Abstract
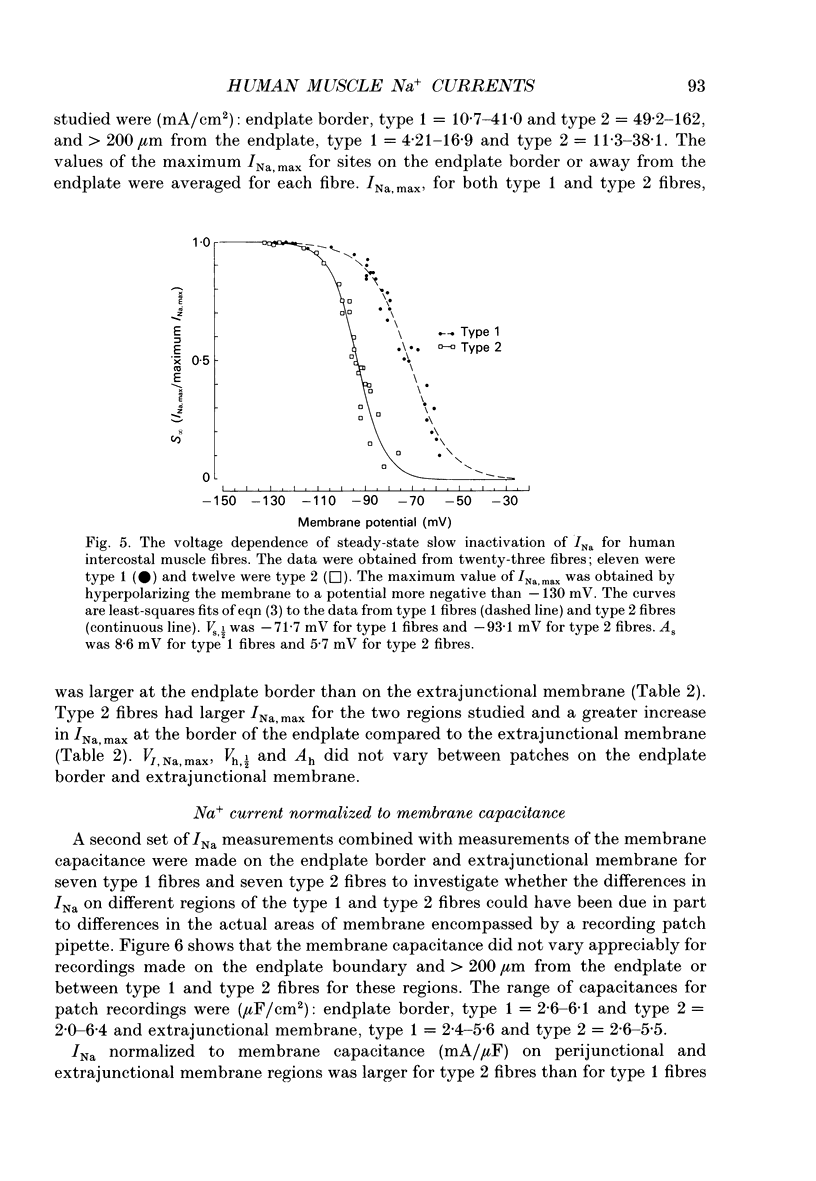
1. Voltage-clamp Na+ currents (INa) were studied in human intercostal muscle fibres using the loose-patch-clamp technique. 2. The fibres could be divided into two groups based upon the properties of INa. The two groups of fibres were called type 1 and type 2. 3. Both type 1 and type 2 fibres demonstrated fast and slow inactivation of INa. 4. Type 1 fibres had lower INa on the endplate border and extrajunctional membrane than type 2 fibres and required larger membrane depolarizations to inactivate Na+ channels by fast or slow inactivation of INa. 5. Type 2 fibres had a higher ratio of INa at the endplate border compared to extrajunctional membrane than Type 1 fibres. 6. Measurement of membrane capacitance suggested that the increase in INa at the endplate border was due to increased Na+ channel density. 7. Histochemical staining of some fibres suggested that type 1 fibres were slow twitch and type 2 fibres were fast twitch. 8. Differences in the properties of Na+ channels between fast- and slow-twitch fibres may contribute to the ability of fast-twitch fibres to operate at high firing frequencies and slow-twitch fibres to be tonically active.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Roberts W. M., Ruff R. L. Voltage clamp of rat and human skeletal muscle: measurements with an improved loose-patch technique. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:751–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker B. Q., Kelly S. S., Robbins N. Neuromuscular transmission and correlative morphology in young and old mice. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:355–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. H., Campbell D. T., Beam K. G. Na channel distribution in vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):907–932. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Everts M. E. K(+)-induced inhibition of contractile force in rat skeletal muscle: role of active Na(+)-K+ transport. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):C799–C807. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Potassium contractures and mechanical activation in mammalian skeletal muscles. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 30;57(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01869590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval A., Léoty C. Ionic currents in slow twitch skeletal muscle in the rat. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:23–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., Retterstøl K., Clausen T. Effects of adrenaline on excitation-induced stimulation of the sodium-potassium pump in rat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Oct;134(2):189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H. Characteristics of single Na+ channels of adult human skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):399–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00373616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig R., Lømo T. Firing patterns of motor units in normal rats. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):164–166. doi: 10.1038/314164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juel C. Muscle action potential propagation velocity changes during activity. Muscle Nerve. 1988 Jul;11(7):714–719. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Anderson M. F. Sodium channel kinetics in normal and denervated rabbit muscle membrane. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Oct;9(8):738–747. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszewski B., Ruff R. L. Effects of glucocorticoid treatment on excitation-contraction coupling. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E363–E369. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Tov A. Junctional transmission in fast- and slow-twitch mammalian motor units. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Mar;57(3):660–671. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.3.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Zelená J. Sensitivity to acetylcholine in rat slow muscle. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):855–856. doi: 10.1038/210855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton R. L., Caldwell J. H. Na current in membrane blebs: implications for channel mobility and patch clamp recording. J Neurosci. 1990 Mar;10(3):885–893. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-03-00885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M. Sodium channels near end-plates and nuclei of snake skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:213–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L. Calcium sensitivity of fast- and slow-twitch human muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve. 1989 Jan;12(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/mus.880120107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L. Ionic channels: I. The biophysical basis for ion passage and channel gating. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Oct;9(8):675–699. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Martyn D., Gordon A. M. Glucocorticoid-induced atrophy is not due to impaired excitability of rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E512–E521. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Comparison between slow sodium channel inactivation in rat slow- and fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:339–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Spiegel P. Ca sensitivity and acetylcholine receptor currents of twitch and tonic snake muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C911–C919. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.6.C911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillau A. H. Capillarity, oxidative capacity and fibre composition of the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of rats in hypothyroidism. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:281–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Slow sodium channel inactivation in rat fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:327–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjøgaard G., Adams R. P., Saltin B. Water and ion shifts in skeletal muscle of humans with intense dynamic knee extension. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):R190–R196. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1985.248.2.R190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterz R., Pagala M., Peper K. Postjunctional characteristics of the endplates in mammalian fast and slow muscles. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Jun;398(1):48–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00584712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


