Abstract
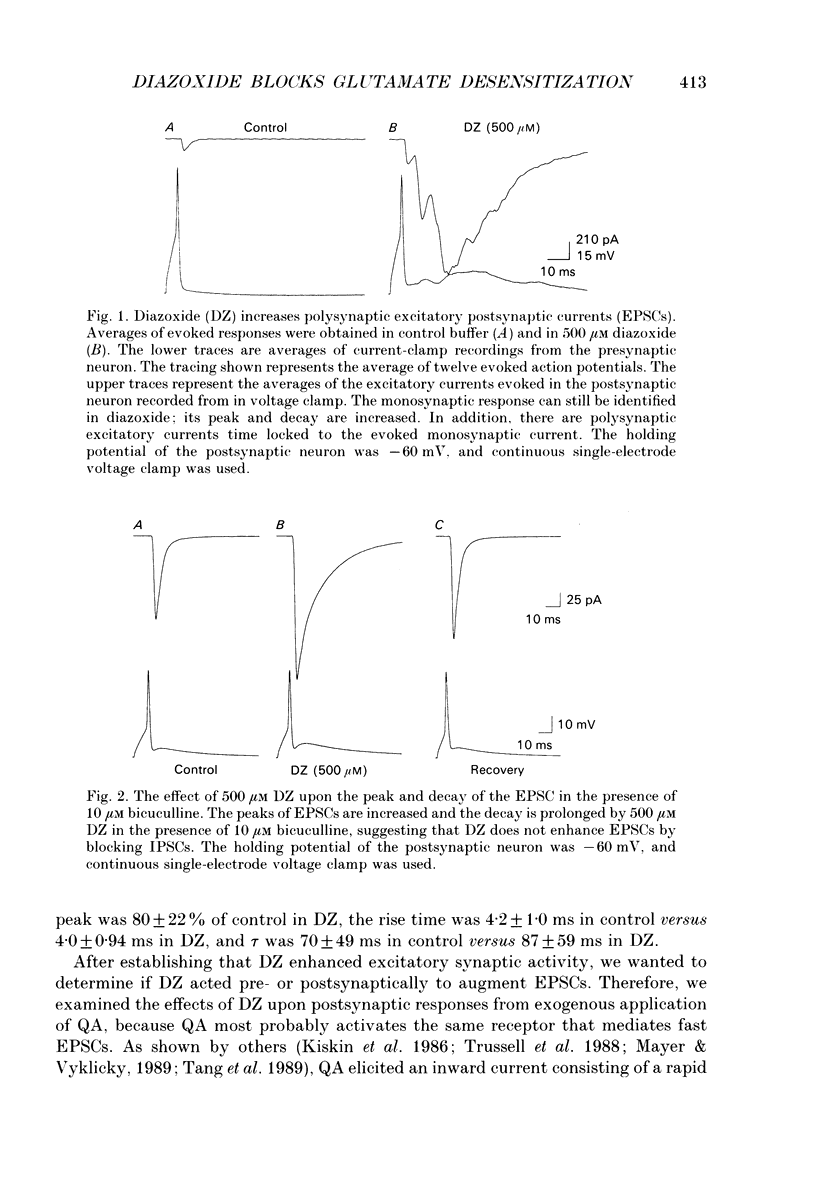
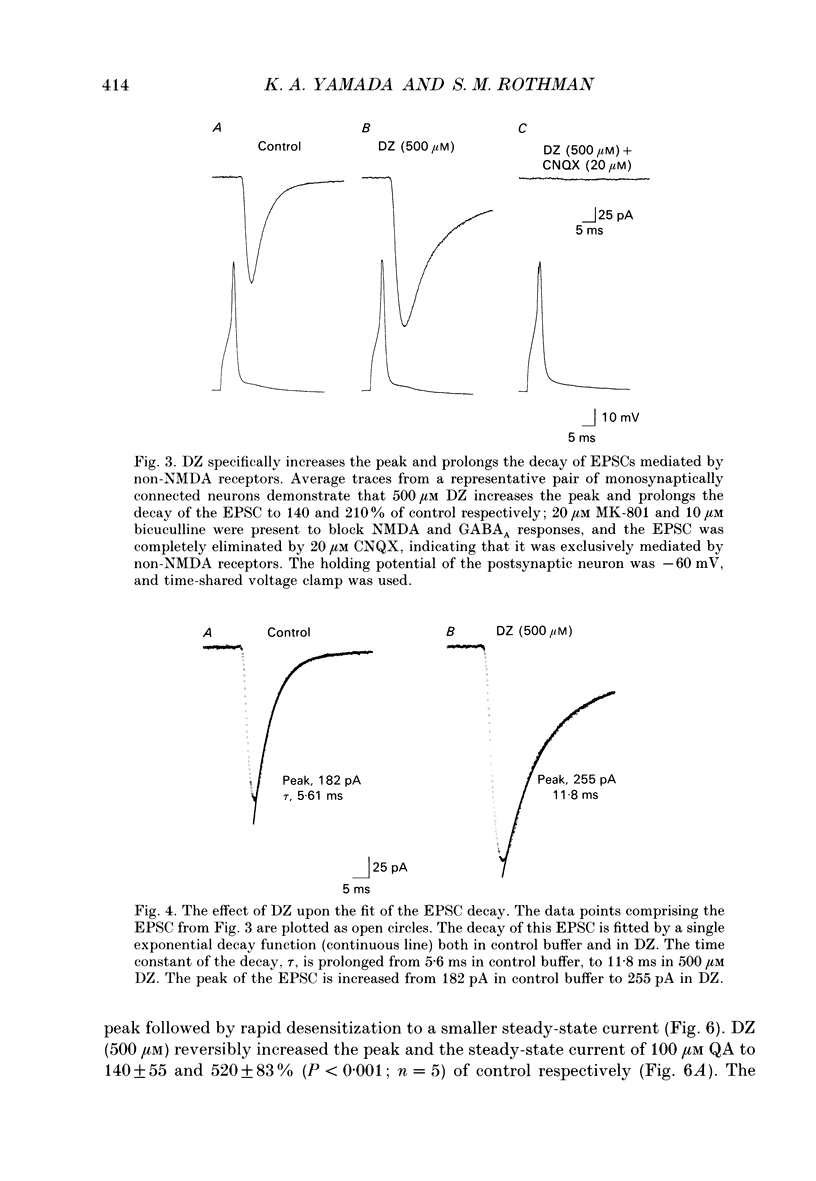
1. The effects of diazoxide (DZ) on synaptic transmission and upon responses to exogenously applied glutamate agonists were examined in cultured hippocampal neurons. 2. DZ reversibly increased the peak amplitude of evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) to 150 +/- 100% of control and prolonged the EPSC decay time constant (tau) from 5.9 +/- 1.2 ms to 14 +/- 6.2 ms (240% of control). 3. Peak and steady-state glutamate (Glu) and quisqualate (QA) currents activated by exogenous application were dramatically increased by DZ at concentrations which did not influence N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), kainate (KA), or GABA currents. These effects were rapidly and completely reversible. Active and passive membrane properties were unaffected by DZ. 4. Inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) were unaffected by the same DZ concentrations. 5. These experiments indicate that desensitization plays an important role in terminating excitatory transmission between mammalian central neurons. DZ and perhaps related compounds will ultimately help us identify the regions of the AMPA/KA receptor responsible for desensitization.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abele A. E., Miller R. J. Potassium channel activators abolish excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jul 31;115(2-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90454-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer C., Sutor B., ten Bruggencate G. Effects of cromakalim (BRL 34915) on potassium conductances in CA3 neurons of the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):465–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00167050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford M. L., Sturgess N. C., Trout N. J., Gardner N. J., Hales C. N. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-sensitive ion channels in neonatal rat cultured central neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Aug;412(3):297–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00582512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Dubinsky J. M., Schwartz E. A. The calcium current in inner segments of rods from the salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) retina. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H. Rapid activation, desensitization, and resensitization of synaptic channels of crayfish muscle after glutamate pulses. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):533–545. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82569-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Illot M. C., Peterson O. H. Interaction of diazoxide, tolbutamide and ATP4- on nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01995702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A., Perkel D. J., Sah P. Analysis of excitatory synaptic action in pyramidal cells using whole-cell recording from rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:203–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson J. S., Nicoll R. A. Aniracetam reduces glutamate receptor desensitization and slows the decay of fast excitatory synaptic currents in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10936–10940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Tanabe S., Kohda A., Sugiyama H. Allosteric potentiation of quisqualate receptors by a nootropic drug aniracetam. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:533–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Konnerth A., Yaari Y. Patch clamp analysis of excitatory synaptic currents in granule cells of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:275–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiskin N. I., Krishtal O. A., Tsyndrenko AYa Excitatory amino acid receptors in hippocampal neurons: kainate fails to desensitize them. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 30;63(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr Concanavalin A selectively reduces desensitization of mammalian neuronal quisqualate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Glucose-regulated potassium channels are sweet news for neurobiologists. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Gee W. M., Gillis K. D., Scharp D. W., Falke L. C. Metabolite-regulated ATP-sensitive K+ channel in human pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):422–427. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Ben Ari Y., Bernardi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas: localization of binding sites in the brain and effects on the hyperpolarization induced by anoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of interactions between kainate and AMPA: evidence for activation of a single receptor in mouse hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):785–798. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90175-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politi D. M., Suzuki S., Rogawski M. A. BRL 34915 (cromakalim) enhances voltage-dependent K+ current in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 1;168(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. In vitro and in vivo comparison of two K+ channel openers, diazoxide and cromakalim, and their inhibition by glibenclamide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. Moving together: K+ channel openers and ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Nov;10(11):431–435. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(89)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah P., Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A. Properties of excitatory postsynaptic currents recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal interneurones. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:605–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Quisqualate activates a rapidly inactivating high conductance ionic channel in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2467378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Shi Q. Y., Katchman A., Lynch G. Modulation of the time course of fast EPSCs and glutamate channel kinetics by aniracetam. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):288–290. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Fischbach G. D. Glutamate receptor desensitization and its role in synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Thio L. L., Zorumski C. F., Fischbach G. D. Rapid desensitization of glutamate receptors in vertebrate central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklicky L., Jr, Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by drugs that reduce desensitization at AMPA/kainate receptors. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):971–984. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90342-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. A., Dubinsky J. M., Rothman S. M. Quantitative physiological characterization of a quinoxalinedione non-NMDA receptor antagonist. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):3230–3236. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Thio L. L., Clark G. D., Clifford D. B. Blockade of desensitization augments quisqualate excitotoxicity in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90033-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


