Abstract
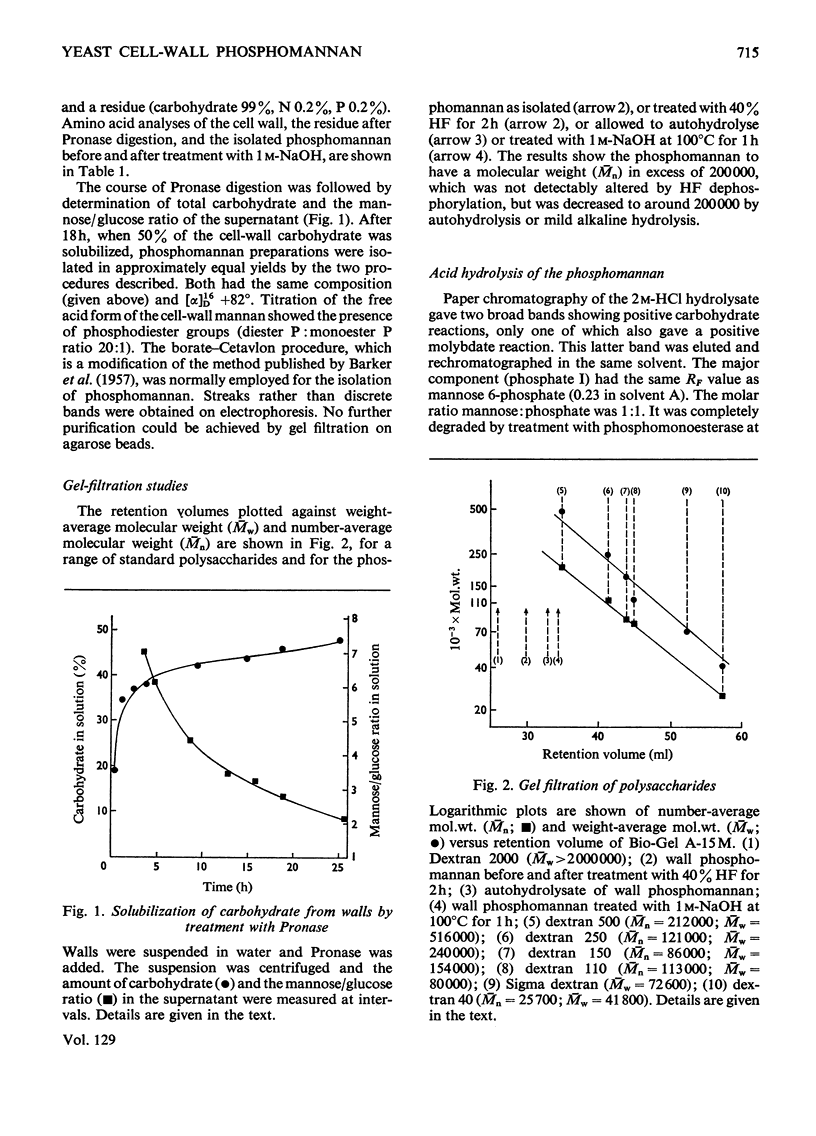
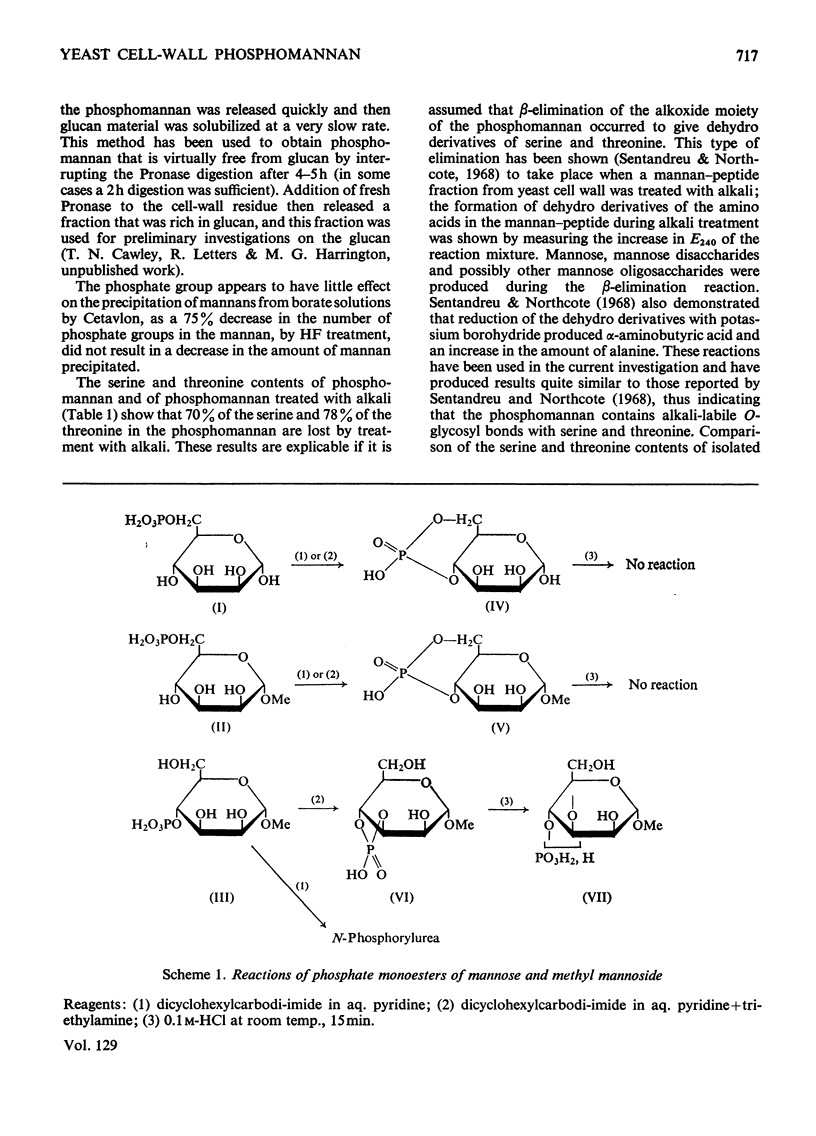
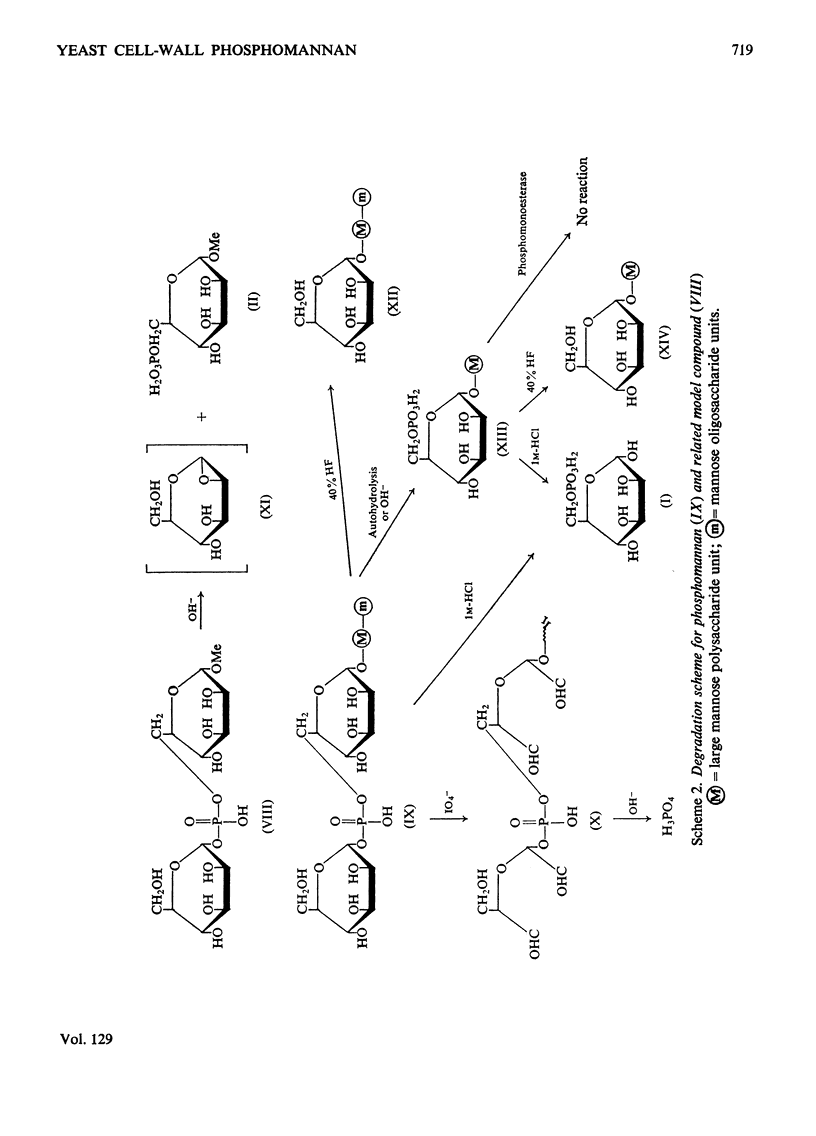
1. The phosphomannan of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was released by Pronase digestion of cell walls and isolated by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose or by precipitation with borate–Cetavlon solutions. Mannose and phosphorus were present in the molar ratio 18:1 and the phosphate groups were in the diester form. 2. Hydrolysis with acid gave mannose 6-phosphate. Under mild acid conditions (autohydrolysis) the phosphate groups were converted into the monoester form, mannose was released and the molecular size of the phosphomannan was substantially decreased. 3. Hydrolysis with alkali also gave a monoester phosphate and a similar decrease in molecular weight. Under mild alkaline conditions the serine and threonine content of the phosphomannan was decreased by about 80%. The phosphate content was not altered. 4. Treatment with 40% (v/v) HF removed 70% of the phosphorus from the phosphomannan with no detectable decrease in molecular weight. 5. Periodate oxidation gave an oxophosphomannan from which 80% of the phosphorus was eliminated under mild alkaline conditions. 