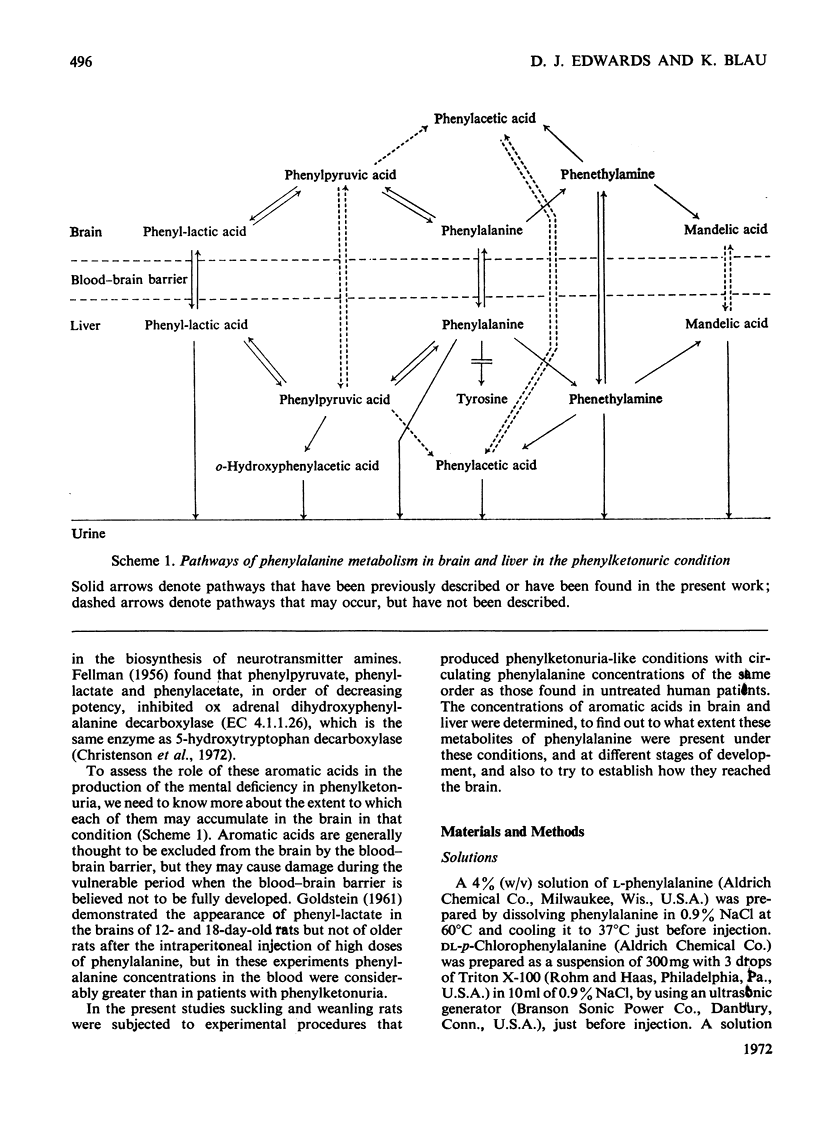
Abstract
1. Aromatic acids were extracted from brain and liver of rats with phenylketonuria-like characteristics produced by administration of phenylalanine, either alone or in combination with p-chlorophenylalanine. The metabolism of the aromatic acids in these tissues was measured by gas chromatography. 2. At 1h after an intraperitoneal injection of l-phenylalanine (1g/kg) in 23-day-old rats, the phenyl-lactate concentration was 2.2μg/g in the liver and 0.43μg/g in the brain, and the concentration of o-hydroxyphenylacetate was 0.26μg/g in the liver. 3. Phenylacetate concentrations in brain and liver were 0.26 and 0.14μg/g respectively. 4. Suckling rats produced phenyl-lactate less rapidly than weanling rats, but accumulated higher concentrations in longer-term experiments. 5. Intraperitoneal injections of phenyl-lactic acid showed that this compound could directly penetrate the blood–brain barrier, and could produce similar brain/liver ratios of phenyllactate to those found after phenylalanine injection. 6. Qualitative and quantitative similarities in urinary excretion of aromatic acids between the rats used in this study and human patients with uncontrolled phenylketonuria indicate that a patient with a circulating phenylalanine concentration of the order of those achieved in the experimental animal may have aromatic acid concentrations in brain and liver comparable with those found in the rats used in the present study.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, STEVENSON L. D., VOGEL F. S., ENGLE R. L., Jr Neuropathological findings in phenyl-pyruvic oligophrenia (phenyl-ketonuria). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1950 Jul;9(3):298–310. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195007000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. E., Guroff G. Enduring behavioral changes in rats with experimental phenylketonuria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):863–867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau K. Aromatic acid excretion in phenylketonuria. Analysis of the unconjugated aromatic acids derived from phenylalanine. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Jan;27(1):5–18. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden J. A., McArthur C. L., 3rd Possible biochemical model for phenylketonuria. Nature. 1972 Jan 28;235(5335):230–230. doi: 10.1038/235230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L., TYMMS V., WOOLF L. I. A chemical investigation of the defects of myelination in phenylketonuria. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 May;25:143–148. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christenson J. G., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343–347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhaver J. H. Determination of p-halogenated phenylalanines and phenylalanine in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLMAN J. H. Inhibition of DOPA decarboxylase by aromatic acids associated with phenylpyruvic oligophrenia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Dec;93(3):413–414. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W. Differences in the regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase in brain and liver. J Neurochem. 1970 Apr;17(4):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN F. B. Biochemical studies on phenylketonuria I. Experimental hyperphenylalanemia in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2656–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL J. B., SUMMER G. K., PENDER M. W., ROSZEL N. O. AN AUTOMATED PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD PHENYLALANINE. Clin Chem. 1965 May;11:541–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney I. M., Hanley W. B., Davidson W., Lindsao L. Phenylketonuria: mental development, behavior, and termination of low phenylalanine diet. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):646–655. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. B., Palmer P. Filter paper blood collection and punching as a means of quantification. Clin Chem. 1969 May;15(5):381–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochella N. J. Automated fluorometric determination of tyrosine in blood. Anal Biochem. 1967 Nov;21(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K., Hornykiewicz O. Occurrence and distribution of L-DOPA decarboxylase in the human brain. Brain Res. 1970 Sep 16;22(3):426–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90489-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. N., Peterson N. A., McKean C. M. Inhibition of sterol synthesis in vitro by metabolites of phenylalanine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;187(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg D. H. Phenylketonuria metabolites in cerebellum culture morphology. Arch Neurol. 1967 Nov;17(5):524–529. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470290078010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL-MALHERBE H., AXELROD J., TOMCHICK R. Blood-brain barrier for adrenaline. Science. 1959 May 1;129(3357):1226–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3357.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G. Inhibition of human brain pyruvate kinase and hexokinase by phenylalanine and phenylpyruvate: possible relevance to phenylketonuric brain damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1365–1369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannoni V. G., Weber W. W. Isolation and properties of aromatic alpha-keto acid reductase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1340–1344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


