Abstract
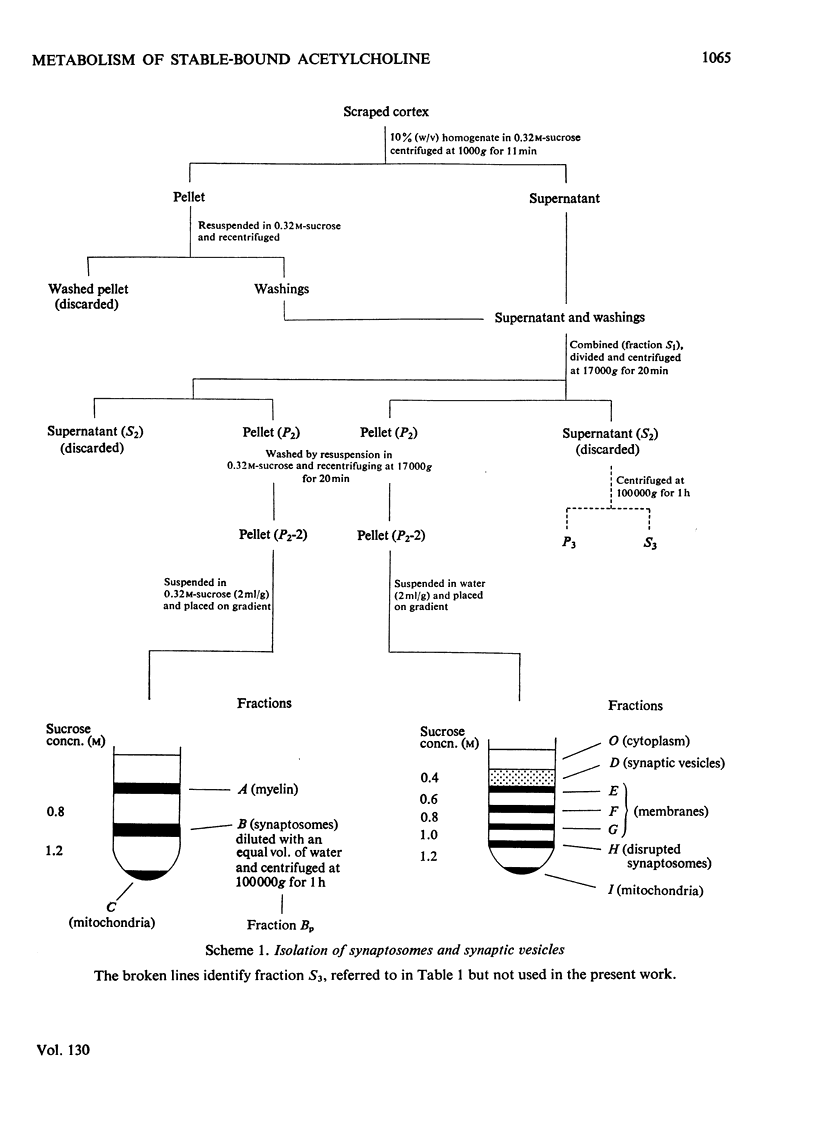
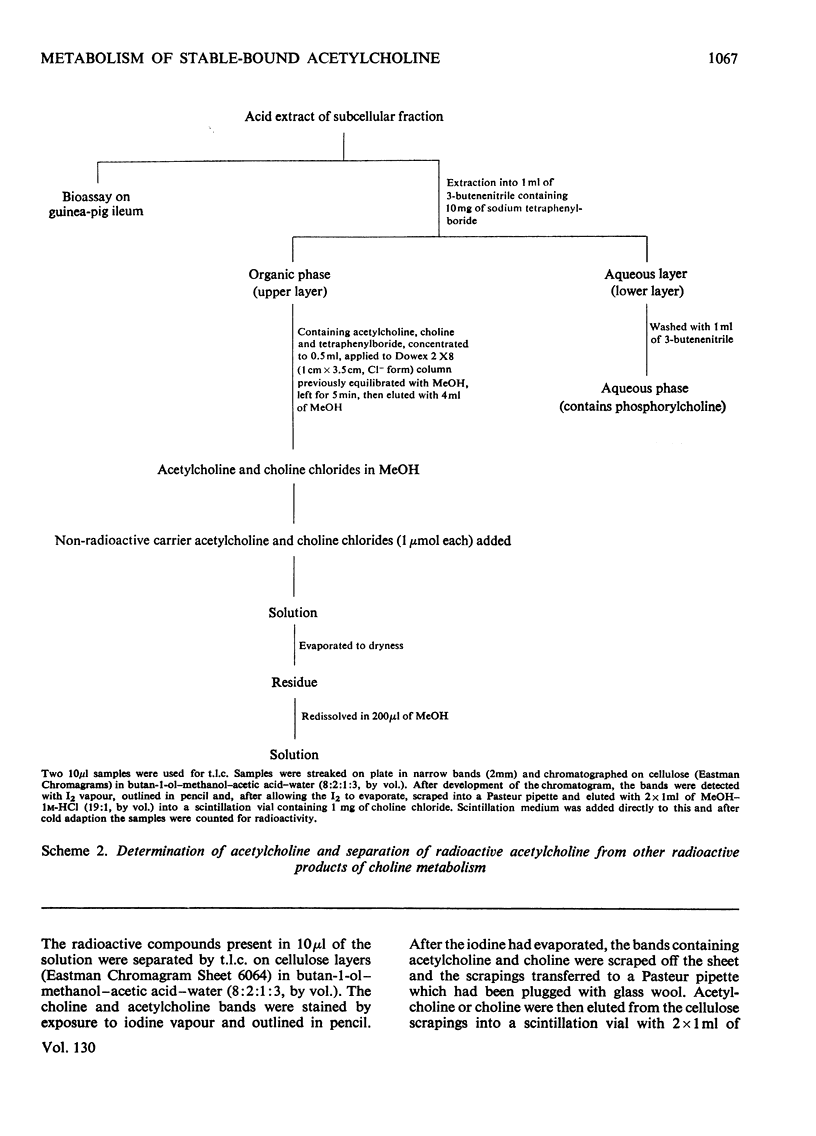
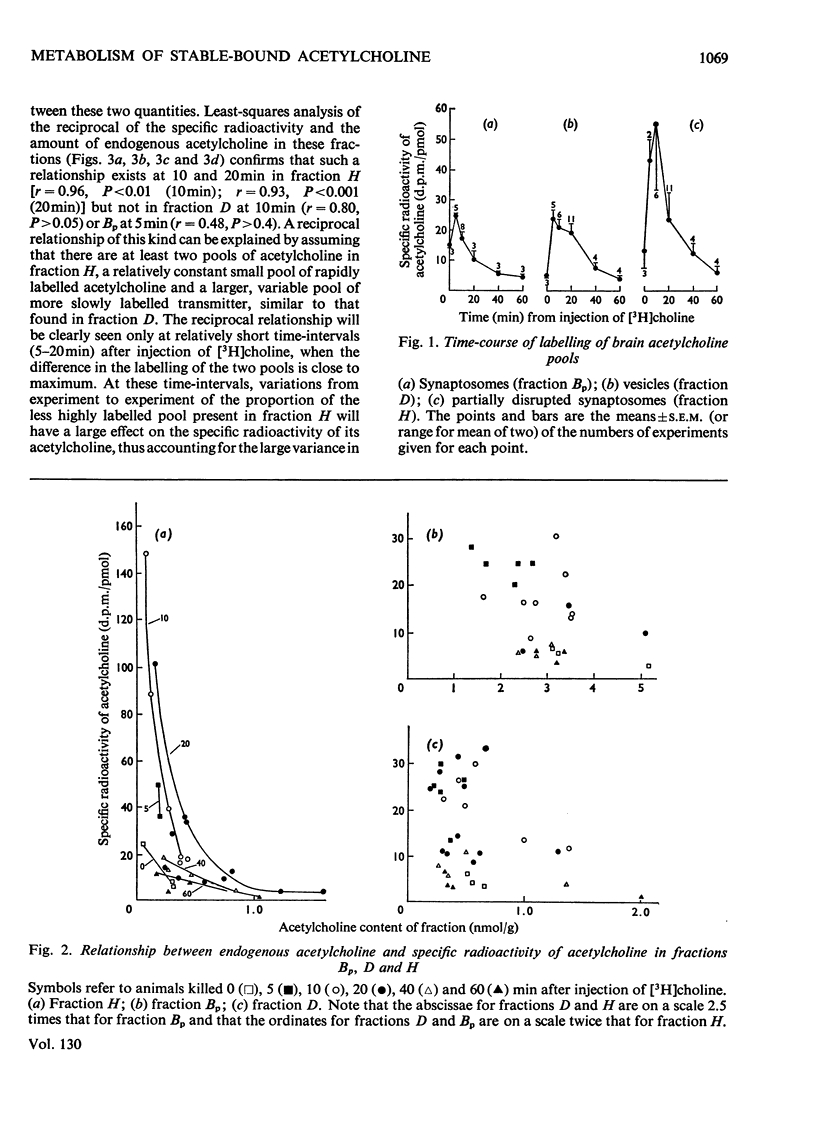
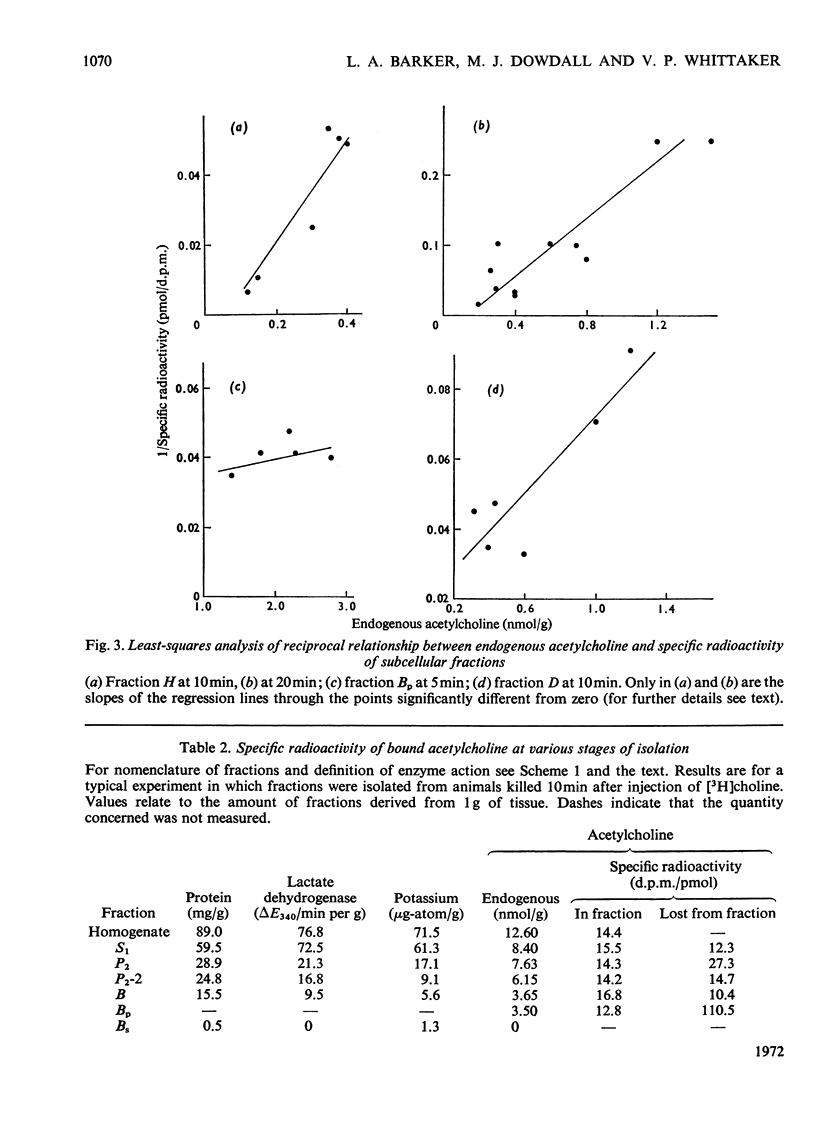
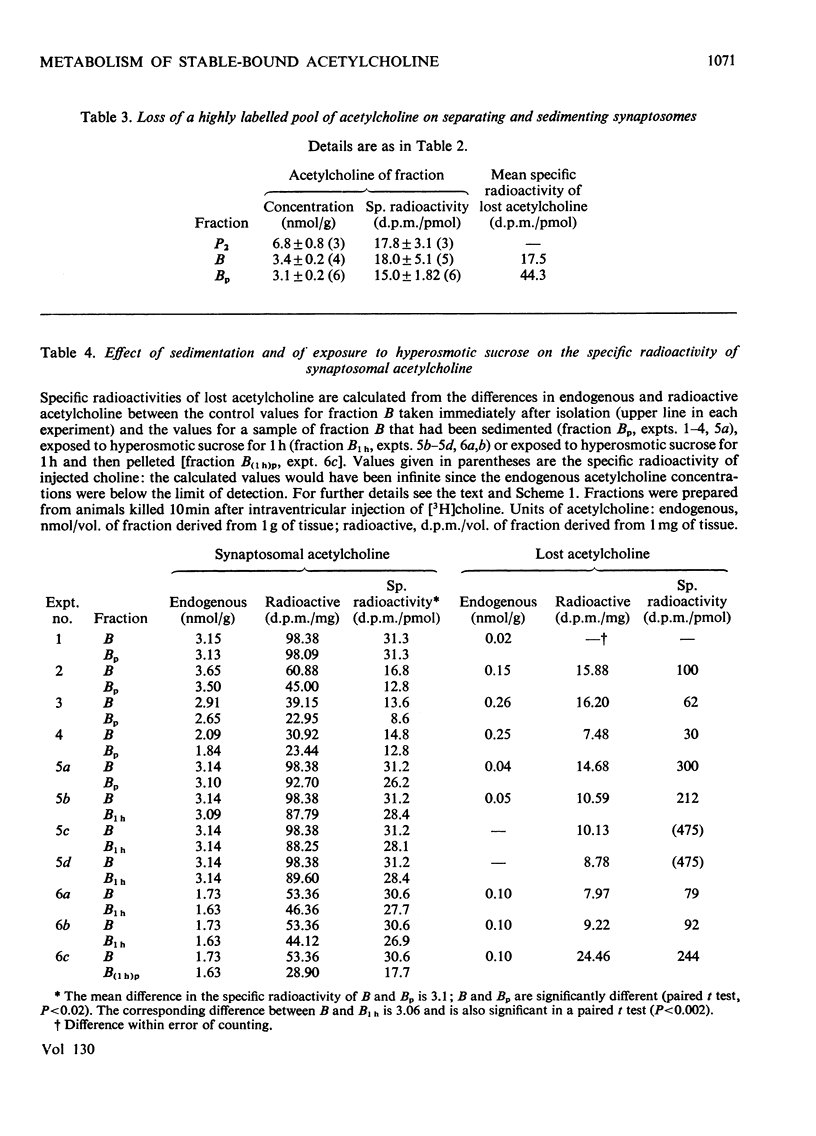
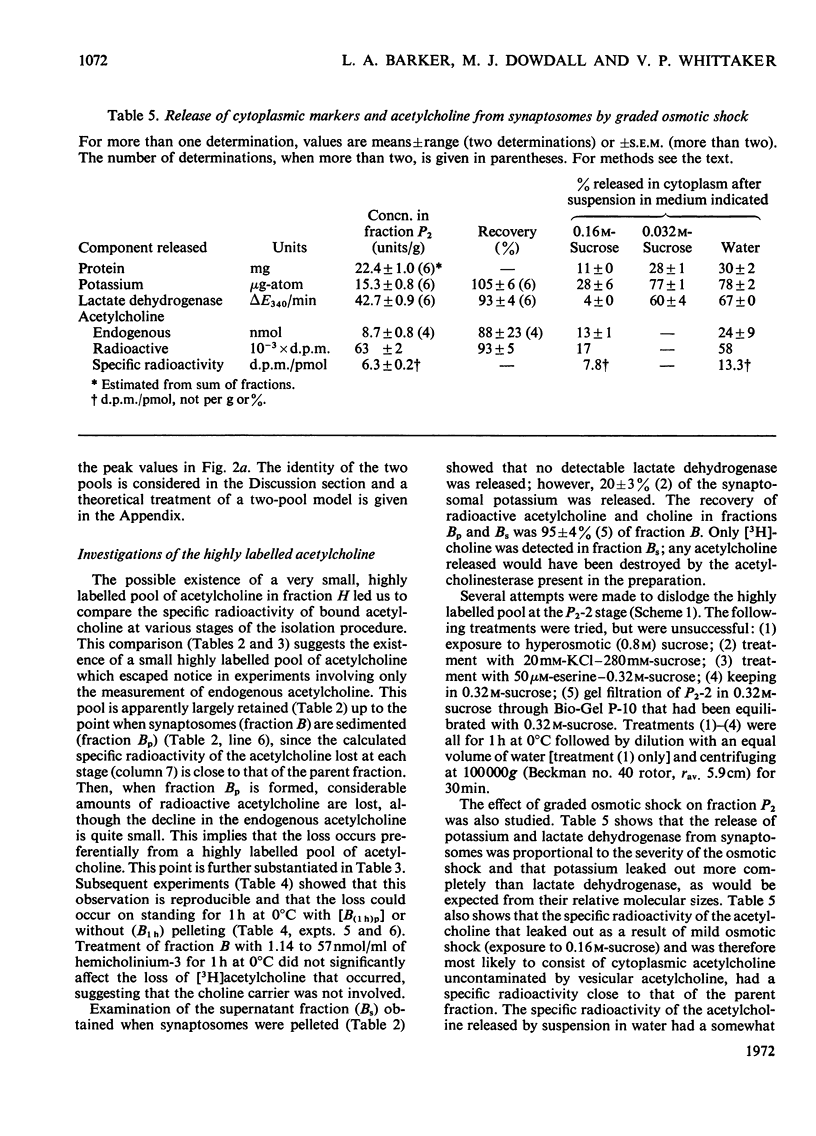
1. The turnover of synaptosomal (vesicular-cytoplasmic) and stable-bound (vesicular) acetylcholine isolated from cortical tissue was investigated after the administration, under local anaesthesia, of [N-Me-3H]choline into the lateral ventricles of guinea pigs. 2. Radioactive acetylcholine and choline present in acid extracts of subcellular fractions were separated by a combination of liquid and column ion-exchange and thin-layer chromatography. 3. The specific radioactivity and pattern of labelling of acetylcholine present in a fraction of monodisperse synaptic vesicles was found to be essentially the same as that of synaptosomal acetylcholine. 4. The specific radioactivity of stable-bound acetylcholine present in partially disrupted synaptosomes (fraction H) at short times (10–20min) after the injection of [N-Me-3H]choline was very variable and inversely related to the yield of acetylcholine in that fraction. 5. Evidence was found for the existence of two small, but highly labelled pools of acetylcholine, one which could be isolated in fraction H and the other which was lost when synaptosomes, after isolation by gradient centrifugation, were left at 0°C or pelleted. 