6. The properties of the phosphomannan are consistent with a structure in which the phosphate groups are located on the outside of the molecule and link C-1 of a terminal mannose unit with C-6 of another mannose unit, which is in turn attached to the polysaccharide backbone of the molecule. 7. The implications of this structure are discussed in relation to flocculation.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. F., CADMUS M. C., BENEDICT R. G., SLODKI M. E. Laboratory production of a phosphorylated mannan by Hansenula holstii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:289–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALLOU C. E. Alkali-sensitive glycosides. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1954;9:59–95. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANES A., PITTSLEY J. E., WATSON P. R., DIMLER R. J. Characterization and properties of the phosphomannan from Hansenula hostii NRRL Y-2448. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Feb;92:343–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letters R. The application of a two-dimensional paper-chromatographic technique to the analysis of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):313–316. doi: 10.1042/bj0930313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERKENSCHLAGER M., SCHLOSSMANN K., KURZ W. Ein mechanischer Zellhomogenisator und seine Anwendbarkeit auf biologische Probleme. Biochem Z. 1957;329(4):332–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan W. L., Jr, Lampen J. O. Phosphomannanase (PR-factor), an enzyme required for the formation of yeast protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):967–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.967-974.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKERSON W. J. SYMPOSIUM ON BIOCHEMICAL BASES OF MORPHOGENESIS IN FUNGI. IV. MOLECULAR BASES OF FORM IN YEASTS. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Sep;27:305–324. doi: 10.1128/br.27.3.305-324.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLODKI M. E. Phosphate linkages in phosphomannans from yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 12;57:525–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentandreu R., Northcote D. H. The structure of a glycopeptide isolated from the yeast cell wall. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):419–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1090419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Bowness J. M. Canine submandibular-gland hyaluronidase. Identification and subcellular distribution. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):9–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1100009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


