Abstract
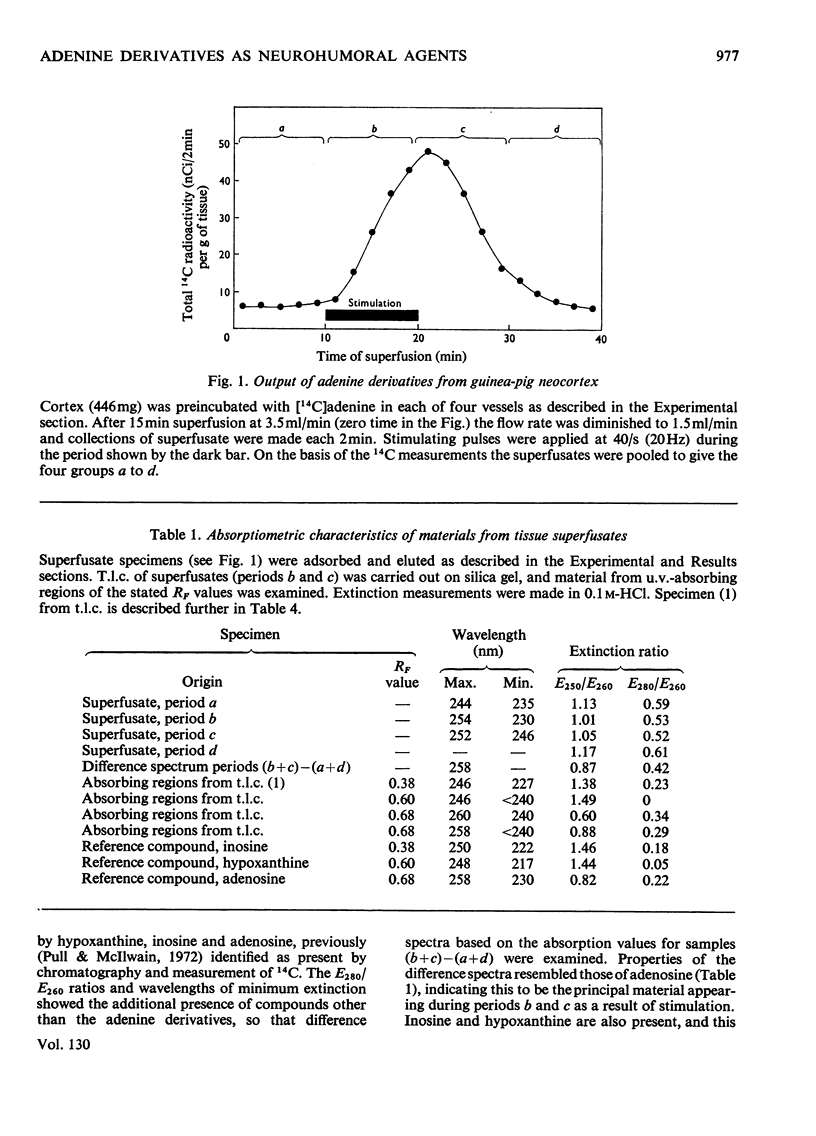
Adenine nucleotides of guinea-pig neocortical tissues were labelled by incubation with [14C]adenine and excess of adenine was then removed by superfusion with precursor-free medium. Adenine derivatives released from the tissue during continued superfusion, including a period of electrical stimulation of the tissue, were collected by adsorption and examined after elution and concentration. The stimulation greatly increased the 14C output, and material collected during and just after stimulation had a u.v. spectrum which indicated adenosine to be a major component. The additional presence of inosine and hypoxanthine was shown by chromatography and adenosine was identified also by using adenosine deaminase. Total adenine derivatives released from the tissue during a 10min period of stimulation were obtained as hypoxanthine, after deamination and hydrolysis of adenosine and inosine, and amounted to 159nmol/g of tissue. This corresponded to the release of approx. 7pmol/g of tissue per applied stimulus. The hypoxanthine sample derived from superfusate hypoxanthine, inosine and adenosine was of similar specific radioactivity to the sample of inosine separated chromatographically, and each was of higher specific radioactivity than the adenine nucleotides obtained by cold-acid extraction of the tissue.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Satchell D., Smythe A. Evidence that adenosine triphosphate or a related nucleotide is the transmitter substance released by non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves in the gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):668–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. A., McIlwain H. Excitatory acidic amino acids and the cation content and sodium ion flux of isolated tissues from the brain. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(2):269–274. doi: 10.1042/bj1080269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W., McIlwain H. The effect of electrical stimulation upon the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in isolated cerebral tissue. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Forn J., Voigt K., Paul M., Gessa G. L. Dynamic aspects of neurohormonal control of cyclic 3',5'-AMP synthesis in brain. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1970;3:155–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H. Regulatory significance of the release and action of adenine derivatives in cerebral systems. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(36):69–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Metabolism of ( 14 C)adenine and derivatives by cerebral tissues, superfused and electrically stimulated. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):965–973. doi: 10.1042/bj1260965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. N., Hempstead K. W., Kopp L. E., Miech R. P. Nucleotide metabolism in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1968 May;15(5):367–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Creveling C. R., Daly J. Stimulated formation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in cerebral cortex: synergism between electrical activity and biogenic amines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Daly J. W., Creveling C. R. A radioisotopic method for measuring the formation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in incubated slices of brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Dec;16(12):1609–1619. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