6. It is concluded that the results are best explained by metabolic differences among the nerve-ending compartments (thought to be vesicles) which contain stable-bound acetylcholine. Computer simulation of our experiments supports this possibility and suggests that the highly labelled pool in fraction H is present in vesicles close to the external membrane.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Megazzini P., Ballotti L., Bernardi G. Drug induced changes in free, labile and stable acetylcholine of guinea-pig brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1315–1324. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Cheramy A., Feltz P., Glowinski J. Release of newly synthesized dopamine from dopamine-containing terminals in the striatum of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrin L. W., Marchbanks R. M., Mitchell J. F., Whittaker V. P. The origin of the acetylcholine released from the surface of the cortex. J Neurochem. 1972 Dec;19(12):2727–2736. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb03810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrin L. W., Whittaker V. P. The subcellular distribution of (N-Me-3H)acetylcholine synthesized by brain in vivo. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1130097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B. The preferential release of newly synthesized transmitter by a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):341–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Kennedy E. P. Carrier-mediated transport of choline into synaptic nerve endings. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3258–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Barker L. A., Whittaker V. P. Choline metabolism in the cerebral cortex of guinea pigs. Phosphorylcholine and lipid choline. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1081–1094. doi: 10.1042/bj1301081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J. The effects of osmotic pressure changes on the spontaneous activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):689–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Isolation of choline esters from aqueous solutions by extraction with sodium tetraphenylboron in organic solvents. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):291–298. doi: 10.1042/bj1130291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. The 'compartmentation' of choline acetyltransferase within the synaptosome. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):262–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1030262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradijan J. R., Bergner P. E. A mathematical model of the acetylcholine compartments in synaptosomes. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1042/bj1301075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradijan J. R., Bergner P. E. Qualitative consequences of randomness in a linear kinetic system. Biometrics. 1972 Jun;28(2):313–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., WHITTAKER V. P. Intracellular distributions of acetylcholine and choline acetylase. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):187–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Kwanbunbumpen S. Evidence for the vesicle hypothesis. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):407–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. F., Kwanbunbumpen S. The effects of nerve stimulation and hemicholinium on synaptic vesicles at the mammalian euromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):31–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopin I. J., Breese G. R., Krauss K. R., Weise V. K. Selective release of newly synthesized norepinephrine from the cat spleen during sympathetic nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jun;161(2):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann P. J., Quastel J. H. The oxidation of choline by rat liver. Biochem J. 1937 Jun;31(6):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj0310869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M., Israël M. Aspects of acetylcholine metabolism in the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. Synthesis, storage and release of [14C]acetylcholine in isolated rat diaphragm muscles. J Physiol. 1970 Jan;206(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. A., Marchbanks R. M. Isolation of ( 3 H) acetylcholine pools by subcellular fractionation of cerebral cortex slices incubated with ( 3 H) choline. J Neurochem. 1971 May;18(5):705–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuberth J., Sparf B., Sundwall A. A technique for the study of acetylcholine turnover in mouse brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 1969 May;16(5):695–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakly J. N. Effect of barbiturates on 'quantal' synaptic transmission in spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):63–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The application of subcellular fractionation techniques to the study of brain function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:39–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The nature of the acetylcholine pools in brain tissue. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:211–222. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


