Abstract
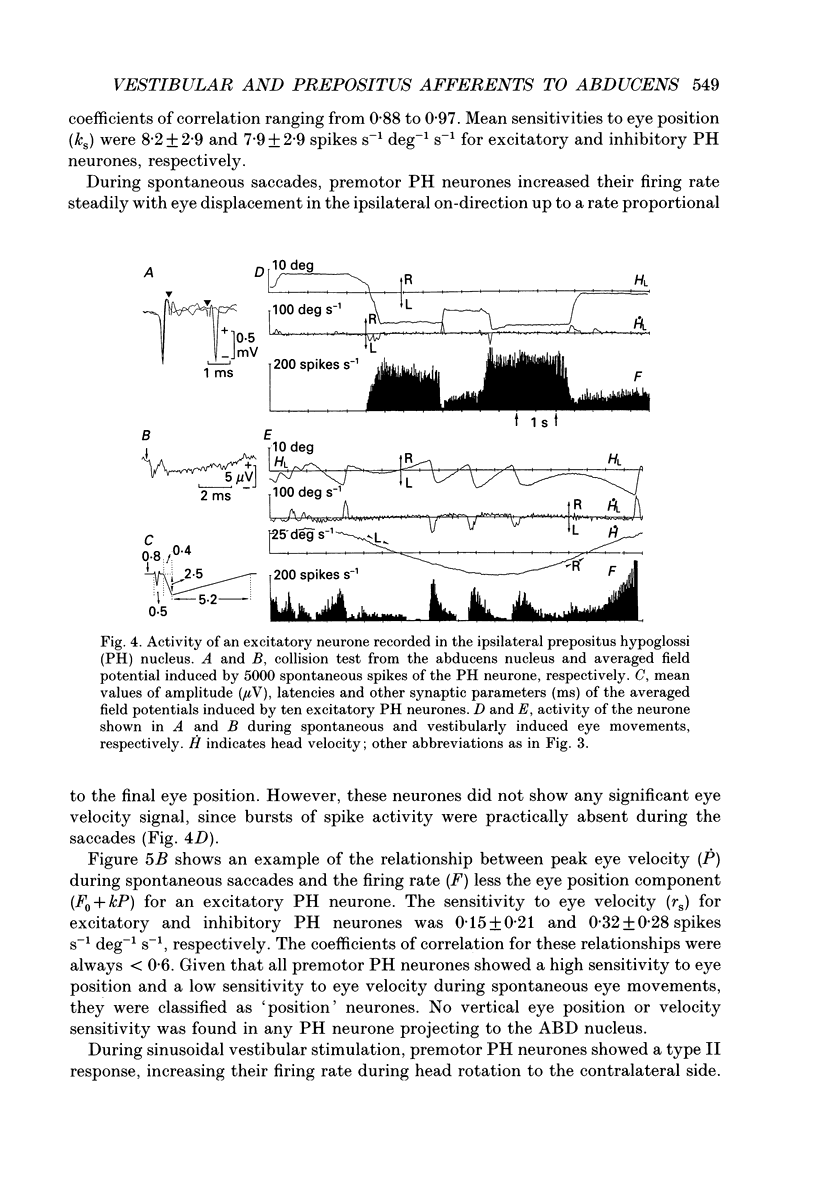
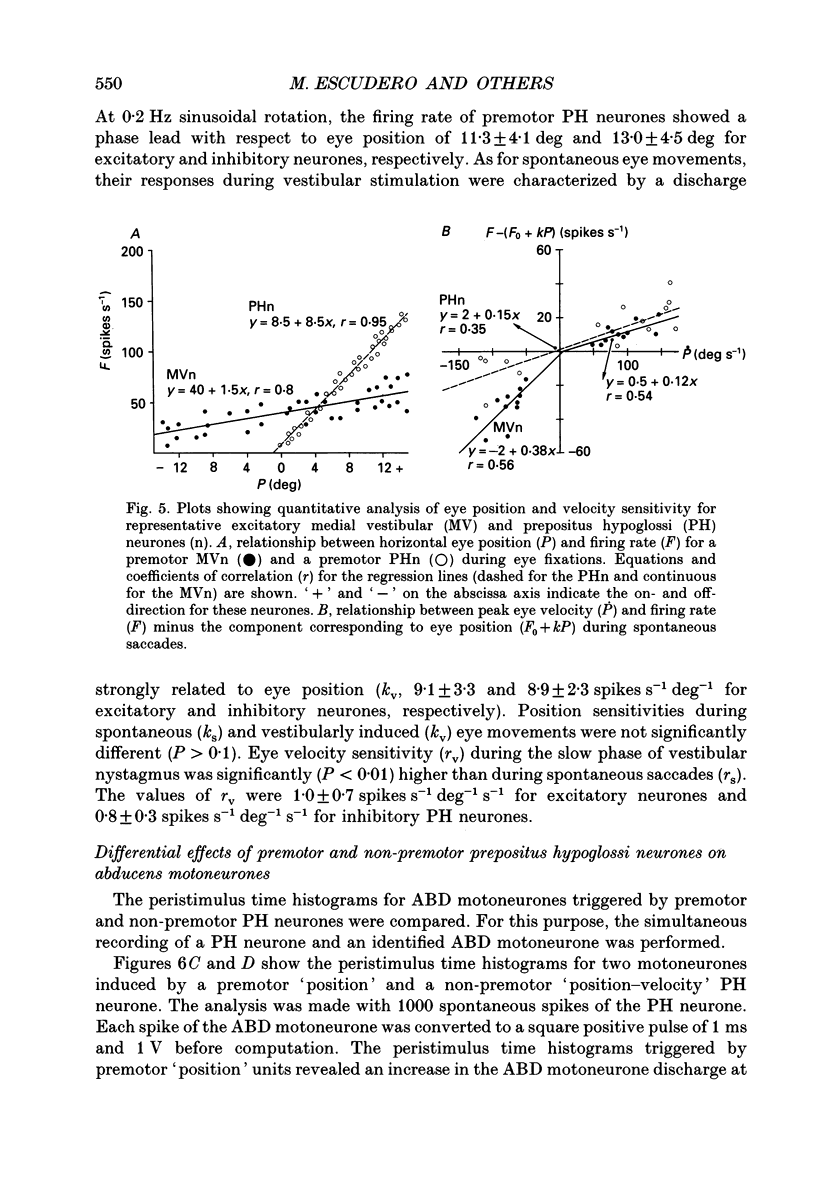
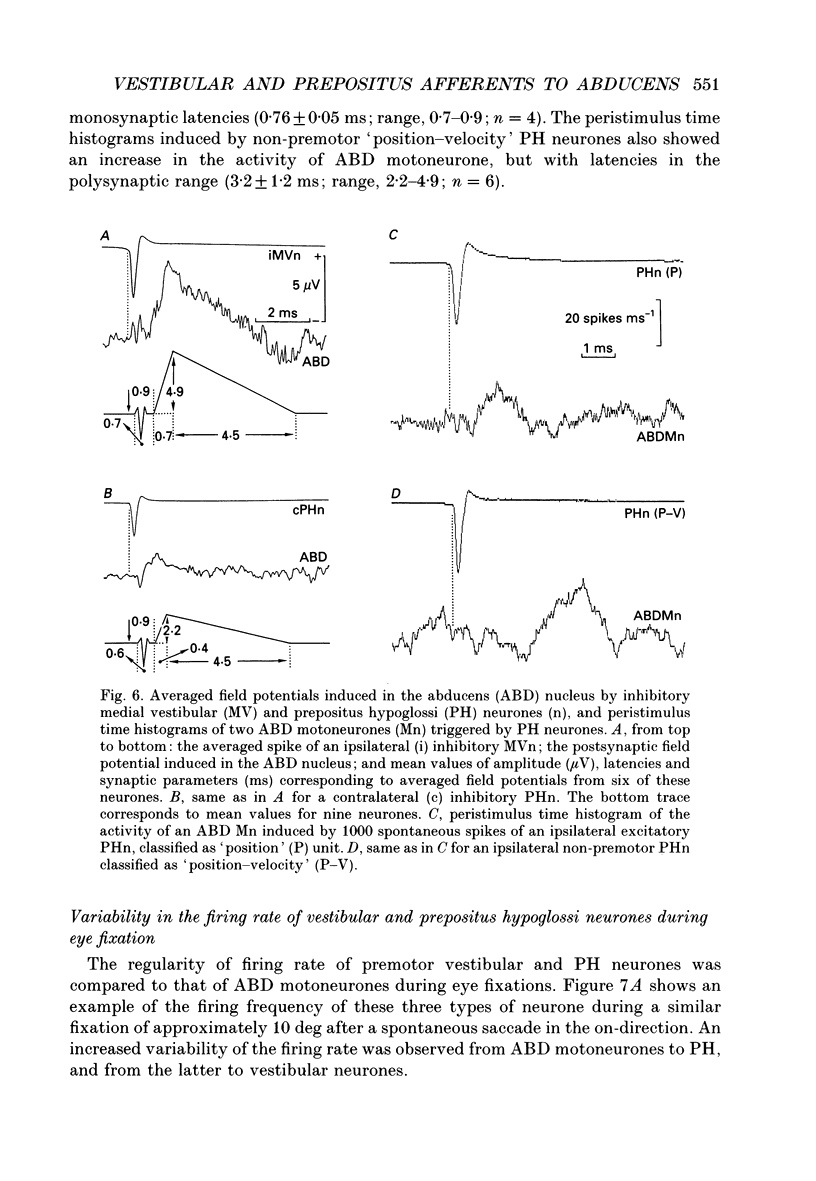
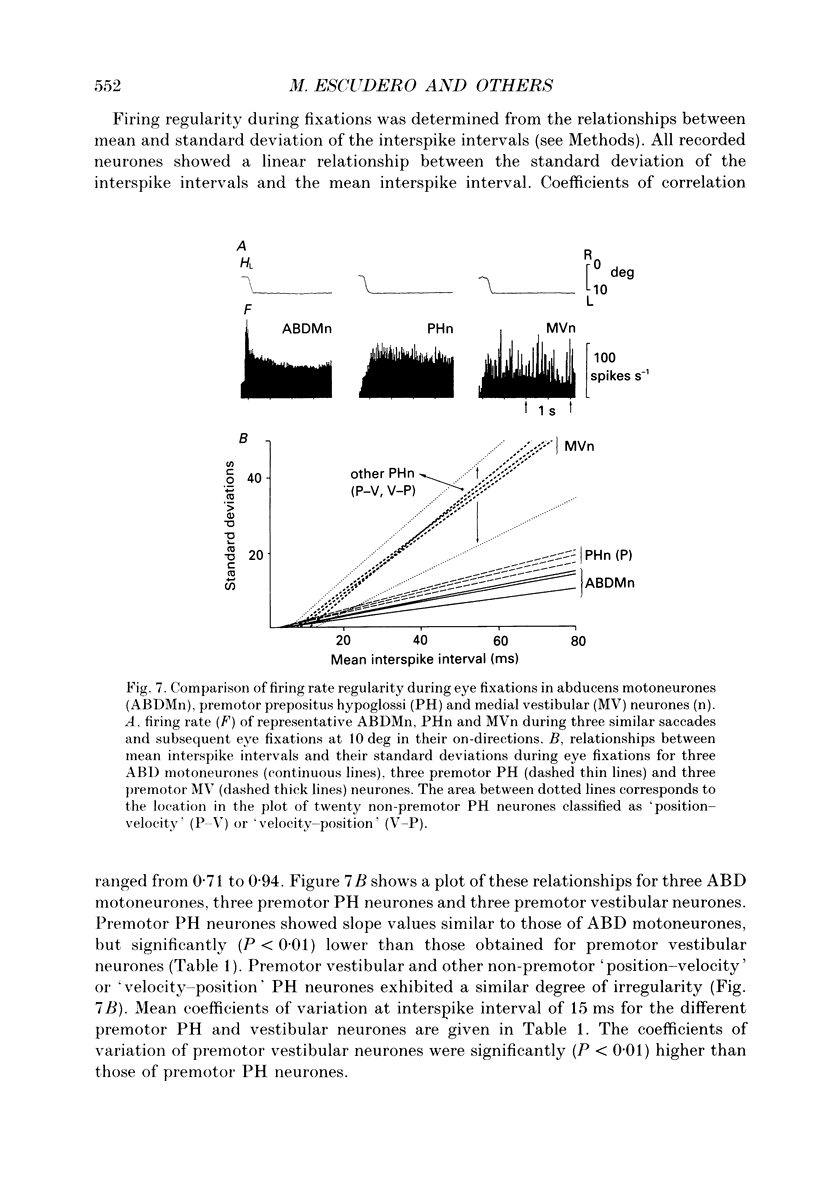
1. Vestibular and prepositus hypoglossi (PH) neurones projecting to the abducens (ABD) nucleus were recorded in the alert cat. Their discharge characteristics were analysed to ascertain the origin of the horizontal eye position signal present in ABD neurones. 2. Neurones were classified according to: their location with respect to the ABD nucleus; their antidromic activation from the ABD nucleus; the synaptic field potential they induced in the ABD nucleus with the spike-triggered averaging technique; and their activity during spontaneous and vestibularly induced eye movements. 3. Vestibular neurones projecting to the ABD nucleus were located in the rostral medial vestibular nucleus. They were excitatory on the contralateral and inhibitory on the ipsilateral ABD neurones. Both types of premotor vestibular neurone showed a firing rate weakly related to eye position, increasing for eye fixations in the contralateral on-direction, and decreasing with ipsilateral fixation. Position sensitivity during eye fixations was (means +/- S.D.) 1.8 +/- 0.9 spikes s-1 deg-1 for excitatory neurones and 2.2 +/- 1.3 spikes s-1 deg-1 for inhibitory neurones. Firing rate exhibited a high variability during eye fixations. Their responses during saccades in the off-direction were characterized by a pause that, although less defined, was occasionally present during saccades in the on-direction. Eye velocity sensitivity during spontaneous saccades in the on-direction was 0.17 +/- 0.15 spikes s-1 deg-1 s-1 for excitatory neurones and 0.15 +/- 0.07 spikes s-1 deg-1 s-1 for inhibitory vestibular neurones. During sinusoidal head stimulation at 0.2 Hz, vestibular neurones showed a type I discharge rate with a phase lead over eye position of 86.0 +/- 14.1 deg for excitatory and 80.2 +/- 12.5 deg for inhibitory neurones. Position sensitivity during vestibular stimulation did not differ significantly from values obtained for spontaneous eye movements. However, the velocity sensitivity of premotor vestibular neurones during head rotation was significantly higher (1.6 +/- 0.2 spikes s-1 deg-1 s-1 for excitatory and 1.5 +/- 0.3 spikes s-1 deg-1 s-1 for inhibitory neurones) than during spontaneous eye movements. 4. PH neurones projecting to the ABD nucleus were located in the rostral one-third of the nucleus. These neurones were excitatory on the ipsilateral and inhibitory on the contralateral ABD nucleus. Their firing rates were correlated mainly with eye position, increasing for abducting eye positions of the ipsilateral eye and decreasing with adduction movements.