Abstract
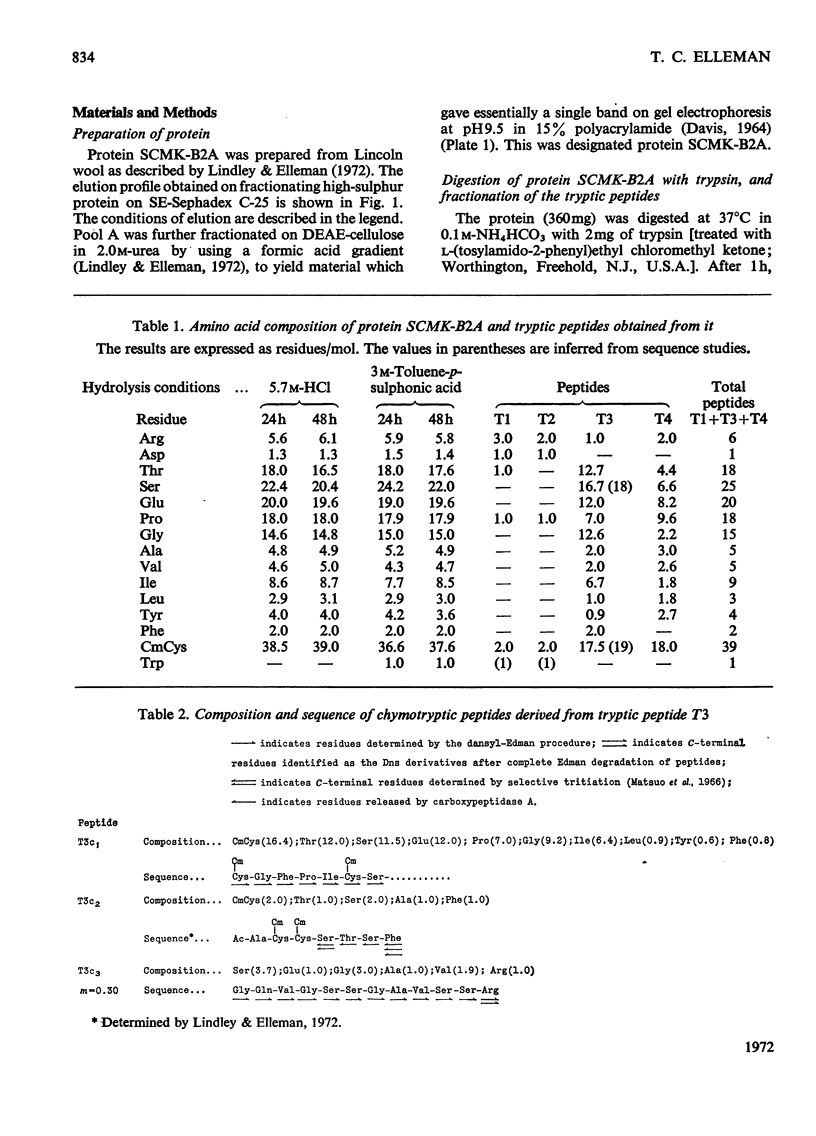
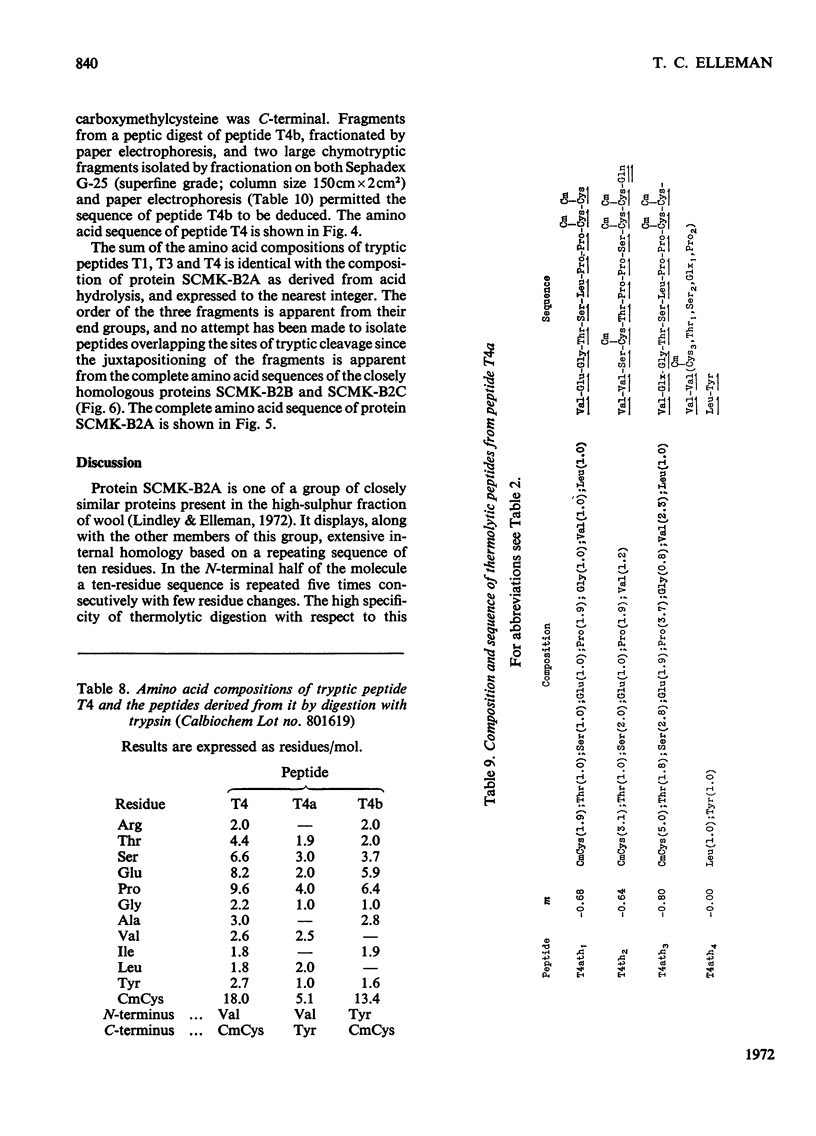
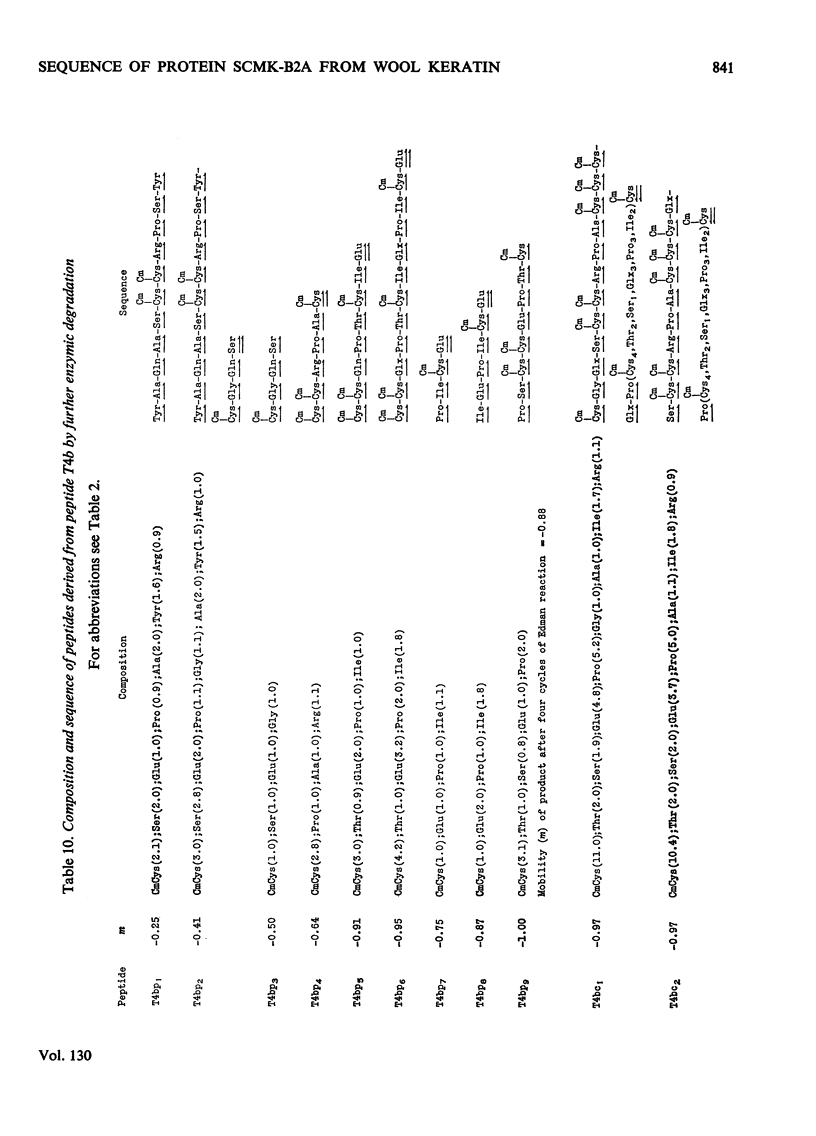
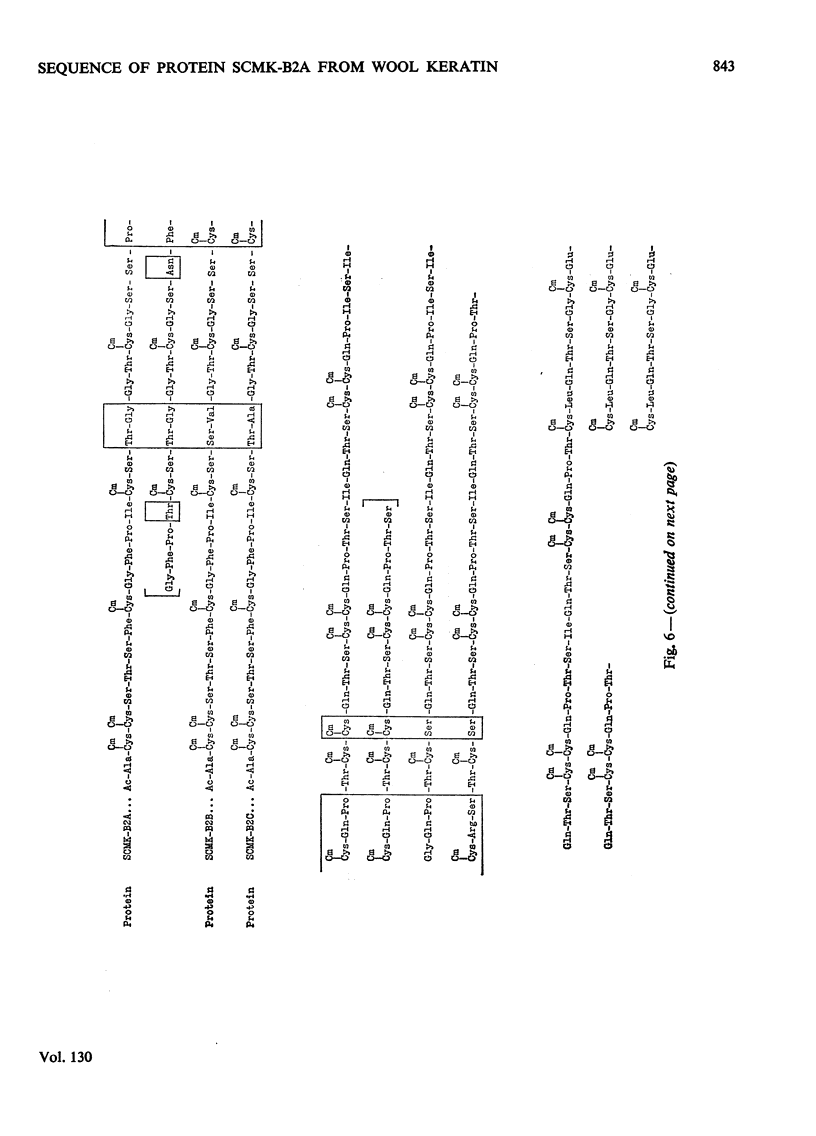
