Abstract
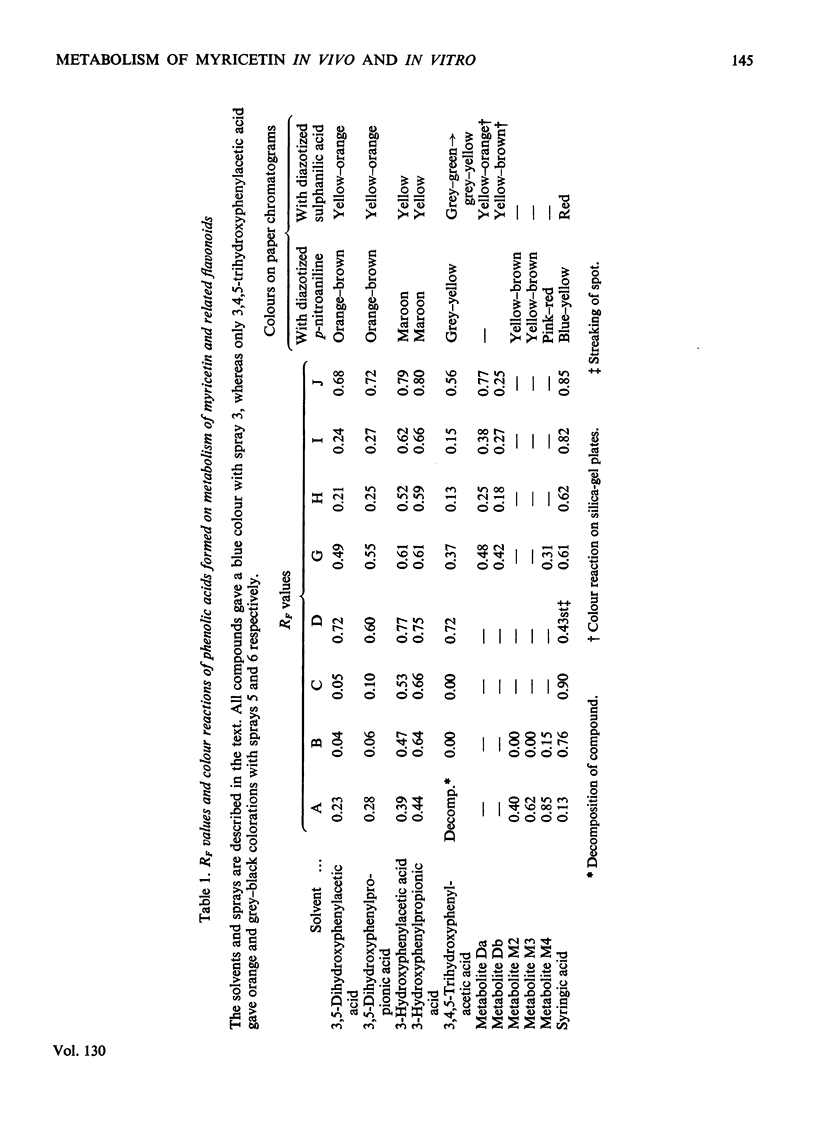
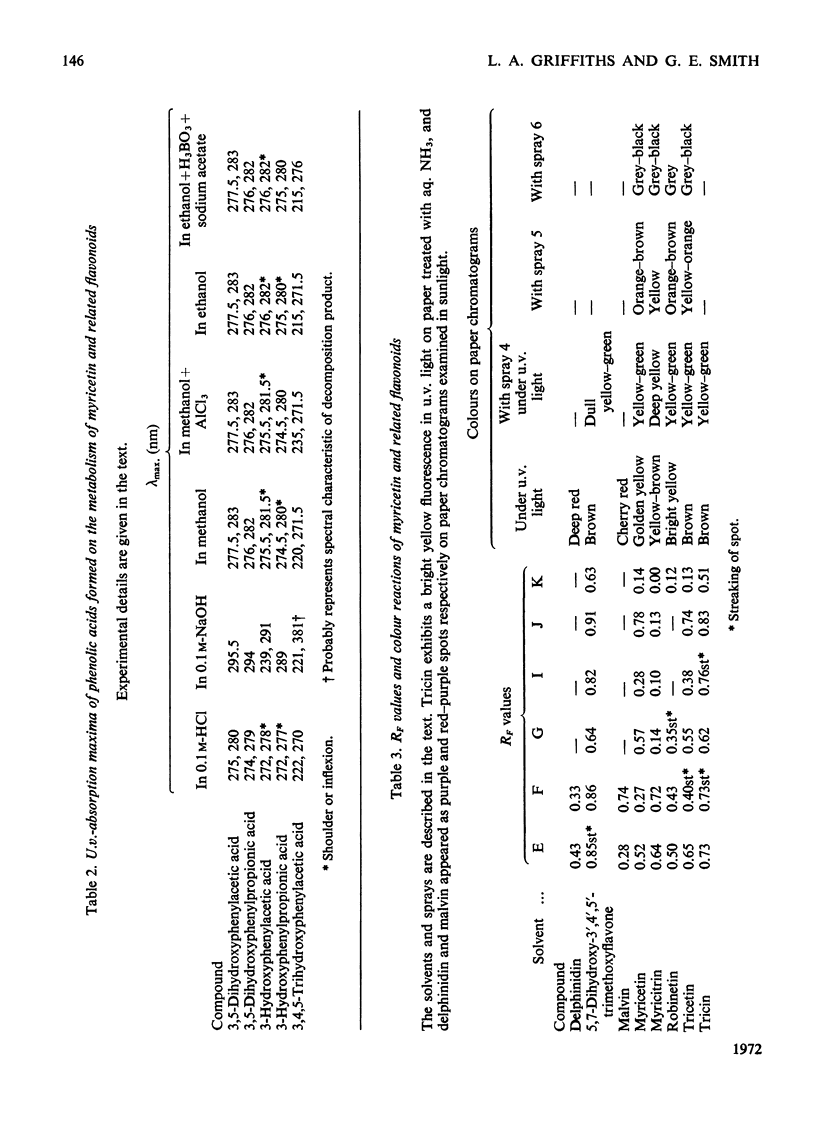
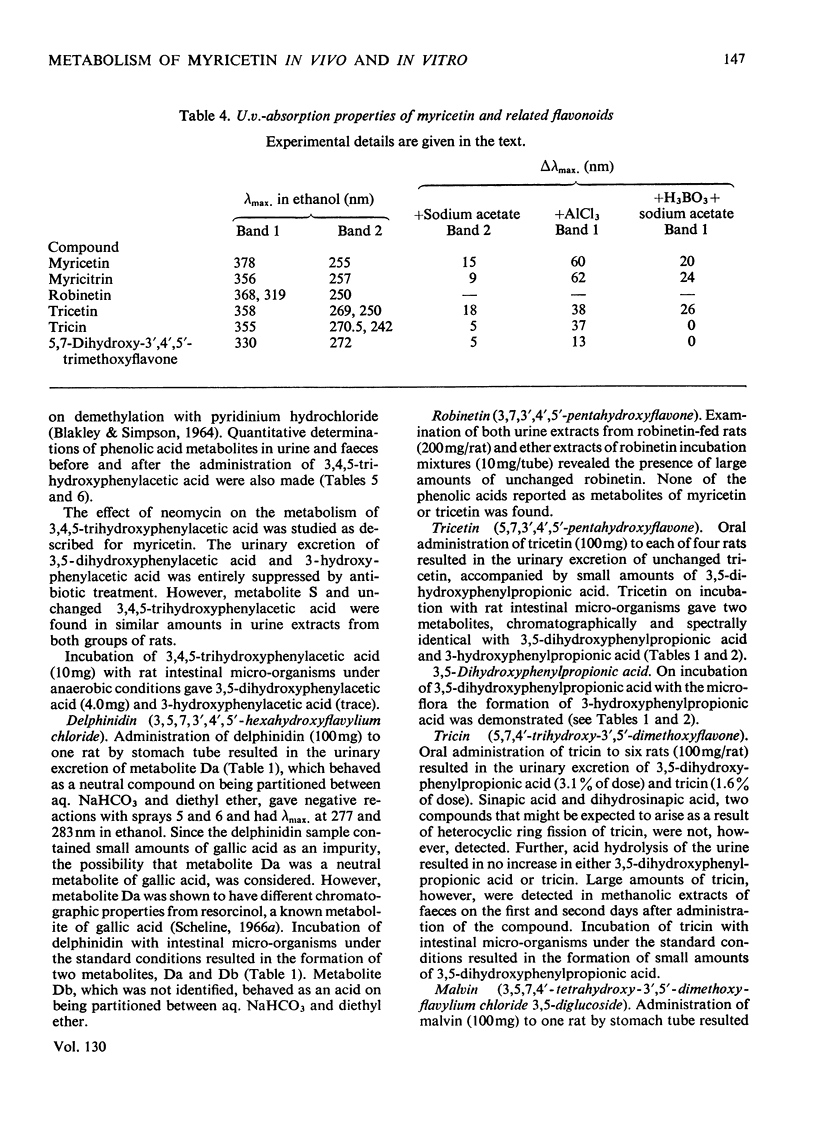
1. The metabolism of a group of polyphenols related in structure to myricetin (3,5,7,3′,4′,5′-hexahydroxyflavone), including myricetin, myricitrin, 3,4,5-trihydroxyphenylacetic acid, delphinidin, robinetin, tricetin, tricin, malvin and 5,7-dihydroxy-3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyflavone, has been studied both in vivo after oral administration to the rat and in vitro in cultures of micro-organisms derived from the intestine of the rat. 2. It was shown that the rat intestinal microflora are able to degrade compounds of this group to the ring-fission products observed in urine after oral administration of the specific flavonoid. 3. All flavones and flavonols possessing free 5- and 7-hydroxyl groups in the A ring and a free 4′-hydroxyl group in the B ring gave rise to ring-fission products that included 3′,5′-dihydroxyphenylacyl derivatives. 4. The metabolites 3,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3,5-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid and 3-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid were isolated and identified by chromatographic and spectral methods. 5. On anaerobic incubation in a thioglycollate medium it was shown that intestinal micro-organisms can effect cleavage of glycosidic bonds, ring fission of certain flavonoid molecules showing 3′,4′,5′-trihydroxyphenyl substitution and dehydroxylation of certain flavonoid metabolites. 6. The urinary excretion of the metabolites 3,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid was completely abolished when neomycin-treated rats were used.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BICKOFF E. M., LIVINGSTON A. L., BOOTH A. N. TRICIN FROM ALFALFA--ISOLATION AND PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY. J Pharm Sci. 1964 Nov;53:1411–1412. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600531131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKINSHAW J. H., BRACKEN A., MICHAEL S. E., RAISTRICK H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms; fuscin, a metabolic product of Oidiodendron fuscum Robak. Part 2. Derivatives and degradation products. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj0480067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKLEY E. R., SIMPSON F. J. THE MICROBIAL METABOLISM OF CINNAMIC ACID. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Apr;10:175–185. doi: 10.1139/m64-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH A. N., DEEDS F., JONES F. T., MURRAY C. W. The metabolic fate of rutin and quercetin in the animal body. J Biol Chem. 1956 Nov;223(1):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH A. N., JONES F. T., DEEDS F. Metabolic and glucosuria studies on naringin and phloridzin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):280–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH A. N., JONES F. T., DeEDS F. Metabolic fate of hesperidin, eriodictyol, homoeridictyol, and diosmin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH A. N., MASRI M. S., ROBBINS D. J., EMERSON O. H., JONES F. T., DE EDS F. The metabolic fate of gallic acid and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:3014–3016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAY H. G., THORPE W. V. Analysis of phenolic compounds of interest in metabolism. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:27–52. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore M. A., Quayle J. R. Microbial growth on oxalate by a route not involving glyoxylate carboligase. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1180053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANDLER B. V. Anthocyanins of blood oranges. Nature. 1958 Oct 4;182(4640):933–933. doi: 10.1038/182933a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. G., McGowan J. C., Bryant S. A. The chlorine-sodium sulphite colour reaction of woody tissues: The bearing of the colour reaction on the constitution of hardwood lignin. Biochem J. 1938 Dec;32(12):2138–2141. doi: 10.1042/bj0322138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Jones G. A., Simpson F. J., Bryant M. P. Isolation and identification of rumen bacteria capable of anaerobic rutin degradation. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1365–1371. doi: 10.1139/m69-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEEDS F., BOOTH A. N., JONES F. T. Methylation and dehydroxylation of phenolic compounds by rats and rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):615–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacre J. C., Scheline R. R., Williams R. T. The role of the tissues and gut flora in the metabolism of [14C]homoprotocatechuic acid in the rat and rabbit. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;20(8):619–625. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1968.tb09823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das N. P., Griffiths L. A. Studies on flavonoid metabolism. Metabolism of (+)-catechin in the guinea pig. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj1100449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das N. P., Griffiths L. A. Studies on flavonoid metabolism. Metabolism of flavone in the guinea pig. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):488–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0980488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON W. S., ASHWORTH DE B., TERRY R. A. Identity of a muscle-inhibiting flavone in lucerne. Nature. 1950 Jul 15;166(4211):116–117. doi: 10.1038/166116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. A. 3,5-Dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid, a further metabolite of sinapic acid. Experientia. 1970;26(7):723–724. doi: 10.1007/BF02232505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. A. Metabolism of sinapic acid and related compounds in the rat. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(4):603–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1130603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. A., Smith G. E. Metabolism of apigenin and related compounds in the rat. Metabolite formation in vivo and by the intestinal microflora in vitro. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):901–911. doi: 10.1042/bj1280901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths L. A. Studies on flavonoid metabolism. Identification of the metabolities of (+)-catechin in rat urine. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):173–179. doi: 10.1042/bj0920173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JURD L. A spectrophotometric method for the detection of o-dihydroxyl groups in flavonoid compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA Y., SHETLAR M. R., WENDER S. H. SPECTRAL IDENTIFICATION STUDIES OF PHENOLIC ACIDS USING ALUMINUM CHLORIDE. Anal Biochem. 1964 Mar;7:374–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA Y., SHETLAR M. R., WENDER S. H. URINARY PRODUCTS FROM QUERCETIN IN NEOMYCIN-TREATED RATS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:233–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAIN T. The identification of coumarins and related compounds by filter-paper chromatography. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(2):200–208. doi: 10.1042/bj0530200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheline R. R. Decarboxylation and demethylation of some phenolic benzoic acid derivatives by rat caecal contents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Oct;18(10):664–669. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheline R. R. The decarboxylation of some phenolic acids by the rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1966;24(2):275–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1966.tb00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


