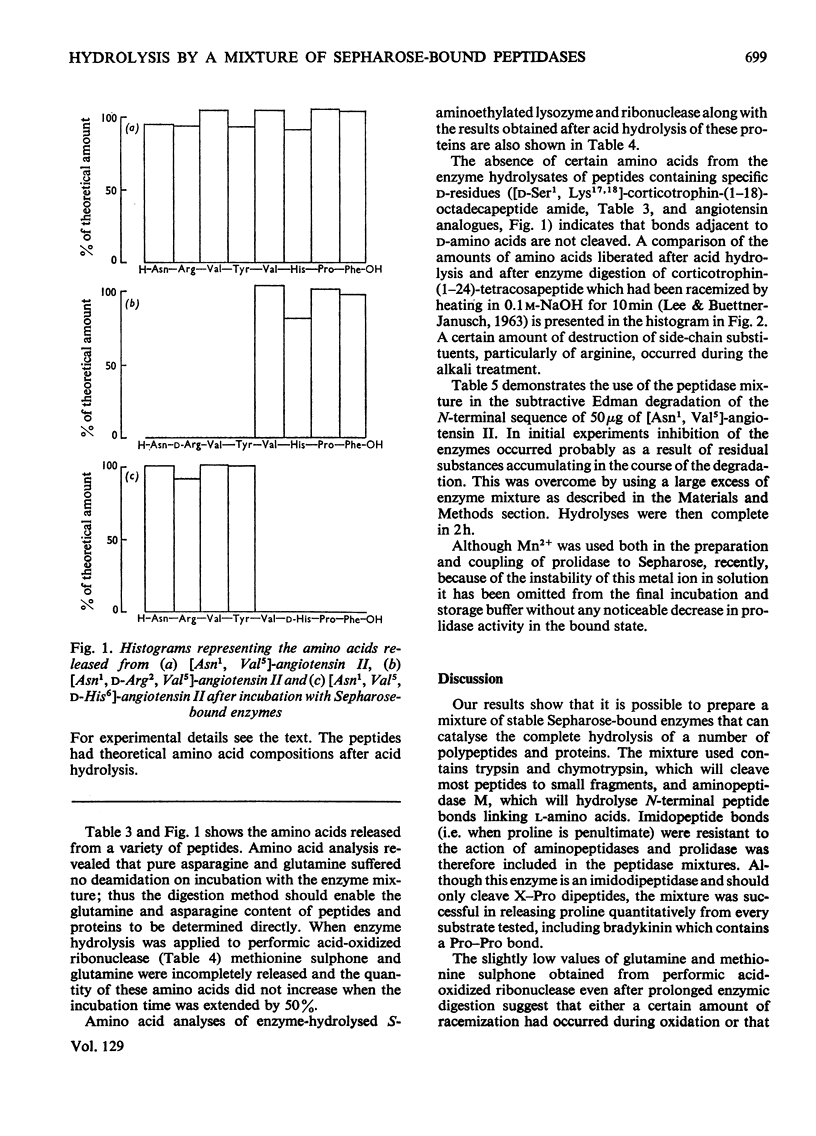
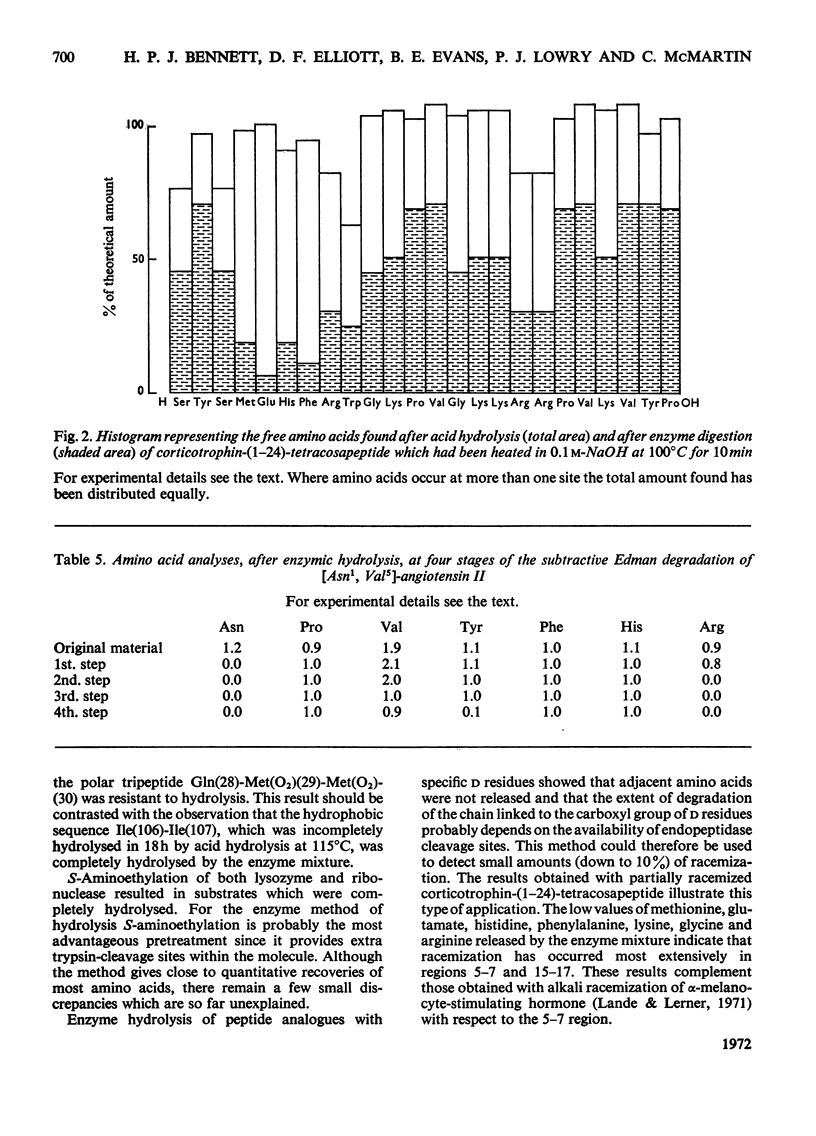
Incubation with a mixture of Sepharose-bound peptidases was shown to result in the quantitative release of amino acids from certain peptides and S-aminoethylated proteins. Subtraction of the low background values of amino acids generated by the enzymes enables amino acid ratios of corticotrophin-(1–24)-tetracosapeptide to be determined with a standard deviation on repeat digestions of 3–5%. Good values were obtained for amino acids that are completely or partially destroyed on acid hydrolysis, i.e. tryptophan, tyrosine, serine, asparagine and glutamine. Experiments with peptides containing d-amino acids showed that the enzyme mixture is stereospecific and could therefore be used to detect the presence of d-residues in peptides. The enzyme mixture completely hydrolyses peptide fragments obtained after Edman degradation and should therefore be useful for determining sequences of peptides containing acid-labile amino acid residues. The activities of the bound enzymes were unaltered over a period of 7 months and they provide a simple, reproducible procedure for the quantitative determination of amino acids in peptides and proteins containing l-amino acids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS N. C., SMITH E. L. Purification and some properties of prolidase of swine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):261–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. L., SCHMIDT W. R. The complete enzymic hydrolysis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz E., Dietrich F. M., Sela M. A sensitive technique for detecting and estimating the peptide hormone angiotensin-II-beta-amide and its antibodies by using chemically modified bacteriophage and activated sepharose. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):273–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE T. H., BUETTNER-JANUSCH V. On the mechanism of sodium hydroxide modification of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2012–2015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lande S., Lerner A. B. Racemization of alpha-melanotropin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 19;251(2):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry P. J., Chadwick A. Purification and amino acid sequence of melanocyte-stimulating hormone from the dogfish Squalus acanthias. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):713–718. doi: 10.1042/bj1180713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riniker B., Rittel W. Die Synthese des corticotrop hochaktiven (1-D-Serin, 17,18-dilysin)-beta-corticotropin-(1-18)-octadecapeptidamids) Helv Chim Acta. 1970;53(3):513–519. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19700530307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riniker B., Sieber P., Rittel W., Zuber H. Revised amino-acid sequences for porcine and human adrenocorticotrophic hormone. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 26;235(56):114–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio235114b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber P., Rittel W., Riniker B. Die Synthese von menschlichem adrenocorticotropem Hormon ( h -ACTH) mit revidierter Aminosäuresequenz. Helv Chim Acta. 1972;55(4):1243–1266. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19720550420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman I., Katchalski E. Water-insoluble derivatives of enzymes, antigens, and antibodies. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:873–908. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