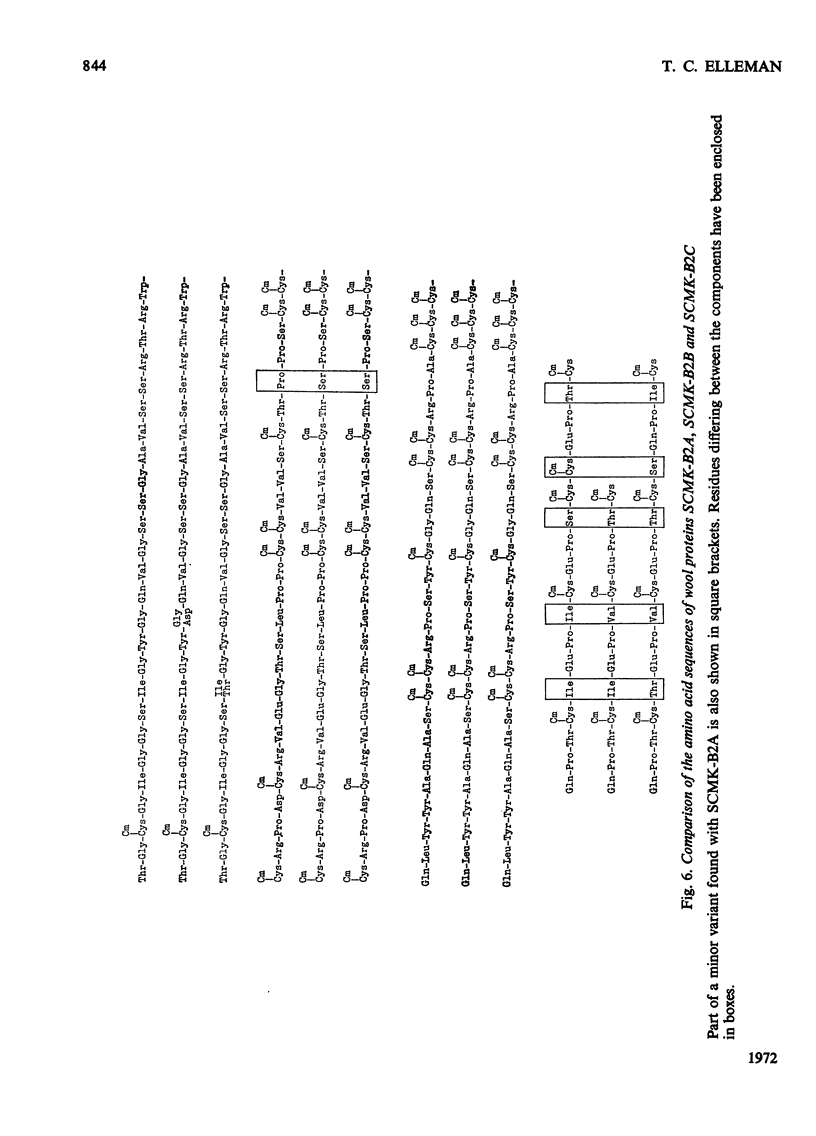
1. The amino acid sequence of protein SCMK-B2A, a reduced and S-carboxymethylated protein from the high-sulphur fraction of wool, has been determined. 2. This protein of 171 amino acid residues displays both a high degree of internal homology and extensive external homology with other members of the SCMK-B2 group of proteins. 3. Evidence is presented which suggests that the SCMK-B2 group of proteins are produced by separate non-allelic genes.
