Abstract
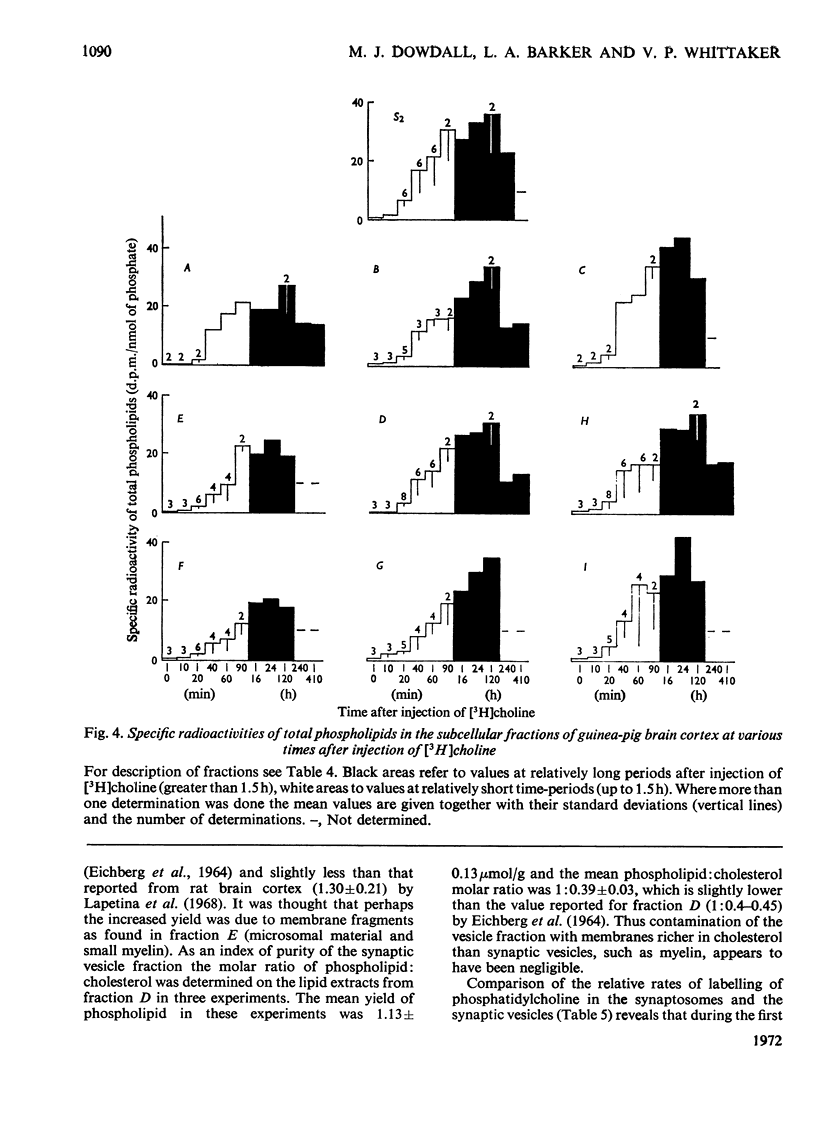
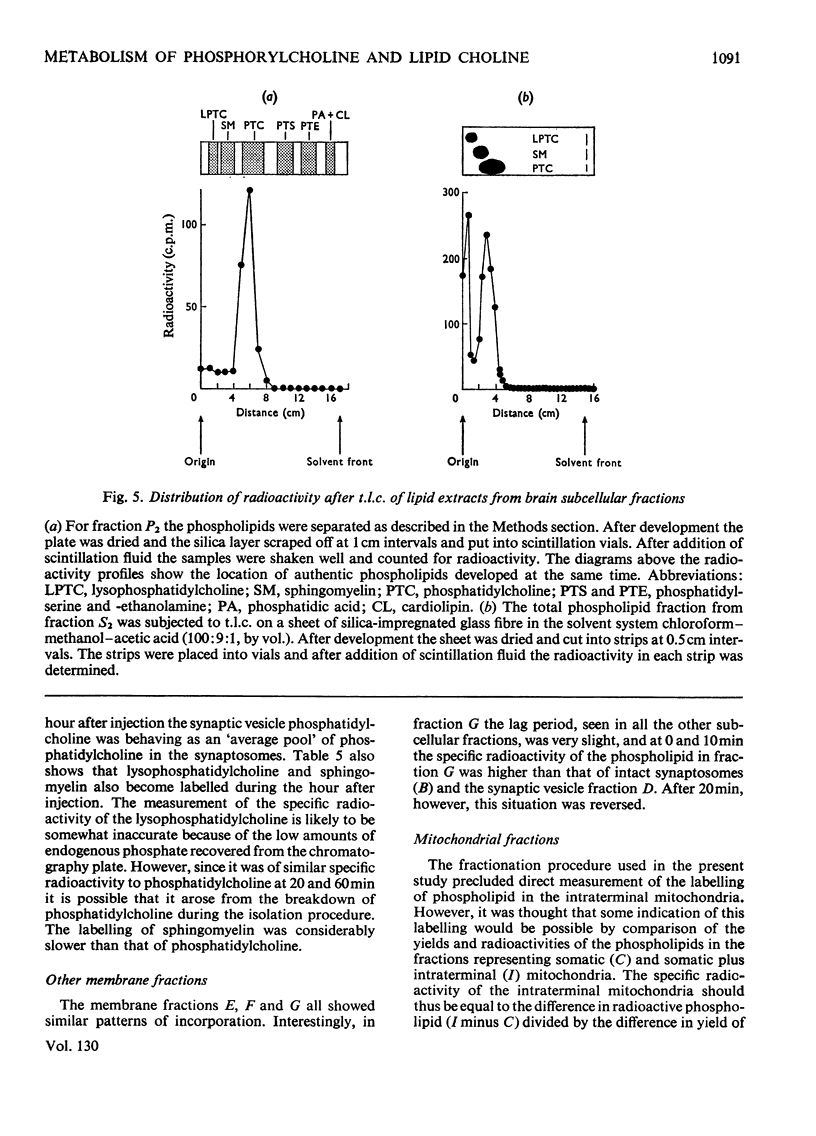
1. The labelling of phosphorylcholine and choline-containing phospholipids in the subcellular fractions of guinea-pig cerebral cortex after the intraventricular injection of [N-Me-3H]choline into conscious animals has been studied. Special emphasis was placed upon the synaptosome fraction and early time-periods after administration. 2. The labelling of phosphorylcholine was rapid compared with that of phospholipid and was confined to two distinct subcellular fractions: the soluble cytoplasmic fraction and the synaptosome fraction. Most of the labelled phosphorylcholine of the synaptosome fraction was readily released by osmotic rupture indicating location in the nerve-ending cytoplasm. The two pools of phosphorylcholine had similar specific radioactivities at all observed times. 3. 3H-labelled phospholipid was found in all membranous fractions. The labelling was confined to choline-containing phospholipids, notably phosphatidylcholine. 4. The labelling of the different membranous fractions was similar. 5. The half-life of the choline-containing phospholipids in the synaptic vesicle fraction was very much greater than the acetylcholine in this fraction. 6. Evidence is presented that synthesis de novo of phosphatidylcholine at nerve terminals occurs in vivo.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A., Smith J. P., Dasher C. A. Rapid appearance of labeled lecithin and protein in isolated nerve endings from rat brain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jul;134(3):850–854. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. The metabolism of [Me-14C]choline in the brain of the rat in vivo. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):201–206. doi: 10.1042/bj1100201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. A., Dowdall M. J., Whittaker V. P. Choline metabolism in the cerebral cortex of guinea pigs. Stable-bound acetylcholine. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1063–1075. doi: 10.1042/bj1301063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD N. An improved method for the determination of free and total cholesterol using the ferric chloride reaction. Clin Chim Acta. 1958 Jul;3(4):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(58)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrin L. W., Shideman F. E., Marrazzi A. S. The in vivo synthesis and release of tritium labeled acetylcholine by cat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 Jul;7(4):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrin L. W., Shideman F. E. Synthesis of acetylcholine from labeled choline by brain. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 Jul;7(4):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrin L. W., Whittaker V. P. The subcellular distribution of (N-Me-3H)acetylcholine synthesized by brain in vivo. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1130097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRUZHININA K. V., KRITSMAN M. G. Letsitinaza C zhivotnykh tkanei. Biokhimiia. 1952 Jan-Feb;17(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Kennedy E. P. Carrier-mediated transport of choline into synaptic nerve endings. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3258–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Whittaker V. P., Dawson R. M. Distribution of lipids in subcellular particles of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):91–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0920091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez M. V., Domino E. F., Sellinger O. Z. The effect of hemicholinium-3 on the in vivo formation of cerebral phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F., HULSE E. V., ROWE C. E. FORM-CELL RETICULOSIS OF MICE: AN INHERITED CONDITION RESEMBLING GAUCHER'S AND NIERMANN-PICK DISEASES. J Med Genet. 1965 Jun;2(2):99–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Lunt G. G., De Robertis E. The turnover of phosphatidyl choline in rat cerebral cortex membranes in vivo. J Neurobiol. 1969;1(3):295–302. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Soto E. F., De Robertis E. Lipids and proteolipids in isolated subcellular membranes of rat brain cortex. J Neurochem. 1968 Jun;15(6):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb08939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt G. G., Lapetina E. G. Incorporation of (Me-14C)choline into phosphatidyl choline of rat cerebral cortex membranes in vitro. Brain Res. 1970 Mar 17;18(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt G. G., Lapetina E. G. Phospholipid metabolism of isolated nerve endings. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 6;17(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M. The uptake of [14C] choline into synaptosomes in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1100533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. K., Dawson R. M. Can mitochondria and synaptosomes of guinea-pig brain synthesize phospholipids? Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):805–821. doi: 10.1042/bj1260805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumphrey A. M. Incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate into brain-slice phospholipids and their precursors. Effects of electrical stimulation. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1120061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuberth J., Sparf B., Sundwall A. A technique for the study of acetylcholine turnover in mouse brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 1969 May;16(5):695–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuberth J., Sparf B., Sundwall A. On the turnover of acetylchonine in nerve endings of mouse brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 1970 Apr;17(4):461–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treble D. H., Frumkin S., Balint J. A., Beeler D. A. The entry of choline into lecithin, in vivo, by base exchange. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hungen K., Mahler H. R., Moore W. J. Turnover of protein and ribonucleic acid in synaptic subcellular fractions from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1415–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. Some properties of synaptic membranes isolated from the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):982–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