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. G., Mano N., Shimazu H. Postsynaptic potentials in abducens motoneurons induced by vestibular stimulation. Brain Res. 1969 Oct;15(2):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R., Berthoz A., Delgado-García J. Monosynaptic excitation of trochlear motoneurons following electrical stimulation of the prepositus hypoglossi nucleus. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 31;121(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90445-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R., Berthoz A. Is the prepositus hypoglossi nucleus the source of another vestibulo-ocular pathway? Brain Res. 1975 Mar 14;86(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90643-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R., Evinger C., McCrea R. A. Some thoughts about the three neurons in the vestibular ocular reflex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;374:171–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb30869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R., Gresty M., Berthoz A. Neuronal activity in the prepositus hypoglossi nucleus correlated with vertical and horizontal eye movement in the cat. Brain Res. 1976 Jan 16;101(2):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoz A., Droulez J., Vidal P. P., Yoshida K. Neural correlates of horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex cancellation during rapid eye movements in the cat. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:717–751. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanks R. H., Volkind R., Precht W., Baker R. Responses of cat prepositus hypoglossi neurons to horizontal angular acceleration. Neuroscience. 1977;2(3):391–403. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., Robinson D. A. Loss of the neural integrator of the oculomotor system from brain stem lesions in monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1987 May;57(5):1383–1409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.5.1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheron G., Gillis P., Godaux E. Lesions in the cat prepositus complex: effects on the optokinetic system. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:95–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheron G., Godaux E. Disabling of the oculomotor neural integrator by kainic acid injections in the prepositus-vestibular complex of the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:267–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheron G., Godaux E., Laune J. M., Vanderkelen B. Lesions in the cat prepositus complex: effects on the vestibulo-ocular reflex and saccades. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:75–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUENSING F., SCHAEFER K. P. Die Aktivität einzelner Neurone im Bereich der Vestibulariskerne bei Horizontalbeschleunigungen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des vestibulären Nystagmus. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1958;198(2):225–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00941383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Cruz R. R., Escudero M., Delgado-García J. M. Behaviour of Medial Rectus Motoneurons in the Alert Cat. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 May;1(3):288–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Garcia J. M., del Pozo F., Baker R. Behavior of neurons in the abducens nucleus of the alert cat--I. Motoneurons. Neuroscience. 1986 Apr;17(4):929–952. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Garcia J. M., del Pozo F., Baker R. Behavior of neurons in the abducens nucleus of the alert cat--II. Internuclear neurons. Neuroscience. 1986 Apr;17(4):953–973. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-García J. M., Vidal P. P., Gómez C., Berthoz A. A neurophysiological study of prepositus hypoglossi neurons projecting to oculomotor and preoculomotor nuclei in the alert cat. Neuroscience. 1989;29(2):291–307. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destombes J., Rouvière A. Ultrastructural study of vestibular and reticular projections to the abducens nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1981;43(3-4):253–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00238366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escudero M., Delgado-García J. M. Behavior of reticular, vestibular and prepositus neurons terminating in the abducens nucleus of the alert cat. Exp Brain Res. 1988;71(1):218–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00247538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. F., Kaneko C. R., Scudder C. A. Brainstem control of saccadic eye movements. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:307–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. F., Luschei E. S. Firing patterns of abducens neurons of alert monkeys in relationship to horizontal eye movement. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):382–392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. F., Robinson D. A. A method for measuring horizontal and vertical eye movement chronically in the monkey. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):1068–1070. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantyn A., Grantyn R. Axonal patterns and sites of termination of cat superior colliculus neurons projecting in the tecto-bulbo-spinal tract. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(2):243–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00237182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantyn A., Ong-Meang Jacques V., Berthoz A. Reticulo-spinal neurons participating in the control of synergic eye and head movements during orienting in the cat. II. Morphological properties as revealed by intra-axonal injections of horseradish peroxidase. Exp Brain Res. 1987;66(2):355–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00243310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantyn R., Grantyn A. Morphological and electrophysiological properties of cat abducens motoneurons. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Feb 15;31(2):249–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00237603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresty M., Baker R. Neurons with visual receptive field, eye movement and neck displacement sensitivity within and around the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi in the alert cat. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Feb 26;24(4):429–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00235008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn V., Cohen B. Quantitative analysis of activity in eye muscle motoneurons during saccadic eye movements and positions of fixation. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Jan;36(1):115–126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highstein S. M., Baker R. Excitatory termination of abducens internuclear neurons on medial rectus motoneurons: relationship to syndrome of internuclear ophthalmoplegia. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Nov;41(6):1647–1661. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.6.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highstein S. M., Karabelas A., Baker R., McCrea R. A. Comparison of the morphology of physiologically identified abducens motor and internuclear neurons in the cat: a light microscopic study employing the intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Jul 10;208(4):369–381. doi: 10.1002/cne.902080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka O., Igusa Y., Imai H. Firing pattern of prepositus hypoglossi and adjacent reticular neurons related to vestibular nystagmus in the cat. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 14;144(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka O., Igusa Y., Nakao S., Shimazu H. Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage of pontomedullary reticular burst neurons with abducens motoneurons in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Nov 15;33(3-4):337–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00235558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka O., Nakao S., Shimazu H. Postsynaptic inhibition underlying spike suppression of secondary vestibular neurons during quick phases of vestibular nystagmus. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jan;16(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka N., Mannen H., Sasaki S., Shimazu H. Axonal branches and terminations in the cat abducens nucleus of secondary vestibular neurons in the horizontal canal system. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Feb;16(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Kitama T., Yoshida K. Vertical eye movement-related secondary vestibular neurons ascending in medial longitudinal fasciculus in cat. II. Direct connections with extraocular motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Apr;63(4):918–935. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.4.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko C. R., Evinger C., Fuchs A. F. Role of cat pontine burst neurons in generation of saccadic eye movements. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Sep;46(3):387–408. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barneo J., Darlot C., Berthoz A., Baker R. Neuronal activity in prepositus nucleus correlated with eye movement in the alert cat. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Feb;47(2):329–352. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barneo J., Ribas J., Delgado-Garcia J. M. Identification of prepositus neurons projecting to the oculomotor nucleus in the alert cat. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 9;214(1):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luschei E. S., Fuchs A. F. Activity of brain stem neurons during eye movements of alert monkeys. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jul;35(4):445–461. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.4.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea R. A., Baker R. Anatomical connections of the nucleus prepositus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jul 15;237(3):377–407. doi: 10.1002/cne.902370308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea R. A., Baker R., Delgado-Garcia J. Afferent and efferent organization of the prepositus hypoglossi nucleus. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:653–665. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea R. A., Yoshida K., Berthoz A., Baker R. Eye movement related activity and morphology of second order vestibular neurons terminating in the cat abducens nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40(4):468–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00236156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao S., Sasaki S., Schor R. H., Shimazu H. Functional organization of premotor neurons in the cat medial vestibular nucleus related to slow and fast phases of nystagmus. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(3):371–385. doi: 10.1007/BF01208597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A. Oculomotor unit behavior in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):393–403. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Shimazu H. Reticulovestibular organization participating in generation of horizontal fast eye movement. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;374:130–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb30866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. F., Sterling P. An electron microscope study of motoneurones and interneurones in the cat abducens nucleus identified by retrograde intraaxonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Nov 1;176(1):65–85. doi: 10.1002/cne.901760105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. F., Wenthold R. J., Baker R. Evidence for glycine as an inhibitory neurotransmitter of vestibular, reticular, and prepositus hypoglossi neurons that project to the cat abducens nucleus. J Neurosci. 1989 Aug;9(8):2718–2736. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-08-02718.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassman A., Highstein S. M., McCrea R. A. Anatomy and physiology of saccadic burst neurons in the alert squirrel monkey. I. Excitatory burst neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 15;249(3):337–357. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassman A., Highstein S. M., McCrea R. A. Anatomy and physiology of saccadic burst neurons in the alert squirrel monkey. II. Inhibitory burst neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 15;249(3):358–380. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., McCrea R., Berthoz A., Vidal P. P. Morphological and physiological characteristics of inhibitory burst neurons controlling horizontal rapid eye movements in the alert cat. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Sep;48(3):761–784. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