Full text
PDF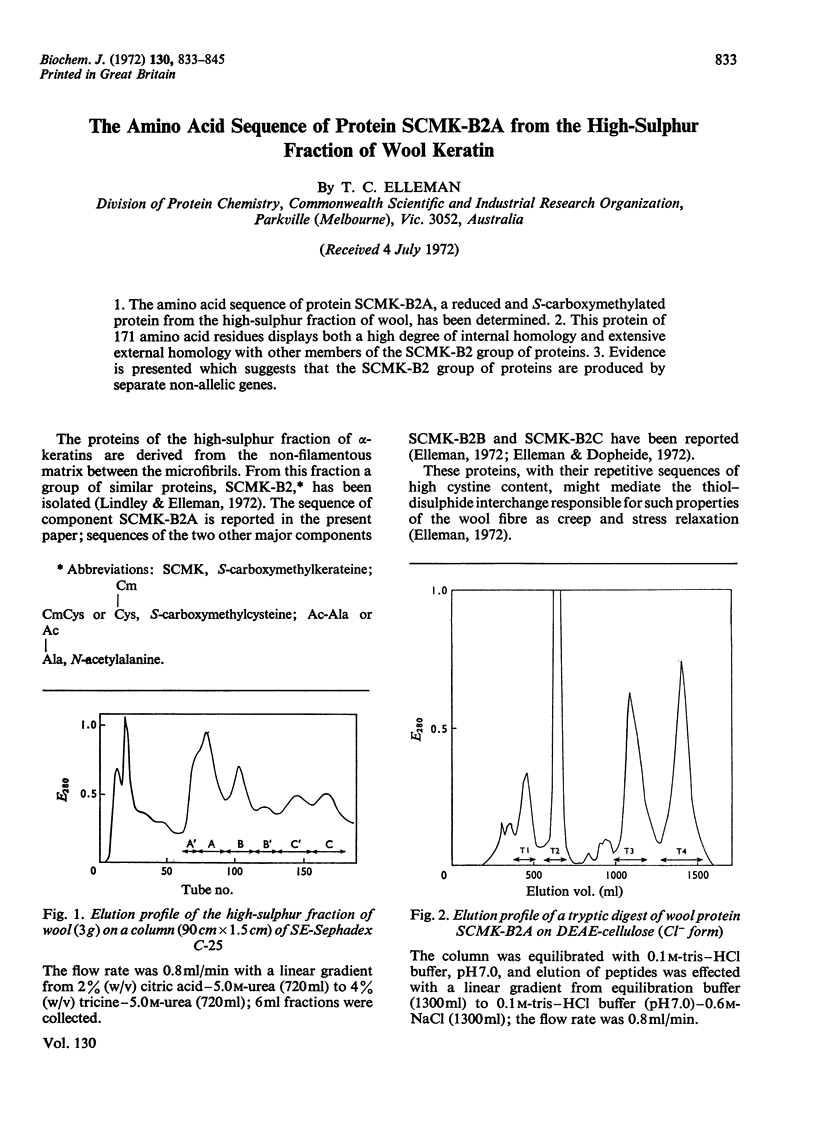








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. ON THE TOPOGRAPHY OF THE GENETIC FINE STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar;47(3):403–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Dopheide T. A. The sequence of SCMK-B2B, a high-sulfur protein from wool keratin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3900–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C. The amino acid sequence of protein SCMK-B2C from the high-sulphur fraction of wool keratin. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1229–1239. doi: 10.1042/bj1281229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. M., Haylett T., Lindley H. Evidence of homology in a high-sulphur protein fraction (SCMK-B2) of wool and hair alpha-keratins. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1100193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley H., Elleman T. C. The preparation and properties of a group of proteins from the high-sulphur fraction of wool. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):859–867. doi: 10.1042/bj1280859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo H., Fujimoto Y., Tatsuno T. A novel method for the determination of C-terminal amino acid in polypeptides by selective tritium labelling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jan 4;22(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Repeating sequences and gene duplication in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(2):417–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90508-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Cross A. M. The diversity and specialization of immunocytes. Prog Allergy. 1970;14:145–207. doi: 10.1159/000289379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands R. J., Lindley H. A theoretical investigation into the potential usefulness of the cathepsin C 'domino' technique. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):685–688. doi: 10.1042/bj1260685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]